Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Case Presentation Lab Results
Transféré par
miss RNDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Case Presentation Lab Results
Transféré par
miss RNDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
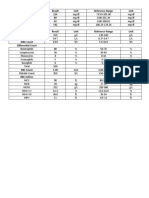
B.
CBC
Reference
Hgb 120 121 120 g/L
Hct 27.7 36 40-54%
MCV 84 84 80-94%
MCHC 36 33 32-37%
RBC 4.3 4.2 4.5-5.0 x 1012/L
WBC 13.3 14.9 5-10 x 109/L
Segmenters 82 73 40-75%
Lymphocytes 17 21 20-45%
Eosinophils 1 6 1-4%
Basophils -
Platelets normal Increased 140-440 x 109/L
RBC morphology normochromic normochromic
normocytic normocytic
The patient has a low hemoglobin, low hematocrit, low MCV but high MCHC, RBC is
slightly lower than normal. WBC is elevated due to the presence of bacterial pneumonia,
platelets are normal size and shape of red blood cells is normal as well. Same
interpretation on the 2nd test except for increased platelet count.
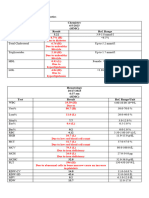
C. Coagulation Studies
Prothrombin Time 12.6
Control 12.0
INR 1.05
% Activity 93.5
Partial Thromboplastin 25.8
Time
Control 30.0
Prothrombin time is normal. Partial thromboplastin Time is slightly delayed.
D. Arterial Blood Gases
Reference
pH 7.403 7.35-7.45
PCO2 31.5 35-45 mmHg
PO2 (arterial) 130 80-100 mmHg
O2 Saturation 99.1% 94-100%
HCO3 20.0 22-26 meq/L
Base Excess -5.2 +/-2
Total CO2 21.0
FiO2 2 LPM
PO2 (venous) 35.5
Temp 36.1 37 ˚ C
RR 36 12-20
Patient’s arterial PO2 is due to the respirator attached to the patient which 2L of O2 /min.
decrease in PCO2 indicates respiratory alkalosis while the decrease in HCO3 indicates
metabolic acidosis. pH level is normal but is slightly on the alkalinic side. Therefore, the
finding is: Fully compensated respiratory alkalosis without hypoxemia.
E. Lipids
Reference
Total Cholesterol 6.5 3.4-6.1 mmo1/L
HDL 1.5 0.6-2.1 mmo1/L
Triglyceride 1.4 Up to 2.4 mmo1/L
LDL 4.4 Up to 3.9 mmo1/L
Total Cholesterol/ HDL 4.3
ratio
Patient’s total cholesterol exceeded the normal value which may cause fatty build up if
not burned
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyD'EverandArterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (4)
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: Diagnostic ExaminationsDocument5 pagesArterial Blood Gas Analysis: Diagnostic ExaminationsstrawberryPas encore d'évaluation
- Infective endocarditis (感染性心內膜炎) : dyspnea and chest pain four days agoDocument11 pagesInfective endocarditis (感染性心內膜炎) : dyspnea and chest pain four days agoapi-19644056Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acid-Base Disorders: Clinical Evaluation and ManagementD'EverandAcid-Base Disorders: Clinical Evaluation and ManagementPas encore d'évaluation
- V. Diagnostic ExaminationDocument3 pagesV. Diagnostic ExaminationArlene MacatangayPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Results TemplateDocument3 pagesLaboratory Results TemplateJames Raynel NonanPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory AnalysisDocument6 pagesLaboratory AnalysisJm CoguincoPas encore d'évaluation
- Interpretation of FBC Part 1Document15 pagesInterpretation of FBC Part 1reuel nareshPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Study: Complete Blood CountDocument5 pagesLaboratory Study: Complete Blood CountNicole Angeli ManuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Clin Med Exam 1 Cases (1472)Document35 pagesClin Med Exam 1 Cases (1472)LalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory and Diagnostic FindingsDocument4 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic FindingsCG Patron BamboPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory and Diagnostics TestDocument7 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostics TestJustin Ric JuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Blood CountDocument3 pagesComplete Blood CountivantototaePas encore d'évaluation
- TESTS (Updated)Document5 pagesTESTS (Updated)laboratory12389Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Responsibilities Before The ProcedureDocument4 pagesNursing Responsibilities Before The ProcedureLorenz Sagayaga ListaPas encore d'évaluation
- ازمایشDocument3 pagesازمایشv.shaakaramiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lipid Profile Result Unit Reference Range Unit 224 89 92 142 CBC Result Unit Reference Range UnitDocument1 pageLipid Profile Result Unit Reference Range Unit 224 89 92 142 CBC Result Unit Reference Range Unitjohnart jimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- 2814 1Document73 pages2814 1Trangia, SharmainePas encore d'évaluation
- Pedia CPC For 2023Document3 pagesPedia CPC For 2023Parth VinaypatilPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hong Kong College of Anaesthesiologists Intermediate Fellowship Examination July-August 2001Document11 pagesThe Hong Kong College of Anaesthesiologists Intermediate Fellowship Examination July-August 2001Jane KoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1-CBC InterpretationDocument10 pages1-CBC Interpretationمصطفي خندقاويPas encore d'évaluation
- 63 Must Know Lab Values Cheat Sheet - NCLEX (Caribbean Nurses of Puerto Rico and Latin America) PDFDocument4 pages63 Must Know Lab Values Cheat Sheet - NCLEX (Caribbean Nurses of Puerto Rico and Latin America) PDFChristineBiankii100% (1)
- Case 222Document33 pagesCase 222jovan teopizPas encore d'évaluation
- 19 HPND Blood Gas ValuesDocument1 page19 HPND Blood Gas ValuesSara OchoaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transfusion Related-Acute Lung Injury A Case Study: Dawn Barten MT (ASCP)Document53 pagesTransfusion Related-Acute Lung Injury A Case Study: Dawn Barten MT (ASCP)asclswisconsin0% (1)
- Its Just HoaxDocument10 pagesIts Just HoaxArkhan HanafiPas encore d'évaluation
- LABORATORYDocument3 pagesLABORATORYKate EscotonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ruppels Manual of Pulmonary Function Testing 10th Edition Mottram Test BankDocument13 pagesRuppels Manual of Pulmonary Function Testing 10th Edition Mottram Test Bankkhuyentryphenakj1100% (30)
- Gastro Translated Terakhir MaybeDocument31 pagesGastro Translated Terakhir MaybetorajasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Results: Seq No Date Profile Method Operator Sample ID 1 Sample ID 2Document1 pageSample Results: Seq No Date Profile Method Operator Sample ID 1 Sample ID 2Prabowo Syasmita BadjakPas encore d'évaluation
- Mam Eden Laboratories Complex Hypogastric MassDocument7 pagesMam Eden Laboratories Complex Hypogastric MassKceey CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Arbie CDocument9 pagesArbie CSusan Tyler-FreerPas encore d'évaluation
- Lapkas 03092020Document7 pagesLapkas 03092020Herison Efrata SinulinggaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 1Document5 pagesCase 1Our Life StoryPas encore d'évaluation
- Bab Ii Laporan KasusDocument8 pagesBab Ii Laporan KasusrismulPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Quiz - CBC Interpretation1 - Hematology 2 LaboratoryDocument15 pagesPractice Quiz - CBC Interpretation1 - Hematology 2 LaboratoryZyza YtreaPas encore d'évaluation
- TN KoesrinDocument5 pagesTN KoesrinCristian RajagukgukPas encore d'évaluation
- Bisitopenia + HyperleukocytosisDocument77 pagesBisitopenia + Hyperleukocytosisdenina setyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hema Lab MidtermDocument130 pagesHema Lab MidtermTrangia, SharmainePas encore d'évaluation
- Progress 3-1Document3 pagesProgress 3-1radhasaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Morning Report: Friday 20 April 2012Document18 pagesMorning Report: Friday 20 April 2012Felicia adeline ChristianPas encore d'évaluation
- Johannes Gerbes, Frauke Van Der Werff - Fit Fürs Goethe-Zertifikat, A2 - Start Deutsch 2, Volume 2 (2007, Hueber Verlag)Document33 pagesJohannes Gerbes, Frauke Van Der Werff - Fit Fürs Goethe-Zertifikat, A2 - Start Deutsch 2, Volume 2 (2007, Hueber Verlag)kareemPas encore d'évaluation
- Almamoon Labs-999611Document3 pagesAlmamoon Labs-999611anajla713Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arterial Blood Gas - ppt1Document53 pagesArterial Blood Gas - ppt1Madhuri100% (1)
- DK Gastro EditDocument65 pagesDK Gastro Editdenina setyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebral Infarction in Risk Factor of Adenoma and Symptomatic Aortic Stenosis Case Report and Literature Reviewp PDFDocument8 pagesCerebral Infarction in Risk Factor of Adenoma and Symptomatic Aortic Stenosis Case Report and Literature Reviewp PDFFortune JournalsPas encore d'évaluation
- DK Gastro KonsulDocument56 pagesDK Gastro Konsuldenina setyaPas encore d'évaluation
- ABG - Acidbase Disorders Elmenya University Hospital EGYPTDocument127 pagesABG - Acidbase Disorders Elmenya University Hospital EGYPTkhaledPas encore d'évaluation
- DK GastroDocument79 pagesDK Gastrodenina setyaPas encore d'évaluation
- DK IKA-5 Raymond - Intra Abdominal Tumor in 7-Y.o-Boy With Renal FailureDocument45 pagesDK IKA-5 Raymond - Intra Abdominal Tumor in 7-Y.o-Boy With Renal FailurepudjoPas encore d'évaluation
- Acidosis Alkalosis BiochemistryDocument31 pagesAcidosis Alkalosis BiochemistryliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abg PDFDocument40 pagesAbg PDFjohn ginnPas encore d'évaluation
- Arterial Blood GasDocument2 pagesArterial Blood GasluanarikoPas encore d'évaluation
- 4) Physiology-Acid Base Balance-PFTsDocument43 pages4) Physiology-Acid Base Balance-PFTsbikedet268Pas encore d'évaluation
- Venous Blood Gases Station Facilitation Guide ObjectivesDocument4 pagesVenous Blood Gases Station Facilitation Guide Objectivesapi-320469090Pas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 6 LabDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 6 Labcess ignacioPas encore d'évaluation
- Report of Mr. Amresh Kshirsagar PDFDocument4 pagesReport of Mr. Amresh Kshirsagar PDFSanket KatharePas encore d'évaluation
- The ImmersionDocument6 pagesThe Immersionmiss RN100% (1)
- Subdural HematomaDocument7 pagesSubdural Hematomamiss RN50% (2)
- SchizophreniaDocument3 pagesSchizophreniamiss RN100% (2)
- StrokeDocument5 pagesStrokemiss RNPas encore d'évaluation
- Stages of LaborDocument3 pagesStages of Labormiss RN100% (8)
- Tuberculosis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageTuberculosis Pathophysiologymiss RN100% (15)
- WorkplanDocument4 pagesWorkplanmiss RN100% (3)
- Respiratory Anatomy Physiology and Dse DefinitionDocument4 pagesRespiratory Anatomy Physiology and Dse Definitionmiss RN100% (2)
- Placenta PreviaDocument6 pagesPlacenta Previamiss RN93% (14)
- Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument3 pagesPeripheral Vascular Diseasemiss RN100% (4)
- PVDDocument7 pagesPVDmiss RNPas encore d'évaluation
- Peripheral Arterial DseDocument2 pagesPeripheral Arterial Dsemiss RNPas encore d'évaluation
- PrioritizationDocument9 pagesPrioritizationmiss RN100% (4)
- Patho EmphysemaDocument1 pagePatho Emphysemamiss RN100% (3)
- Individual Pyschotherapy2Document1 pageIndividual Pyschotherapy2miss RNPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Nursing AssessmentDocument8 pagesPediatric Nursing Assessmentmiss RN87% (15)
- NCP Quadriplegia ParaplegiaDocument3 pagesNCP Quadriplegia Paraplegiamiss RN50% (2)
- Initial Data Base For Family Nursing PracticeDocument12 pagesInitial Data Base For Family Nursing Practicemiss RN67% (18)
- Gordon S Functional Health Pattern Assessment ToolDocument17 pagesGordon S Functional Health Pattern Assessment Toolmiss RN96% (45)
- Osteogenesis ImperfectaDocument6 pagesOsteogenesis Imperfectamiss RN100% (2)
- Individual Psycho FlashcardsDocument2 pagesIndividual Psycho Flashcardsmiss RNPas encore d'évaluation
- Head TraumaDocument13 pagesHead Traumamiss RN100% (1)
- Individual PyschotherapyDocument1 pageIndividual Pyschotherapymiss RNPas encore d'évaluation
- Gordons 11 Functional Patterns..QuestionsDocument1 pageGordons 11 Functional Patterns..Questionsmiss RN81% (32)
- Endometrial Cancer - Info1Document3 pagesEndometrial Cancer - Info1miss RNPas encore d'évaluation
- Coxa Plana PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCoxa Plana Pathophysiologymiss RN100% (4)
- Endometrial Cancer Risk FactorsDocument3 pagesEndometrial Cancer Risk Factorsmiss RNPas encore d'évaluation
- Formatlabresults NCP DruganaDocument12 pagesFormatlabresults NCP Druganamiss RNPas encore d'évaluation
- DysphagiaDocument1 pageDysphagiamiss RN100% (1)
- A. Community Structure, Characteristics and Dynamics: 5 6 A B C D E F G HDocument7 pagesA. Community Structure, Characteristics and Dynamics: 5 6 A B C D E F G Hmiss RNPas encore d'évaluation
- Dsa 1032Document166 pagesDsa 1032Shalu PurushothamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Therapy PresentationDocument11 pagesRespiratory Therapy Presentation003cbty9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Richard Belli WorkshopDocument62 pagesRichard Belli WorkshopalicefreespiritPas encore d'évaluation
- Cariogram E BookDocument90 pagesCariogram E BookAlifianPas encore d'évaluation
- Lyme DiseaseDocument133 pagesLyme Diseaseernestval100% (3)
- The Pathophysiology of Alzheimer'S Disease and Directions in TreatmentDocument15 pagesThe Pathophysiology of Alzheimer'S Disease and Directions in TreatmentEnerolisa ParedesPas encore d'évaluation
- PMDT Referrals - Ver 2Document15 pagesPMDT Referrals - Ver 2Mark Johnuel DuavisPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Phenomenology: Experience of Chronic Kidney Failure Patients of Aspects Psychosocial in Hospital JambiDocument7 pagesStudy Phenomenology: Experience of Chronic Kidney Failure Patients of Aspects Psychosocial in Hospital JambiInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Checking Vital Signs Objectives:: English 3, 2019 Faculty of Nursing, UNAND 2 and 3 MeetingDocument2 pagesChecking Vital Signs Objectives:: English 3, 2019 Faculty of Nursing, UNAND 2 and 3 MeetingVita Delfi YantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Filaria PPT - ClassDocument59 pagesFilaria PPT - ClassGauravMeratwal100% (2)
- Intertrigo Facts: Obesity ItchingDocument3 pagesIntertrigo Facts: Obesity Itchingyyfan98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mentalizing in Clinical PracticeDocument424 pagesMentalizing in Clinical PracticeJosé Di Sipio95% (22)
- Breech PresentationDocument27 pagesBreech PresentationNurkamilawati AristaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mergency Medicine, Second Edition: 60 Acid-Base DisordersDocument21 pagesMergency Medicine, Second Edition: 60 Acid-Base DisordersLukman NurfauziPas encore d'évaluation
- Core Curriculum For The Dialysis Nurse - Module 1Document7 pagesCore Curriculum For The Dialysis Nurse - Module 1green_archerPas encore d'évaluation
- Stroke (Brain Attack)Document16 pagesStroke (Brain Attack)Nhayr Aidol100% (1)
- Ham D PDFDocument1 pageHam D PDFRabiatul AdawiyahPas encore d'évaluation
- CareerAssessmentQuestionnaire v8!1!14Document1 pageCareerAssessmentQuestionnaire v8!1!14Alain CheryPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Thinking Case Study-SkillsDocument1 pageCritical Thinking Case Study-SkillsRaquel M. MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- SPC 138523Document4 pagesSPC 138523Pankaj ArgalPas encore d'évaluation
- Barcelona 2014Document92 pagesBarcelona 2014ckeshavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Analysis SchizoDocument4 pagesCase Analysis SchizoiamELHIZAPas encore d'évaluation
- DVT PreventionDocument8 pagesDVT PreventionRonald ThakorPas encore d'évaluation
- DjdlkjsaljdljlDocument18 pagesDjdlkjsaljdljlEricPas encore d'évaluation
- Airway Management - AdultDocument13 pagesAirway Management - AdultD M Shawkot HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Effectiveness of Locking Compression Plate in Wedge Fracture of Diaphysis of Radius and Ulna in Adults: A Descriptive Case SeriesDocument23 pagesEffectiveness of Locking Compression Plate in Wedge Fracture of Diaphysis of Radius and Ulna in Adults: A Descriptive Case SeriesRanjit SahPas encore d'évaluation
- Zoll M Series Defibrillator Manual PDFDocument111 pagesZoll M Series Defibrillator Manual PDFAhmad TanveerPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Overdose: Dr. Diah Ari Safitri, SPPDDocument9 pagesDrug Overdose: Dr. Diah Ari Safitri, SPPDmkafabillahPas encore d'évaluation
- First Referral UnitDocument24 pagesFirst Referral Unitjay5ar5jamorabon5torPas encore d'évaluation