Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Form 4 Chapter 4-Protein
Transféré par
Farain RashdiDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Biology Form 4 Chapter 4-Protein
Transféré par
Farain RashdiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
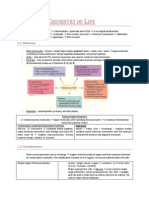
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of The Cell.
1. Primary - linear sequence of amino acids. -types of bonds present : peptide bonds (between amino acids) 2. Secondary - peptide chain is folded and twisted forming helix structure or pleated sheets. - types of bonds present : peptide bonds (between amino acids) and hydrogen bonds ( the maintain the and structures.) -example : Keratin (hair protein) and Silk. 3. Tertiary - helix structure or pleated sheets are folded in various ways to form a globular proteins. - types of bonds present : peptide bonds (between amino acids), hydrogen bonds and disulphide bonds (to maintain globular structure.) -example : enzymes, hormones, antibodies. 4. Quaternary
-C, H, O, N, P, S MADE OF ELEME NTS
- amino acids. - amino acids bind together to form polypeptide chain. - peptide bond forms between 2 amino acids. ex : amino + amino dipeptide + H2O acid acid 1. First Class - provides all the essential amino acids. - example: meat, fish, milk. 2. Second Class - does not have essential amino acids. all the
PROTEI N
STRUCT URES
CLASSES
TYPES
FUNCTIO N TESTS
- to produce new cells for growth. - forms energy during famine. - production of antibodies, enzymes, hormones, haemoglobins. -forms connective tissues, example cartilage, tendons, muscles, ligaments. -forms protein molecules in plasma membrane.
1. Essential -the amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body. -must be taken through food. 2. Non-essential - the amino acids that can be synthesized by the body. - intake through food is not necessary.
1. Millons test. test - Add 2ml testing solution
NaOH + 2ml of testing + 2ml Millons reagent . Heat. of CuSO4 . Shake. (i) if brick red precipitate solution forms, present, means protein present. (i)
2. Biuret
-Add 1ml of solution +2 drops if purple colour
means protein is
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition Oft He CellDocument18 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 4 Chemical Composition Oft He CellAngie Kong Su MeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Chapter 2 Topical ExerciseDocument3 pagesBiology Chapter 2 Topical ExerciseAlan WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2Document13 pagesBiology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2SanjeefKumrIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 SPM Biology Chapter 5Document5 pagesForm 4 SPM Biology Chapter 5Janice NgPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Form 4 ScriptDocument5 pagesBiology Form 4 ScriptsivanesshniPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Document4 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Autumn JJ40% (5)
- Biology Updated 2 Iza and IkmalDocument25 pagesBiology Updated 2 Iza and IkmalEva WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind MapDocument1 pageChapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind Maphuileng_wongPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document7 pagesChapter 3api-3841154Pas encore d'évaluation
- SPM Biology Perlis 2010Document0 pageSPM Biology Perlis 2010Clement TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Form 4 RevisionDocument18 pagesBiology Form 4 RevisionAyu YunusPas encore d'évaluation
- Science concepts explainedDocument8 pagesScience concepts explainedCheng NiePas encore d'évaluation
- SOLAF 2014 Biologi SPM Modul 3: JPN Perak 1Document7 pagesSOLAF 2014 Biologi SPM Modul 3: JPN Perak 1AZIANA YUSUFPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM Biology NotesDocument32 pagesSPM Biology NotesAin Fza0% (1)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 ExerciseDocument7 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 ExerciseAngie Kong Su MeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbonyl ChemistryDocument53 pagesCarbonyl Chemistrysujithhr1233395Pas encore d'évaluation
- Compilation of Experiments Form 4Document13 pagesCompilation of Experiments Form 4Marzila MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 5 Biology (Chapter 1: Transport)Document10 pagesForm 5 Biology (Chapter 1: Transport)Gerard Selvaraj88% (26)
- Skema Jawapan Kertas 3 PatDocument10 pagesSkema Jawapan Kertas 3 PatSitinorsyahidah JantanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ps - Skema Jawapan Kertas 2 - EseiDocument43 pagesPs - Skema Jawapan Kertas 2 - EseiNadira Bt IsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- Topical Test Biology Form 4Document14 pagesTopical Test Biology Form 4Siti Wahida SuleimanPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM Form 4 Notes - Introduction to ChemistryDocument1 pageSPM Form 4 Notes - Introduction to ChemistryMimie Yasmin KamalPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM Biology Form 4 Chapter 2.1 Cell Structures and Functions (ALL 12 Structures of Plant Cell and Animal Cell)Document4 pagesSPM Biology Form 4 Chapter 2.1 Cell Structures and Functions (ALL 12 Structures of Plant Cell and Animal Cell)Felicia LingPas encore d'évaluation
- Sains - Chemistry Form 4Document65 pagesSains - Chemistry Form 4Sekolah Portal92% (24)
- Nota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 2Document12 pagesNota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 2Firas Muhammad100% (2)
- Matter States and PropertiesDocument33 pagesMatter States and PropertiesyokekeannPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOLOGY 2 (4551/2) : Answering Questions Techniques SECTION A: STRUCTURED QUESTIONS (5 Compulsory Questions)Document6 pagesBIOLOGY 2 (4551/2) : Answering Questions Techniques SECTION A: STRUCTURED QUESTIONS (5 Compulsory Questions)Jedidah Jong100% (2)
- Form 4 Revision QuizDocument80 pagesForm 4 Revision QuizEnvira LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Form 1 - 2.3Document18 pagesForm 1 - 2.3ardylea100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Biology Form 4: EnzymesDocument26 pagesChapter 4 Biology Form 4: EnzymesNurul Husna100% (1)
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Document24 pagesBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Nitya Dewi100% (2)
- Scheme of Work and Activities for Science Form 2 Biodiversity and EcosystemDocument20 pagesScheme of Work and Activities for Science Form 2 Biodiversity and EcosystemBestah Joewellster Teo100% (1)
- Gozobiochem - Form 5 Biology Topic 1Document16 pagesGozobiochem - Form 5 Biology Topic 1Eunice TangPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes: Biochemical Reactions Which Occur in Cells Are Called MetabolismDocument30 pagesEnzymes: Biochemical Reactions Which Occur in Cells Are Called MetabolismAZIANA YUSUFPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise Chapter 2 Physics Form 4Document4 pagesExercise Chapter 2 Physics Form 4afiqiman8950% (2)
- Proteins Structure, Classification and Biological Functions: DR - AchyuthaDocument33 pagesProteins Structure, Classification and Biological Functions: DR - AchyuthaMohammad AadilPas encore d'évaluation
- Proteins: Submitted To: Mam Saima Khubaib Submitted By: Muhammad HannanDocument13 pagesProteins: Submitted To: Mam Saima Khubaib Submitted By: Muhammad HannanMuhammad HannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity No. 4.3 EssayDocument4 pagesActivity No. 4.3 EssayZeal Alexis MontellorPas encore d'évaluation
- Simranjeet Singh's Chemistry Report on Biomolecules and ProteinsDocument16 pagesSimranjeet Singh's Chemistry Report on Biomolecules and ProteinsMadhur SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Proteins: NH (Amine) Group COOH (Carboxylic) GroupDocument5 pagesProteins: NH (Amine) Group COOH (Carboxylic) GroupPriyanthi FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit -14 Biomolecules Classification and PropertiesDocument4 pagesUnit -14 Biomolecules Classification and PropertiesGaurav SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bimolecules G10Document15 pagesBimolecules G10hmoncatar.bulPas encore d'évaluation
- Proteins Ppt. (By CDM)Document31 pagesProteins Ppt. (By CDM)Aldren MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- BiomoleculesDocument4 pagesBiomoleculesiyahh5.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem MidtermsDocument4 pagesBiochem MidtermschristinejeancenabrePas encore d'évaluation
- ProteinsDocument22 pagesProteinsassmmPas encore d'évaluation
- 1E Activity No. 4.3 Essay - 1EDocument4 pages1E Activity No. 4.3 Essay - 1EZeal Alexis MontellorPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Protein?: Objectives PART A: Understanding ProteinsDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Protein?: Objectives PART A: Understanding ProteinsBaby KylePas encore d'évaluation
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument48 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinsSteph VeePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 7 ProteinsDocument140 pagesUnit 7 ProteinsJan Ariel AficialPas encore d'évaluation
- PROTEINDocument90 pagesPROTEINYo1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document7 pagesChapter 6Chocopud LeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins: Structures, Properties, FunctionsDocument16 pagesChemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins: Structures, Properties, FunctionsJesziePas encore d'évaluation
- Proteins chemistry: Amino acids and their propertiesDocument29 pagesProteins chemistry: Amino acids and their propertiesDr. Mohamed ShamsPas encore d'évaluation
- ProteinDocument31 pagesProteinShiela Marie BanggotPas encore d'évaluation
- Protein PDFDocument27 pagesProtein PDFSumaiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2Kate Wen GuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3-ProteinsDocument9 pagesLecture 3-ProteinsOminousCroakPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary Structures of A ProteinDocument21 pagesPrimary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary Structures of A ProteinDALITSO CHIKOYA100% (1)
- Foods and Nutrition Paper OneDocument119 pagesFoods and Nutrition Paper OneNaduku EridadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Step by Wicked StepDocument9 pagesStep by Wicked StepHari ShankerPas encore d'évaluation
- Hosts UmbrellaDocument1 pageHosts UmbrellaFabsor SoralPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 4-LipidDocument1 pageBiology Form 4 Chapter 4-LipidFarain RashdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind MapDocument1 pageChapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind Maphuileng_wongPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Document15 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Farain RashdiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.2 Motion GraphDocument11 pages2.2 Motion GraphWong Kam FookPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.8 Gravitational Force - Doc Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 ForceDocument12 pages2.8 Gravitational Force - Doc Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 ForceEzra Loganathan MuniandiPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Document17 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Farain RashdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Chapter 2 Form 4Document3 pagesBiology Chapter 2 Form 4Farain RashdiPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Intro To PhysicsDocument33 pages1 Intro To Physicsharshasoni100% (6)
- Marine Pollution Bulletin: Sivanandham Vignesh, Krishnan Muthukumar, Rathinam Arthur JamesDocument11 pagesMarine Pollution Bulletin: Sivanandham Vignesh, Krishnan Muthukumar, Rathinam Arthur JamesGeorgiana-LuizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microsoft Word - SOP ON DispensingDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Word - SOP ON DispensingPalawan Baptist HospitalPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions To Exercises, Chapter 19: Okuyama & Maskill: Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesSolutions To Exercises, Chapter 19: Okuyama & Maskill: Organic ChemistryM Irfan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Outcome of Pelvic Fractures Identi Fied in 75 Horses in A Referral Centre: A Retrospective StudyDocument8 pagesOutcome of Pelvic Fractures Identi Fied in 75 Horses in A Referral Centre: A Retrospective StudyMaria Paz MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Wastewater Collection Systems Comparison: William T. Hensley, International Territory Manager, Orenco Systems, IncDocument5 pagesWastewater Collection Systems Comparison: William T. Hensley, International Territory Manager, Orenco Systems, IncmeskbPas encore d'évaluation
- Plateau Pressure Ventilation MeasurementDocument1 pagePlateau Pressure Ventilation MeasurementImtiaz AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Series NRX With PXR - Type NF Low Voltage Power (Air) Circuit Breaker Instruction ManualDocument70 pagesSeries NRX With PXR - Type NF Low Voltage Power (Air) Circuit Breaker Instruction ManualHamilton GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- 0 BOSH FrameworkDocument18 pages0 BOSH Frameworkharold fontiveros100% (1)
- Face SerumDocument10 pagesFace SerumLiliana CojocaruPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 FertilityDocument30 pagesLecture 3 Fertilityანთეა აბრამიშვილიPas encore d'évaluation
- Vitamin D DeficinyDocument11 pagesVitamin D DeficinyسالمPas encore d'évaluation
- Eye, E.N.T. & Dental AnaesthesiaDocument22 pagesEye, E.N.T. & Dental AnaesthesiawellawalalasithPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation and Operating Instructions DPV and DPLHS PumpsDocument36 pagesInstallation and Operating Instructions DPV and DPLHS PumpsSergeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ukite 2011Document123 pagesUkite 2011pikacu19650% (2)
- Cakes Amp Sugarcraft - April-May 2019 EditDocument45 pagesCakes Amp Sugarcraft - April-May 2019 Editapi-197110397100% (1)
- The Design of The 2016-17 Young Lives School Survey in EthiopiaDocument10 pagesThe Design of The 2016-17 Young Lives School Survey in EthiopiaFuadPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Medicine 1 50Document33 pagesRespiratory Medicine 1 50Ahmed Kh. Abu WardaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cooling & Heating: ShellmaxDocument3 pagesCooling & Heating: Shellmaxvijaysirsat2007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Integration of The Saprobic System Into The European Union Water Framework DirectiveDocument14 pagesIntegration of The Saprobic System Into The European Union Water Framework DirectiveMihaela MirabelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Description of Gambat South Gas Processing FacilityDocument13 pagesProcess Description of Gambat South Gas Processing FacilitywaheedPas encore d'évaluation
- E1cc E3ccDocument219 pagesE1cc E3ccSARAMQRPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel Gas Superheater 195-E-301 A/B: Mechanical - Data SheetDocument3 pagesFuel Gas Superheater 195-E-301 A/B: Mechanical - Data SheetZulfikar N JoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Changes in Demand and Supply of Face Masks Under CovidDocument3 pagesChanges in Demand and Supply of Face Masks Under CovidHanh HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- ISA CCST Task List Reference GuideDocument13 pagesISA CCST Task List Reference GuideNaseer HydenPas encore d'évaluation
- HLF Sharing Fitness Business CooperationDocument17 pagesHLF Sharing Fitness Business Cooperationbhardwajharsh2706Pas encore d'évaluation
- Calculation of shell and dish thicknessDocument2 pagesCalculation of shell and dish thicknessThiru AnanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Jose Irizarry ResumeDocument2 pagesJose Irizarry ResumeAnastasia GloverPas encore d'évaluation
- Using Casts For ImmobilizationDocument17 pagesUsing Casts For Immobilizationmpmayer2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Confined Space Planning ChecklistDocument3 pagesConfined Space Planning ChecklistKB100% (1)
- 1.4 Market FailureDocument42 pages1.4 Market FailureRuban PaulPas encore d'évaluation