Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
General Embryology Mnemonics
Transféré par
Fajar Rudy QimindraDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
General Embryology Mnemonics
Transféré par
Fajar Rudy QimindraDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
General Embryology Mnemonics
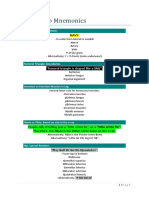
2nd, 3rd and 4th weeks of development: Week 2 : Bilaminar germ disc Week 3 : Trilaminar germ disc Week 4 : Appearance of 4 limbs Major Neural Crest Derivatives: GAMES Glial cells of peripheral ganglia Arachnoid and Pia Sheath Melanocytes Enteric ganglia Schwann cells Neuroectoderm derivatives Neurons Neuroglia Neurohypophysis piNeurol (pineal) gland Foregut derivatives Little Embryo People Do Like Swallowing, Producing Gas Lungs Esophagus Pancreas Duodenum (proximal) Liver Stomach Pancreas Gall bladder Occurrence of Teratogenesis TEratogenesis Between Third and Eighth weeks of gestation. Derivatives of Mesoderm:
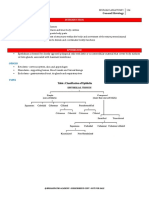
Derivatives of 3 germ layers
MESODERM Mesothelium (peritoneal, pleural, pericardial)/ Muscle (striated, smooth, cardiac) Embryologic Spleen/ Soft tissue/ Serous linings/ Sarcoma/ Somite Osseous tissue/ Outer layer of suprarenal gland (cortex)/ Ovaries Dura/ Ducts of genitalia Endothelium Renal Microglia Mesenchyme/ Male gonad Branchial apparatus: CAP covers from outside to inside. C for Clefts : derived from ectoderm A for Arches : derived from mesoderm and neural crest P for Pouches : derived from endoderm Chromosomal disorders: Edward syndrome : election age-ch-18 Down syndrome : drinking age-ch-21 Patau syndrome : puberty age-ch-13 Fetal Hemopoesis (for Physiology): Young Liver Synthesizes Blood Y : Yolk Sac (from 3 weeks) L : Liver (from 3 months) S : Spleen (from 3 months) B : Bone marrow (5 month onwards) After birth hemopoesis occurs only in bone marrow except in case of emergency when bone marrow falls. Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS): FAS F : Facial hypoplasia and Forebrain malformation A : Attention defecit disorder and Altered joints S : Short stature, Septal defects and Small I.Q Neural Crest Derivatives 4 Gang MEN wore CAP A. 4 Gang (4 ganglias)
Dorsal root ganglia of spinal nerves Ganglia of V, VII, IX and X cranial nerves Sympathetic & parasympathetic ganglia (autonomic ganglia) Ganglion cell layer of retina B. MEN
Melanoblast of the skin Enamel of teeth Neurilemma (Schwann cells) C. CAP
Chromaffin cells and Cranio-facial skeleton Arachnoid and Pia Maters
Derivatives of branchial arches
First Branchial Arch: IMPACTS Most of the aspects associated with the first arch begin with the letter M and the rest with I, P, A, C, T or S.
o o o o o
o o o o
Name : Mandibular arch. Muscles : Muscles of Mastication (Masseter, Temporalis, Medial & Lateral Pterygoids) Mylohyoid Anterior belly of Digastric Tensor tympani and Tensor palatini Cartilage : Meckels cartilage Malleus & Incus, Sphenomandibular ligament & Anterior ligament of Malleus Innervation : Mandibular nerve, Chorda tympani Cartilage derivatives of 2nd branchial arch: 5 S Stapes Styloid process Stylohyoid ligament Smaller (lesser) cornu of hyoid Superior part of body of hyoid Derivatives of Pharyngeal Pouches: 1A, 2P, 3 TIP, 4 SPUB 1A (1st Pharyngeal Pouch Auditory) Epithelial lining of Auditory tube , middle ear cavity and mastoid antrum 2P (2nd Pharyngeal Pouch Palatine) Epithelial lining of crypts of Palatine tonsil 3 TIP (3rd Pharyngeal Pouch Thymus and Inferior Parathyroid gland) Thymus and Inferior Parathyroid gland 4 SPUB (4th Pharyngeal Pouch Superior Parathyroid gland and Ultimobranchial Body) Superior Parathyroid gland and Ultimobranchial Body Nerves:
March 5, 7910 1 : V3 (March for 3 and 5 for V) 2 : VII (7) 3 : IX (9) 4 & 6 : X (10)
Popularity: 17% Tags: embryology, Mnemonics, pneumonics
Read more General Embryology Mnemonics | Medchrome
Embryology Mnemonics
Embryology Mnemonics
Mitosis: events at 4 stages Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase: Prophase: Chromosomes and spindles are Produced. Metaphase: chromosomes MetAlign themselves. Anaphase: [Ana] divorced or separated. Telophase: Tell-O'Brien his daughter cells are ready.
Woffian duct (mesonephric duct) derivatives. Gardener's SEED: Female: Gartner's duct, cyst Male: Seminal vesicles Epididymis Ejaculatory duct Ductus deferens
Potter syndrome: features POTTER: Pulmonary hypoplasia Oligohydrominios Twisted skin (wrinkly skin) Twisted face (Potter facies) Extremities defects Renal agenesis (bilateral)
Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS): features FAS: Facial hypoplasia/ Forebrain malformation Attention defecit disorder/ Altered joints Short stature/ Septal defects/ Small I.Q
Tetrology of Fallot PROVe: Pulmonary stenosis Right ventricular hypertrophy Overriding aorta Ventricular septal defect
Neuroectoderm derivatives Neuroectoderm gives rise to:
Neurons Neuroglia Neurohypophysis piNeurol (pineal) gland
Foregut derivatives "Little Embryo People Do Like Swallowing, Producing Gas": Lungs Esophagus Pancreas Duodenum (proximal) Liver Stomach Pancreas Gall bladder
Heart: primitive heart chambers in fetal heart "The Broken Vein Always Stenoses, But Veins Are Smooth": The order of the compartments is: <b<t< b>runcus, bulbus Primitive Ventricle Primitive Atrium Sinus venosus The connections are: Bulbotruncal junctionVentriculobulbar foramen Atrioventricular canal Sinuatrial junction
Tetrology of Fallot "Problems Of Small Hearts": Pulmonary stenosis Overriding aorta Ventricular Septal defect Hypertrophy of right ventricle
Weeks 2, 3, 4 of development: an event for each Week Two: Bilaminar germ disc. Week Three: Trilaminar germ disc. Week Four: Fourlimbs appear.
Lung development phases "Every Premature Child Takes Air": Embryonic period Pseudoglandular period Canalicular peroid Terminal sac period Alveolar period
Branchial arch giving rise to aorta "Aor- from Four": Aorta is from fourth arch.
Placenta-crossing substances "WANT My Hot Dog": Wastes Antibodies Nutrients Teratogens Microorganisms Hormones/ HIV Drugs
Cranial and spinal neural crest: major derivatives GAMES: Glial cells (of peripheral ganglia) Arachnoid (and pia) Melanocytes Enteric ganglia Schwann cells
Tetrology of Fallot "Don't DROP the baby": Defect (VSD) Right ventricular hypertrophy Overriding aorta Pulmonary stenosis
Mesoderm components MESODERM: Mesothelium (peritoneal, pleural, pericardial)/ Muscle (striated, smooth, cardiac) Embryologic Spleen/ Soft tissue/ Serous linings/ Sarcoma/ Somite Osseous tissue/ Outer layer of suprarenal gland (cortex)/ Ovaries Dura/ Ducts of genitalia Endothelium Renal Microglia/ Mesenchyme/ Male gonad
Tetrology of Fallot "IHOP-International House of Pancakes": Interventricular septal defect Hypotrophy of right ventricle Overriding aorta Pulmonary stenosis
Teratogenesis: when it occurs TEratogenesis is most likely during organogenesis--between the: Third and Eighth weeks of gestation.
Vitelline duct: closure time VItelline duct normally closes around week VI of intrauterine life.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Anatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsD'EverandAnatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (15)
- Embryologypracticequestionswithanswers 140707144050 Phpapp02Document120 pagesEmbryologypracticequestionswithanswers 140707144050 Phpapp02oopie0% (1)
- Clinical Anatomy QuestionsDocument9 pagesClinical Anatomy QuestionszuftPas encore d'évaluation
- GROSS ANATOMY-Review Notes PDFDocument56 pagesGROSS ANATOMY-Review Notes PDFgreen_archerPas encore d'évaluation
- Embryology MCQ Fetal PeriodDocument2 pagesEmbryology MCQ Fetal Periodthevampire2010482579% (14)
- Brs Embryology Q&ADocument41 pagesBrs Embryology Q&ASURG BLOCK100% (1)
- Embryology+Anatomy Study Questions ONLYDocument10 pagesEmbryology+Anatomy Study Questions ONLYAnca Badoiu75% (4)
- Embryo REVIEWnotesDocument90 pagesEmbryo REVIEWnotesKapee Theva75% (4)
- Anatomy Quest.Document9 pagesAnatomy Quest.Ade AlcarazPas encore d'évaluation
- Mnemonics Head NeckDocument8 pagesMnemonics Head NeckMartin Susanto, MD100% (2)
- Rapid Review of Embryology, First PDFDocument137 pagesRapid Review of Embryology, First PDFmayurdadhaniya100% (1)
- Anatomy QuestionsDocument104 pagesAnatomy QuestionsJohn Christopher Luces100% (1)
- Practise Questions Keith & Moore 5th Edition - Should ReadDocument113 pagesPractise Questions Keith & Moore 5th Edition - Should ReadAmirsalar Eslami83% (6)
- Embryology QuestionDocument19 pagesEmbryology QuestionVarun Arunagiri100% (17)
- Embryology practice questions and answersDocument33 pagesEmbryology practice questions and answersElizabeth Gabriel HoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Questions 3600Document133 pagesAnatomy Questions 3600Clare Rizer100% (8)
- MCQ PerineumDocument4 pagesMCQ PerineumEman Hamada100% (2)
- Upper Limb Mcq PDF FREE DOWNLOADDocument7 pagesUpper Limb Mcq PDF FREE DOWNLOADTendai Chirisa100% (1)
- Viva Questions AnatomyDocument7 pagesViva Questions AnatomyAhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Body Fluids MCQsDocument10 pagesBody Fluids MCQsAbdulkadir Waliyy Musa50% (2)
- MCQ Head & NeckDocument5 pagesMCQ Head & NeckSyafiqah Ahmad100% (2)
- Embryology Revision NotesDocument10 pagesEmbryology Revision NotesvamshidhPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes On EmbryologyDocument30 pagesNotes On EmbryologyArwa100% (9)
- Anatomy MCQs (Thorax)Document2 pagesAnatomy MCQs (Thorax)Adil Shabbir100% (2)
- Histology Final Exam Practice Test KeyDocument13 pagesHistology Final Exam Practice Test Keynbaumgartner0100% (7)
- Test Bank Larsens Human Embryology 5th EditionDocument22 pagesTest Bank Larsens Human Embryology 5th EditionRichard1LauritsenPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQs On Anatomy of The Pelvis - Part 2Document3 pagesMCQs On Anatomy of The Pelvis - Part 2soban100% (5)
- Mnemonics Anatomy 1st SemDocument4 pagesMnemonics Anatomy 1st SemNastassja Callmedoctor Douse67% (3)
- 2-Epithelium MCQ Asnan Ainshams DR - Zahra 2020Document9 pages2-Epithelium MCQ Asnan Ainshams DR - Zahra 2020Shay Os100% (1)
- Histology World Histology TestbankDocument6 pagesHistology World Histology TestbankRalp Barrios100% (1)
- Embryology Exam - I PDFDocument8 pagesEmbryology Exam - I PDFuprince100100% (1)
- Head and Neck Anatomy QuizDocument6 pagesHead and Neck Anatomy QuizMatt Cooper100% (4)
- Embryology QuestionsDocument29 pagesEmbryology QuestionsRan Acc100% (2)
- Upper Limb Anatomy GuideDocument48 pagesUpper Limb Anatomy GuideFarhad Ali100% (2)
- Anat 5.2 Pelvis and Perineum - ElevazoDocument14 pagesAnat 5.2 Pelvis and Perineum - Elevazolovelots1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pelvis Anatomy MCQDocument1 pagePelvis Anatomy MCQkhamkham19100% (4)
- NeuroanatomyDocument3 pagesNeuroanatomyModoro0% (1)
- Anatomy MCQDocument9 pagesAnatomy MCQAmmarah KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz Anatomy Part 1 of 3Document44 pagesQuiz Anatomy Part 1 of 3MedShare92% (24)
- Anatomy MCQ 2Document63 pagesAnatomy MCQ 2Pirabakar MahendranPas encore d'évaluation
- Waxman - Neuroanatomy Self-Assessment MCQsDocument46 pagesWaxman - Neuroanatomy Self-Assessment MCQsNikunj94% (33)
- Embryology Notes by Dr. NajeebDocument572 pagesEmbryology Notes by Dr. NajeebMajid Masood100% (6)
- Lower Limb Mnemonics (Highlighted)Document8 pagesLower Limb Mnemonics (Highlighted)Saajid Amra100% (5)
- General Histology FinalDocument60 pagesGeneral Histology FinalDr P N N ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Comprehensive Exam: Pregnancy Issues and Congenital AbnormalitiesDocument15 pagesComprehensive Exam: Pregnancy Issues and Congenital AbnormalitiesDr-Jahanzaib GondalPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology Practice PracticalDocument38 pagesHistology Practice PracticalDeep Patel88% (8)
- Anatomy I MCQDocument10 pagesAnatomy I MCQARIJITBANIK36100% (3)
- AHEAD Test and Discussions - ANATOMYDocument3 pagesAHEAD Test and Discussions - ANATOMYJesna Jesna V100% (2)
- Histology QuestionsDocument3 pagesHistology QuestionsAlec Maquiling100% (1)
- Embryology of the HeartDocument3 pagesEmbryology of the HeartFlorence BamigbolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Questions in Anatomy and Neurobiology for UndergraduatesD'EverandMultiple Choice Questions in Anatomy and Neurobiology for UndergraduatesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (5)
- Sweet Biochemistry: Remembering Structures, Cycles, and Pathways by MnemonicsD'EverandSweet Biochemistry: Remembering Structures, Cycles, and Pathways by MnemonicsPas encore d'évaluation
- "Games": 2nd, 3rd and 4th Weeks of DevelopmentDocument5 pages"Games": 2nd, 3rd and 4th Weeks of DevelopmentAlej DonesaPas encore d'évaluation
- Branchial ArchesDocument49 pagesBranchial ArchesSherin ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- 002.pre-Natal & Post-Natal Growth & Development of MaxillaDocument153 pages002.pre-Natal & Post-Natal Growth & Development of Maxillapriti adsul100% (1)
- Derivatives of Pharyngeal ArchesDocument36 pagesDerivatives of Pharyngeal ArchesMARKS OMFSPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Embryology PDFDocument13 pagesReview Embryology PDFShubham HiralkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Embryology Notes emDocument32 pagesEmbryology Notes emSavita HanamsagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ovid - Virology, Immunology and Pathology of Human Rabies During TreatmentDocument10 pagesOvid - Virology, Immunology and Pathology of Human Rabies During TreatmentFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.3 Area Under Any Normal Curve: Normal Curves and Sampling DistributionsDocument15 pages6.3 Area Under Any Normal Curve: Normal Curves and Sampling DistributionsFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- MRS NotesDocument9 pagesMRS NotesFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Hav Steen 2014Document7 pagesHav Steen 2014Fajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Steyerberg Prediction Modeling 7 Steps Jan10Document45 pagesSteyerberg Prediction Modeling 7 Steps Jan10Fajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- B4 HAND DefinitionDocument13 pagesB4 HAND DefinitionFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- NIH Public AccessDocument12 pagesNIH Public AccessFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- HIV-associated Neurocognitive Disorders: Review Open AccessDocument10 pagesHIV-associated Neurocognitive Disorders: Review Open AccessFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Penelitian DR Lilik - JoiDocument16 pagesPenelitian DR Lilik - JoiFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- S Pss Moving From ExcelDocument2 pagesS Pss Moving From ExcelAnggah KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cognitive HivDocument14 pagesCognitive HivFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Word Academician Thesis 1.1Document30 pagesWord Academician Thesis 1.1khairul_aPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Callosal Disconnection J StrokeDocument5 pagesPDF Callosal Disconnection J StrokeFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurogenic Pulmonary EdemaDocument12 pagesNeurogenic Pulmonary EdemaFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- The Neurology of Eclampsia: Some Observations: Views and ReviewsDocument8 pagesThe Neurology of Eclampsia: Some Observations: Views and ReviewsFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Revue Neurologique Volume 169 Issue 10 2013 (Doi 10.1016/j.neurol.2013.07.022) Debette, S. - Vascular Risk Factors and Cognitive DisordersDocument8 pagesRevue Neurologique Volume 169 Issue 10 2013 (Doi 10.1016/j.neurol.2013.07.022) Debette, S. - Vascular Risk Factors and Cognitive DisordersFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Vancouver Style PDFDocument25 pagesVancouver Style PDFwewwewPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Clinical and Paraclinical Manifestations of Methanol Poisoning in Outcome PredictionDocument6 pagesRole of Clinical and Paraclinical Manifestations of Methanol Poisoning in Outcome PredictionFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Aphasia TableDocument2 pagesAphasia TableFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal Pone HivDocument9 pagesJournal Pone HivFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Arv HivDocument5 pagesArv HivFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- WNL204606Document9 pagesWNL204606Fajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Seizure Prophylaxis Guidelines for Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument8 pagesSeizure Prophylaxis Guidelines for Traumatic Brain InjuryvinodksahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Auto Testing PatientsDocument2 pagesAuto Testing PatientsFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Gio G Karaki 2013Document13 pagesGio G Karaki 2013Fajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Picone 2015Document14 pagesPicone 2015Fajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- The effect of risk factors on the duration of cognitive impairmentDocument28 pagesThe effect of risk factors on the duration of cognitive impairmentFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Guns Tad 2008Document6 pagesGuns Tad 2008Fajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- SDTM Qs - Mhis-Nacc v1 Public DomainDocument7 pagesSDTM Qs - Mhis-Nacc v1 Public DomainFajar Rudy QimindraPas encore d'évaluation
- Allen Bradley Power Monitor 3000 Manual PDFDocument356 pagesAllen Bradley Power Monitor 3000 Manual PDFAndrewcaesar100% (1)
- 19 - Speed, Velocity and Acceleration (Answers)Document4 pages19 - Speed, Velocity and Acceleration (Answers)keyur.gala100% (1)
- LOGARITHMS, Exponentials & Logarithms From A-Level Maths TutorDocument1 pageLOGARITHMS, Exponentials & Logarithms From A-Level Maths TutorHorizon 99Pas encore d'évaluation
- NASA Technical Mem Randum: E-Flutter N78Document17 pagesNASA Technical Mem Randum: E-Flutter N78gfsdg dfgPas encore d'évaluation
- Flame Configurations in A Lean Premixed Dump Combustor With An Annular Swirling FlowDocument8 pagesFlame Configurations in A Lean Premixed Dump Combustor With An Annular Swirling Flowعبدالله عبدالعاطيPas encore d'évaluation
- Function and Euqations - Quantitative Aptitude Questions MCQDocument4 pagesFunction and Euqations - Quantitative Aptitude Questions MCQAnonymous v5QjDW2eHxPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document33 pagesChapter 1Salihah AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Etoh Membrane Seperation I&ec - 49-p12067 - 2010 - HuangDocument7 pagesEtoh Membrane Seperation I&ec - 49-p12067 - 2010 - HuangHITESHPas encore d'évaluation
- SmartRunway SmartLandingDocument39 pagesSmartRunway SmartLandingMikePas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument4 pagesSurgical InstrumentsWafa L. AbdulrahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Speech for pecha kuchaDocument6 pagesSpeech for pecha kuchaaira mikaela ruazolPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument340 pagesUntitledFelipe Batista RetkePas encore d'évaluation
- Standardization Parameters For Production of Tofu Using WSD-Y-1 MachineDocument6 pagesStandardization Parameters For Production of Tofu Using WSD-Y-1 MachineAdjengIkaWulandariPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm C27Document2 pagesAstm C27nee2790Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ampersand MenuDocument5 pagesAmpersand MenuJozefPas encore d'évaluation
- Vishwabhanu Oct '18 - Jan '19Document26 pagesVishwabhanu Oct '18 - Jan '19vedicvision99100% (3)
- Myths of Greece and Rome PDFDocument247 pagesMyths of Greece and Rome PDFratheesh1981Pas encore d'évaluation
- Configuration & Options List: 30Xw0452 1752 Water Cooled Liquid ChillerDocument22 pagesConfiguration & Options List: 30Xw0452 1752 Water Cooled Liquid ChillerOctavio Farid Rossi YumhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aubrey Debut ScriptDocument5 pagesAubrey Debut ScriptKevin Jones CalumpangPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomechanics of The Knee During Closed Kinetic Chain and Open KineticDocument17 pagesBiomechanics of The Knee During Closed Kinetic Chain and Open KineticArmando NetoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cosmic Freedom: David MolineauxDocument2 pagesCosmic Freedom: David Molineauxsalomon46Pas encore d'évaluation
- MPC-006 DDocument14 pagesMPC-006 DRIYA SINGHPas encore d'évaluation
- White Paper Without Track ChangesDocument7 pagesWhite Paper Without Track Changesapi-609064761Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kerala Electricity Regulatory Commission Schedule of TariffDocument36 pagesKerala Electricity Regulatory Commission Schedule of TariffvjtheeePas encore d'évaluation
- EM-CABLE Product CatalogDocument96 pagesEM-CABLE Product Catalogm00h00Pas encore d'évaluation
- Combustion Cat 2008Document32 pagesCombustion Cat 2008Miguel LinaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Cricothyroidotomy and Needle CricothyrotomyDocument10 pagesCricothyroidotomy and Needle CricothyrotomykityamuwesiPas encore d'évaluation
- IruChem Co., Ltd-Introduction of CompanyDocument62 pagesIruChem Co., Ltd-Introduction of CompanyKhongBietPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimensional Analysis Similarity Lesson2 Dimensional Parameters HandoutDocument11 pagesDimensional Analysis Similarity Lesson2 Dimensional Parameters HandoutRizqi RamadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- College of Medicine & Health SciencesDocument56 pagesCollege of Medicine & Health SciencesMebratu DemessPas encore d'évaluation