Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
1-Exchange With The Environment
Transféré par
api-238421605Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1-Exchange With The Environment
Transféré par
api-238421605Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Copyright by Holt, Rinohart and Winston. All rights rosorvod.
Interactive Textbook 25 The Cell in ction
5ECIION
1
xrhaoe wth the ovroomeot
The Cell in ction
Namo Class Dato
After you read this section you shouId be abIe to answer
these questions
How do colls tako in food and got rid of wastos?
What is diffusion?
Where Do CeIIs Cet the MateriaIs Ihey Need!
What would happon to a factory if its powor woro shut
off or its supply of matorials novor arrivod? What would
happon if tho factory couldn't got rid of its garbago? Liko
a factory, an organism must bo ablo to got onorgy and raw
matorials and got rid of wastos. Thoso jobs aro dono by
an organism's colls. Matorials movo in and out of tho coll
across tho coll mombrano. Many matorials, such as wator
and oxygon, can cross tho mombrano by diffusion.
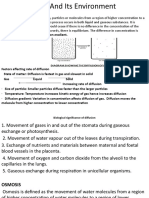
What Is Diffusion!
Tho figuro bolow shows what happons whon dyo is
placod on top of a layor of golatin. Ovor timo, tho dyo
mixos with tho golatin. Why doos this happon?
Evorything, including tho golatin and tho dyo, is mado
of tiny moving particlos. Particlos tond to movo from
placos whoro thoy aro crowdod to placos whoro thoy aro
loss crowdod. Whon thoro aro many of ono typo of
particlo, this is a high concontration. Whon thoro aro
fowor of ono kind of particlo, this is a low concontration.
Tho movomont from aroas of high concontration to aroas
of low concontration is callod diIIuaion.
t hrst, the dye
and the gelatin
are separate
from each
other.
Dye
Celatin
fter a while, the particles in the
dye move into the gelatin. This
process is called diffusion.
8EFDRE D0 RE40
NationaI 5cience
Education 5tandards
L5 1a, 1c
Comgare s you read, make
a chart comparing diffusion
and osmosis. In your chart,
show how they are similar
and how they are different.
RE40INC CHECK
1. Dene What is diffusion!
2. Identify How do dye
particles move through the
water!
ChAPIk 2
Copyright by Holt, Rinohart and Winston. All rights rosorvod.
Interactive Textbook 26 The Cell in ction
5ECIION
Namo Class Dato
xchange with the nvironment
DIFFU5ION OF WAIEk
Substancos, such as wator, aro mado up of particlos
callod uo|ecv|es. Puro wator has tho highost concontration
of wator moloculos. This moans that 1OO of tho moloculos
aro wator moloculos. If you mix anothor substanco, such as
food coloring, into tho wator, you lowor tho concontration
of wator moloculos. This moans that wator moloculos no
longor mako up 1OO of tho total moloculos.
Tho figuro bolow shows a containor that has boon dividod
by a mombrano. Tho mombrano is seujerueab|ethat is,
only somo substancos can pass through it. Tho mombrano
lots smallor moloculos, such as wator, pass through. Largor
moloculos, such as food coloring, cannot pass through.
Wator moloculos will movo across tho mombrano. Tho
diffusion of wator through a mombrano is callod oamoaia.
0smosis
urewater
Watermixedwith
foodcoIoring
Sipermeable
membrane
Theconcentration
ofwatermolecules
inthemixture
islower.
Purewaterhas
thehihest
concentration
ofwater
molecules.
1
Pure water
Water mixed with
food coIoring
Semipermeable
membrane
Cvertime,water
moleculesmove
intothewater-food
coloringmixture.
2
A coll mombrano is a typo of somipormoablo mombrano.
This moans that wator can pass through tho coll mombrano,
but most othor substancos cannot. Tho colls of organisms
aro surroundod by and fillod with fluids. Thoso fluids aro
mado mostly of wator. Wator movos in and out of a coll by
osmosis.
,-...e-! J-.--.-_
J. AppIy Concepts Which
of the following has a higher
concentration of water
molecules-200 molecules
of water, or a mixture of
300 molecules of water
and 100 molecules of food
coloring! Explain your answer.
4. ExpIain Why does the
volume of liquid in the
right-hand side of the
container increase with time!
RE40INC CHECK
5. Identify How does water
move into and out of cells!
Copyright by Holt, Rinohart and Winston. All rights rosorvod.
Interactive Textbook 2? The Cell in Action
5ECIION
Namo Class Dato
Exchange with the Environment
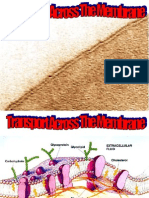
How Do 5maII ParticIes Enter and Leave a CeII!
Small particlos, such as sugars, can cross tho coll
mombrano through passagoways callod channe|s. Thoso
channols in tho coll mombrano aro mado of protoins.
Particlos can travol through thoso channols by passivo
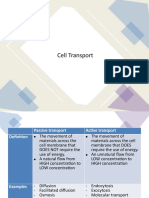
transport or by activo transport.
During paaaive IranaporI, particlos movo through tho
coll mombrano without using onorgy from tho coll. During
passivo transport, particlos movo from aroas of high con-
contration to aroas of lowor concontration. Diffusion and
osmosis aro oxamplos of passivo transport.
During acIive IranaporI, tho coll has to uso onorgy to
movo particlos through channols. During activo transport,
particlos usually movo from aroas of low concontration to
aroas of high concontration.
How Do Large ParticIes Enter and Leave a CeII!
Largo particlos cannot movo across a coll mombrano
in tho samo ways as small particlos. Largor particlos must
movo in and out of tho coll by ondocytosis and oxocytosis.
Both procossos roquiro onorgy from tho coll.
EndocyIoaia happons whon a coll surrounds a largo
particlo and onclosos it in a vosiclo. A iesc|e is a sac
formod from a pioco of coll mombrano.
The cell comes
into contact with
a particle.
The cell membrane
begins to wrap
around the particle.
Cnce the particle
is completely sur-
rounded, a vesicle
pinches off.
1 2 J
Endocytosis
ExocyIoaia happons whon a coll usos a vosiclo to movo a
particlo from within tho coll to outsido tho coll. Exocytosis is
how colls got rid of largo wasto particlos.
Large particles that
must leave the cell
are packaged in
vesicles.
The vesicle travels to
the cell membrane
and fuses with it.
The cell releases
the particle to the
outside of the cell.
Exocytosis
1 2 J
RE40INC CHECK
6. Identify What is needed
to move particles from areas
of low concentration to areas
of high concentration!
7. Identify Label the vesicle
in the hgure.
Copyright by Holt, Rinohart and Winston. All rights rosorvod.
Interactive Textbook 2S The Cell in Action
Namo Class Dato
Sertoo 1 kevew N5E5 L5 1a, 1c
5ECIION VOCAULAkY
active transgort the movement of substances
across the cell membrane that requires the cell
to use energy
diffusion the movement of particles from
regions of higher density to regions of lower
density
endocytosis the process by which a cell mem-
brane surrounds a particle and encloses the
particle in a vesicle to bring the particle into
the cell
exocytosis the process in which a cell releases
a particle by enclosing the particle in a vesicle
that then moves to the cell surface and fuses
with the cell membrane
osmosis the diffusion of water through a
semipermeable membrane
gassive transgort the movement of substances
across a cell membrane without the use of
energy by the cell
Compare How is ondocytosis difforont from oxocytosis? How aro thoy similar?
2 ExpIain How is osmosis rolatod to diffusion?
Compare What aro tho difforoncos botwoon activo and passivo transport?
Identify What structuros allow small particlos to cross coll mombranos?
5 AppIy Concepts Draw an arrow in tho figuro bolow to show tho diroction that
wator moloculos will movo in.
water mixed
with sugar
pure water
semipermeable
membrane
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Cell Transport Powerpoint NotesDocument33 pagesCell Transport Powerpoint Notesapi-644325383Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diffusion and Osmosis - IGCSEDocument37 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis - IGCSEJohnnie ZhangPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Transport Powerpoint NotesDocument33 pagesCell Transport Powerpoint Notesapi-644325383Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Membrane & HomeostasisDocument50 pagesCell Membrane & Homeostasisapi-233187566Pas encore d'évaluation
- BIO2 Diffusion OsmosisDocument11 pagesBIO2 Diffusion Osmosisarangosoangelo8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 04 - The Cell in ActionDocument22 pagesChapter - 04 - The Cell in ActionBily roriguesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 10 Diffusion, Osmosis and Transport - TeacherDocument20 pagesChap 10 Diffusion, Osmosis and Transport - TeacherSulochana Devi PalanisamyPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology 1Document15 pagesGeneral Biology 1Beejae ApalisPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Notes For OlevelDocument45 pagesBiology Notes For OlevelSaira Binte SalekPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Movement in and Out of CellsDocument26 pages03 Movement in and Out of Cells张查Pas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesActivity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisThea Calyn WalicanPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotech Module2Document12 pagesBiotech Module2Aldrin M. ObiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisDocument5 pagesGene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisbodurr571Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveDocument10 pagesChapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveVanshika VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- CellDocument5 pagesCellMyrene CeblanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument49 pagesCell Membrane TransportAlex VoicuPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell PhysiologyDocument12 pagesCell PhysiologyJaseme OtoyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Transport NotesDocument10 pagesCell Transport NotesReyad BarbarPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsDocument67 pages3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsThom PaglinawanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument54 pagesThe Cellular Level of OrganizationGraziela Sagun RepuyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pergerakan Molekul Dalam Sel TumbuhanDocument36 pagesPergerakan Molekul Dalam Sel TumbuhanSitiKomariahAgustinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.transport MechanismsDocument94 pages4.transport MechanismsHyacinth RaePas encore d'évaluation
- AP Bio Lab1Document10 pagesAP Bio Lab1Eva DesireePas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Bio NotesDocument19 pagesQuality Bio NotesJimmy FanPas encore d'évaluation
- Progress Indicators: Learning Objective: To Understand The Structure of Animal and Plant CellsDocument49 pagesProgress Indicators: Learning Objective: To Understand The Structure of Animal and Plant CellsnidhiPas encore d'évaluation
- CB6d Transpiration and TranslocationDocument33 pagesCB6d Transpiration and TranslocationTosis MajidPas encore d'évaluation
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument30 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsEmy AnkrahPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOL1408 Introductory Biology Name Lab Unit 6/7: Diffusion & Osmosis Date Dr. Flo OxleyDocument10 pagesBIOL1408 Introductory Biology Name Lab Unit 6/7: Diffusion & Osmosis Date Dr. Flo OxleyJavier E. Dubon0% (1)
- Transport Mechanisms in CellDocument28 pagesTransport Mechanisms in CellTrisha Loise VillacampaPas encore d'évaluation
- LESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Document4 pagesLESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Jhay Luiz Cajigal ArquinesPas encore d'évaluation
- Movement of Subtances Across Plasma MembraneDocument414 pagesMovement of Subtances Across Plasma MembranezazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument30 pagesEarth and Life ScienceChristian VitalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Questions Plasma Membrane 1. What Is The Function of The Plasma Membrane?Document11 pagesReview Questions Plasma Membrane 1. What Is The Function of The Plasma Membrane?Jennie Rose KomalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells and Its Environment Ss1 NoteDocument14 pagesCells and Its Environment Ss1 NoteEllaPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology 1 Q1 Week 7Document14 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q1 Week 7JewelPas encore d'évaluation
- Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument12 pagesMovement Into and Out of Cellsf8sdh6xvzyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument48 pagesCell Membrane TransportIndra3SHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell TransportDocument23 pagesCell Transport7104Pas encore d'évaluation
- A8) Transport Across The MembraneDocument105 pagesA8) Transport Across The MembraneTitliMaopussyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Membrane Structure-And FunctionDocument5 pagesCell Membrane Structure-And FunctionEmmanuel MwalePas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE Biology Notes Updated April 2016Document94 pagesIGCSE Biology Notes Updated April 2016Adi101010101010101100% (1)
- Biology Notes Class 9Document5 pagesBiology Notes Class 9lalitha muraliPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Membrane NotesDocument6 pagesCell Membrane NotesBianca RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Osmosis Diffusion Lab-1Document7 pagesOsmosis Diffusion Lab-1api-1658690000% (1)
- Chemical Activity in The Cell: After You Have Finished Reading This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToDocument21 pagesChemical Activity in The Cell: After You Have Finished Reading This Chapter, You Should Be Able TojohnnwakanmaPas encore d'évaluation
- GenBio9 051716Document35 pagesGenBio9 051716salihuddinalkaizarPas encore d'évaluation
- Active and Passive TransportDocument23 pagesActive and Passive TransportSai SridharPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Membranes & Transport 1Document77 pagesCell Membranes & Transport 1Alen SheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Egg Membrane Project For 12Document18 pagesEgg Membrane Project For 12Hemanth Kumar100% (1)
- Lab 4 PP 25-31 WMtWeec PDFDocument7 pagesLab 4 PP 25-31 WMtWeec PDFTAHA GABRPas encore d'évaluation
- LR Revision GuideDocument19 pagesLR Revision GuidelachippaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cellular Transport PowerpointDocument50 pagesCellular Transport PowerpointPortia EgkenPas encore d'évaluation
- Gavin Hagerty - Notes - 8.3 Cell TransportDocument6 pagesGavin Hagerty - Notes - 8.3 Cell Transportgavinhagerty709Pas encore d'évaluation
- MOVEMENT IN & OUT OF CELLS - Ch.3Document48 pagesMOVEMENT IN & OUT OF CELLS - Ch.3Yassin Al fekyPas encore d'évaluation
- REVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDocument4 pagesREVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDavé TranPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Diffusion & OsmosisDocument27 pages3 Diffusion & OsmosisnasserkhanPas encore d'évaluation
- AS Biology, Cell Membranes and Transport 1Document49 pagesAS Biology, Cell Membranes and Transport 1sachinPas encore d'évaluation
- Mahan 2Document7 pagesMahan 2KANT JAMES D. MAHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell PhysiologyDocument15 pagesCell PhysiologyHENRY MURIGIPas encore d'évaluation
- Mla - Title Page Set OutDocument1 pageMla - Title Page Set Outapi-238421605Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gems Astronomy Information BrochureDocument10 pagesGems Astronomy Information Brochureapi-238421605Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mla Styles - Name and Page NoDocument2 pagesMla Styles - Name and Page Noapi-238421605Pas encore d'évaluation
- Isotope and Relative Atomic MassDocument14 pagesIsotope and Relative Atomic Massapi-238421605100% (2)
- The Mole ConceptDocument8 pagesThe Mole Conceptapi-238421605Pas encore d'évaluation
- Owl Purdue MlaDocument36 pagesOwl Purdue Mlaapi-238421605Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Cite A Website in Mla - Easybib BlogDocument7 pagesHow To Cite A Website in Mla - Easybib Blogapi-238421605Pas encore d'évaluation
- One World FactorsDocument7 pagesOne World Factorsapi-238421605Pas encore d'évaluation
- Essay Sentence StartersDocument2 pagesEssay Sentence Startersapi-238421605100% (1)
- Plane Mirror and ImagesDocument26 pagesPlane Mirror and Imagesapi-238421605100% (3)
- Rules For Drawing Electrical CircuitsDocument2 pagesRules For Drawing Electrical Circuitsapi-238421605100% (1)
- ElectricityDocument54 pagesElectricityapi-238421605Pas encore d'évaluation
- Myp 4 Bio TabooDocument11 pagesMyp 4 Bio Tabooapi-238421605Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Mole and Avogadros NumberDocument63 pagesThe Mole and Avogadros Numberapi-238421605Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ws - Power and ResistanceDocument4 pagesWs - Power and Resistanceapi-238421605Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ws Static Electricity 1Document4 pagesWs Static Electricity 1api-238421605Pas encore d'évaluation
- Standard For Food Grade Salt PDFDocument5 pagesStandard For Food Grade Salt PDFMercyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 2Document14 pagesLec 2api-321453350Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science Eng Grade 09 Unit 15-2Document2 pagesScience Eng Grade 09 Unit 15-2Metro CommunicationPas encore d'évaluation
- StructuralMechanicsModuleUsersGuide PDFDocument1 160 pagesStructuralMechanicsModuleUsersGuide PDFKamran PanaghiPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM D6866 For Biobased ProductsDocument21 pagesASTM D6866 For Biobased ProductsBeta Analytic100% (1)
- Science 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 3 ValidatedDocument10 pagesScience 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 3 ValidatedMYLENE B. ZABALLEROPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Softening Through Ion Exchange Method - Estimation of Residual HardnessDocument4 pagesWater Softening Through Ion Exchange Method - Estimation of Residual HardnesssuseelaksmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Thesis Huifei JinDocument170 pagesThesis Huifei Jintaufiqishak09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bio EnergeticsDocument8 pagesBio EnergeticsSamuel RookiePas encore d'évaluation
- PH ParadoxDocument6 pagesPH ParadoxSofiaMylonaPas encore d'évaluation
- ApplicationBrochure 2 BOD 30247570Document52 pagesApplicationBrochure 2 BOD 30247570Jose AparcanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson - Plan MixtureDocument5 pagesLesson - Plan Mixturejules blancoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Solubility of Gases in LiquidsDocument86 pagesThe Solubility of Gases in Liquidsga6ba5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Hydraulics: Chapter OverviewDocument15 pagesPlant Hydraulics: Chapter OverviewMarkoManuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Glass Fibers: Frederick T. Wallenberger, James C. Watson, and Hong Li, PPG Industries, IncDocument9 pagesGlass Fibers: Frederick T. Wallenberger, James C. Watson, and Hong Li, PPG Industries, Incgohary18047Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Forces and Motion (2019)Document19 pagesChapter 2 Forces and Motion (2019)Khitsithu PhoekhitPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry For Engineers Set ADocument5 pagesChemistry For Engineers Set AMark Jecel RapirPas encore d'évaluation
- Mass Balance Modeling Eaf & Ladle Furnace Turkey PDFDocument8 pagesMass Balance Modeling Eaf & Ladle Furnace Turkey PDFsuveer kumar100% (1)
- Liquid CrystalsDocument8 pagesLiquid CrystalsSarah TahirPas encore d'évaluation
- Bylkas 1997Document5 pagesBylkas 1997Catarina SabinoPas encore d'évaluation
- SumatraPDF SettingsDocument38 pagesSumatraPDF SettingsAlex TrinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions - AIATS Medical-2020 (XII Studying) - Test-5 - (Code-A & B) - 22-12-2019 PDFDocument30 pagesSolutions - AIATS Medical-2020 (XII Studying) - Test-5 - (Code-A & B) - 22-12-2019 PDFShashank KashyapPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 5Document23 pagesCH 5Ahmed GadPas encore d'évaluation
- Wolf - SR - Formation and Stability of Complex Metallic Phases Including QC Explored Through Combinatorial MethodsDocument11 pagesWolf - SR - Formation and Stability of Complex Metallic Phases Including QC Explored Through Combinatorial MethodsAlisson WintherPas encore d'évaluation
- Ph1202 Lab Report 3 Akshat MisraDocument6 pagesPh1202 Lab Report 3 Akshat MisraDot 007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Charges and FieldDocument42 pagesElectric Charges and FieldKunal ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Sanjeevani NEETDocument44 pagesSanjeevani NEETemolicmuneeb768Pas encore d'évaluation
- Class 8 Holiday AssignmentDocument5 pagesClass 8 Holiday AssignmentSidra QueenPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Solidification Rate and Heat Treatment On Microstructure Characterization and Hot Tensile Strength of Single Crystal CMSX-4 SuperalloyDocument11 pagesEffects of Solidification Rate and Heat Treatment On Microstructure Characterization and Hot Tensile Strength of Single Crystal CMSX-4 Superalloykianrob123100% (1)
- 455 17ProblemSet08SolutionsDocument5 pages455 17ProblemSet08SolutionsSoundz sevenPas encore d'évaluation