Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pronoun
Transféré par
Norazlin UjangCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pronoun
Transféré par
Norazlin UjangDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pronouns
Definition:
A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun. Pronouns can be in one of three cases: Subject, Object, or Possessive.
Rule 1
Subject pronouns are used when the pronoun is the subject of the sentence. You can remember subject pronouns easily by filling in the blank subject space for a simple sentence. Example: ______ did the job. I, you, he, she, it, we, and they all fit into the blank and are, therefore, subject pronouns.
Rule 2
Subject pronouns are also used if they rename the subject. They follow to be verbs such as is, are, was, were, am, and will be. Examples: It is he. This is she speaking. It is we who are responsible for the decision to downsize. NOTE: In spoken English, most people tend to follow to be verbs with object pronouns. Many English teachers support (or at least have given in to) this distinction between written and spoken English. Example: It could have been them. Better: It could have been they. Example: It is just me at the door. Better: It is just I at the door.
Rule 3
Object pronouns are used everywhere else (direct object, indirect object, object of the preposition). Object pronouns are me, you, him, her, it, us, and them.
Examples: Jean talked to him. Are you talking to me? To be able to choose pronouns correctly, you must learn to identify clauses. A clause is a group of words containing a verb and subject.
Rule 4a
A strong clause can stand on its own. Examples: She is hungry. I am feeling well today.
Rule 4b
A weak clause begins with words such as although, since, if, when, and because. Weak clauses cannot stand on their own.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chemistry Form FourDocument55 pagesChemistry Form FourNorazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2Norazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- Proverbs Throughout The WorldDocument2 pagesProverbs Throughout The WorldNorazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Form FiveDocument23 pagesChemistry Form FiveNorazlin Ujang100% (1)
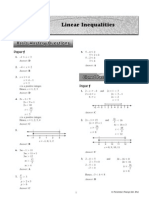
- 5 Linear Inequalities: 1. - 1 X, 3 D 2. - 4, X 2 B 3. X + 1 4 8. 5 - H 2Document4 pages5 Linear Inequalities: 1. - 1 X, 3 D 2. - 4, X 2 B 3. X + 1 4 8. 5 - H 2Norazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2Norazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- AMaths - 2013Document17 pagesAMaths - 2013Raphaella GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Form FourDocument55 pagesChemistry Form FourNorazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- Drifting PoemDocument1 pageDrifting PoemNorazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Indices: e e Answer: H H Answer: P PDocument5 pages3 Indices: e e Answer: H H Answer: P PNorazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Form5 Locomotion and SupportDocument40 pagesBiology Form5 Locomotion and SupportNorazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Algebraic Formulae: Abbbb AbbbbDocument4 pages2 Algebraic Formulae: Abbbb AbbbbNorazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistics Version 2012Document21 pagesStatistics Version 2012Norazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- (Skema) Trial SPM TRG 2012 MatematikDocument16 pages(Skema) Trial SPM TRG 2012 MatematikeyongjuanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Generation of ElectricityDocument42 pagesThe Generation of ElectricityNorazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetism: GCSE PhysicsDocument43 pagesElectromagnetism: GCSE PhysicsNorazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigo V2010Document31 pagesTrigo V2010WeteachPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Law 2010Document14 pagesLinear Law 2010Norazlin UjangPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)