Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Circuit Description
Transféré par
Johnson PhilipTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Circuit Description
Transféré par
Johnson PhilipDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
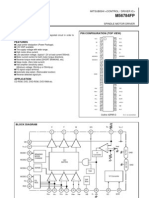
SG3525A.
Circuit description This IC is designed for use in switched mode power supplies, but can be configured to work nicely for our requirements. To explain the function of this circuit it is helpful to look at the innards of the chip, shown below:
The speed demand signal is input at pin 2, the op amp non-inverting input. The internal op amp is wired as a simple unity gain follower, and the demand signal is then applied to the PWM comparator. This compares the demand level with the oscillator output, in the same fashion as that shown in section 2.1.1. The frequency of the oscillator, and therefore the PWM signal produced, is governed by the value of the resistor to ground on the RT pin. The sync and osc out pins are not required for our purposes.
The output stage is a little odd, since it is designed for driving bipolar transformers in SMPS circuits. However, we can wire it so it produces a simple single PWM waveform. By not using the bottom transistor of the totem-pole output stages on both OutA and OutB outputs, tying OutA and OutB to ground, attaching a pull-up resistor to the Vc pin, then the bottom transistors of the output stages simply switch the Vc pin to ground, and the signal at the Vc pin is our required PWM signal. The IC also has two protection mechanisms for use in SMPS circuits which we can also make use of. The soft start feature prevents the output from saturating at 100% ratio when the chip is powering up. This is useful for us as it stops the motors from being driven as our circuits are powering up. The Shutdown input is an active-high input that immediately shuts down the outputs, and resets the soft-start feature. This can be used by current-limiting circuitry to turn off the power MOSFETs in the speed controller, and the soft-start will back-off the PWM while the problem can be addressed by the driver.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Évaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- Arcam Alpha10 10p Power Amplifier Service ManualDocument19 pagesArcam Alpha10 10p Power Amplifier Service Manual王宗超Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Best Transformerless Inverters With Circuit DiagramsDocument35 pages3 Best Transformerless Inverters With Circuit Diagramswinkyi100% (1)
- Pure Sine Invereter InfoDocument107 pagesPure Sine Invereter Infoolawale gbadeboPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuit Stepper Motor DriverDocument17 pagesCircuit Stepper Motor DriverkalpicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mini ProjectsDocument55 pagesMini ProjectsSampath KumarPas encore d'évaluation
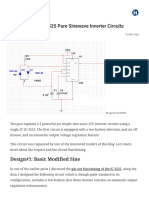
- 3 High Power SG3525 Pure Sinewave Inverter Circuits - Homemade Circuit ProjectsDocument20 pages3 High Power SG3525 Pure Sinewave Inverter Circuits - Homemade Circuit ProjectsANKUR RATHIPas encore d'évaluation
- Railway GateDocument46 pagesRailway GateRocky SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Speed Control Using MatlabDocument23 pagesSpeed Control Using MatlabNidan TegarPas encore d'évaluation
- PWM DC Motor Speed Control Using 555Document16 pagesPWM DC Motor Speed Control Using 555Karthik Dm67% (3)
- EDN Design Ideas 2008Document124 pagesEDN Design Ideas 2008chag1956100% (2)
- PCB Project DetailsDocument4 pagesPCB Project DetailsmohanPas encore d'évaluation
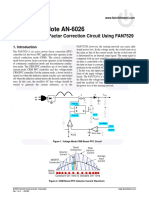
- Application Note AN-6027: Design of Power Factor Correction Circuit Using FAN7530Document16 pagesApplication Note AN-6027: Design of Power Factor Correction Circuit Using FAN7530Malanie Sriya De SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
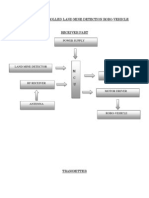
- WIRE LESS Land Mine Detection Robo-VehicleDocument35 pagesWIRE LESS Land Mine Detection Robo-VehicleDebashish BeheraPas encore d'évaluation
- Arduino Driving Power Mosfet uRiZsEVG6kDocument11 pagesArduino Driving Power Mosfet uRiZsEVG6kahas viyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- An 6026Document23 pagesAn 6026Иван АлексиевPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Inverter Output Voltage Correction Circuit - Homemade Circuit ProjectsDocument7 pagesAutomatic Inverter Output Voltage Correction Circuit - Homemade Circuit ProjectsK. RAJA SEKARPas encore d'évaluation
- Protection v2 2Document16 pagesProtection v2 2Alexandr SemenkoffPas encore d'évaluation
- SMPSDocument7 pagesSMPSDebashish RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Collins PTT Line Interface For ICOM IC-706 FamilyDocument2 pagesCollins PTT Line Interface For ICOM IC-706 FamilyJim FischerPas encore d'évaluation
- AN4105 Power Switching ICDocument23 pagesAN4105 Power Switching ICatomo33100% (1)
- Railway Accident Monitoring System: A Project Report ONDocument13 pagesRailway Accident Monitoring System: A Project Report ONPrateek SrivastavPas encore d'évaluation
- An 1138Document18 pagesAn 1138Marco Tulio Da SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Module Driver Circuit,: November1995Document3 pagesPower Module Driver Circuit,: November1995Narendra BholePas encore d'évaluation
- IJSRDV2I3100Document10 pagesIJSRDV2I3100Yash KalraPas encore d'évaluation
- ELM327DSDocument0 pageELM327DSroccandradoPas encore d'évaluation
- WorkingDocument3 pagesWorkingAnuj TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- A3953 Datasheet PDFDocument12 pagesA3953 Datasheet PDFfelres87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Speed Control of 1-Ph Induction MotorDocument41 pagesAutomatic Speed Control of 1-Ph Induction MotorPrakash Dudharkar100% (1)
- Chapter Three2Document12 pagesChapter Three2Fuh ValleryPas encore d'évaluation
- L6599ADDocument35 pagesL6599ADjuliojuder100% (1)
- Concept Paper EditedDocument7 pagesConcept Paper EditedJr BongabongPas encore d'évaluation
- Novel Low Cost Green-Power PWM Controller: FeaturesDocument15 pagesNovel Low Cost Green-Power PWM Controller: FeaturesHermanPas encore d'évaluation
- LM5015 Evaluation Board SchematicDocument8 pagesLM5015 Evaluation Board SchematicLokesh EshwaraiahPas encore d'évaluation
- KA3525 IC UpdatedDocument10 pagesKA3525 IC UpdatedKarthik DmPas encore d'évaluation
- PWM Signal Generators: Testing Status: Mixed. Some Untested, Some SPICE SimulatedDocument15 pagesPWM Signal Generators: Testing Status: Mixed. Some Untested, Some SPICE SimulatedSivareddy MudiyalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Slua 080Document24 pagesSlua 080HauvuPas encore d'évaluation
- Report MosfetDocument13 pagesReport MosfetaiswaryaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1) Smps Using Viper22A: Circuit DiagramDocument6 pages1) Smps Using Viper22A: Circuit DiagramBhadreshkumar SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ac Voltage Controller Using Thyristor Project Report by SandeepDocument29 pagesAc Voltage Controller Using Thyristor Project Report by SandeepSANDEEP DHANDA100% (1)
- Scoreboard Circuit FRFRDocument7 pagesScoreboard Circuit FRFRKeil Yow Yow YowPas encore d'évaluation
- PWM Based Induction Motor Control - 1Document25 pagesPWM Based Induction Motor Control - 1jagannathpressbdkPas encore d'évaluation
- Fabrication of Unconventional Compressor For Heavy Truck (Demo Model)Document8 pagesFabrication of Unconventional Compressor For Heavy Truck (Demo Model)vijayant gautamPas encore d'évaluation
- New Gate Driver Baser Ir2110Document4 pagesNew Gate Driver Baser Ir2110Ayoub RajawiPas encore d'évaluation
- PDFDocument8 pagesPDFanterommxPas encore d'évaluation
- Dsa 265104Document20 pagesDsa 265104foxx034Pas encore d'évaluation
- The LM324 Quad Op-Amp Line Follower Robot With Pulse Width ModulationDocument15 pagesThe LM324 Quad Op-Amp Line Follower Robot With Pulse Width ModulationMeyersson BeltranPas encore d'évaluation
- XX3842 Series FunctionDocument7 pagesXX3842 Series FunctionbernabethPas encore d'évaluation
- Sage EDM Stepper Conversion Description V2Document4 pagesSage EDM Stepper Conversion Description V2Nacer MezghichePas encore d'évaluation
- Circuito Regulador de Voltaje Ob2216Document9 pagesCircuito Regulador de Voltaje Ob2216Wcarlos Ob RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter One Controlling The Operation of Wind-Solar Hybrid Power System Using Arduino-Based Hybrid MPPT ControllerDocument48 pagesChapter One Controlling The Operation of Wind-Solar Hybrid Power System Using Arduino-Based Hybrid MPPT ControllerOdebunmi NathanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Ci Driver Do Motor Do CD Rom DatasheetDocument11 pagesCi Driver Do Motor Do CD Rom DatasheetAdriano TameouvindoPas encore d'évaluation
- 12-Basic Knowledge of LDO Voltage Regulator enDocument19 pages12-Basic Knowledge of LDO Voltage Regulator enKirti Susan VarghesePas encore d'évaluation
- Etco 2017 GRP 8Document3 pagesEtco 2017 GRP 8RohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Boost Converter Using The PIC16F753 Analog Features: Performance SpecificationsDocument9 pagesBoost Converter Using The PIC16F753 Analog Features: Performance SpecificationsSheik Ashiq AmeerPas encore d'évaluation
- PW M Generator Curso e Faça Voce MesmoDocument6 pagesPW M Generator Curso e Faça Voce MesmoEcoteck TécnicaPas encore d'évaluation
- PWM-QR Ic: Control IC For Switched-Mode Power Supplies Using MOS-TransistorsDocument24 pagesPWM-QR Ic: Control IC For Switched-Mode Power Supplies Using MOS-TransistorsCarlos ArturoPas encore d'évaluation
- February 28 - March 03, Kochi - Kerala: The Kerala State 'A' Grade Electrical Contractors' AssociationDocument4 pagesFebruary 28 - March 03, Kochi - Kerala: The Kerala State 'A' Grade Electrical Contractors' AssociationJohnson PhilipPas encore d'évaluation
- LM 7805 RegulatorDocument12 pagesLM 7805 RegulatorFadel BairuniPas encore d'évaluation
- 3525Document8 pages3525Johnson PhilipPas encore d'évaluation
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission Systems Technology Review PaperDocument19 pagesHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission Systems Technology Review PaperDavid Jose Poma GuillenPas encore d'évaluation
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission Systems Technology Review PaperDocument19 pagesHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission Systems Technology Review PaperDavid Jose Poma GuillenPas encore d'évaluation
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission Systems Technology Review PaperDocument19 pagesHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission Systems Technology Review PaperDavid Jose Poma GuillenPas encore d'évaluation
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission Systems Technology Review PaperDocument19 pagesHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission Systems Technology Review PaperDavid Jose Poma GuillenPas encore d'évaluation
- "HVDC Transmission": Mrs. Shaija P JDocument20 pages"HVDC Transmission": Mrs. Shaija P JJohnson PhilipPas encore d'évaluation