Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
8086 Internal Block Diagram Enotes
Transféré par
veeraCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
8086 Internal Block Diagram Enotes
Transféré par
veeraDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
8086 Internal Block diagram (Intel Corp.
)
eNotes
By
Prof. S. Jagannathan,
HOD – Department of Electronics and
Communication Engineering,
R.V. College of Engineering, Bangalore
Prof. S. Jagannathan,HOD – Dept of E & C Engg,R.V. C. E, Bangalore
Session - III
ADVANCED MICROPROCESSORS
Contents
• Block Diagram of 8086
• segment registers
• 8086 flag register format
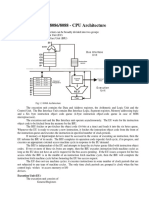
8086 Internal Block diagram (Intel Corp.)
The block diagram of 8086 is as shown. This can be subdivided into two parts, namely
the Bus Interface Unit and Execution Unit. The Bus Interface Unit consists of segment
registers, adder to generate 20 bit address and instruction prefetch queue.
Once this address is sent out of BIU, the instruction and data bytes are fetched from
memory and they fill a First In First Out 6 byte queue.
Prof. S. Jagannathan,HOD – Dept of E & C Engg,R.V. C. E, Bangalore
Execution Unit:
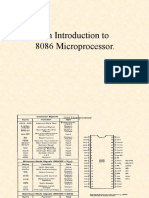
The execution unit consists of scratch pad registers such as 16-bit AX, BX, CX and DX
and pointers like SP (Stack Pointer), BP (Base Pointer) and finally index registers such as
source index and destination index registers. The 16-bit scratch pad registers can be split
into two 8-bit registers. For example, AX can be split into AH and AL registers. The
segment registers and their default offsets are given below.
Segment Register Default Offset
CS IP (Instruction Pointer)
DS SI, DI
SS SP, BP
ES DI
The Arithmetic and Logic Unit adjacent to these registers perform all the operations. The
results of these operations can affect the condition flags.
Different registers and their operations are listed below:
Register Operations
AX Word multiply, Word divide, word I/O
AL Byte Multiply, Byte Divide, Byte I/O, translate, Decimal Arithmetic
AH Byte Multiply, Byte Divide
BX Translate
CX String Operations, Loops
CL Variable Shift and Rotate
DX Word Multiply, word Divide, Indirect I/O
Prof. S. Jagannathan,HOD – Dept of E & C Engg,R.V. C. E, Bangalore
8086/8088 MPU MEMORY
00000016
IP Instruction Pointer
CS Code Segment Register
Code Segment (64Kb)
DS Data Segment Register
SS Stack Segment Register
Data Segment (64Kb)
ES Extra Segment Register
AX AH AL
Stack Segment (64Kb)
BX BE BL
CX CE CL
Extra Segment (64Kb)
DX DH DL
SP Stack Pointer Register
FFFFF16
BP Break Pointer Register
SI Source Index Register
DI Destination Index Register
SR Status Register
Generation of 20-bit Physical Address:
Prof. S. Jagannathan,HOD – Dept of E & C Engg,R.V. C. E, Bangalore
LOGICAL ADDRESS
SEGMENT REGISTER 0000
ADDER
20 BIT PHYSICAL MEMORY ADDRESS
Prof. S. Jagannathan,HOD – Dept of E & C Engg,R.V. C. E, Bangalore
8086 flag register format
BIT 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
U U U U 0F DF IF TF SF ZF U AF U PF U CF
U= UNDEFINED (a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
(g)
(h)
(i)
(a) : CARRY FLAG – SET BY CARRY OUT OF MSB
(b) : PARITY FLAG – SET IF RESULT HAS EVEN PARITY
(c) : AUXILIARY CARRY FLAG FOR BCD
(d) : ZERO FLAG – SET IF RESULT = 0
(e) : SIGN FLAG = MSB OF RESULT
(f) : SINGLE STEP TRAP FLAG
(g) : INTERRUPT ENABLE FLAG
(h) : STRING DIRECTION FLAG
(i) : OVERFLOW FLAG
There are three internal buses, namely A bus, B bus and C bus, which interconnect the
various blocks inside 8086.
The execution of instruction in 8086 is as follows:
The microprocessor unit (MPU) sends out a 20-bit physical address to the memory and
fetches the first instruction of a program from the memory. Subsequent addresses are sent
Prof. S. Jagannathan,HOD – Dept of E & C Engg,R.V. C. E, Bangalore
out and the queue is filled upto 6 bytes. The instructions are decoded and further data (if
necessary) are fetched from memory. After the execution of the instruction, the results
may go back to memory or to the output peripheral devices as the case may be.
Prof. S. Jagannathan,HOD – Dept of E & C Engg,R.V. C. E, Bangalore
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Rating Sheet FinalDocument7 pagesRating Sheet FinalJazelle FacunPas encore d'évaluation
- Embedded Controller Forth For The 8051 FamilyD'EverandEmbedded Controller Forth For The 8051 FamilyÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Raspberry Pi BScIT Practicals ManualDocument64 pagesRaspberry Pi BScIT Practicals ManualSancheetPas encore d'évaluation
- Cmd-V4 Service ManualDocument442 pagesCmd-V4 Service ManualGABRIELA100% (1)
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxD'EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Beamforming (TDD) Feature Parameter DescriptionDocument56 pagesBeamforming (TDD) Feature Parameter DescriptionMohammed ShakilPas encore d'évaluation
- Combinatorial Algorithms: For Computers and CalculatorsD'EverandCombinatorial Algorithms: For Computers and CalculatorsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- ERICSSON Business Objects KPIs Generation Process DocumentationDocument13 pagesERICSSON Business Objects KPIs Generation Process DocumentationAbhishek Sharma100% (2)
- EC8691-Microprocessor and Microcontroller Department of CSE & IT 2020-2021Document20 pagesEC8691-Microprocessor and Microcontroller Department of CSE & IT 2020-2021dkPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet MicorDocument42 pagesSheet MicorFiras TaherPas encore d'évaluation
- 8086 Full Full Notes of MicroprocessorDocument75 pages8086 Full Full Notes of MicroprocessorFired BoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Lab 2Document9 pagesPractical Lab 2Vishal KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Architecture of 8086 Microprocessor: Microprocessors LabDocument7 pagesArchitecture of 8086 Microprocessor: Microprocessors LabljjbPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec6504 Microprocessor and Microcontroller QBW (r2013)Document14 pagesEc6504 Microprocessor and Microcontroller QBW (r2013)KEERTHANA NVPas encore d'évaluation
- CS401 ProbvDocument11 pagesCS401 Probvaamir shahzad khanPas encore d'évaluation
- 21 Feb Up MpiDocument3 pages21 Feb Up MpiSahil ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Eee MPMC Mid-2 BitsDocument8 pagesEee MPMC Mid-2 BitsPOTTI GNANESWARPas encore d'évaluation
- Examples of Machine Language Instruction SetDocument10 pagesExamples of Machine Language Instruction Setعبدالرحيم اودينPas encore d'évaluation
- B.Tech II Year I Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations June 2017Document2 pagesB.Tech II Year I Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations June 2017Kareem KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 8085 Lab AssignmentDocument4 pages8085 Lab AssignmentShaswata Dutta50% (2)
- 8086 arch-SNKDocument7 pages8086 arch-SNKzelalem2022Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 3, 4 & 5 - MPMC r13 With ProgramsDocument14 pagesAssignment 3, 4 & 5 - MPMC r13 With Programssai bharadwajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Switching Theory and Logic DesignDocument8 pagesSwitching Theory and Logic Designkrishna chaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mid1 QP MPMC Ii-Ii Cse 15a04407 Microprocessor & InterfacingDocument2 pagesMid1 QP MPMC Ii-Ii Cse 15a04407 Microprocessor & InterfacingThil PaPas encore d'évaluation
- Instruction SetDocument104 pagesInstruction SetKrishnaveni DhulipalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet PDFmichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Microprocessor & Assembly Language ProgrammingDocument2 pagesMicroprocessor & Assembly Language ProgrammingharshimogalapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- Intel 8088 (8086) Microprocessor Structure: Haibo Wang ECE Department Southern Illinois University Carbondale, IL 62901Document16 pagesIntel 8088 (8086) Microprocessor Structure: Haibo Wang ECE Department Southern Illinois University Carbondale, IL 62901Chandrashekhar PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Programmer's Model 8086-80486Document20 pagesProgrammer's Model 8086-80486Shreyash SillPas encore d'évaluation
- 5-Introduction To 8086microprocessorDocument20 pages5-Introduction To 8086microprocessorBenjamin AkingeneyePas encore d'évaluation
- Eee MPMC Mid-2 BitsDocument7 pagesEee MPMC Mid-2 BitsPOTTI GNANESWARPas encore d'évaluation
- EC8691 (R-2017) V Sem Cse & It: Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument21 pagesEC8691 (R-2017) V Sem Cse & It: Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersOOPS&HCI testPas encore d'évaluation
- MC - CT2 - Scheme & KeyDocument4 pagesMC - CT2 - Scheme & Keyjinto0007Pas encore d'évaluation
- CEG 2131 - Fall 2003 - FinalDocument14 pagesCEG 2131 - Fall 2003 - FinalAmin DhouibPas encore d'évaluation
- CS2252 NolDocument117 pagesCS2252 NolYogeshkumar PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- MPMC Seminar - 720820103029Document12 pagesMPMC Seminar - 720820103029testttPas encore d'évaluation
- Cse 4223Document2 pagesCse 4223sayem12Pas encore d'évaluation
- CSC319 - 356 - 141 - CSC319Document5 pagesCSC319 - 356 - 141 - CSC319Aniket AmbekarPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 MPDocument19 pages3 MPsnPas encore d'évaluation
- Btech Biomed 4 Sem Digital Electronics Circuit Pbm4i102 2018Document3 pagesBtech Biomed 4 Sem Digital Electronics Circuit Pbm4i102 2018Narinder MauryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 3 2022 StudentsDocument5 pagesTutorial 3 2022 StudentsIndongo EliaserPas encore d'évaluation
- (412037753) UNDERSTANDING8085 - 8086 - Cap14 - Instruccion - SetDocument14 pages(412037753) UNDERSTANDING8085 - 8086 - Cap14 - Instruccion - SetVara LakshmiPas encore d'évaluation
- 002 Computer Science - November 2019 - SMCS11 Smse11Document6 pages002 Computer Science - November 2019 - SMCS11 Smse11SandipPas encore d'évaluation
- CT-2 Question Paper-Batch 2 MP Rev1Document1 pageCT-2 Question Paper-Batch 2 MP Rev1Safa MPas encore d'évaluation
- JUNE 2013: Code: AC78 Subject: Advanced MicroprocessorsDocument3 pagesJUNE 2013: Code: AC78 Subject: Advanced MicroprocessorspraveenPas encore d'évaluation
- MPI Compre PartA 2019 SolDocument2 pagesMPI Compre PartA 2019 SolVishweshRaviShrimaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Yellow Highlighted Are The Unsolved Questions and Red Highlighted Are The Ones I Got in My Exam 28-2-2013 From This FileDocument27 pagesYellow Highlighted Are The Unsolved Questions and Red Highlighted Are The Ones I Got in My Exam 28-2-2013 From This FileMuhammad Sheharyar MohsinPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecen 3104 - 2018 PDFDocument2 pagesEcen 3104 - 2018 PDFAjinkya HimanshuPas encore d'évaluation
- Microprocessor Laboratory: Introduction To DebugDocument8 pagesMicroprocessor Laboratory: Introduction To Debugnather bassamPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec1206 DPSDDocument8 pagesEc1206 DPSDkingraajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Identify Addressing Mode in Each of These Instructions and If The Instruction Accesses TheDocument4 pagesIdentify Addressing Mode in Each of These Instructions and If The Instruction Accesses Theheaven letaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Answers Summer 2015 - 17431Document35 pagesModel Answers Summer 2015 - 17431Ubaid Saudagar67% (3)
- STUDY OF 8086/8088: Assembler Is An Intermediate Program, Which Converts AssemblyDocument15 pagesSTUDY OF 8086/8088: Assembler Is An Intermediate Program, Which Converts AssemblyShashank SoodPas encore d'évaluation
- EC8691 - Microprocessors and Microcontrollers (Ripped From Amazon Kindle Ebooks by Sai Seena)Document636 pagesEC8691 - Microprocessors and Microcontrollers (Ripped From Amazon Kindle Ebooks by Sai Seena)gokulPas encore d'évaluation
- 8086 MicroprocessorDocument38 pages8086 MicroprocessorSiddhartha OntelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microprocessors - Introduction To 8086Document21 pagesMicroprocessors - Introduction To 8086navydevilzPas encore d'évaluation
- Objective Test1Document1 pageObjective Test1Gargi UpadhyayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer OrganizationDocument1 pageComputer OrganizationMaharshi JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- QBank DPSD cs2202Document6 pagesQBank DPSD cs2202kunarajPas encore d'évaluation
- M68HC11Document107 pagesM68HC11Govardhan HegdePas encore d'évaluation
- M A K A U T, W B: Aulana BUL Alam ZAD Niversity of Echnology EST EngalDocument4 pagesM A K A U T, W B: Aulana BUL Alam ZAD Niversity of Echnology EST EngalHimadri Sekhar DuttaPas encore d'évaluation
- L-3/T - 2/EEE Date: 28/0312022: IS) +D (I, 3,6,7)Document19 pagesL-3/T - 2/EEE Date: 28/0312022: IS) +D (I, 3,6,7)Sanjid ElahiPas encore d'évaluation
- SPKR DemoDocument3 pagesSPKR DemoAyan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Intel 8088 Architecture and Instruction SetDocument4 pagesThe Intel 8088 Architecture and Instruction SetSaad AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to LSID'EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to LSIPas encore d'évaluation
- tph3206psb 20171130Document13 pagestph3206psb 20171130Gan XuekaiPas encore d'évaluation
- EsquemaaDocument96 pagesEsquemaaPaulo Henrique LopesPas encore d'évaluation
- Danfoss Fotocellen 2018Document2 pagesDanfoss Fotocellen 2018veunderPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Hilux (Cont. Next Page) : Power Source Cruise Control (1KD-FTV W/o DPF)Document6 pages6 Hilux (Cont. Next Page) : Power Source Cruise Control (1KD-FTV W/o DPF)Alfian AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- 555 Timer DoctronicsDocument18 pages555 Timer DoctronicsGaneshVenkatachalamPas encore d'évaluation
- Samplechapter 2018080110032088Document25 pagesSamplechapter 2018080110032088MasoudPas encore d'évaluation
- Upgrade Dedicated Internet Services (Rev.01) - PT. Dardela Yasa Guna - Do...Document10 pagesUpgrade Dedicated Internet Services (Rev.01) - PT. Dardela Yasa Guna - Do...Rachmat HidayatPas encore d'évaluation
- Security Analysis of India's Electronic Voting MachinesDocument25 pagesSecurity Analysis of India's Electronic Voting MachinesSrikanth SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 3GPP Newcomer Introduction & Overview of 5G Status: Georg Mayer, 3GPP SA ChairmanDocument57 pages3GPP Newcomer Introduction & Overview of 5G Status: Georg Mayer, 3GPP SA ChairmanSudipta DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Spacecraft Computer Systems: Colonel John E. KeeseeDocument34 pagesSpacecraft Computer Systems: Colonel John E. KeeseeErickGarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pic Microcontroller Block DiagramDocument15 pagesPic Microcontroller Block DiagramNandaKiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Arducam Mega Product BriefDocument7 pagesArducam Mega Product BriefaabejaroPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.3 Autocorrelation and Power Spectral Density of Random Pulse TrainsDocument10 pages3.3 Autocorrelation and Power Spectral Density of Random Pulse TrainsYaseenPas encore d'évaluation
- Two Stage AmplifierDocument8 pagesTwo Stage AmplifierTharakaKaushalyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 ALCE Low Voltage Transformers 13R01Document28 pages4 ALCE Low Voltage Transformers 13R01Amílcar DuartePas encore d'évaluation
- AOC E2043fs LCD MonitorDocument50 pagesAOC E2043fs LCD MonitorFranko Ney FélixPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuit Analysis Open EndedDocument8 pagesCircuit Analysis Open EndedHuzaifaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1022 Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument1 page1022 Optical Fiber CommunicationrambabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Timing and Control UnitDocument22 pagesTiming and Control Unitaditya88_4u0% (1)
- Manual de La Radio SC Sb-Ak780Document20 pagesManual de La Radio SC Sb-Ak780Oscar Pinedo MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Single-Switch Transformerless DC-DC Converter With Universal Input Voltage For Fuel Cell Vehicles Analysis and DesignDocument12 pagesA Single-Switch Transformerless DC-DC Converter With Universal Input Voltage For Fuel Cell Vehicles Analysis and Designreza mohajeryPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimized Rat-Race Coupler With Different Shapes of Defected Ground StructureDocument4 pagesOptimized Rat-Race Coupler With Different Shapes of Defected Ground Structureravi010582Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4100 0031 PDFDocument10 pages4100 0031 PDFsqamar68Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 1Z621144312 PDFDocument101 pages1 1Z621144312 PDFvijeshvijayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment For DSPDocument2 pagesAssignment For DSPAjiteshAwasthiPas encore d'évaluation