Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3: Coordination and Response
Transféré par
Nurfatin JamaludinTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter 3: Coordination and Response
Transféré par
Nurfatin JamaludinDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CHAPTER 3 : COORDINATION AND RESPONSE
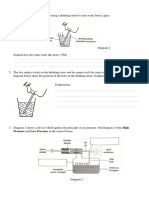
1. Diagram 1 shows a simple reflex arc. (a) Name the structure labeled P, Q, R, S, T and U. (b) What makes up the (i) white matter (ii) grey matter (c) What is the function of the interneurone? (d) Often, we are aware of the reflex action because some impulses have been sent to the brain. (i) Which neurone sends the impulse to the brain? (ii) Where does this occur? 2. Diagram 2 shows a simplified drawing of a nephron in the kidney. (a) What are the physical processes that occur at X and Y during excretion? (b) Compare the composition of blood P entering the glomerulus and blood Q leaving the glomerulus. (c) What is the composition of the fluid in R? (d) A patient suffering from an infection of the bladder or urethra was advised to drink a lot of water. Explain why. (e) Name two other organs that also remove water from our body and the mechanism involved. 3. Our bodys temperature regulating mechanism is similar to an oven thermostat, which switches on and off the controlling regulator to adjust the temperature of the oven. (a) What is the main controlling regulator for our bodys temperature? (b) List two ways in which the control center in the body may pass information to the temperature regulator. (c) How would the body respond to the regulator mechanism after it has detected a deviation of the bodys temperature from the normal? (d) What would happen if the body temperature of a person falls below 34C? (e) In what way does the human body lose heat to the surroundings when the body temperature is above normal? (f) Some people tend to drink alcohol when they are cold to get a false sense of warmth. (i) How does alcohol give a sensation of warmth to the drinker? (ii) Why should a person stop drinking more alcohol when the body temperature has returned to normal?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ANZCA Primary Physiology QuestionsDocument34 pagesANZCA Primary Physiology Questionspriyavirdi100% (1)
- Bio Form 4 Cell StructureDocument12 pagesBio Form 4 Cell StructureNurfatin JamaludinPas encore d'évaluation
- Combined Past Paper Questions On Excretion and HomeostasisDocument76 pagesCombined Past Paper Questions On Excretion and HomeostasisRamesh Iyer81% (26)
- Respiratory & Circulatory System Regents QuestionsDocument10 pagesRespiratory & Circulatory System Regents Questionsabisantiago613140% (5)
- SPIROMETRYDocument5 pagesSPIROMETRYJayarubini JeyapalPas encore d'évaluation
- Auto Digestion of The PancreasDocument13 pagesAuto Digestion of The PancreasJincy JosePas encore d'évaluation
- Human Body System Regents QuestionsDocument11 pagesHuman Body System Regents Questionsabisantiago613125% (4)
- 2020 Form 5 Biology Mock Exam: A Saliva Secretion Is An Involuntary Action Controlled by U (Medulla)Document22 pages2020 Form 5 Biology Mock Exam: A Saliva Secretion Is An Involuntary Action Controlled by U (Medulla)UniversityJCPas encore d'évaluation
- BOARD EXAM QUESTION PAPER 2023 Biology (Chapter 1, 2)Document8 pagesBOARD EXAM QUESTION PAPER 2023 Biology (Chapter 1, 2)Anisha ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Test 3Document3 pagesClass Test 3Balakrishnan MarappanPas encore d'évaluation
- Jeep 107Document8 pagesJeep 107KunalKumarSinghPas encore d'évaluation
- HomeostasisDocument3 pagesHomeostasisbaone segaetshoPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Assignment-Class 10Document5 pagesRevision Assignment-Class 10Sidra QueenPas encore d'évaluation
- Cbse Assignments Class - X Biology For Sa-1Document2 pagesCbse Assignments Class - X Biology For Sa-1Purvesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncert - Exemplar - Control and CoordinationDocument18 pagesNcert - Exemplar - Control and CoordinationRagini BaghelPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution For Problem 1Document15 pagesSolution For Problem 1A APas encore d'évaluation
- Respiration QuestionsDocument2 pagesRespiration QuestionsAnonymous Azxx3Kp9100% (1)
- Summer Vacation Assignment - QuestionsDocument7 pagesSummer Vacation Assignment - QuestionsSidra QueenPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Test Science Year 10Document2 pagesSimple Test Science Year 10Dara MoorePas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Question Paper Set L SolvedDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Question Paper Set L SolvedUpal PramanickPas encore d'évaluation
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisD'EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Questions Class 10 - Science CBSEDocument9 pagesQuestions Class 10 - Science CBSEViolet TsirblouPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 10 Biology Chemistry and Physics Extra QuestionsDocument4 pagesClass 10 Biology Chemistry and Physics Extra QuestionsSankalp KharayatPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology TheoryDocument13 pagesBiology TheoryZaw Linn PhyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Homeostasis 1Document6 pagesHomeostasis 1challista amandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 6.2Document3 pagesBio 6.2zwindows123456789Pas encore d'évaluation
- S2 ExercisesDocument3 pagesS2 ExercisesNSABIMANA JANVIERPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 Lecture 1 Tutorial Questions PDFDocument2 pages2015 Lecture 1 Tutorial Questions PDFFafa MusPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFDocument7 pagesChapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFben martin100% (1)
- BIO271 - Practice MCQDocument6 pagesBIO271 - Practice MCQEric LuongPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Questions PT 2 XI BIODocument6 pagesPractice Questions PT 2 XI BIOpratyushpradhan929Pas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Cells Components Function(s)Document9 pagesBlood Cells Components Function(s)Lyna NaderPas encore d'évaluation
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Solution For Term 2 Exam 2021 22Document8 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Solution For Term 2 Exam 2021 22VedantPas encore d'évaluation
- 101 Modul Hebat Bio 2021 - PDF - Eng-65-70Document6 pages101 Modul Hebat Bio 2021 - PDF - Eng-65-70BF CLPas encore d'évaluation
- Compare and Contrast Both Animal and Plant Cell. (A) : Structure QuestionsDocument4 pagesCompare and Contrast Both Animal and Plant Cell. (A) : Structure QuestionsKoh Zhi YangPas encore d'évaluation
- English Biology Test IiDocument7 pagesEnglish Biology Test IiCindy PitalokaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ans02 HomeostasisDocument6 pagesAns02 Homeostasisngsuan.2020Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3: Disorders of Water and Electrolytes MetabolismDocument57 pagesChapter 3: Disorders of Water and Electrolytes MetabolismLiezel CauilanPas encore d'évaluation
- DocumentDocument7 pagesDocumentTanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology WorkbookDocument198 pagesPhysiology Workbooks8903082Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chandulal - Nanavati - Bio - Prelim Class 10th IcseDocument4 pagesChandulal - Nanavati - Bio - Prelim Class 10th IcseOmMen GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- NERVOUS SYSTEM (IB-DP BIOLOGY) - Multiple Choice Type QuestionsDocument5 pagesNERVOUS SYSTEM (IB-DP BIOLOGY) - Multiple Choice Type QuestionsVishnu SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class X Additional Homework On Life ProcessesDocument2 pagesClass X Additional Homework On Life ProcessesBornil Bikash BhuyanPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 P T 2 BiologyDocument2 pages11 P T 2 Biologydivya pathakPas encore d'évaluation
- Term Test 2Document12 pagesTerm Test 2languagetuitionlabzPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 5969878728963002643Document21 pages4 5969878728963002643peternady202Pas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 2 Biology 1996 Paper 2+ansDocument19 pagesPaper 2 Biology 1996 Paper 2+ansapi-3812894100% (1)
- Class XI Annual - 2022-23Document6 pagesClass XI Annual - 2022-23Farhan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 7 Control N Cordboard QTN ScienceDocument3 pagesLesson 7 Control N Cordboard QTN ScienceSarvesh KotkarPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Bio - Worksheet 2022-23Document5 pages10 Bio - Worksheet 2022-23skyskyPas encore d'évaluation
- © Praadis Education Do Not Copy: Chapter-1 Worksheet - 3Document4 pages© Praadis Education Do Not Copy: Chapter-1 Worksheet - 3[33] Shaai Shankar.SPas encore d'évaluation
- AQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationDocument6 pagesAQA GCSE Organisation Questions: A. Principles of OrganisationJoePas encore d'évaluation
- Kendriya Vidyalaya SangathanDocument4 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya SangathanAdi KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise On Coordination and ResponseDocument8 pagesExercise On Coordination and ResponseNorliyana AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Homeostasis Test SolutionDocument3 pagesHomeostasis Test SolutionhumaPas encore d'évaluation
- LSS 2 2014Document2 pagesLSS 2 2014Jenny LowsleyPas encore d'évaluation
- HHW Summer IX 23-24Document8 pagesHHW Summer IX 23-24Raman JenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 WW1 Q1Document5 pagesGrade 9 WW1 Q1JOEL MONTERDEPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise PDFDocument12 pagesExercise PDFAmsyidi Asmida100% (1)
- Answer All Questions in This Section: Biology P2 One Hour 30 MinutesDocument10 pagesAnswer All Questions in This Section: Biology P2 One Hour 30 MinutesNicole LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Paper (Class - 10) : EYSE (AY 2020 - 2021) PhysicsDocument14 pagesSample Paper (Class - 10) : EYSE (AY 2020 - 2021) PhysicsPrincePas encore d'évaluation
- Air PressureDocument1 pageAir PressureNurfatin JamaludinPas encore d'évaluation
- Contribution of Science and Technology To Human ReproductionDocument27 pagesContribution of Science and Technology To Human ReproductionNurfatin JamaludinPas encore d'évaluation
- Support in PlantsDocument1 pageSupport in PlantsNurfatin JamaludinPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology 2015 - BestDocument42 pagesBiology 2015 - BestNurfatin JamaludinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pollination: Prepared by Nurfatin JamaludinDocument13 pagesPollination: Prepared by Nurfatin JamaludinNurfatin JamaludinPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion: Active TransportDocument2 pagesSimple Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion: Active TransportNurfatin JamaludinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 5 Bio F5 (Module)Document5 pagesChap 5 Bio F5 (Module)Nurfatin JamaludinPas encore d'évaluation
- SMK ST Xavier, Pulau Pinang Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2013Document8 pagesSMK ST Xavier, Pulau Pinang Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2013Nurfatin JamaludinPas encore d'évaluation
- Test 1 Biology F4Document12 pagesTest 1 Biology F4Nurfatin JamaludinPas encore d'évaluation
- WAJA JPN PerakDocument2 pagesWAJA JPN PerakNurfatin Jamaludin100% (3)
- Waja Bio F4Document1 pageWaja Bio F4Nurfatin JamaludinPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology F4 Teaching ModuleDocument13 pagesBiology F4 Teaching ModuleNurfatin Jamaludin100% (1)