Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
GSM Network Basics: Authentication Process of A Subscriber
Transféré par
Sameer SulemanTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
GSM Network Basics: Authentication Process of A Subscriber
Transféré par
Sameer SulemanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
8/2/13
Authentication
GSM Network Basics
An Introduction to GSM Networks
AUTHENTICATION PROCESS OF A SUBSCRIBER
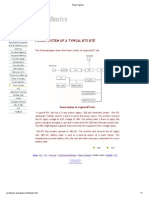
Subscriber authentication process At subscription time, each subscriber is assigned a subscriber authentication Key (Ki). Ki is stored in the AUC (Authentication Center) along with the subscribers IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity). Both are used in the process of providing a triplet. The same Ki and IMSI are also stored in the SIM. 1. A non-predictable random number, RAND, is generated at the Authentication Center. 2. RAND and Ki are used to calculate Signed Response (SRES) and Kc, using two different algorithms, A3 and A8 respectively. 3. RAND, SRES and Kc are delivered together to the HLR as a triplet. 4. The MSC/VLR transmits the RAND to the MS. 5. The MS computes the signature SRES using RAND and the subscriber authentication key (Ki) through the A3 algorithm. 6. The MS computes the Kc by using Ki and RAND through A8 algorithm. Kc will thereafter be used for ciphering and deciphering in MS. 7. The signature SRES is sent back to MSC/VLR, which performs authentication, by checking whether, the SRES from the MS and the SRES from the AUC match. If so, the subscriber is permitted to use the network. If not, the subscriber is barred from network access.
gsmbasics.awardspace.info/authentication.htm
1/2
8/2/13
Authentication
Home | BSS | NSS | GSM Cell | Transmission Planning | Tower & Antenna | Power System | WCDMA | SS7
Chathuranga Perera, Electrical Engineer Ceylon Electricity Board
gsmbasics.awardspace.info/authentication.htm
2/2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Security MethodsDocument2 pagesThe Security MethodsManivannanMudhaliarPas encore d'évaluation
- A3 AlgorithmDocument13 pagesA3 AlgorithmChetan Sri KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Authentication and CipheringDocument10 pagesAuthentication and CipheringMilica MilicicPas encore d'évaluation
- SEP - GSM Authentication & Ciphering - Telecommunication SystemsDocument8 pagesSEP - GSM Authentication & Ciphering - Telecommunication SystemsMuneeb KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM SIM & SecurityDocument31 pagesGSM SIM & SecuritymanthasaikarthikPas encore d'évaluation
- Day-04 GSM SecurityDocument4 pagesDay-04 GSM SecurityAnonymous cQAi2l7Pas encore d'évaluation
- C46 Exp3Document10 pagesC46 Exp3pravintp123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Authentication ProcessDocument1 pageAuthentication ProcessMd Irshad AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Comm Securiy 5Document27 pagesWireless Comm Securiy 5abdulsahibPas encore d'évaluation
- COMP128 WangKleiner ReportDocument5 pagesCOMP128 WangKleiner Reportdeadlyvirus4mePas encore d'évaluation
- 2734-Article Text-2709-1-10-20180901Document2 pages2734-Article Text-2709-1-10-20180901Rabiu kaosarat morenikejiPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.3 Security-Related Network Functions and Encryption: 6 Coding, Authentication, and CipheringDocument4 pages6.3 Security-Related Network Functions and Encryption: 6 Coding, Authentication, and CipheringTushar SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM SecurityDocument19 pagesGSM SecurityKuda BetinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.11 Authentication and EncryptionDocument3 pages1.11 Authentication and Encryptiondungnt84Pas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Authentication Algorithm COMP128': J U S TDocument14 pagesGSM Authentication Algorithm COMP128': J U S TAbelPas encore d'évaluation
- Security, Authentication and Encryption: Ligin MathewDocument28 pagesSecurity, Authentication and Encryption: Ligin MathewSurya6556Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3 GSM Communication FlowDocument118 pages3 GSM Communication Flowvarinz100% (1)
- 01-06 Authentication ProcedureDocument9 pages01-06 Authentication ProcedureabuzarshazliPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Security and AuthenticationDocument14 pagesGSM Security and AuthenticationMuhammad Riaz KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Communication FlowDocument118 pagesGSM Communication FlowVishnu Namboodiri P50% (2)
- GSM Security Concerns: OperatorsDocument36 pagesGSM Security Concerns: Operatorsgkutty9Pas encore d'évaluation
- A3 and A5 AlgorithmsDocument14 pagesA3 and A5 AlgorithmsG Karthik Reddy100% (1)
- Information Technology Mobile Computing Module: GSM SecurityDocument8 pagesInformation Technology Mobile Computing Module: GSM SecurityAbelPas encore d'évaluation
- Final PPT BvritDocument20 pagesFinal PPT BvritRakesh MuppaneniPas encore d'évaluation
- Security Algorithms For Mobile NetworksDocument10 pagesSecurity Algorithms For Mobile NetworksPrarit LambaPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Security Overview (Part 2) : Max StepanovDocument38 pagesGSM Security Overview (Part 2) : Max StepanovVijayakumar KPPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Security Overview (Part 2)Document38 pagesGSM Security Overview (Part 2)munzali surajoPas encore d'évaluation
- MCC Expt 6 GSM A5 - A8Document5 pagesMCC Expt 6 GSM A5 - A8AlkaPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM SecurityDocument26 pagesGSM SecurityMegBPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM SecurityDocument38 pagesGSM SecurityEric TraorePas encore d'évaluation
- CyBOK v1.1.0-5Document200 pagesCyBOK v1.1.0-5Adrian NPas encore d'évaluation
- LTE Authentication. Delving Into The Underlying Crypto - by Sudheesh Singanamalla - Uwcse-Ictd - MediumDocument23 pagesLTE Authentication. Delving Into The Underlying Crypto - by Sudheesh Singanamalla - Uwcse-Ictd - Mediumak_waiPas encore d'évaluation
- MCC Expt 5 GSM A3Document6 pagesMCC Expt 5 GSM A3AlkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment Number: 08: Aim TheoryDocument6 pagesExperiment Number: 08: Aim Theoryrockey harrisonPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM & Umts - SecurityDocument21 pagesGSM & Umts - SecurityVikas1984301Pas encore d'évaluation
- Security in GSMDocument17 pagesSecurity in GSMmarwashable100% (2)
- MD - Hasanuzzaman Assignment01Document17 pagesMD - Hasanuzzaman Assignment01MD HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Security and Encryption by Poonam SharmaDocument27 pagesGSM Security and Encryption by Poonam SharmaVikas SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 17.authentication CenterDocument2 pages17.authentication Centerdeepak19mPas encore d'évaluation
- Extension of Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol (AKA) For Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS)Document10 pagesExtension of Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol (AKA) For Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS)Vikash SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Network: Carte À Puce Et Java Card ATAC 2011-2012Document81 pagesGSM Network: Carte À Puce Et Java Card ATAC 2011-2012marcosPas encore d'évaluation
- 22 KerberosDocument22 pages22 KerberosSpoorthy HUPas encore d'évaluation
- FALLSEM2023-24 ECE4009 ETH VL2023240102914 2023-10-06 Reference-Material-IDocument24 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 ECE4009 ETH VL2023240102914 2023-10-06 Reference-Material-IPraneshPas encore d'évaluation
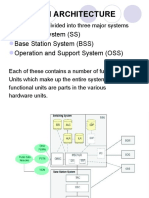
- GSM Architecture: Switching System (SS) Base Station System (BSS) Operation and Support System (OSS)Document19 pagesGSM Architecture: Switching System (SS) Base Station System (BSS) Operation and Support System (OSS)aimslifePas encore d'évaluation
- AbstractcDocument4 pagesAbstractcraytec123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ic:19960522Document4 pagesIc:19960522sheomePas encore d'évaluation
- Gsm3gsecurity 150624162840 Lva1 App6892Document26 pagesGsm3gsecurity 150624162840 Lva1 App6892Aatqa HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Milenage Algorithm (Auth, Crypto)Document8 pagesMilenage Algorithm (Auth, Crypto)KcreamPas encore d'évaluation
- Authentication and Ciphering in 3G and Simulation: Presentation OnDocument54 pagesAuthentication and Ciphering in 3G and Simulation: Presentation OnshailendrabagriPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM SecurityDocument20 pagesGSM SecurityAnand PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM OverviewDocument81 pagesGSM OverviewImran Khan100% (1)
- How Mobile Comm WorksDocument6 pagesHow Mobile Comm WorksShone DripPas encore d'évaluation
- How Mobile Comm WorksDocument6 pagesHow Mobile Comm WorksJack SikoliaPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM (2G) Authentication Procedure: General DetailsDocument10 pagesGSM (2G) Authentication Procedure: General DetailsArbabPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Communications Security: Solutions for the Internet of ThingsD'EverandWireless Communications Security: Solutions for the Internet of ThingsPas encore d'évaluation
- New Frontiers in Cryptography: Quantum, Blockchain, Lightweight, Chaotic and DNAD'EverandNew Frontiers in Cryptography: Quantum, Blockchain, Lightweight, Chaotic and DNAPas encore d'évaluation
- ARM Microcontrollers Programming for Embedded SystemsD'EverandARM Microcontrollers Programming for Embedded SystemsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Information Security of Intelligent Vehicles Communication: Overview, Perspectives, Challenges, and Possible SolutionsD'EverandInformation Security of Intelligent Vehicles Communication: Overview, Perspectives, Challenges, and Possible SolutionsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Summary of Andreas M. Antonopoulos, Olaoluwa Osuntokun & René Pickhardt's Mastering the Lightning NetworkD'EverandSummary of Andreas M. Antonopoulos, Olaoluwa Osuntokun & René Pickhardt's Mastering the Lightning NetworkPas encore d'évaluation
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-Elements of PKI i.e CA/RA/CRL/CPS (Domain-5)D'EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-Elements of PKI i.e CA/RA/CRL/CPS (Domain-5)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- GSM Network Basics: Wcdma TechnologyDocument2 pagesGSM Network Basics: Wcdma TechnologySameer SulemanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tower & AntennaDocument3 pagesTower & AntennaSameer SulemanPas encore d'évaluation
- Site Master S325D: Cable and Antenna Analyzer, 250 MHZ To 2500 MHZDocument12 pagesSite Master S325D: Cable and Antenna Analyzer, 250 MHZ To 2500 MHZSameer SulemanPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Network Basics: Transmission PlanningDocument4 pagesGSM Network Basics: Transmission PlanningSameer SulemanPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Network Basics: Power System of A Typical Bts SiteDocument1 pageGSM Network Basics: Power System of A Typical Bts SiteSameer SulemanPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Network BasicsDocument2 pagesGSM Network BasicsSameer SulemanPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM IdentitiesDocument3 pagesGSM IdentitiesSameer SulemanPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM CellDocument2 pagesGSM CellSameer SulemanPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Network Basics: Mobile Originating CallDocument2 pagesGSM Network Basics: Mobile Originating CallSameer SulemanPas encore d'évaluation