Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Physioex 9.0 Exercise 3 Act 1
Transféré par
Adela LhuzTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Physioex 9.0 Exercise 3 Act 1
Transféré par
Adela LhuzDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Name: Ashlei Sickles Exercise 3: Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses: Activity 1: The Resting Membrane Potential Lab Report Pre-lab
Quiz Results You scored 100% by answering 4 out of 4 questions correctly. 1. What is the approximate concentration of K+ inside a typical cell (intracellular concentration)? You correctly answered: a. 150 mM 2. What is the approximate concentration of K+ outside a cell (extracellular concentration)? You correctly answered: b. 5 mM 3. What is the approximate concentration of Na+ inside a cell (intracellular concentration)? You correctly answered: b. 5 mM 4. What is the approximate concentration of Na+ outside a cell (extracellular concentration)? You correctly answered: a. 150 mM
05/20/13
page 1
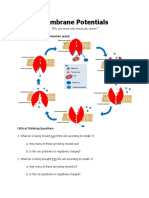
Experiment Results Predict Question: Predict Question: Predict what will happen to the resting membrane potential if the extracellular K+ concentration is increased. Your answer : b. The resting membrane potential will become less negative. Stop & Think Questions: What is the polarity of the resting membrane potential (voltage)? You correctly answered: b. negative What does it mean that the voltage just inside the membrane is negative? You correctly answered: b. There are more negative charges than positive charges just inside the membrane. The membrane of most cells, including neurons, contains passive, open, K+ leak channels. Given the normal K+ concentrations and the resultant concentration gradient, which direction would K+ be expected to move (diffuse) through these leak channels? You correctly answered: b. out of the cell What effect does increasing extracellular K+ have on the net diffusion of K+ out of the cell? You correctly answered: b. It decreases the net diffusion of K+ . Which way would Na+ move across the membrane if there were open Na+ channels? You correctly answered: a. Na+ would diffuse into the cell. The membrane has open K+ channels, and changing extracellular K+ concentration results in a change in membrane potential. Changing the extracellular Na+ concentration does not significantly change the membrane potential. What do your results suggest about the number or state (open or closed) of Na+ channels in the resting membrane of a neuron? You correctly answered: b. Na+ channels are mostly closed. Experiment Data: Extracellular Fluid (ECF) Control Control Control Control High K+ High K+ High K+ High K+ Low Na+ Low Na+ Low Na+ Low Na+ Microelectrode Position Cell body extracellular Cell body intracellular Axon extracellular Axon intracellular Axon intracellular Axon extracellular Cell body extracellular Cell body intracellular Cell body intracellular Cell body extracellular Axon extracellular Axon intracellular Voltage (mV) 0 -70 0 -70 -40 0 0 -40 -72 0 0 -72
05/20/13
page 2
05/20/13
page 3
05/20/13
page 4
05/20/13
page 5
05/20/13
page 6
Post-lab Quiz Results You scored 100% by answering 3 out of 3 questions correctly. 1. A negative membrane potential was recorded when the tip of the microelectrode was You correctly answered: d. both inside the cell body and inside the axon. 2. Which of the following caused a change in membrane potential from -70 to -40 in the cell body? You correctly answered: a. an increase in extracellular K+ 3. Which of the following has the most negative voltage? You correctly answered: c. between the inside of the axon and the outside of the axon with control K+ ECF
05/20/13
page 7
Review Sheet Results 1. Explain why increasing extracellular K+ reduces the net diffusion of K+ out of the neuron through the K+ leak channels. Your answer: Increasing the extracellular K+ causes the membrane potential to change to a less negative value because when K+ ionsdiffuse out across the membrane they are leaving behind a net negative charge. 2. Explain why increasing extracellular K+ causes the membrane potential to change to a less negative value. How well did the results compare with your prediction? Your answer: Potassium ions diffuse out across the membrane, leaving behind a net negative charge. Therefore, the resting potential membrane will become less negative. 3. Explain why a change in extracellular Na+ did not significantly alter the membrane potential in the resting neuron? Your answer: There are less leakage sodium channels than leakage potassium channels, and more of the potassium channels are open. 4. Discuss the relative permeability of the membrane to Na+ and K+ in a resting neuron. Your answer: Membrane permeability to sodium is very low because there are only a few sodium leakage channels. Sodium ions doslowly diffuse inward, down their concentration gradient. Left unchecked, such inward leakage of sodium would eventuallydestroy the resting membrane potential. The sodium potassium pumps offset the small inward sodium leak and outward leak of potassium. 5. Discuss how a change in Na+ or K+ conductance would affect the resting membrane potential. Your answer: The resting period potential is a difference between the inside of the cell and the outside of the cell across the membrane. It depends on the resting permeability of the membrane and on the intracellular and extracellular concentrations of those ions to which the membrane is permeable.
05/20/13
page 8
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Somatosensory Teachers Manual: for Somatosensory Science FactsD'EverandSomatosensory Teachers Manual: for Somatosensory Science FactsPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Evolution WorksheetDocument4 pagesMolecular Evolution WorksheetYaelPas encore d'évaluation
- General Connective TissueDocument36 pagesGeneral Connective Tissuelogang48Pas encore d'évaluation
- Problems 1st Set - PDF S2 PDFDocument8 pagesProblems 1st Set - PDF S2 PDFZinca IoanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Conization of CervixDocument4 pagesConization of Cervixdrnareshkumar3281Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 9 NotesjanetotheohPas encore d'évaluation
- HistoDocument8 pagesHistoFatima AmaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- MicturitionDocument29 pagesMicturitionHifza Anjum KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 26 Phylum PoriferaDocument51 pagesCH 26 Phylum Poriferaapi-244168124Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physio Ex 3-01Document8 pagesPhysio Ex 3-01edie tyler100% (4)
- Pex 03 01Document8 pagesPex 03 01aexillis100% (2)
- PEX 03 01 GhinaSH 23215333Document8 pagesPEX 03 01 GhinaSH 23215333Ghina Sujanifa HanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pex 03 01Document8 pagesPex 03 01Bianca D. SerlsPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 1 - Noor Alia Devina LDocument8 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 1 - Noor Alia Devina LadelPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurofisiología Del Impulso Nervioso-Actividades Del 1 Al 9 Cod 20120353.Document58 pagesNeurofisiología Del Impulso Nervioso-Actividades Del 1 Al 9 Cod 20120353.Anthony Huaman Alayo100% (3)
- PhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 1Document8 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 1Suci syawaliahPas encore d'évaluation
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument8 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsMARILYN MARIANA HERNANDEZ MENDOZAPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 1Document7 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 1liv tiffanyPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 1Document8 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 1tasyaauliatabina1122Pas encore d'évaluation
- Review SheetDocument1 pageReview SheetAhmad SutriPas encore d'évaluation
- + Grupo 05, Práctica 7 - Neurofisiología Del Impulso NerviosoDocument58 pages+ Grupo 05, Práctica 7 - Neurofisiología Del Impulso NerviosoMichellePas encore d'évaluation
- 04Document4 pages04Dany BerlinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pex 03 08Document4 pagesPex 03 08aexillisPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 1Document8 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 1Jenna Picard100% (1)
- Exercice 3 Actividad 1Document8 pagesExercice 3 Actividad 1EVELYN BRIGGITE AVILES SANMARTINPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 1 - Subkelompok 4Document8 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 3 Activity 1 - Subkelompok 4Syarifina PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- Pex 03 01Document8 pagesPex 03 01Jose Maria RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- Praktikum Faal - PhysioEx Saraf MotorikDocument4 pagesPraktikum Faal - PhysioEx Saraf MotorikFeri AlmanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument7 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsPavel MilenkovskiPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysioEX Exercise 3 Activity 1Document8 pagesPhysioEX Exercise 3 Activity 1patricia ankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous KeyDocument10 pagesNervous KeyAngel Natty NewPas encore d'évaluation
- PEX-03-01-Pot de Repaus PDFDocument8 pagesPEX-03-01-Pot de Repaus PDFAlexandru BurdeniucPas encore d'évaluation
- Pex 03 08Document4 pagesPex 03 08Jila HafiziPas encore d'évaluation
- Pex 03 08Document4 pagesPex 03 08Andra PratamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Physic Human Physic Bio Chem Test Ready Stuff of TestDocument36 pagesHuman Physic Human Physic Bio Chem Test Ready Stuff of TestnaifPas encore d'évaluation
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument8 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsAurelia RaihaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Gusgus 1Document8 pagesGusgus 1Mateo MoncayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pex 03 01Document8 pagesPex 03 01Luthfi Putra SusenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Block1 Physiology LectureQuestionsDocument10 pagesBlock1 Physiology LectureQuestionsToni-Krys Hardy100% (1)
- Laily Nur Rohmah - 2250341117 (Act 1)Document8 pagesLaily Nur Rohmah - 2250341117 (Act 1)Laily Nur RohmahPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions ExplanationDocument17 pagesQuestions ExplanationnomintmPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology 7th Edition Koeppen Test BankDocument18 pagesPhysiology 7th Edition Koeppen Test Bankstringy.devest4avfbk100% (25)
- Pex 03 01Document8 pagesPex 03 01Rul'sPas encore d'évaluation
- 01Document8 pages01Dany BerlinPas encore d'évaluation
- Test 1 2017 Questions.1605348206176Document7 pagesTest 1 2017 Questions.1605348206176Derrick ThompsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pex 03 01Document8 pagesPex 03 01Juan AlemánPas encore d'évaluation
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument8 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsJoashan VacPas encore d'évaluation
- Membrane Potentials: "Why Are Some Cells Electrically Active?"Document5 pagesMembrane Potentials: "Why Are Some Cells Electrically Active?"yasmine laarajPas encore d'évaluation
- E3A1 Modul NeurosainsDocument8 pagesE3A1 Modul NeurosainsAinunIffahNsgPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm 1 2017 QuestionsDocument11 pagesMidterm 1 2017 QuestionsDerrick ThompsonPas encore d'évaluation
- RestingMembranePotential RevisionDocument5 pagesRestingMembranePotential RevisionshaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.membrane Physiology, Nerve and MuscleDocument6 pages2.membrane Physiology, Nerve and MuscleCLEMENT100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Membrane PhysiologyDocument11 pagesChapter 2 - Membrane Physiologytahira UroojPas encore d'évaluation
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument3 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsAnggina SiregarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous Tissue and Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesNervous Tissue and Nervous Systemruthdaisy507Pas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set 2 NeurophysiologyDocument2 pagesProblem Set 2 NeurophysiologyTiffany YehPas encore d'évaluation
- RestingMembranePotential JeffLindoDocument8 pagesRestingMembranePotential JeffLindoAbraham AberaPas encore d'évaluation
- M 3032Document251 pagesM 3032Muhammad NasirPas encore d'évaluation
- Resting Membrane PotentialDocument8 pagesResting Membrane PotentialAhmad Atiq MalikiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pex 03 03Document7 pagesPex 03 03Jila Hafizi100% (1)
- Physioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 4Document4 pagesPhysioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 4Adela Lhuz100% (1)
- Physioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 3Document4 pagesPhysioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 3Adela Lhuz100% (1)
- Physioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 1Document5 pagesPhysioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 1Adela LhuzPas encore d'évaluation
- Physioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 2Document4 pagesPhysioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 2Adela Lhuz100% (1)
- Activity 5 Physioex 9.0 Exercise 1Document4 pagesActivity 5 Physioex 9.0 Exercise 1Adela Lhuz50% (2)
- Nmat Suppl Handout March 2012Document2 pagesNmat Suppl Handout March 2012zxyker029Pas encore d'évaluation
- HydrocephalusDocument15 pagesHydrocephalusAdela Lhuz100% (3)
- House MDocument4 pagesHouse MGabriella Wide GucianoPas encore d'évaluation
- DRILLING #3 Classification of Living ThingDocument6 pagesDRILLING #3 Classification of Living ThingMuhammad MunawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercises About People, Animal, ThingsDocument1 pageExercises About People, Animal, ThingsFirman IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- The Wreck of The Zanzibar ResourcesDocument18 pagesThe Wreck of The Zanzibar ResourcesMonica Scaltrito100% (1)
- Virtual Field Trip Report To Kopf Family Reservation July 2021Document41 pagesVirtual Field Trip Report To Kopf Family Reservation July 2021Western Cuyahoga AudubonPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum Arthropoda: by DwiDocument40 pagesPhylum Arthropoda: by DwiNisa RPas encore d'évaluation
- MONILOPHYTADocument38 pagesMONILOPHYTAAmalia ZaidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cigüeñas, Ibis, Espatulas PDFDocument392 pagesCigüeñas, Ibis, Espatulas PDFJose Raul Olmedo Moreno100% (2)
- Program Script: Invertebrates 1Document87 pagesProgram Script: Invertebrates 1anscprogramsPas encore d'évaluation
- Helpful Insects, Spiders and PathogensDocument138 pagesHelpful Insects, Spiders and PathogensAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- Histo Soruları PDFDocument178 pagesHisto Soruları PDFtalhaburakturaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesDiversity in Living Organismssumendra singhPas encore d'évaluation
- The Early Upper Miocene Aceratherium Incisivum (Mammalia: Rhinocerotidae) From Bozieni (Moldavian Platform, Romania)Document5 pagesThe Early Upper Miocene Aceratherium Incisivum (Mammalia: Rhinocerotidae) From Bozieni (Moldavian Platform, Romania)Ratoi Bogdan GabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- ĐÁNH VẦN TIẾNG ANH oxford phonics worldDocument30 pagesĐÁNH VẦN TIẾNG ANH oxford phonics worldoanh siuPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hair CycleDocument3 pagesThe Hair CycleanithadesialaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vocabulary For ExamsDocument53 pagesVocabulary For ExamsRajat AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- BeautyDocument2 pagesBeautyPraghashrajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Receptors, Chemistry Of: Advanced ArticleDocument10 pagesNuclear Receptors, Chemistry Of: Advanced ArticleazzaassPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheep PresentationDocument17 pagesSheep PresentationBrittoney MckenziePas encore d'évaluation
- Chloroleucon É A Denominação Cientifica Que Engloba Toda Uma EspécieDocument2 pagesChloroleucon É A Denominação Cientifica Que Engloba Toda Uma EspécieRosangela Matter KamlaPas encore d'évaluation
- WK Sheet Connect Plus Model AnsweDocument5 pagesWK Sheet Connect Plus Model Answemarinasabry123456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology I MCQ PDFDocument0 pagePhysiology I MCQ PDFRaj Cella100% (2)
- Soal Ulangan II Ganjil Kelas 8 Pack ADocument1 pageSoal Ulangan II Ganjil Kelas 8 Pack AAjie SmoothLandPas encore d'évaluation
- Introductory Biology Worksheet1Document3 pagesIntroductory Biology Worksheet1Richie LewisPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Instructions Heart Dissection (Pig)Document6 pagesLab Instructions Heart Dissection (Pig)Sandy HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Vein Vs ArteryDocument4 pagesVein Vs ArterySaarwin MuruganPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Nervous System (Earthworm & Fish)Document18 pagesAnimal Nervous System (Earthworm & Fish)Keth LaurelPas encore d'évaluation
- Annelida PresentationDocument20 pagesAnnelida PresentationtariPas encore d'évaluation
- Eoc ReviewDocument33 pagesEoc Reviewapi-237316144Pas encore d'évaluation
- Comparing Extracellular Secretion Mechanisms in E. Coli Strains BL21 (DE3) and Nissle 1917Document10 pagesComparing Extracellular Secretion Mechanisms in E. Coli Strains BL21 (DE3) and Nissle 1917vikramreddy041302Pas encore d'évaluation