Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Clinical Presentation, Diagnostic Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis
Transféré par
Benedict TenorioTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Clinical Presentation, Diagnostic Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis
Transféré par
Benedict TenorioDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation and differential diagnosis
Headache and visual disturbances with occipital lobe edema are common symptoms of eclamptic encephalopathy. Hyperperfusion and edema occur most often and more pronounced posteriorly in the subcortical white matter of the occipital lobes, although gray matter and anterior circulation is involved in the most severe cases. Seizures may be focal or secondary generalized. Some women have neurological complications without seizures, including confusion, aphasia, cognitive deficits, and depressed level of consciousness. Although hypertension and preeclampsia occur most often in eclamptic women, it is not uncommon for women to present with seizures in late-pregnancy and early postpartum with mild or absent hypertension, as discussed above. The diagnosis of eclampsia is based on the findings of encephalopathy or seizures in latepregnancy or postpartum with imaging. Computed tomography or MR imaging should be used to show evidence of edema and rule out alternative brain lesions or hemorrhage. MR imaging with diffusion-weighted imaging can be useful to distinguish reversible edema from ischemic stroke. Patients may have intracerebral or cerebellar hemorrhage that can be due to vascular anomalies or can result from trauma associated with seizure. Other common causes of seizure during pregnancy, other than eclampsia, include idopathic epilepsy, trauma, congenital defects, neoplasms, meningitis, intracerebral hemorrhage, and drug and alcohol toxicity.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 61 Rab Nawaz (Stroke DD)Document23 pages61 Rab Nawaz (Stroke DD)SardarChangezKhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Stroke 1982 Heros 106 9Document5 pagesStroke 1982 Heros 106 9Rika FitriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 14. The Dizzy Patient The Dizzy Patient: IntroductionDocument9 pagesChapter 14. The Dizzy Patient The Dizzy Patient: IntroductionjumabarrientosPas encore d'évaluation
- Seizure Versus SyncopeDocument10 pagesSeizure Versus SyncopeArmando Diaz PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- UWorld Notes NeurologyDocument6 pagesUWorld Notes NeurologysarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Ns-Reeves and SwensonDocument112 pagesDisorders of Ns-Reeves and SwensonSuganya BalachandranPas encore d'évaluation
- By/ Doha Rasheedy AlyDocument81 pagesBy/ Doha Rasheedy AlyDoha EbedPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Eklamsia 6-8Document5 pagesJurnal Eklamsia 6-8Baiq HestyPas encore d'évaluation
- Extra OffDocument9 pagesExtra OffDonya Bani HaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Vasospasm After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: NeurologyDocument8 pagesVasospasm After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: NeurologyGary MiguelPas encore d'évaluation
- 1b. EclampsiaDocument14 pages1b. EclampsiaJuan P. RuedaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 1016@j Preghy 2020 10 013Document25 pages10 1016@j Preghy 2020 10 013Saira MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) Infarction: Jenis Stroke IskemikDocument7 pagesMiddle Cerebral Artery (MCA) Infarction: Jenis Stroke IskemiksarelriskyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebrovascular Diseases Risk Factors:: o o o o oDocument4 pagesCerebrovascular Diseases Risk Factors:: o o o o otrinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case ReportDocument4 pagesCase ReportkatherinePas encore d'évaluation
- Common Neurologic Symptoms: Na ShaoDocument31 pagesCommon Neurologic Symptoms: Na ShaoArvindhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Background: Hemiplegia Dysphasia HematomaDocument16 pagesBackground: Hemiplegia Dysphasia HematomaAndreea DanielaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardinal Manifestations HeadacheDocument51 pagesCardinal Manifestations HeadacheRoby KieranPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolic Coma DRDocument32 pagesMetabolic Coma DRKintan UtamiPas encore d'évaluation
- PRES (Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome) and Eclampsia-ReviewDocument5 pagesPRES (Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome) and Eclampsia-ReviewAvicena M IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Code: Nurs 513 Course Title: Community Health Seminar Seminar PresentationDocument26 pagesCourse Code: Nurs 513 Course Title: Community Health Seminar Seminar PresentationHadiza Adamu AuduPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebral Palsy Practice Essentials: Signs and SymptomsDocument11 pagesCerebral Palsy Practice Essentials: Signs and SymptomsTahsinur RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ax & DX SAHDocument5 pagesAx & DX SAHMohammadAwitPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurology 5Document5 pagesNeurology 5Loyla RosePas encore d'évaluation
- Comatose PTDocument20 pagesComatose PTNinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Perinatal Asphyxia: For C-IDocument35 pagesPerinatal Asphyxia: For C-IYemata HailuPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 2Document3 pagesCase 2AyidhPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolic Encephalopathy and Metabolic ComaDocument14 pagesMetabolic Encephalopathy and Metabolic ComaqlinlynPas encore d'évaluation
- Penatalaksanaan Anestesia Pada Preeklampsia Dan Eklampsia U. Kaswiyan ADocument19 pagesPenatalaksanaan Anestesia Pada Preeklampsia Dan Eklampsia U. Kaswiyan AReyhan CalabroPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypertensive Encephalopathy in Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument7 pagesHypertensive Encephalopathy in Diagnosis and TreatmentAjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Encephalopathy and CausesDocument7 pagesTypes of Encephalopathy and CausesApriansyah Arfandy AzisPas encore d'évaluation
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (Pres) in A Patient With Late Postpartum Eclampsia: Case ReportDocument4 pagesPosterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (Pres) in A Patient With Late Postpartum Eclampsia: Case ReportIJAR JOURNALPas encore d'évaluation
- Pontine Reversible EdemaDocument4 pagesPontine Reversible Edemaseaside16girlPas encore d'évaluation
- Geriatric Syncope CaseDocument8 pagesGeriatric Syncope CaseStarr NewmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sin CopeDocument3 pagesSin CopeCarouselofTinaPas encore d'évaluation
- RuggGunn PDFDocument15 pagesRuggGunn PDFxuexuePas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Neurology (Cerebellar Ataxia)Document11 pagesPractical Neurology (Cerebellar Ataxia)idno1008Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pa Pill EdemaDocument13 pagesPa Pill Edemarutuparna383Pas encore d'évaluation
- An Approach To The Evaluation of A Patient For Seizures and EpilepsyDocument8 pagesAn Approach To The Evaluation of A Patient For Seizures and EpilepsyGaneshRajaratenamPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Task Lecture 22Document3 pagesLearning Task Lecture 22Anonymous a6cBRA6P4mPas encore d'évaluation
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy SyndDocument7 pagesPosterior Reversible Encephalopathy SyndasasakopPas encore d'évaluation
- Guardance Intructor: Dedy Respianto. Akademic IC Rangga Husada 2010/2011Document9 pagesGuardance Intructor: Dedy Respianto. Akademic IC Rangga Husada 2010/2011pitaapriyaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CVA SsDocument39 pagesCVA SsAnushri ManePas encore d'évaluation
- Vertigo in Cerebrovascular DiseasesDocument8 pagesVertigo in Cerebrovascular DiseasesNAILAH NASYWA RUSMAWATI -Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hypertensive Crisis: Philip Shayne and Catherine A. LynchDocument11 pagesHypertensive Crisis: Philip Shayne and Catherine A. LynchDong HkPas encore d'évaluation
- DD Nyeri Kepala Skenario 1Document8 pagesDD Nyeri Kepala Skenario 1Ika Putri YulianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurology Equations Made Simple: Differential Diagnosis and NeuroemergenciesD'EverandNeurology Equations Made Simple: Differential Diagnosis and NeuroemergenciesPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebrovascular Function in Pregnancy and EclampsiaDocument12 pagesCerebrovascular Function in Pregnancy and EclampsiaayubahriPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydro Cep Hal UsDocument5 pagesHydro Cep Hal UsEka Putra PrayogaPas encore d'évaluation
- Síndrome PRES - GeneralidadesDocument6 pagesSíndrome PRES - GeneralidadesLaura VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- J Emc 2016 06 017 PDFDocument17 pagesJ Emc 2016 06 017 PDFnonniPas encore d'évaluation
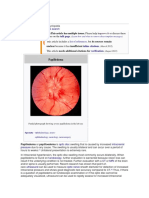
- Papiledema & Neuritis OpticDocument42 pagesPapiledema & Neuritis OpticNadine Wang0% (1)
- Papilledema: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument4 pagesPapilledema: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchEri DooPas encore d'évaluation
- Vascular Disorders of The Posterior Circulation - An Anatomico-Clinical OverviewDocument3 pagesVascular Disorders of The Posterior Circulation - An Anatomico-Clinical OverviewSagar GopaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Eclampsia - UpToDate2019Document16 pagesEclampsia - UpToDate2019Carlos Jeiner Díaz SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Eye and Visual System in The Preeclampsiaeclampsia SyndromeDocument3 pagesThe Eye and Visual System in The Preeclampsiaeclampsia SyndromeFerdyPas encore d'évaluation
- Index - : Professor Yasser MetwallyDocument11 pagesIndex - : Professor Yasser MetwallyDrhikmatullah SheraniPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurological Manifestations of Vascular DementiaDocument5 pagesNeurological Manifestations of Vascular DementiaDumitruAuraPas encore d'évaluation
- Kopel, Et Al. (2021)Document18 pagesKopel, Et Al. (2021)CARLOS SANTIAGO PEREZ RODRIGUEZPas encore d'évaluation
- The Myth of Autism: How a Misunderstood Epidemic Is Destroying Our ChildrenD'EverandThe Myth of Autism: How a Misunderstood Epidemic Is Destroying Our ChildrenÉvaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (8)
- MANAGEMENTDocument2 pagesMANAGEMENTBenedict TenorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Postpartum Preeclampsia Mayo ClinicDocument1 pagePostpartum Preeclampsia Mayo ClinicBenedict TenorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Pqepaqed By: Jiezl Anne P.: Recaido, RN MAN StudentDocument14 pagesPqepaqed By: Jiezl Anne P.: Recaido, RN MAN StudentBenedict TenorioPas encore d'évaluation
- "Precious": Gerry R. Pingen Marciana P. de Vera, Ed. DDocument2 pages"Precious": Gerry R. Pingen Marciana P. de Vera, Ed. DBenedict TenorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Cultural DiversityDocument28 pagesCultural DiversityBenedict Tenorio100% (1)
- PenalDocument1 pagePenalBenedict TenorioPas encore d'évaluation
- PassDocument4 pagesPassBenedict TenorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Crossword FactoringDocument1 pageCrossword FactoringBenedict TenorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Child AbuseDocument4 pagesChild AbuseGerry Pingen100% (1)