Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Genetic Recombination in Eukaryotes Multiple Choice Questions
Transféré par
Jon HosmerDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Genetic Recombination in Eukaryotes Multiple Choice Questions
Transféré par
Jon HosmerDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter 6: Genetic Recombination in Eukaryotes
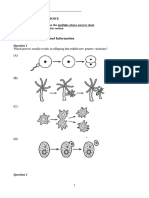
Multiple-Choice Questions 1. In a dihybrid the genes are located on different chromosomes. Which of the following diagrams does not represent a stage of meiosis in this organism? (Note: For each answer only some chromosomes may be represented.) A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
2. A plant of genotype C/C ; d/d is crossed to c/c ; D/D and an F1 testcrossed to c/c ; d/d. If the genes are unlinked, the percentage of c/c ; d/d recombinants will be A) 10 B) 20 C) 25 D) 50 E) 75 3. A plant of genotype C/C ; d/d is crossed to c/c ; D/D and an F1 testcrossed to c/c ; d/d. If the genes are linked, and 20 map units apart, the percentage of c/c ; d/d recombinants will be A) 10 B) 20 C) 25 D) 50 E) 75 4. In Drosophila, the genes R and S are linked. Flies of genotype Rs/Rs and rS/rS are crossed and an F1 obtained. The F1 allele arrangement is called A) recombinant. B) complementary. C) coupling(cis). D) repulsion (trans). E) crossover.
Test Bank: Chapter Nineteen
5. In Drosophila, the two genes w and sn are X-linked and 25 map units apart. A female fly of genotype w+sn+/w sn is crossed to a male from a wild-type line. What percent of male progeny will be w+sn? A) 0 B) 12.5 C) 25 D) 37.5 E) 50 6. The maize genes sh and bz are linked, 40 map units apart. If a plant sh+bz/sh bz+ is selfed, what proportion of the progeny will be sh bz/sh bz? A) 0.40 B) 0.20 C) 0.50 D) 0.10 E) 0.04 7. In maize, two plants that are both heterozygous for the recessive alleles a and b are crossed. What frequency of double-mutant progeny will appear if a and b are 7.2 map units apart, and both parents carry a and b in repulsion (trans)? A) 0.036 B) 0.063 C) 0.001 D) 0.005 E) 0.072 16. In the Meselson-Radding model, which of the following comes last? A) Strand invasion B) Branch migration C) Chain removal D) Resolution E) Ligation Open-Ended Questions 2. The P, Q, and R loci are all on different autosomes in a certain mammalian species. The S locus however is X-linked. P, Q, R, and S are completely dominant alleles. The following cross was made: female P/p ; Q/q ; R/r ; S/s male p/p ; Q/q ; r/r ; S. With respect to these four genes (a) what proportion of sons will phenotypically resemble their fathers? (b) what proportion of sons will phenotypically resemble their mothers? (c) what proportion of daughters will phenotypically resemble their mothers? (d) what proportion of daughters will phenotypically resemble their fathers? (e) what proportion of daughters will genotypically resemble their mothers? (f) what proportion of progeny will have one of the parental phenotypes? 1. In the following cross the genes are inherited independently except for C and D, which are tightly linked and show zero recombination: A/A ; b/b ; c/c ; D/D ; e/e ; F/F a/a ; B/B ; C/C ; d/d ; E/E ; f/f. In the F2 what proportion of individuals will be (a) pure breeding? (e) phenotypically like either parent? (b) heterozygous for all loci? (f) phenotypically unlike either parent? (c) homozygous recessive for all loci? (g) genotypically like either parent? (d) A/a ; B/B ; c/c ; D/D ; E/e ; f/f? (h) genotypically unlike either parent? 4. A fruit fly of genotype A/a.B/b (parent 1) is crossed to another fruit fly of genotype a/a.b/b (parent 2). The progeny of this cross were: Genotype Number of individuals
Evolutionary Genetics
A/a.B/b 38 a/a.b/b 37 A/a.b/b 12 a/a.B/b 13 (a) What gametes were produced by parent 1 and in what proportions? (b) Do these proportions demonstrate independent assortment of the two genes? (c) What can be deduced from these proportions? (d) Draw chromosomal diagram(s) to illustrate the arrangement of the genes on the chromosomes in parents 1 and 2. (e) Draw a diagram or diagrams to explain the origin of the two rarest progeny genotypes. 5. In humans the allele N causes an abnormal shape of the patella in the knee (n is the normal allele). A separate gene is concerned with finger length, and the allele B causes abnormally short fingers, whereas b gives normal length. A study focused on people who have both abnormal patellae and short fingers (they were most likely N/n.B/b in genotype), having inherited the N allele from one parent and the B allele from the other parent. These N/n.B/b people mated with normal spouses, producing 40 progeny classified as follows: Normal 3 Abnormal knees and fingers 2 Abnormal knees only 17 Abnormal fingers only 18 (a) Draw the chromosomes of the N/n.B/b individuals, their parents, and their four types of children, showing the positions of the alleles. (b) Explain why the four types of children were in the proportions shown.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Concepts of Genetics 10th Edition Klug Test BankDocument12 pagesConcepts of Genetics 10th Edition Klug Test Bankhutaq100% (1)
- Test Bank For Essentials of Genetics 10th Edition William S KlugDocument11 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Genetics 10th Edition William S Klugashleyhaaswxcbmagsde100% (28)
- 2009 MidtermI Form1Document12 pages2009 MidtermI Form1svPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics Exam 3 - KeyDocument6 pagesGenetics Exam 3 - KeyGestinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics Ch04 Test Bank PDFDocument10 pagesGenetics Ch04 Test Bank PDFejanlindsay50% (2)
- Test Bank For Principles of Genetics 6th Edition D Peter Snustad Michael J SimmonsDocument15 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Genetics 6th Edition D Peter Snustad Michael J Simmonsshawncookcoqgardemf100% (27)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsD'EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Behavior Final Exam 2013Document2 pagesAnimal Behavior Final Exam 2013Jon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Test Bank Full Chapter PDFarthur.hendricks257100% (12)
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 6Th Edition Pierce Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument37 pagesGenetics A Conceptual Approach 6Th Edition Pierce Test Bank Full Chapter PDFsoojeebeautied9gz3h100% (10)
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition Pierce Test Bank DownloadDocument27 pagesGenetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition Pierce Test Bank DownloadMax Martinez100% (21)
- Heredity Practice Exam KEYDocument4 pagesHeredity Practice Exam KEYjacky qianPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio WorksheetDocument5 pagesBio WorksheethbbrskzbtstxtPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics ExamDocument6 pagesGenetics ExamanewflorescaPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions and Problems 3Document8 pagesQuestions and Problems 3Arnytha VebrianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology MCQDocument5 pagesBiology MCQSungdeok MinPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Test BankDocument45 pagesGenetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Test BankHeatherAllencejrx100% (9)
- Assignment For MSC Animal Breeding and Genetics Students Final 2020Document8 pagesAssignment For MSC Animal Breeding and Genetics Students Final 2020Hundeessaa OliiqaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Principles of Life 2nd Edition HillisDocument33 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Life 2nd Edition Hillispatrickgarciaewzrbtosai100% (18)
- Part A: Multiple Choice: Answer With The Best Choice. Make Sure That You Clearly Circle TheDocument8 pagesPart A: Multiple Choice: Answer With The Best Choice. Make Sure That You Clearly Circle TheQueng ElediaPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Wessler Carroll Doebley 1464109486 9781464109485 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Wessler Carroll Doebley 1464109486 9781464109485 Full Chapter PDFjane.boyles334100% (14)
- Gr-10 Heredity-Worksheet With AnswersDocument12 pagesGr-10 Heredity-Worksheet With Answerskfjg47zq26Pas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics Problems and SolutionsDocument18 pagesGenetics Problems and SolutionsDeblina JanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neet Pedigree Questions Worksheet 5ef6eb6eca031Document8 pagesNeet Pedigree Questions Worksheet 5ef6eb6eca031sarudarshinij.s123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Taller 1, Genética MendelianaDocument3 pagesTaller 1, Genética MendelianaalesssssPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Paper 2023 Task 1Document18 pagesPractice Paper 2023 Task 1Elissa ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- CHPT 15 Genetics Practice ProblemsDocument7 pagesCHPT 15 Genetics Practice ProblemsFatimah AliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 400 Q For G11 1st TermDocument85 pages400 Q For G11 1st Termromaehab201912Pas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics and Heredity Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument32 pagesGenetics and Heredity Multiple Choice QuestionsMensah Vilas FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- GENETICSDocument5 pagesGENETICSkundhanathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Inheritance & Variation-Neet Pyqs-6290457667-SampleDocument95 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance & Variation-Neet Pyqs-6290457667-Sampleseetharaman8341Pas encore d'évaluation
- 103期末Document7 pages103期末Rose FuPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument25 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and VariationAshwani PathakPas encore d'évaluation
- SplitPDFFile 237 To 245Document9 pagesSplitPDFFile 237 To 245TejPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics PracticeDocument4 pagesGenetics PracticeYanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Genetics 6Th Edition Snustad Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesPrinciples of Genetics 6Th Edition Snustad Test Bank Full Chapter PDFBrettClinewdjc100% (9)
- Principles of Genetics 6th Edition Snustad Test BankDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Genetics 6th Edition Snustad Test Bankmarthajessegvt100% (30)
- Principal of Inheritance and VariationDocument27 pagesPrincipal of Inheritance and VariationChiranjeeviPas encore d'évaluation
- 1090 F18 Midterm 35 MC V1-Answers - 2Document9 pages1090 F18 Midterm 35 MC V1-Answers - 2rachelhershoranPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 03Document9 pagesCH 03SpringjesJiesiPas encore d'évaluation
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Biology Chapter 5Document21 pagesNCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Biology Chapter 5Me RahaviPas encore d'évaluation
- 10th Biology Assignment Module 4 - HEREDITYDocument9 pages10th Biology Assignment Module 4 - HEREDITYanshikaas240Pas encore d'évaluation
- TBDocument403 pagesTBT.Son50% (2)
- Bio XII BotanyDocument200 pagesBio XII BotanytanmaysjadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics Practice Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesGenetics Practice Multiple Choice QuestionsVenakadalakshmi Kannappan100% (1)
- Practice Exam 3 CH 11-15 QuestionsDocument6 pagesPractice Exam 3 CH 11-15 QuestionsJeff SandersPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Individu 1C. Guiding QuestionsDocument16 pagesTugas Individu 1C. Guiding QuestionsAmelia Sukma Wati325Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prac Ex 01Document11 pagesPrac Ex 01Jinal PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Patterns of Inheritance in Plants and AnimalsDocument8 pagesPatterns of Inheritance in Plants and Animalsmzunl25476Pas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Inheritance AND Variation: Parth Goyal AppDocument92 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance AND Variation: Parth Goyal AppShayan AnsariPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 03Document10 pagesCH 03Maiah Phylicia LatoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapt 05Document23 pagesChapt 05vaishali shuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Heredity and EvolutionDocument6 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Heredity and EvolutionDeepakPas encore d'évaluation
- Mendelian Genetics 2Document6 pagesMendelian Genetics 2Joonie JoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics Take Home TestDocument12 pagesGenetics Take Home TestEdgarTriff50% (2)
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation: Practice QuestionsDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and Variation: Practice QuestionsPriyanka BalathandayuthamPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Life On Earth With Physiology 10Th Edition Audesirk Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument48 pagesBiology Life On Earth With Physiology 10Th Edition Audesirk Test Bank Full Chapter PDFodetteisoldedfe100% (15)
- Full Download Genetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Test BankDocument21 pagesFull Download Genetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Test Bankbeliechopper05srz100% (31)
- Mcqs On GeneticsDocument10 pagesMcqs On Geneticspkm7929100% (2)
- Test Bank For Genetics Canadian 2Nd Edition by Hartwell Goldberg Fischer Isbn 1259370887 9781259370885 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Genetics Canadian 2Nd Edition by Hartwell Goldberg Fischer Isbn 1259370887 9781259370885 Full Chapter PDFdavid.caple542100% (13)
- Topical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2D'EverandTopical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Understanding Communication DisordersDocument28 pagesUnderstanding Communication DisordersJon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise in Ecological GeneticsDocument4 pagesExercise in Ecological GeneticsJon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Greg Maroney BreatheDocument14 pagesGreg Maroney Breathespiderman1388% (8)
- 05 Child Lang Dis Lecture SupDocument21 pages05 Child Lang Dis Lecture SupJon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Transmission Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesDNA Transmission Cell DivisionJon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus 2013 (Revised)Document3 pagesSyllabus 2013 (Revised)Jon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- HarryPotter ThemeDocument4 pagesHarryPotter ThemeJon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Mumf and SonsDocument8 pagesMumf and SonsJon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology 3300: Principles of Evolution Study Guide For Midterm #2Document4 pagesBiology 3300: Principles of Evolution Study Guide For Midterm #2Jon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene Function MCQs and Codon TranslationDocument5 pagesGene Function MCQs and Codon TranslationJon Hosmer0% (1)
- CSD 1080 Transcription - Sean MaloneyDocument1 pageCSD 1080 Transcription - Sean MaloneyJon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Text 0Document1 pageText 0Jon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Soc 2600Document7 pagesSoc 2600Jon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacterial Recombination MCQsDocument3 pagesBacterial Recombination MCQsJon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- ExtensionsDocument3 pagesExtensionsJon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus 2013 (Revised)Document3 pagesSyllabus 2013 (Revised)Jon HosmerPas encore d'évaluation
- #Sasha Waybright On Tumblr 3Document5 pages#Sasha Waybright On Tumblr 3Josephine GlassenbergPas encore d'évaluation
- Transient Receptor Potential Channels and MechanosensationDocument28 pagesTransient Receptor Potential Channels and MechanosensationSamuel BeaumontPas encore d'évaluation
- HeadDocument360 pagesHeadfeliciostenio100% (1)
- Perfect TOEFL Junior Practice Test Book 1Document151 pagesPerfect TOEFL Junior Practice Test Book 1Harum WibowoPas encore d'évaluation
- English - Creole - French - TamilDocument7 pagesEnglish - Creole - French - TamilLakshminarayanan BaluPas encore d'évaluation
- Cacao Insects Research Philippines 1904Document172 pagesCacao Insects Research Philippines 1904Mia ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Membrane and TransportDocument25 pagesMembrane and TransportHafsa JalisiPas encore d'évaluation
- Syl LB Hms 240809Document102 pagesSyl LB Hms 240809sharma_anand73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wildlife Fact File - Birds - Pgs. 251-260Document20 pagesWildlife Fact File - Birds - Pgs. 251-260ClearMind84100% (2)
- 5 - Amphibians - WeeblyDocument13 pages5 - Amphibians - Weeblyapi-375285021Pas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus - Zoology (Honours & General)Document18 pagesSyllabus - Zoology (Honours & General)api-19803189Pas encore d'évaluation
- Animals Lapbook COLORDocument7 pagesAnimals Lapbook COLORIrynaPas encore d'évaluation
- Zoology Report 1st Year 1Document15 pagesZoology Report 1st Year 1Friend Goog75% (4)
- Animal Nutrition ScienceDocument452 pagesAnimal Nutrition ScienceMuhammad Rizwanullah Tahir70% (10)
- Cell Biology Practical 6 and Practical 7 PDFDocument14 pagesCell Biology Practical 6 and Practical 7 PDFEswaran SingamPas encore d'évaluation
- Meiosis Study SheetDocument3 pagesMeiosis Study SheetDPas encore d'évaluation
- BiologyDocument176 pagesBiologyvijivinayakaPas encore d'évaluation
- SongsDocument7 pagesSongsJulien Elisse Santiago DullasPas encore d'évaluation
- Cytology 3 ReportDocument93 pagesCytology 3 ReportMoganambikai RagavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rhodophyta Fact SheetDocument3 pagesRhodophyta Fact Sheetapi-299846771Pas encore d'évaluation
- JBS Haldane On Being The Right SizeDocument8 pagesJBS Haldane On Being The Right Sizeboygenius21_39464798100% (2)
- Trung Tâm Anh NG Nhung PH M 27N7A KĐT Trung Hòa Nhân Chính - 0946 530 486 - 0964 177 322Document4 pagesTrung Tâm Anh NG Nhung PH M 27N7A KĐT Trung Hòa Nhân Chính - 0946 530 486 - 0964 177 322Trung PhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Inheritance Patterns in DragonsDocument8 pagesInheritance Patterns in Dragonsmarinmatic18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Student Homework on Reading Comprehension and ConnectorsDocument52 pagesStudent Homework on Reading Comprehension and ConnectorsJohanZafiro 123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Compound EyeDocument5 pagesCompound EyeWael ElwekelPas encore d'évaluation
- Leucrotta, Changesteed: CombatDocument1 pageLeucrotta, Changesteed: CombatAnonymous tkaqro0MPas encore d'évaluation
- Zooplankton Session IDocument87 pagesZooplankton Session Imonica_gabbyellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microscope Lab Pro Vs EukDocument5 pagesMicroscope Lab Pro Vs Eukapi-304326920Pas encore d'évaluation
- Neotropical PhyllanthusDocument88 pagesNeotropical PhyllanthusRayaneRibeiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Two-Photon Polarization Microscopy Reveals Protein Structure and FunctionDocument26 pagesTwo-Photon Polarization Microscopy Reveals Protein Structure and FunctionrajasebastianPas encore d'évaluation