Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion
Transféré par
Liza Marie Cayetano AdarneCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion
Transféré par
Liza Marie Cayetano AdarneDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
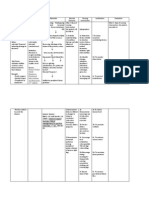
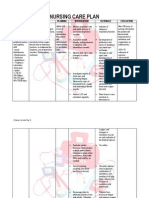
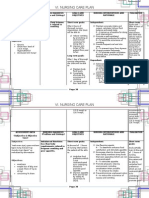
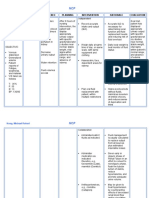
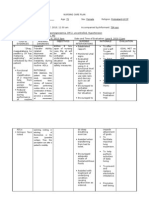
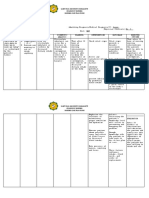
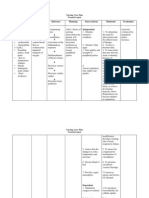
Assessment Objective: -Vital Signs: BP: 80/50 RR: 34 CR: 120 - Low HGB level: 98g/L (normal 120170g/L)
- Low HCT level: 30: anemia (normal 0.370.54) -Pale palpebral conjunctiva -Nausea -Edema -Hematuria -Increased BUN and creatinine -Melena -Hematemesis
Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective Tissue Perfusion related to anemia
Rationale Transport of oxygen is impaired with anemia. In anemia, the Hemoglobin is lacking or number of RBCs is too low to carry adequate oxygen to tissues and hypoxia develops.
Goals and Objectives After 4.5 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will be able to:
Nursing Interventions 1. Monitor and Record Vital Signs. 2. Maintain on bed rest 3. Assess patient general condition. 4. Encourage quiet and restful atmosphere. 5. Provide safety by raising side rails 6. Administer supplemental oxygen as ordered 7. Administer IV fluids as ordered. 8. Monitor laboratory studies such as hemoglobin, hematocrit and RBC. 9. Blood component therapy (Blood transfusion) as ordered. 10. Render health teachings such as: a. Avoid straining. b. Deep breathing exercises c. Eat foods rich in iron
Rationale 1. To have a baseline data. 2. Restricted activity reduces oxygen demands of the heart and other organs. 3. To have a baseline data and note any abnormal findings. 4. To conserve energy and lower tissue oxygen demands. 5. Weakness, fatigue and restlessness are signs of hypoxia which may cause injury to the patient. 6. Oxygen increase arterial saturation. 7. Maintains circulating volume to maximize tissue perfusion. 8. Normal values indicate adequate tissue perfusion. 9. Blood transfusion increas es the patients blood volume and
Evaluation After 4.5 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will be able to:
raising the hemoglobin level. Hemoglobin is a component of the red blood cell that carries oxygen to different tissues and organs throughout the body. 10. A. Straining for a bowel movement further impairs cardiac output and it demands more oxygen. B. Deep breathing exercises help in lung expansion. C. to increase the capacity of the RBC to carry oxygen throughout the body.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Brain Injury Nursing CareDocument1 pageBrain Injury Nursing CareEm Castillo50% (2)
- Afib NCPDocument3 pagesAfib NCPGen RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Early Theories of Cancer PDFDocument16 pagesEarly Theories of Cancer PDFLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Early Theories of Cancer PDFDocument16 pagesEarly Theories of Cancer PDFLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP 1: Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument14 pagesNCP 1: Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Cerebrovascular AccidentKyle Jingco100% (2)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusionsyderman999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputTiffany Mathis100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionRosalie Delfin90% (10)
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPTracy Camille EscobarPas encore d'évaluation
- NURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaAce Dioso Tubasco100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodYllejann Manez60% (20)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument4 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionClariz Basco100% (1)
- Osteopathic Considerations in Systemic Dysfunction (2nd Ed)Document296 pagesOsteopathic Considerations in Systemic Dysfunction (2nd Ed)Natan Babek100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathyDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To Cardiomyopathywen_pil75% (8)
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP On Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument4 pagesNCP On Electrolyte Imbalancefreyah_bc67% (3)
- Concepts of Food, Nutrition and Hygiene 23 NovDocument39 pagesConcepts of Food, Nutrition and Hygiene 23 NovanamikapokhariaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP. Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesNCP. Decreased Cardiac OutputJillian AmponinPas encore d'évaluation
- Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output NCPbaba69baba100% (1)
- Activity Intolerance (NCP)Document3 pagesActivity Intolerance (NCP)Sonia Letran Singson100% (3)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionKristine Maghari83% (6)
- Learning Styles Questionnaire Short Version Aug10Document3 pagesLearning Styles Questionnaire Short Version Aug10api-267898429Pas encore d'évaluation
- Qbase Medicine 1 MCQs For The MRCPDocument132 pagesQbase Medicine 1 MCQs For The MRCPsosoposo2100% (2)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageIneffective Tissue PerfusionEuanne Orellano85% (13)
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac OutputSid Artemis FriasPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Intolerance NCPDocument6 pagesActivity Intolerance NCPDoo NahPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP)Sha PinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionRhoel John Bartolome92% (13)
- NCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionLeigh Kristel Andrion0% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionAngelo ︻╦̵̵͇̿̿̿̿╤── Bulacan50% (6)
- Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMr. whitePas encore d'évaluation
- SchistosomiasisDocument92 pagesSchistosomiasisIvan Juan75% (4)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionClaidelyn De Leyola100% (1)
- Liver AbscessDocument18 pagesLiver AbscessBheru Lal100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of CHOLELITHIASISDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of CHOLELITHIASISLiza Marie Cayetano Adarne57% (7)
- Pathophysiology of CHOLELITHIASISDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of CHOLELITHIASISLiza Marie Cayetano Adarne57% (7)
- Guide to Saudi Board Residency Programs & SMLEDocument26 pagesGuide to Saudi Board Residency Programs & SMLEShafeeque ApvPas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument4 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Ineffective Tissue Perfusionderic83% (29)
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument5 pagesNCP Activity IntoleranceRea HashimPas encore d'évaluation
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputEdrianne J.100% (2)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP Excess Fluid VolumeTrixia CamporedondoPas encore d'évaluation
- Esrd NCPDocument7 pagesEsrd NCPSharmaine Camille de LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Myocardial Infarction Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Myocardial Infarction Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationsweethoney220% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageIneffective Tissue PerfusionRhae RaynogPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPJet Ray-Ann GaringanPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Ischemic StrokeDocument3 pagesNCP Ischemic StrokeEyySiEffVee100% (1)
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Nursing Care PlansDocument21 pages"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Nursing Care PlansCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care DeficitDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care DeficitFrances Anne Pasiliao100% (3)
- Respiratory Anatomy GuideDocument9 pagesRespiratory Anatomy GuideLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion NCPDocument5 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion NCPJasmin Calata50% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Eclampsia)Document1 pageNCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Eclampsia)Jenny AjocPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionAngel Hernandez100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusioniammkrissa33% (3)
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Skin IntegrityLiza Marie Cayetano Adarne93% (14)
- NCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyDocument3 pagesNCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyGidget de Leon100% (7)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plankehyrie100% (2)
- NCP Risk For FallDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For FallHero Tauro0% (2)
- Neonatal and Pediatric VesselsDocument6 pagesNeonatal and Pediatric VesselsAhmed Gaber100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan for Electrolyte ImbalanceManuel Jacob YradPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionMitsika AnadiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Improving Neonatal Tissue Perfusion for SepsisDocument2 pagesImproving Neonatal Tissue Perfusion for SepsisNiña Montejo Ealdama100% (1)
- Activity Intolerance Related To AmeniaDocument1 pageActivity Intolerance Related To AmeniaSiti Syazana Mohamad MogriPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Cva Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageNCP Cva Ineffective Tissue Perfusionexcel21121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ncp-Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Aortic Stenosis)Document2 pagesNcp-Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Aortic Stenosis)Daniel Vergara Arce67% (3)
- DIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT SubjectiveDocument1 pageDIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT Subjectivemawel100% (1)
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNCP Activity Intolerancerobbiematro100% (1)
- NCP-Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP-Risk For InfectionJea Joel Mendoza100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - Activity Intolerance - AnemiaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Activity Intolerance - AnemiaTrish SuarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesImpaired Tissue PerfusionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Tamponade Aortic DissectionDocument3 pagesCardiac Tamponade Aortic DissectionJhoeverly TebrioPas encore d'évaluation
- Types, Causes, Symptoms of AnemiaDocument66 pagesTypes, Causes, Symptoms of AnemiaKristel AnnePas encore d'évaluation
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputAdnan Khan100% (1)
- Drug Ana NDDocument2 pagesDrug Ana NDLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Articiafical Airways Mechanical Ventilator - MachineDocument1 pageArticiafical Airways Mechanical Ventilator - MachineLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Ca - SciDocument2 pagesCa - SciLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP N.D.Document3 pagesNCP N.D.Liza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Ana NDDocument2 pagesDrug Ana NDLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Breast CancerDocument2 pagesBreast CancerLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Cover and Table of ContentsDocument4 pagesCover and Table of ContentsLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Death and DyingDocument5 pagesDeath and DyingLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Acknowledgement and AbstractDocument2 pagesAcknowledgement and AbstractLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection on Sibling Relationships and UniquenessDocument1 pageReflection on Sibling Relationships and UniquenessLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Vignette 2Document18 pagesVignette 2Krista P. AguinaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Rev - PROPOSAL Template June 2011 For MIX METHODS Quali & Quanti RESEARCH CorrectedDocument17 pagesRev - PROPOSAL Template June 2011 For MIX METHODS Quali & Quanti RESEARCH CorrectedLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- LoveDocument32 pagesLoveLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Legal Responsibilites of The NurseDocument4 pagesLegal Responsibilites of The NurseLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Review of SystemsDocument3 pagesReview of SystemsLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer CareDocument3 pagesCancer CareLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection Paper 1 and 2Document3 pagesReflection Paper 1 and 2Liza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Letter of AssentDocument2 pagesLetter of AssentLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Definitions of Branches of FeminisnDocument3 pagesDefinitions of Branches of FeminisnJennilyn TugelidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Soc-Anthro Social Institutions LectureDocument2 pagesSoc-Anthro Social Institutions LectureLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Ashd Phys AssDocument10 pagesAshd Phys AssLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Final Social ConventionDocument23 pagesFinal Social ConventionLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- Sources For RRLDocument1 pageSources For RRLLiza Marie Cayetano AdarnePas encore d'évaluation
- ICM Standard List For Competency-Based Skills TrainingDocument40 pagesICM Standard List For Competency-Based Skills TrainingRima SartikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Do You Want To Be A DoctorDocument7 pagesWhy Do You Want To Be A Doctoramal20022011100% (1)
- Kern AttestationDocument120 pagesKern AttestationBakersfieldNowPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Esl Topics Quiz HealthDocument2 pages12 Esl Topics Quiz HealthSiddhartha Shankar NayakPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.3.1 Triage in Light of Four Hour TargetDocument16 pages4.3.1 Triage in Light of Four Hour TargetWilliam Wagner Müller XavierPas encore d'évaluation
- Intravenous Thrombolytic Therapy For Acute Ischemic StrokeDocument12 pagesIntravenous Thrombolytic Therapy For Acute Ischemic Strokeidno1008100% (1)
- Jennifer Tripodi ResumeDocument2 pagesJennifer Tripodi Resumeapi-242986811Pas encore d'évaluation
- Confidential United Nations Nations Unies Employment Medical Review QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesConfidential United Nations Nations Unies Employment Medical Review QuestionnaireHaythem FarhatiPas encore d'évaluation
- History Taking Checklist.Document4 pagesHistory Taking Checklist.لو ترىPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 JMSCR PDFDocument5 pages10 JMSCR PDFSubi SureshPas encore d'évaluation
- Perfect 2015Document6 pagesPerfect 2015windaPas encore d'évaluation
- Emma D'epagnier 3/12/202 0 4 Jenny PerryDocument3 pagesEmma D'epagnier 3/12/202 0 4 Jenny PerryEmma d'EpagnierPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Topical Steroids on Acanthamoeba Keratitis OutcomesDocument8 pagesImpact of Topical Steroids on Acanthamoeba Keratitis OutcomesDiana BaagilPas encore d'évaluation
- Rabie CateiDocument3 pagesRabie CateiC LPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypoplasia, Flurosis, Amelogenesis Imperfecta and Abnormal DVPT of ToothDocument49 pagesHypoplasia, Flurosis, Amelogenesis Imperfecta and Abnormal DVPT of ToothcrazieelorraPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Lists Patient PlanDocument1 pageProblem Lists Patient Planangel23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quality of Postnatal Care ServicesDocument10 pagesQuality of Postnatal Care Servicessaleha sultanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Duty Report 02-09-2023 MFDDocument20 pagesDuty Report 02-09-2023 MFDDede KurniawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Bag TechniqueDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Bag TechniqueClare AlcoberPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Education H.O.P.E 1 Module 6Document17 pagesPhysical Education H.O.P.E 1 Module 6Reynaldo Jr LundagPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Proving: The Base of Homoeopathic System of Medicine As Well As The Vital Force of HomoeopathyDocument2 pagesDrug Proving: The Base of Homoeopathic System of Medicine As Well As The Vital Force of Homoeopathyskandan s kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Exodontia Limu 2016 Two Slides PDFDocument89 pagesExodontia Limu 2016 Two Slides PDFSharath K KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- S.S. Hospital OPD ScheduleDocument4 pagesS.S. Hospital OPD Schedulegaurav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Review On Nature of Inter Display Between Covid 19 and Systemic DiseaseDocument9 pagesReview On Nature of Inter Display Between Covid 19 and Systemic DiseaseKhalid NPas encore d'évaluation