Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
The Endocrine System
Transféré par
api-236094936Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The Endocrine System
Transféré par
api-236094936Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
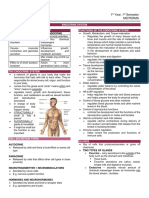
The Endocrine System The purpose of the endocrine system is to secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
Glands are endocrine organs that perform the function of secretion. Endocrine glands and exocrine glands are different. Endocrine glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream. Those are also known as ductless glands. Exocrine glands release hormones or secretions into other organs. Endocrine glands include: (2) adrenal, (2) ovaries (female), (4) parathyroid, pancreas (islets of Langerhans), pituitary, (2) testes (male), thymus, and the thyroid gland. Adrenal glands are found on top of the kidneys. The prefix ad- means toward and renal refers to the kidneys. The cortex is outer part of the adrenal cortex. Corticosteriods are the hormones that are maintained by the adrenal cortex. Minerals like sodium and potassium are regulated by the mineralocorticoid hormone and aldosterone. Carbs are regulated by the glucocorticoid hormone (cortisol). Steroid sex hormones are also secreted by the adrenal cortex. Those hormones include estrogen, androgen, and progesterone. The medulla secretes epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine. Blood pressure, heart rate, and respiration levels are increased in times of emergency. Ovaries are the female gonads that produce estrogen and progesterone. Those are female sex hormones. Progesterone helps keep a regulated uterine environment for the fetus during pregnancy. Estrogen controls the menstrual cycle. They also help with sexual characteristics. The parathyroid glands are found on the back side of the thyroid. They regulate calcium levels. Sometimes calcium levels fall too low. If this occurs, bone breakdown will happen. More calcium will be released into the blood. The pancreas is found behind the stomach. It functions as both an endocrine and exocrine gland. Endocrine sections produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that controls the levels of sugar in the blood. Exocrine glands release enzymes into the small intestines through the ducts. Behind the optic nerve is the pituitary gland. Other endocrine glands are regulated by the pituitary, giving it the nickname the master gland. Two sections divide the pituitary: anterior and posterior. The anterior portion of the pituitary gland secrets the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and the growth hormone (GH). GH stimulates growth cells to grow and divide. TSH controls the thyroid. The adrenal cortex is regulated by ACTH. Milk production comes after birth became of prolactin. FSH and LH are part of the male and female gonads. MSH tells melanocytes to produce melanin. The posterior only secretes ADH and oxytocin. ADH controls water reabsorption. Oxytocin controls uterine contractions. Testes are male gonads. They produce sperm (male sex cells). It also produces testosterone. Testosterone is the sex hormone of males. Last, it regulates production of the sperm. The thymus is found above the heart (mediastinal cavity). It secretes thymosin. The thymus main function is immune system development. T cells are necessary for the immune system. T cells stand for thymic lymphoid cells. You can find the thyroid between the trachea and larynx. Thyroxine is produced by the thyroid. It is also known as the T4 hormone. T3 hormone or triiodothyronine is also produced by the thyroid. Metabolism is maintained by the thyroid. Another hormone secreted is calcitonin.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Feedback Mechanism LabDocument5 pagesFeedback Mechanism LabBeverly Carballo - Moguel0% (1)
- Integumentary SystemDocument1 pageIntegumentary Systemapi-236094936Pas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper On Seizure DogsDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Seizure Dogsapi-236094936Pas encore d'évaluation
- Melanoma PPDocument11 pagesMelanoma PPapi-236094936Pas encore d'évaluation
- Integumentary DiseasesDocument1 pageIntegumentary Diseasesapi-236094936Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Urinary SystemDocument1 pageThe Urinary Systemapi-236094936Pas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Failure PamphletDocument2 pagesRenal Failure Pamphletapi-236094936Pas encore d'évaluation
- Definitions of Respiratory DiseasesDocument1 pageDefinitions of Respiratory Diseasesapi-236094936Pas encore d'évaluation
- Musculoskeletal DiseasesDocument1 pageMusculoskeletal Diseasesapi-236094936Pas encore d'évaluation
- Definitions of Nervous System DiseasesDocument1 pageDefinitions of Nervous System Diseasesapi-236094936Pas encore d'évaluation
- Power PointDocument9 pagesPower Pointapi-236094936Pas encore d'évaluation
- Definitions of Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument1 pageDefinitions of Cardiovascular Diseasesapi-236094936Pas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal Aortic AneurysmDocument6 pagesAbdominal Aortic Aneurysmapi-236094936Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument7 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationAnonymous -Pas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine System NotesDocument4 pagesEndocrine System NotesSashaPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank Pharmacology 3rd Edition Brenner StevensDocument36 pagesTest Bank Pharmacology 3rd Edition Brenner Stevenspieloutou4794100% (31)
- AP13 EndocrineDocument12 pagesAP13 EndocrinePay per PrintPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine GlandsDocument3 pagesEndocrine Glandsdan 123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fisiologi Hormon TiroidDocument54 pagesFisiologi Hormon Tiroidaan SyamhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Allostasis and AdaptogensDocument24 pagesAllostasis and Adaptogensrobynklein100% (1)
- Endocrine Notes (Harrisons)Document27 pagesEndocrine Notes (Harrisons)Valerie Gonzaga-CarandangPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Hormones On GI TractDocument4 pagesEffect of Hormones On GI TractIrene SiauPas encore d'évaluation
- Neo-Psychosomatics For Massage Therapists and MoreDocument130 pagesNeo-Psychosomatics For Massage Therapists and MoreGabrielaMirelaAlexePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 35Document11 pagesChapter 35JanahAbedinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11-Human Body SystemDocument48 pagesChapter 11-Human Body SystemTrần MạnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurotransmitter Cell CommunicationDocument25 pagesNeurotransmitter Cell CommunicationOtnil DPas encore d'évaluation
- Williams Textbook of Endocrinology 14Th Edition Shlomo Melmed MBCHB Macp All ChapterDocument67 pagesWilliams Textbook of Endocrinology 14Th Edition Shlomo Melmed MBCHB Macp All Chapterchristina.brown369100% (16)
- The Role of Hormone ReceptorsDocument8 pagesThe Role of Hormone ReceptorsnaimaguilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument22 pagesIntroduction To EndocrinologyUrwah KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Discussion Notes (Anaphy)Document49 pagesDiscussion Notes (Anaphy)jade tanPas encore d'évaluation
- Big Book Reading Comprehension 2Document40 pagesBig Book Reading Comprehension 2upscprepPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus For 2-Year Semester in M.sc. (Zoology), University of CalcuttaDocument41 pagesSyllabus For 2-Year Semester in M.sc. (Zoology), University of Calcuttamy.dear.sir100% (2)
- Can Plants CommunicateDocument19 pagesCan Plants CommunicateIemaaNaimaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Psychology RevisedDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Psychology RevisedArsalan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology-Class 10Th Chapter: Control and Co-Ordination: Very Short Answer Type Question (1 Mark)Document5 pagesBiology-Class 10Th Chapter: Control and Co-Ordination: Very Short Answer Type Question (1 Mark)junaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Terminology of Unani NameDocument5 pagesTerminology of Unani NameWalid Hasan Towkir Ahammed sarkar100% (1)
- Cell Signaling Write UpDocument4 pagesCell Signaling Write Upinfinity chronusPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology,: Lecture OutlineDocument79 pagesAnatomy and Physiology,: Lecture OutlineJorelyn Giron NaniongPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Face Yoga Method Ebook Fumiko TakatsuDocument70 pagesFree Face Yoga Method Ebook Fumiko Takatsumagdalena0% (3)
- Complications of MarasmusDocument3 pagesComplications of MarasmusNathania LongkutoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam Qs HWDocument11 pagesExam Qs HWMiguel Oubiña SánchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Kseeb SSLC Class 10 Science Previous Year Paper 2019Document12 pagesKseeb SSLC Class 10 Science Previous Year Paper 2019ghs niduvani niduvaniPas encore d'évaluation