Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map - Sepsis
Transféré par
markyabresTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Concept Map - Sepsis
Transféré par
markyabresDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
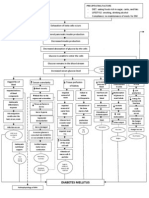
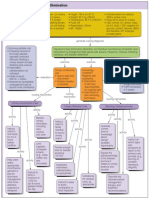
Causative Agent
Transmission
Enter the bloodstream
Release of bacterial cell wall components Endotoxin ( Lipopolysaccharide) Substance release from pathogen and damaged tissues Leukocyte Activation (macrophage & mononuclear cells) Brings transcriptional changes Exotoxins (Peptoglycans)
Regulate adhesion molecules on the vascular endothelium
Regulate Production
Pro inflammatory Cytokines (TNF, INF, IL6)
Antiinflammatory Cytokines (IL10, IL8)
Activation of complement pathway
Generate C3B
Neutrophils
Production C5A
Production C3A & C4A
Coats Pathogen Opsonization Activated Neutrophils
Arresting and Activating rolling Neutrophils in the vascular wall Decreased expression of B2 integrins in Neonatal Vascular Space Continues rolling along the vascular wall Inability to adhere to vascular endothelium Move to site of injury Does not change shape Phagocytes C3b coated organisms Inability to pass between endothelial cells
Degranulation of mast cells
Contraction of Smooth Muscle
Change Shape
Increased permeability of vascular endothelium
Pass through vessel wall Allow activated cells to move out of the vessels
Poor transmigration of Neutrophils and chemotaxis
Lack of localization of infection
Bloodstream infection
Circulation
Cross Blood Brain Barrier (BBB)
Via circumventricular vascular organs known as organum vascolosum laminae terminalis
Hypothalamic Endothelium
Arachidonic Acid Pathway PGE2
Cyclic AMP
Inhibited
Sympathetic Nervous System
Activation
Stimulate Sweat Glands Evaporation Loss
Vasoconstriction of Skin Vessels
Shivering Center Activation
Increased Muscle Heat Production Secretion of Neurotransmitter Increased Cell Metabolism Heat Production
Heat Conservation
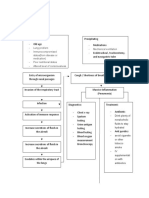
Catalyzed by the microsomal enzyme heme oxygenase
biliverdin
Cytosolic enzyme reductase
bilirubin
Unconjugated (not soluble) Free Bound to serum Indirecyt albumin
Deposit in Skin Pigment
Oxidation Reaction HEME
Cross BBB
Travels Liver
Kernicterus
Hemoglobin Phagocytosed by Macrophages
Increased Lysis or degradation
Glucuronic Acid
Brain Damage
Conjugated (water soluble) GLOBIN Protein degraded into amino acids Catalyzed by Uridine diphosphate glucorynyl transferase (UDGPT)
Excreted from Liver
Urobilinogen
Intestinal Bacteria
Biliary duct & Cystic duct as part of bile
Stercobilinogen
Oxidized Stercobilin
Reabsorbed by Transported in the intestinal cells blood
Passed out in feces
Kidney
Urobilin
Passed out in the urine
ATP disruption (dependent resting membrane potential)
Na+ flow into neuron
K+ flow out of neuron
Increased released of Glutamate
Burst of electrical activity from the cortex Long lasting depolarization of the neuronal cell membrane
Alteration in the integrity of neuronal cell membrane
Discharges of electrochemical energy
Nerve cells fire an increased in frequency and amplitude of impulse
Continuous impulse
Increased intensity of discharges
Spread to adjacent normal neurons Blocking of normal inhibition
Perpetuate a feedback loop (threshold)
AURA (a premonitory or warning sensation; it can be visual, auditory or olfactory
Inhibitory neurons in the cortex, anterior thalamus & basal ganglia slow the neuronal firing Produce an intermittent contraction relaxation phase at the muscle fibers Continuous stimulation of impulses throughout the body Continuous muscle contraction (TONIC) Exhaustion of the epileptic neurons (CLONIC)
Building of inhibitory process
Depresses CNS
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)D'EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sepsis Content Concepts MapDocument2 pagesSepsis Content Concepts Mapghodghod1230% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study of the Lack of Hiv/Aids Awareness Among African American Women: a Leadership Perspective: Awareness That All Cultures Should Know AboutD'EverandA Study of the Lack of Hiv/Aids Awareness Among African American Women: a Leadership Perspective: Awareness That All Cultures Should Know AboutÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Pathophysiology and Pharmacotherapy of Myocardial InfarctionD'EverandThe Pathophysiology and Pharmacotherapy of Myocardial InfarctionNabil El-SherifPas encore d'évaluation
- Severe Sepsis and Septic ShockDocument39 pagesSevere Sepsis and Septic ShockYogi Agil MurdjitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary Tract Infection in Children - Classification, Diagnosis and TreatmentD'EverandUrinary Tract Infection in Children - Classification, Diagnosis and TreatmentPas encore d'évaluation
- Infective Endocarditis: A Multidisciplinary ApproachD'EverandInfective Endocarditis: A Multidisciplinary ApproachArman KilicPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ethic of Care: A Moral Compass for Canadian Nursing Practice - Revised EditionD'EverandThe Ethic of Care: A Moral Compass for Canadian Nursing Practice - Revised EditionPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypertension, Cardiovascular Disease, Analgesics, and Endocrine DisordersD'EverandHypertension, Cardiovascular Disease, Analgesics, and Endocrine DisordersJack Z. YetivPas encore d'évaluation
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsD'EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular DiseaseDocument37 pagesHemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular Diseasejbvaldez100% (1)
- International Guidelines For ManagementDocument24 pagesInternational Guidelines For ManagementSiti Novita KumanPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Concept MapDocument8 pagesRenal Concept MapXtine CajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusPong's Teodoro SalvadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute GlumerulonephritisDocument77 pagesAcute GlumerulonephritisNicolePas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology PneumoniaChiro Rouy Malaluan100% (2)
- Cardio and Hema - DR PueyoDocument161 pagesCardio and Hema - DR Pueyoapi-3735995100% (2)
- Sepsis Is The Consequence of A Dysregulated Inflammatory Response To An Infectious InsultDocument11 pagesSepsis Is The Consequence of A Dysregulated Inflammatory Response To An Infectious InsultShrests SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cellular AbberationDocument198 pagesCellular AbberationKristel AnnePas encore d'évaluation
- CHH Drug Study Week 3Document21 pagesCHH Drug Study Week 3maryxtine24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sepsis: Fajar Yuwanto SMF Penyakit Dalam RS Abdul MoeloekDocument58 pagesSepsis: Fajar Yuwanto SMF Penyakit Dalam RS Abdul MoeloekamirazhafrPas encore d'évaluation
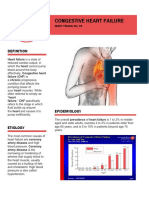
- CHF PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesCHF PathophysiologyVirtudazo JessaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypovolemic Shock Pathophysiology, Symptoms, Signs, Treatment - EHealthStarDocument15 pagesHypovolemic Shock Pathophysiology, Symptoms, Signs, Treatment - EHealthStarKaloy KamaoPas encore d'évaluation
- STEMI Patho/Concept MapDocument1 pageSTEMI Patho/Concept Maplaylers_0767% (3)
- Uremic EncephalophatyDocument48 pagesUremic EncephalophatySindi LadayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pa Tho Physiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Congestive Heart FailureErin MariePas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument49 pagesCardiogenic Shockmaibejose0% (1)
- Schistosomiasis Case StudyDocument5 pagesSchistosomiasis Case Studyapi-318749549Pas encore d'évaluation
- Narrative PathophysiologyDocument18 pagesNarrative PathophysiologyNica Georgelle Maniego SamontePas encore d'évaluation
- ESRD PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesESRD Pathophysiologynursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study: Congestive Heart FailureDocument7 pagesCase Study: Congestive Heart FailureXI-E / 21 / MARY TRIANAPas encore d'évaluation
- MM M M MDocument20 pagesMM M M MAshok KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ate Mitch HN DRUG STUDYDocument23 pagesAte Mitch HN DRUG STUDYMarice VenPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Transfusion ProcedureDocument0 pageBlood Transfusion ProcedureDanielcc LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS)Document21 pagesHyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS)Malueth AnguiPas encore d'évaluation
- Heparin Drip - PortfolioDocument20 pagesHeparin Drip - Portfolioapi-306657745100% (1)
- Objectives: General Objective: Specific ObjectivesDocument8 pagesObjectives: General Objective: Specific ObjectivesLora CarpioPas encore d'évaluation
- Thinking UpstreamDocument1 pageThinking UpstreamDONITA DALUMPINESPas encore d'évaluation
- Multi Organ Dysfunction SyndromeDocument40 pagesMulti Organ Dysfunction SyndromeDr. Jayesh PatidarPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument15 pages2 Acute Myocardial InfarctionpauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapapi-252910411Pas encore d'évaluation
- Caselet School HealthDocument3 pagesCaselet School HealthchoobiPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard Case Definitions For The Diseases Under Surveillance in EthiopiaDocument4 pagesStandard Case Definitions For The Diseases Under Surveillance in Ethiopiamihret gashayePas encore d'évaluation
- Urine Elmination Concept Map PDFDocument1 pageUrine Elmination Concept Map PDFRichard RLPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophy - Nephrotic SyndromeedDocument1 pagePathophy - Nephrotic Syndromeedianecunar100% (1)
- UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)Document9 pagesUTI (Urinary Tract Infection)Carson BirthPas encore d'évaluation
- Congestive Heart Failure OverviewDocument12 pagesCongestive Heart Failure OverviewkazellePas encore d'évaluation
- NCM103 12th Endoc IIDocument9 pagesNCM103 12th Endoc IIKamx MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Sepsis, Septic Shock, MODSDocument19 pagesSepsis, Septic Shock, MODSPaul Zantua80% (5)
- Hypovolemic Shock Nursing Care Management and Study GuideDocument1 pageHypovolemic Shock Nursing Care Management and Study GuideRoselyn VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Anuj Raj BijukchheDocument95 pagesDR Anuj Raj BijukchheMUHAMMAD JAWAD HASSANPas encore d'évaluation
- Stroke and Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument14 pagesStroke and Cerebrovascular DiseaseMarwan M.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Presented by Asmaa Abdelhameed AhmedDocument24 pagesPresented by Asmaa Abdelhameed AhmedSoma Al-mutairiPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug LipitorDocument1 pageDrug LipitorSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- 2Document1 page2markyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Maria Fe LDocument2 pagesMaria Fe LmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Story #1: The Weight of The GlassDocument4 pagesStory #1: The Weight of The GlassmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- NCBTSDocument3 pagesNCBTSmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- BK Reading Ed62Document2 pagesBK Reading Ed62markyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Math ProblemDocument2 pagesMath ProblemmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO MidtermDocument11 pagesBIO MidtermmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- July IterinaryDocument2 pagesJuly IterinarymarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- College of NursingDocument114 pagesCollege of NursingmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Cover Letter BasicsDocument12 pagesCover Letter BasicsrounaqgandhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Douglas Adams (March 11,1952-May, 11,2001) : March 11, 1952, Cambridge, United KingdomDocument2 pagesDouglas Adams (March 11,1952-May, 11,2001) : March 11, 1952, Cambridge, United KingdommarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- January 2014: DOH Annual CalendarDocument4 pagesJanuary 2014: DOH Annual CalendarmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Related Readings - Summary and ReactionDocument10 pagesRelated Readings - Summary and ReactionmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 2 Report PlanDocument6 pagesGroup 2 Report PlanmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Travel BrochureDocument2 pagesTravel BrochuremarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- History 56 - Spanish FiestasDocument11 pagesHistory 56 - Spanish FiestasmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Brief Lgu ProfileDocument4 pagesBrief Lgu ProfilemarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Attendance Sheet: Name SignatureDocument3 pagesAttendance Sheet: Name SignaturemarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Report Plan Hand OutDocument2 pagesReport Plan Hand OutmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Attendance Sheet: Name SignatureDocument3 pagesAttendance Sheet: Name SignaturemarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Bemonc WordDocument10 pagesBemonc Wordmarkyabres100% (1)
- List of Players For SportfestDocument1 pageList of Players For SportfestmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- His Year's ProposalDocument3 pagesHis Year's ProposalmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- In TramsDocument3 pagesIn TramsmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Bemonc WordDocument10 pagesBemonc Wordmarkyabres100% (1)
- Bemonc WordDocument10 pagesBemonc Wordmarkyabres100% (1)
- Case JournalDocument4 pagesCase JournalmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Outline - Inc. ICPDocument4 pagesOutline - Inc. ICPmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- FNCP - FinalDocument6 pagesFNCP - FinalmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- January 2014: DOH Annual CalendarDocument4 pagesJanuary 2014: DOH Annual CalendarmarkyabresPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical CorrelationDocument14 pagesClinical CorrelationjazzPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9: Nursing Care of The Growing FetusDocument20 pagesChapter 9: Nursing Care of The Growing FetusiMaibelle BellePas encore d'évaluation
- Female Genital SystemDocument35 pagesFemale Genital SystemBio ChePas encore d'évaluation
- Extec Crusher c10 Maintenance Manual EsDocument22 pagesExtec Crusher c10 Maintenance Manual Esbrittanymorales200602rzd100% (95)
- Third Return DemonstrationDocument12 pagesThird Return DemonstrationBianca SandovalPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Medical AbbreviationsDocument10 pagesCommon Medical AbbreviationsPrincess MariscotesPas encore d'évaluation
- Dulutalias - Chapter18-THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEMDocument10 pagesDulutalias - Chapter18-THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEMGwen Valerie DulutaliasPas encore d'évaluation
- MPSC Exams of Ophthalmology 3Document7 pagesMPSC Exams of Ophthalmology 3Hussein AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Science10 Q3 Ver4 Mod3Document31 pagesScience10 Q3 Ver4 Mod3Berliese FriasPas encore d'évaluation
- Orchidopexy For Testicular TorsionDocument25 pagesOrchidopexy For Testicular TorsionPutri Nirmala DewiPas encore d'évaluation
- Meningitis: Meningitis Is An Inflammatory Process of The Leptomeninges and CSFDocument20 pagesMeningitis: Meningitis Is An Inflammatory Process of The Leptomeninges and CSFSwagath NPas encore d'évaluation
- Normal Growth and Development of NewbornDocument18 pagesNormal Growth and Development of Newbornmathio medhatPas encore d'évaluation
- C14 - Coloana Vertebrala Engleza 2Document109 pagesC14 - Coloana Vertebrala Engleza 2Andreea DanielaPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary Progressive Aphasia: Neurological ProgressDocument8 pagesPrimary Progressive Aphasia: Neurological ProgressDranmar AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Cerebral Herniation and ImagingDocument13 pagesTypes of Cerebral Herniation and ImagingPaulo LuizPas encore d'évaluation
- Jeffrey David Rudie, MD PHDDocument10 pagesJeffrey David Rudie, MD PHDJeff RudiePas encore d'évaluation
- Spanish For Medical ProfessionalsDocument372 pagesSpanish For Medical ProfessionalsJean MallipudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Placenta Types and GradingDocument37 pagesPlacenta Types and GradingNishant RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus ANP1105Document10 pagesSyllabus ANP1105Nusrat TazkiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nasal PolypDocument10 pagesNasal PolypHetvi ParmarPas encore d'évaluation
- HematuriaDocument86 pagesHematuriaMohamad Arif MustaphaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bahsa Inggris 1.17Document6 pagesBahsa Inggris 1.17Rizki AdiPas encore d'évaluation
- CGHS Rates - TrivandrumDocument79 pagesCGHS Rates - Trivandrumimran kureshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Central Nervous System Tumors: GeneralDocument35 pagesCentral Nervous System Tumors: GeneralleartaPas encore d'évaluation
- Micro - Male Repro (Sec A) PDFDocument5 pagesMicro - Male Repro (Sec A) PDFKaren ValdezPas encore d'évaluation
- MEM Devices For Drug DeliveryDocument52 pagesMEM Devices For Drug DeliveryTechnautsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Quantum Encyclopedia1Document2 602 pagesThe Quantum Encyclopedia1zara moreno barba100% (2)
- Evidence of different mediators of central inflammation in dysfunctional and inflammatory pain - Interleukin-8 in fibromyalgia and interleukin-1 β in rheumatoid arthritisDocument7 pagesEvidence of different mediators of central inflammation in dysfunctional and inflammatory pain - Interleukin-8 in fibromyalgia and interleukin-1 β in rheumatoid arthritisShirley AlvesPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnancy and Embryonic DevelopmentDocument10 pagesPregnancy and Embryonic DevelopmentShubhendu AmitabhPas encore d'évaluation
- One Point TreatmentDocument39 pagesOne Point TreatmentaummirraPas encore d'évaluation