Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
States of Matter Activity 1
Transféré par
hisham saeedDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
States of Matter Activity 1
Transféré par
hisham saeedDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NAME: ……………………………………
CLASS: 8 STATES OF MATTER
ACTIVITY 1
Answer the following
(1) State the processes;
LIQUID
A.________________________
B. ________________________
C. ________________________
D. ________________________
SOLID GAS
E. ________________________
F. ________________________
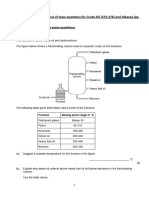
(2) Use the data in the table below to answer the following questions.
(Consider the room temperature as 25°C)
Name of substance Melting point/oC Boiling point/oC
Argon -189 -186
Petrol -40 62
Helium -270 -269
Carbon dioxide Sublimes at -78 -
Benz amide 132 290
(a) Draw the arrangement of particles of the following substances at room temperature and pressure.
Argon Benz amide Petrol
(b) Define the terms melting point and boiling point.
......................................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................................
(c) Explain in terms of kinetic particle theory, what happens when a solid melts to form a liquid
....................................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................................
Dharumavantha School Chemistry Department - 2009
(d) On the grid below, sketch the heating curve for petrol.
Complete the crossword puzzle
DOWN
1 The change in state of matter when ethanol
vapor changes to ethanol liquid
2 The change in state of matter when water
changes to ice
5 The type energy particles gain on heating
6 The temperature at which ice start to melt
7 The force of attraction between the particles are
negligible
8 Have a fixed volume but no definite shape
ACROSS
3 The exact temperature at which a pure liquid
changes to a gas
4 Anything that has a mass and occupies space
9 The change in state of matter from a liquid to a gas
below the boiling point
10 Particles can only vibrate in fixed position
11 An example of a substance that undergoes
sublimation
Dharumavantha School Chemistry Department - 2009
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Class 11 Final Exam 2018-2019 PDFDocument84 pagesClass 11 Final Exam 2018-2019 PDFSiddharth ChhabraPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Paper-01 Physics (Theory) Class - XI Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsDocument3 pagesSample Paper-01 Physics (Theory) Class - XI Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsShekhar kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Power Energy PDFDocument28 pagesWork Power Energy PDFShabbir KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 4 GQ SolutionDocument9 pagesWeek 4 GQ SolutionrqrwerwetPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.1 ParabolaDocument11 pages5.1 ParabolaRamchandra MurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Jee Adv CRP (Ph-1) (Paper - 1) Set - BDocument10 pagesJee Adv CRP (Ph-1) (Paper - 1) Set - BChirag JainPas encore d'évaluation
- SHMDocument54 pagesSHMSiddhant ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton S Laws Force Friction 291Document20 pagesNewton S Laws Force Friction 291Shorya KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Particle Theory End of Chapter WSDocument3 pagesParticle Theory End of Chapter WSmanthanPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkanes Notes and Naming PDFDocument4 pagesAlkanes Notes and Naming PDFyad e baiza nawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Structure ReviewDocument7 pagesAtomic Structure ReviewKinal PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Relative Motion PDFDocument14 pagesRelative Motion PDFTanishq KapoorPas encore d'évaluation
- CapacitanceDocument40 pagesCapacitancerishi0% (1)
- Counting Techniques: Discrete MathematicsDocument41 pagesCounting Techniques: Discrete MathematicsUser UserPas encore d'évaluation
- Everything You Need To Know About AlkanesDocument2 pagesEverything You Need To Know About AlkanesJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Class IX Biology: Chapter 6: TissueDocument5 pagesClass IX Biology: Chapter 6: Tissuesidd230100% (2)
- Quantum Numbers Structure 2Document22 pagesQuantum Numbers Structure 2vishalsingh1997Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Topic: Fluid Statics: Class Assignment (For IIT JEE 2013 Batch)Document6 pagesPhysics Topic: Fluid Statics: Class Assignment (For IIT JEE 2013 Batch)Vikrant VatsalPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise-1: Mcqs With One Correct Answer TypeDocument21 pagesExercise-1: Mcqs With One Correct Answer TypeVanshdip RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Elasticity and Fluid Machanics-04-Objective Unsolved Level1Document6 pagesElasticity and Fluid Machanics-04-Objective Unsolved Level1Raju SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Mass - Volume.density - Notes PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 2 Mass - Volume.density - Notes PDFJohn JensenPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Atomic Structure JH Sir-2611Document30 pagesAssignment Atomic Structure JH Sir-2611Ghost Phyton RoorkeePas encore d'évaluation
- Quantum Numbers OrbitalsDocument4 pagesQuantum Numbers OrbitalsBeeta Khanna100% (1)
- STUDENT WORKSHEET HydrocarbonDocument5 pagesSTUDENT WORKSHEET HydrocarbonFiryal Nabilah Q APas encore d'évaluation
- The Ideal Gas LawDocument3 pagesThe Ideal Gas LawGovind RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- L.Tarasov - Questions & Answers in School Physics2020 (Bản Eng)Document327 pagesL.Tarasov - Questions & Answers in School Physics2020 (Bản Eng)GiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Probability and Random VariablesDocument4 pagesProbability and Random Variables123habib123fikriPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Biology - Ecological Pyramids - Worksheet PDFDocument6 pagesAP Biology - Ecological Pyramids - Worksheet PDFVictoria LowmanPas encore d'évaluation
- How Did Cell Theory DevelopedDocument4 pagesHow Did Cell Theory DevelopedLourence BajariasPas encore d'évaluation
- Nomenclature WorksheetDocument5 pagesNomenclature WorksheetJapphetPas encore d'évaluation
- Highschool Physics Measurement and UncertaintiesDocument37 pagesHighschool Physics Measurement and UncertaintiesMaanav GanjooPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.intro To Organic Chem-PracticeDocument2 pages1.intro To Organic Chem-PracticeZul Abror Bin Ya'akopPas encore d'évaluation
- Art and ScienceDocument1 pageArt and ScienceAshley AquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulation and Gas ExchangeDocument164 pagesCirculation and Gas ExchangeZuliyanto ZakariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Modern PhysicsDocument28 pagesModern PhysicsShubham KarandePas encore d'évaluation
- Newton's Law of MotionDocument31 pagesNewton's Law of MotionPraveen KumarpillaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument32 pagesPeriodic Table of ElementsJodell BuensalidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electron ConfigurationDocument28 pagesElectron ConfigurationphillipPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkyne - Organic ChemistryDocument9 pagesAlkyne - Organic ChemistryHazhir IsmaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Iit Jee FunctionsDocument4 pagesIit Jee Functionsparita adhiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.4 Pure Substances Mixtures PPTDocument42 pages1.4 Pure Substances Mixtures PPTFebbie YanPas encore d'évaluation
- Surface TensionDocument18 pagesSurface TensionMD CHHIMPAPas encore d'évaluation
- Nano TechnologyDocument12 pagesNano Technologyrenuka mulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 SolidDocument59 pagesChapter 3 Solidatikah roshanPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 Cell TheoryDocument1 page1.1 Cell TheoryLucca PiaggioPas encore d'évaluation
- GC06 - Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsDocument21 pagesGC06 - Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsVince DulayPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Notes PDFDocument211 pagesBiology Notes PDFamar lalPas encore d'évaluation
- Blue and Pink Modern Technology Keynote Presentation PDFDocument13 pagesBlue and Pink Modern Technology Keynote Presentation PDFHana AdivaPas encore d'évaluation
- BiosphereDocument27 pagesBiosphereJamaika Sofia LetimPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic STR - CY1101 - SLS PDFDocument68 pagesAtomic STR - CY1101 - SLS PDFAbhijeet DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Separation Techniques WorksheetDocument2 pagesSeparation Techniques WorksheetYerlin MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument25 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproduceSubrata MallickPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank Chapter 3Document10 pagesTest Bank Chapter 3mrbookoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch. 6 - Photosynthesis - Biology - Class X - ICSE (2019-2020) - Unlocked PDFDocument22 pagesCh. 6 - Photosynthesis - Biology - Class X - ICSE (2019-2020) - Unlocked PDFthe lillyPas encore d'évaluation
- Motion of Charge in Magnetic FieldDocument18 pagesMotion of Charge in Magnetic FieldAsif HameedPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument8 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsNighin NazerPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Equations & ReactionsDocument64 pagesChemical Equations & ReactionsMary Grace Jerna Artazo Nozal-CuadraPas encore d'évaluation
- Projectile MotionDocument24 pagesProjectile MotionNoel BinuPas encore d'évaluation
- Y11 Chem Holiday Homework DecDocument8 pagesY11 Chem Holiday Homework Deckrishmadaan100Pas encore d'évaluation
- LNG Fire Protection and Emergency ResponseDocument152 pagesLNG Fire Protection and Emergency ResponseDesigner Forever100% (2)
- Quiz-Intermolecular ForcesDocument2 pagesQuiz-Intermolecular Forcesadrian nenengPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 14 Unitary System IIDocument24 pagesLesson 14 Unitary System IIJoshua SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Project Methods of Purification of Organic Substances by Sanjit Govindraj of Class 11A1 Done On 8.12.23Document10 pagesChemistry Project Methods of Purification of Organic Substances by Sanjit Govindraj of Class 11A1 Done On 8.12.23sanjitgovind20dataPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Make Electrum Magicum For A Magic MirrorDocument5 pagesHow To Make Electrum Magicum For A Magic Mirrorqbl777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Water PropertiesDocument12 pagesBasic Water PropertiesBryan GraczykPas encore d'évaluation
- Dasar Keteknikan Pengolahan Pangan: Sudarminto Setyo YuwonoDocument147 pagesDasar Keteknikan Pengolahan Pangan: Sudarminto Setyo Yuwonoarif prasetyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phase/State Transitions of Confectionery Sweeteners: Thermodynamic and Kinetic AspectsDocument16 pagesPhase/State Transitions of Confectionery Sweeteners: Thermodynamic and Kinetic AspectsAlicia MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- States of Matter Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesStates of Matter Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceAntoinette CrumptonPas encore d'évaluation
- PROJECT On CondensationDocument23 pagesPROJECT On Condensationnabajyoti19877363100% (1)
- Plant DesignDocument39 pagesPlant DesignHaiqal Aziz100% (1)
- Exam Juba F1Document7 pagesExam Juba F1Hossam Abdalla SalehPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporation CalculationsDocument33 pagesEvaporation CalculationsSuhadahafiza ShafieePas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Approach On Heating Ventilation & Air Conditioning Technology - Best in HVAC-Designing, A - AMRUTHA RAO MALLIDocument198 pagesPractical Approach On Heating Ventilation & Air Conditioning Technology - Best in HVAC-Designing, A - AMRUTHA RAO MALLIsitender kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- PLP E 6 2003, Fractionators 2nd Ed RosenDocument69 pagesPLP E 6 2003, Fractionators 2nd Ed Rosenivanov5559Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 5 Enthalpy of VaporizationDocument4 pagesLab 5 Enthalpy of VaporizationFrolian MichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- FM Approved - 500 Pre-Engineered ManualDocument28 pagesFM Approved - 500 Pre-Engineered ManualSierra_Reveles0% (1)
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2Marco LuigiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry IGCSE Paper 6 Revision GuideDocument16 pagesChemistry IGCSE Paper 6 Revision GuideLucas SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of Organic CompoundsDocument3 pagesProperties of Organic CompoundshydeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Final PracticeDocument5 pagesFinal Practicelisbethlc1989Pas encore d'évaluation
- EN 61010-2-040 2005 enDocument36 pagesEN 61010-2-040 2005 enКуртимир ЕкатериновPas encore d'évaluation
- Phase Diagram of Pure Substance: 相圖 如何繪製相圖-實驗法 如何繪製相圖-Clapeyron Eqn. 相平衡的維持 不同溫度下的蒸氣壓-Clausius Clapeyron Eqn. 額外加壓對蒸氣壓的影響Document71 pagesPhase Diagram of Pure Substance: 相圖 如何繪製相圖-實驗法 如何繪製相圖-Clapeyron Eqn. 相平衡的維持 不同溫度下的蒸氣壓-Clausius Clapeyron Eqn. 額外加壓對蒸氣壓的影響Garcia RaphPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge Primary Checkpoint: Science 0846/01Document168 pagesCambridge Primary Checkpoint: Science 0846/01esraa ali100% (1)
- LR Energy Guidance Notes For The Calculation of Probabilistic Explosion Loads PDFDocument18 pagesLR Energy Guidance Notes For The Calculation of Probabilistic Explosion Loads PDFJay JayPas encore d'évaluation
- AA IGCSE Unit 1,2Document9 pagesAA IGCSE Unit 1,2Yee MeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 240 Lab Manual - 2013Document56 pagesChem 240 Lab Manual - 2013VanandiPas encore d'évaluation
- t3 All Questions Topic 3Document58 pagest3 All Questions Topic 3Michael FanPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDocument16 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and TechniquesAbhayPas encore d'évaluation
- Msds ThiopheneDocument5 pagesMsds ThiopheneNeel VaderaPas encore d'évaluation