Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Risk For Bleeding Related To Decreased Platelet Count
Transféré par
KC IgnacioDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NCP Risk For Bleeding Related To Decreased Platelet Count
Transféré par
KC IgnacioDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
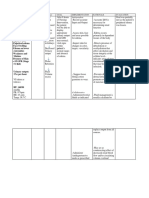
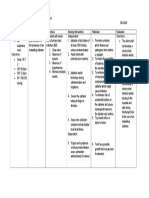
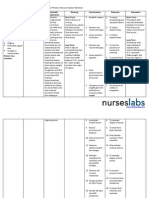
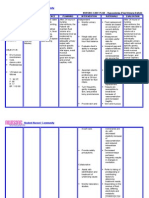
Patient Name: A.M.V. Assessment Subjective: Mejo okay na, pero ayan nanghihina parin as verbalized by clients wife.
Risk for bleeding related to decreased platelet count Nursing Diagnosis
CHINESE GENERAL HOSPITAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND LIBERAL ARTS NURSING CARE PLAN Age:53 Diagnosis: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Inference Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. White blood cells help your body fight infection. Your blood cells form in your bone marrow. In leukemia, however, the bone marrow produces abnormal white blood cells. These cells crowd out the healthy blood cells, making it hard for blood to do its work. In acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), there are too many of specific types of white blood cells called lymphocytes or lymphoblast. These leukemic cells are not able to fight infection very well. Also, as the number of leukemic cells increases in the blood and bone Goal Short Term: After 6 hours of nursing interventions Nursing Intervention Rationale Early detection of bleeding helps prevent significant blood loss and potential shock. Occult blood shows internal hemorrhage Intracranial bleeding affects mental status and LOC. Evaluation Short Term: After 3 hours of nursing interventions Skin is intact with no sign of bleeding Mucous membrane is intact Long Term: After 4 days of nursing interventions, the client will: Urine and stool are free from blood Normalized RBC count
Objective: -Weak-looking -Ecchymoses over anterior lower extremities -Pale palpebral conjunctiva -Blood count shows reduced HGB- 88 Platelet59 HCT0.246
Independent Assess vital signs every 4 hours and body systems every shift for bleeding: Skin will remain Skin, mucous intact with no signs membranes for of bleeding petechiae, ecchymoses, and hematoma Mucous membrane formation. will remain intact Gums and nasal membranes for bleeding Long Term: Vomitus, stool and urine After 4 days of for visible occult blood nursing interventions, Neurologic changes the client will: (e.g., headache, visual changes, decreased Urine and stool will LOC seizure) be free from blood. Encourage use of softbristle toothbrush, Restores/normalizes sponge or mild RBC count mouthwash to clean teeth and gums. Instruct client to avoid forceful blowing, coughing, sneezing and straining to have a bowel movement. Apply pressure to
Fragile tissues and altered clotting mechanisms increase the risk of hemorrhage following even minor trauma. These activities can damage mucous membrane increasing the risk of bleeding.
Pressure prevents
marrow, there is less room for healthy white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. This may cause infection, anemia, and easy bleeding. Source: www.cancer.gov (Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia)
injection sites for 3 - 5 min. and arterial punctures for 15 to 20 min. Avoid invasive procedures as possible (e.g., rectal temperature and suppositories, parenteral injection) Provide soft diet Collaborative Monitor laboratory studies; e.g., platelets, Hb/Hct, clotting. Administer RBCs, platelets, clotting factors.
prolonged bleeding prompting hemostasis and clot formation motility. To prevent tissue trauma and bleeding.
May help reduce gum irritation. Decreasing Hb/Hct is indicative of bleeding (may be occult). Restores/normalizes RBC count and oxygencarrying capacity to correct anemia. Used to prevent/treat hemorrhage. Helpful in reducing straining at stool which can cause trauma to rectal tissues.
Dependent Prescribe medication (e.g., stool softeners)
Kris Charmaine E. Ignacio 3A Group 2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Study Notes PediatricsDocument86 pagesStudy Notes PediatricsMedShare100% (19)
- 2012 NCCAOM Herbal Exam QuestionsDocument10 pages2012 NCCAOM Herbal Exam QuestionsElizabeth Durkee Neil100% (2)
- Vascular Review PDFDocument263 pagesVascular Review PDFaskjagPas encore d'évaluation
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument67 pagesIschemic Heart Diseasealfaz lakhani80% (5)
- Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective Therapeutic Regimen Management RelatedDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Ineffective Therapeutic Regimen Management RelatedbizzykenPas encore d'évaluation
- Final NCP Risk For BleedingDocument2 pagesFinal NCP Risk For Bleedingsteffi100% (1)
- Fatigue NCPDocument2 pagesFatigue NCPclydell joyce masiar100% (6)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPDocument2 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute PainDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute PainBakushido50% (6)
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocument2 pagesFluid Volume ExcessRodel Yacas100% (5)
- Perioperative Nursing - 50 ItemsDocument6 pagesPerioperative Nursing - 50 Itemsapi-371817496% (26)
- NCP Risk For BleedingDocument1 pageNCP Risk For BleedingJen Garzo75% (4)
- FatigueDocument3 pagesFatigueIande CornerPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular Physical TherapDocument7 pagesCardiovascular Physical TherapJadie Prenio100% (4)
- NCP Template ObDocument7 pagesNCP Template ObMae CeaesarPas encore d'évaluation
- Iii. Nursing Care PlansDocument13 pagesIii. Nursing Care PlansLharra Cagulada-Postrano100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodYllejann Manez60% (20)
- PantoprazoleDocument1 pagePantoprazoleKC Ignacio100% (1)
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationHaon Anasu67% (3)
- NCP On Dengue Risk For BleedingDocument13 pagesNCP On Dengue Risk For BleedingCazze Sunio100% (4)
- NCP Fluid Volume ExcessDocument2 pagesNCP Fluid Volume ExcessAngel Moorer92% (12)
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficitprickybiik100% (1)
- Or NCP (Risk For Bleeding)Document1 pageOr NCP (Risk For Bleeding)Nikki M. Arapol100% (1)
- NCP AfDocument3 pagesNCP AfAngelica Mercado SirotPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionLeigh Kristel Andrion0% (1)
- NCP Acute Pain RT CancerDocument3 pagesNCP Acute Pain RT CancerCharissa Magistrado De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk For Bleeding NCP ProperDocument2 pagesRisk For Bleeding NCP ProperJohn Michael Solis0% (1)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPDidith AbanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Volume Excess NCPDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Excess NCPƦя de GuzмѧN80% (5)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP Excess Fluid VolumeMei Payumo100% (1)
- NCP LeukemiaDocument3 pagesNCP LeukemiaLuige Avila100% (5)
- NCP LymphedemaDocument1 pageNCP Lymphedemayasira50% (2)
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageNCP - Risk For Infectionjanelee2824100% (1)
- Trinity University of Asia: St. Luke's College of NursingDocument18 pagesTrinity University of Asia: St. Luke's College of NursingKate Duque100% (1)
- NCP For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument7 pagesNCP For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaLilian Linogao100% (10)
- NCP For LeukemiaDocument2 pagesNCP For Leukemiaخالد الغامديPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP-risk For BleedingDocument3 pagesNCP-risk For BleedingAce Dioso Tubasco100% (2)
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumerobbychuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk For BleedingDocument4 pagesRisk For Bleedinglouie roderos100% (1)
- NCP Acute PainDocument4 pagesNCP Acute PainSj 斗力上Pas encore d'évaluation
- Schistosomiasis Case StudyDocument5 pagesSchistosomiasis Case Studyapi-318749549Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCP DengueDocument3 pagesNCP DengueRichmund Earl Geron100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageIneffective Tissue PerfusionEuanne Orellano85% (13)
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocument4 pagesFluid Volume ExcessTamil Villardo100% (2)
- Dengue NCP (Risk For Bleeding)Document5 pagesDengue NCP (Risk For Bleeding)Bernadette Malamug50% (6)
- NCP Risk For Bleeding 3Document2 pagesNCP Risk For Bleeding 3Jayson Olile100% (1)
- Risk For BleedingDocument2 pagesRisk For Bleedingmikebry72% (25)
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDocument3 pagesNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For HypocalcemiaDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For Hypocalcemiamariejo78% (18)
- NCP BleedingDocument3 pagesNCP Bleedingapi-316491996Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageIneffective Tissue PerfusionRhae RaynogPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophsiology of DementiaDocument1 pagePathophsiology of DementiaKC IgnacioPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Intolerance Related To AmeniaDocument1 pageActivity Intolerance Related To AmeniaSiti Syazana Mohamad MogriPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP For Risk of Infectiong R/T Indwelling Catheter Post PartumDocument1 pageNCP For Risk of Infectiong R/T Indwelling Catheter Post PartumJared Mabulay100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective TissueDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective TissueFhel AragonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of AMLDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AMLjake251996100% (1)
- PEDIA NCP Risk For BleedingDocument2 pagesPEDIA NCP Risk For BleedingTricia DogilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionDiane ReyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Volume Excess CRFDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Excess CRFDana Fajardo RezanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Pain NCPDocument2 pagesAcute Pain NCPBobby Valencerina100% (1)
- Risk For InfectionDocument3 pagesRisk For InfectioncamziiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocument2 pagesRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPkatrina_velasco_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPChris Denver BancalePas encore d'évaluation
- Deficit)Document2 pagesDeficit)Lee DeePas encore d'évaluation
- n320 Peds NCP wk3Document2 pagesn320 Peds NCP wk3api-301826049Pas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Blood Countuhgob87toDocument13 pagesComplete Blood Countuhgob87toWhanda OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument9 pagesAplastic AnemiaGaluh Dyah PrameswariPas encore d'évaluation
- Leukemia PDFDocument63 pagesLeukemia PDFErfan Syahid AzhariPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Blood CountDocument19 pagesComplete Blood Countzainab aliPas encore d'évaluation
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologyKC IgnacioPas encore d'évaluation
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsKC IgnacioPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG StudyDocument2 pagesDRUG StudyKC IgnacioPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKC IgnacioPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG StudyDocument2 pagesDRUG StudyKC IgnacioPas encore d'évaluation
- MetronidazoleDocument2 pagesMetronidazoleKC IgnacioPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebral Sinus ThrombosisDocument23 pagesCerebral Sinus ThrombosisHerinanda Fahmy FahleviePas encore d'évaluation
- First Term QuizDocument22 pagesFirst Term QuizJaylord VerazonPas encore d'évaluation
- Venessa Shannen Wah Pei Yue 2020277834 - Elc 231 - Mid Sem TestDocument8 pagesVenessa Shannen Wah Pei Yue 2020277834 - Elc 231 - Mid Sem TestVenessa WahPas encore d'évaluation
- Viral Gastroenteritis-1Document17 pagesViral Gastroenteritis-1Abdus SubhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of High TSHDocument3 pagesEffects of High TSHSreream KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- HIV - Human Immunodeficiency Virus.: The Greatest Medical Science Challenge of The Last 40 Years!Document37 pagesHIV - Human Immunodeficiency Virus.: The Greatest Medical Science Challenge of The Last 40 Years!blueblemishPas encore d'évaluation
- Dehydration OutlineDocument4 pagesDehydration OutlinemariusjayzafraPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study6 For HS 103 Week 7Document7 pagesCase Study6 For HS 103 Week 7Rijane Tabonoc OmlangPas encore d'évaluation
- Non US HCF Triage ChecklistDocument6 pagesNon US HCF Triage ChecklistyudaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal Vascular Injury - UpToDateDocument3 pagesAbdominal Vascular Injury - UpToDateAnca StanPas encore d'évaluation
- ENT - Ear-Nose-Throat PDFDocument15 pagesENT - Ear-Nose-Throat PDFMa SakhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Congestive Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes: Prevalence, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDocument6 pagesCongestive Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes: Prevalence, Incidence, and Risk FactorsFini Riski Aulia SagalaPas encore d'évaluation
- STROKEDocument61 pagesSTROKEK.MERCYPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Nursing Practice - MidtermDocument24 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Practice - MidtermShene Claire VigillaPas encore d'évaluation
- History (Awasir)Document37 pagesHistory (Awasir)Yousef TaqatqehPas encore d'évaluation
- My Experience With Topical Homoeopathic Application in A Case of Stage Iv Decubitus UlcerDocument5 pagesMy Experience With Topical Homoeopathic Application in A Case of Stage Iv Decubitus UlcerHomoeopathic PulsePas encore d'évaluation
- Ancylostoma DuodenaleDocument2 pagesAncylostoma DuodenaleBlessy BreganzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mapping R5B PDFDocument12 pagesMapping R5B PDFSulung Ade PratamaPas encore d'évaluation
- CareofolderadultsDocument8 pagesCareofolderadultsMonique FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Torsio TestisDocument19 pagesTorsio TestisRandy HarrisPas encore d'évaluation
- The Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Musculoskeletal Disorders Among BankersDocument21 pagesThe Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Musculoskeletal Disorders Among BankersNdayambaje EmmanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Epilepsy: Dr. Hj. Meiti Frida, SP.SDocument47 pagesEpilepsy: Dr. Hj. Meiti Frida, SP.SZacky Aulia MursiPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary Tract Infection in Older Adults: DefinitionsDocument10 pagesUrinary Tract Infection in Older Adults: DefinitionsWila AnandaPas encore d'évaluation