Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
(BIO) 03 - Animal Tissues (Calsado)
Transféré par
sodiumboyupinthishoeDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
(BIO) 03 - Animal Tissues (Calsado)
Transféré par
sodiumboyupinthishoeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Animal Tissue
Major Animal Tissues
• Epithelial Tissue
• Connective Tissue
• Muscular Tissue
• Nervous Tissue
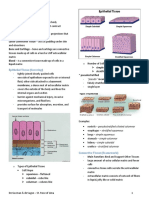
Epithelial Tissue
• Function: lines internal organs
and covers the body
• Outer part is exposed to air or
internal fluid; other side is
composed of basement
membrane
• Cells are tightly packed
• Function?
Epithelial Tissue
• Types
– According to shape
• Squamous
• Cuboidal
• Columnar
– According to arrangement of cell
• Simple
• Stratified
• Pseudostratified
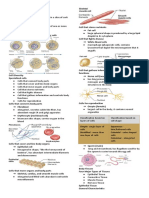
Connective Tissue
• Blood
• Bones
• Cartilage
• Loose and Dense Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue
• Function: Binding and support
• Cells are embedded in an extracellular matrix
• Cells secrete the matrix
• Matrix: jelly-like or solid
Muscular Tissue
• Function: for movement/contraction; heat
• Three types:
– Skeletal
– Smooth
– Cardiac
Nervous Tissue
• Senses stimuli and
transmits signals called
nerve impulses from one
part of an animal to
another
• Consists of a cell body
and long extensions
called dendrites (towards
cell body) and axons
(towards another cell or
an effector
Tissue Type Epithelial Connective Muscle Nerve
Cell Shape Flattened, cuboidal, Irregular or round Elongated Cell appendages
columnar branched
Cell Arrangement Single ◊ multilayered Scattered in matrix In sheets or bundles Isolated or networked
Location Body covering or lining Supports other organs Lining internal organs, Concentrated in brain
organs or cavities make skeletal muscles and spinal cord + all
over the body
Surface Feature of Cilia, microvilli - - -
Cells
Matrix Type Basement membrane Varied – protein fibers + - -
liquid, gelatinous, firm
to calcified
Matrix Amount Minimal Extensive Absent Absent
Unique Feature No direct blood supply, Cartilage has no blood Can generate electrical Can generate electrical
except for glands supply signals, force and signal
movement
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Medical Histology MCQSDocument3 pagesMedical Histology MCQSmoonfire200983% (12)
- Essential Quick Review PERIODONTICSDocument258 pagesEssential Quick Review PERIODONTICSJude Aldo Paul100% (2)
- Tissue of The BodyDocument12 pagesTissue of The BodyJuliet Aira Cabero Quibilan100% (1)
- Introduction To Equine Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Equine Anatomy and PhysiologySavannah Simone Petrachenko100% (1)
- (CHEM) Chemical ReactionsDocument32 pages(CHEM) Chemical Reactionssodiumboyupinthishoe100% (2)
- Tissues: Types, Functions & ClassificationDocument18 pagesTissues: Types, Functions & ClassificationZainab AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Urine Cytology: Christine BadilloDocument21 pagesUrine Cytology: Christine BadilloChristine BadilloPas encore d'évaluation
- TissuesDocument60 pagesTissuesLeo PietroPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant and Animal TissuesDocument27 pagesPlant and Animal TissuesDoods GaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.skin PathologyDocument38 pages3.skin PathologyFaisal MehboobPas encore d'évaluation
- Lung CancerDocument52 pagesLung CancerHealth Education Library for People50% (4)
- Odontogenic Cyst and Non Odontogenic CystDocument67 pagesOdontogenic Cyst and Non Odontogenic CystLuthfieHaq0% (1)
- Four Types of Animal TissuesDocument8 pagesFour Types of Animal TissuesAngel IgarPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Tissues 1Document8 pagesAnimal Tissues 1Valen IgnacioPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal and Plant TissueDocument48 pagesAnimal and Plant TissuePortia EgkenPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal & Plant Tissue TypesDocument10 pagesAnimal & Plant Tissue TypesYenyen C. BagtasosPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio CHP 7 Sem 1Document60 pagesBio CHP 7 Sem 1Aliaa AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Body Tissues: 1. Epithelial TissueDocument18 pagesBody Tissues: 1. Epithelial TissueHi SseulgiPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology of Cell and Tissue: Chapter 7: TissuesDocument53 pagesHistology of Cell and Tissue: Chapter 7: TissuesAmirah AdlinaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Document33 pagesThe Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Maira Garcia C.100% (2)
- Basic Tissues of the Body: Epithelial, Connective, Muscular & NervousDocument6 pagesBasic Tissues of the Body: Epithelial, Connective, Muscular & NervousAngela Kate BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Body TissuesDocument51 pagesHuman Body TissuesKubun Ginta GintingPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOL223-Lab 9Document53 pagesBIOL223-Lab 9chicken fries100% (1)
- Animal TissueDocument47 pagesAnimal TissueJoshua Verzosa PalconitPas encore d'évaluation
- Identify & Describe The Type - Describe The Function - Name One LocationDocument22 pagesIdentify & Describe The Type - Describe The Function - Name One LocationSpencer WebbPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells and Tissues: Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesCells and Tissues: Structure and Functiongrafei pennaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell OrganizationDocument8 pagesCell OrganizationKiele Nicole Calansingin100% (1)
- Epithelial Tissue Lecture 1Document8 pagesEpithelial Tissue Lecture 1Arleen ColacionPas encore d'évaluation
- BSCI 4001 Transcript MidtermDocument4 pagesBSCI 4001 Transcript MidtermLynell Caraang BarayugaPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Tissues PPTDocument40 pagesHuman Tissues PPTKeneth CandidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5 Tissues, Cell CyclesDocument90 pagesLecture 5 Tissues, Cell Cyclesaidar.seralinPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structures & Functions: Biology Unit Perak Matriculation CollegeDocument50 pagesCell Structures & Functions: Biology Unit Perak Matriculation CollegeMarjorie DenorogPas encore d'évaluation
- Connective Tissue, VnaDocument78 pagesConnective Tissue, Vnavaryvira6677Pas encore d'évaluation
- TissueDocument27 pagesTissueemilpauloquibilanPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Connective Tissues 22 July 2021Document46 pages5 Connective Tissues 22 July 2021T KPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 TissueDocument60 pages10 TissuebeyonduckPas encore d'évaluation
- M4 TiisuesDocument8 pagesM4 TiisuesGemarela Salas CapitenioPas encore d'évaluation
- Connective Tissues Types FunctionsDocument30 pagesConnective Tissues Types Functionsarmish junaid100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKrizel angel CayabyabPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyTalha AbbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Four Major Tissue Types: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle and Nervous (less than 40 charsDocument29 pagesThe Four Major Tissue Types: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle and Nervous (less than 40 charsGievel Enoroba LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andDocument5 pagesChapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andMonika MehanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ang Paggamit NG IbaDocument3 pagesAng Paggamit NG IbakikomagsaysayPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle and Nervous Tissue FunctionsDocument21 pagesMuscle and Nervous Tissue FunctionsMae Anthonete TulinPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 2 Homeostasis 1mar17Document58 pagesBio 2 Homeostasis 1mar17nicolePas encore d'évaluation
- Human TissuesDocument41 pagesHuman TissuesMae Ann Mejico EspirituPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology - 4th SemDocument76 pagesPhysiology - 4th SemSandeep AdapalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Organization and HomeostasisDocument2 pagesAnimal Organization and HomeostasisLara CarisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Tissue TypesDocument48 pagesCell Tissue Typeschristian josh magtarayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Connective Tissue NotesDocument6 pagesConnective Tissue Notesferdinand padillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal TissuesDocument46 pagesAnimal TissuesTrisha ZamboangaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular Organisms: D.salleh2021Document21 pages2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular Organisms: D.salleh2021Dewi SallehPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3 - HistologyDocument25 pagesLab 3 - HistologyRite2summaiya SumiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tissues 1Document42 pagesTissues 1Patricia JalbanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio100 - Le3 ReviewerDocument20 pagesBio100 - Le3 ReviewerMariel De Leon GinesPas encore d'évaluation
- Connective Tissues: Sunil Shrestha Human BiologyDocument23 pagesConnective Tissues: Sunil Shrestha Human Biologyyordin deontaPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal TissuesDocument37 pagesAnimal Tissueshero samilinPas encore d'évaluation
- K3 - Jaringan DasarDocument33 pagesK3 - Jaringan DasarAndi Pratiwi Indah LestariPas encore d'évaluation
- The Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument31 pagesThe Tissue Level of OrganizationYunandhika RizkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells and Tissues & Integumentary SystemDocument21 pagesCells and Tissues & Integumentary SystemTaehyung KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Tissues NTBDocument39 pagesTissues NTBAuthor ClubPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology 1Document11 pagesBiology 1Francois Isabelo EspirituPas encore d'évaluation
- التشريح نظري م 2 غير مترجمةDocument10 pagesالتشريح نظري م 2 غير مترجمةبايPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 - Body Tissues (Basic Types & Classification)Document54 pagesLecture 3 - Body Tissues (Basic Types & Classification)brightonebarack03Pas encore d'évaluation
- Structural OrganizationDocument119 pagesStructural OrganizationAVS COPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 A NewDocument62 pages9 A NewPrejith KPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaseous StateDocument30 pagesGaseous Statesodiumboyupinthishoe100% (1)
- (BIO) Animal TransportDocument30 pages(BIO) Animal TransportsodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (BIO) RespirationDocument74 pages(BIO) RespirationsodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (CHEM) Pairwork Chem NomencDocument1 page(CHEM) Pairwork Chem NomencsodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (CHEM) Written Laboratory Report FormatDocument2 pages(CHEM) Written Laboratory Report FormatsodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (CHEM) Workshop - Types of Chemical RXNDocument3 pages(CHEM) Workshop - Types of Chemical RXNsodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (CHEM) Homework NomenclatureDocument2 pages(CHEM) Homework NomenclaturesodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- Rules For Assigning An Oxidation NumberDocument1 pageRules For Assigning An Oxidation NumbernegrabellePas encore d'évaluation
- (CHEM) Chem NomenclatureDocument23 pages(CHEM) Chem NomenclaturesodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (CHEM) Nomenclature Basic GChemDocument13 pages(CHEM) Nomenclature Basic GChemsodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (BIO) 06 - Plant Transport CrisologoDocument20 pages(BIO) 06 - Plant Transport CrisologosodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (CHEM) Flowchart NamingDocument1 page(CHEM) Flowchart Namingsodiumboyupinthishoe100% (1)
- Chemical-Bonding & Inter Molecular ForcesDocument6 pagesChemical-Bonding & Inter Molecular ForcesLMT_GORDON100% (1)
- (BIO) 04 - Plant Tissues (Calsado)Document50 pages(BIO) 04 - Plant Tissues (Calsado)sodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (CHEM) Course OutlineDocument3 pages(CHEM) Course OutlinesodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (BIO) 06 - Plant Transport (Calsado)Document14 pages(BIO) 06 - Plant Transport (Calsado)sodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (BIO) Course OutlineDocument3 pages(BIO) Course OutlinesodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (BIO) 05 - Animal DigestionDocument42 pages(BIO) 05 - Animal DigestionsodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (BIO) 04 - Plant Tissues CrisologoDocument15 pages(BIO) 04 - Plant Tissues CrisologosodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (BIO) 01 - Hierarchy of Biological OrganizationDocument22 pages(BIO) 01 - Hierarchy of Biological Organizationsodiumboyupinthishoe100% (1)
- (BIO) PreLab 1Q-LA2Document3 pages(BIO) PreLab 1Q-LA2sodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (BIO) 02 - Origin of Multicellularity CrisologoDocument21 pages(BIO) 02 - Origin of Multicellularity CrisologosodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- (BIO) 02 - Origin of Multicellularity (Calsado)Document16 pages(BIO) 02 - Origin of Multicellularity (Calsado)sodiumboyupinthishoe100% (1)
- (BIO) Quiz Bee (Circulatory) TermsDocument1 page(BIO) Quiz Bee (Circulatory) TermssodiumboyupinthishoePas encore d'évaluation
- Book Reviews: Craniofacial Development, Growth and EvolutionDocument3 pagesBook Reviews: Craniofacial Development, Growth and EvolutionSthefannia TobarPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal TissuesDocument44 pagesAnimal TissuesMary Sutingco100% (1)
- Solution Manual For Introduction To Veterinary Science 3rd Edition Lawhead Baker 1319013384 9781111542795Document11 pagesSolution Manual For Introduction To Veterinary Science 3rd Edition Lawhead Baker 1319013384 9781111542795michellePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument64 pagesChapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationNurul Fatihah Binti MamatPas encore d'évaluation
- The Logic of Immunity Deciphering An EnigmaDocument204 pagesThe Logic of Immunity Deciphering An EnigmaSatyabrataSahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Repair Cornea SuturesDocument14 pagesRepair Cornea SuturesBima RizkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Barrett's Esophagus & Esophageal Tumors GuideDocument52 pagesBarrett's Esophagus & Esophageal Tumors GuideTehreem NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- The Impact of The Flexible Partial Denture Base On The Alveolar Mucosa in Comparison To Metallic Denture RCT and Histological StudyDocument7 pagesThe Impact of The Flexible Partial Denture Base On The Alveolar Mucosa in Comparison To Metallic Denture RCT and Histological StudyZachary DuongPas encore d'évaluation
- Swim Bladder Malformation in Hatchery-Reared Striped Trumpeter Latris Lineata LatridaeDocument14 pagesSwim Bladder Malformation in Hatchery-Reared Striped Trumpeter Latris Lineata LatridaenarePas encore d'évaluation
- Medtech Git Upper and LowerDocument72 pagesMedtech Git Upper and LowerBabe YamonganPas encore d'évaluation
- The Integumentary System: A Comprehensive Review of Its Morphology and FunctionsDocument11 pagesThe Integumentary System: A Comprehensive Review of Its Morphology and FunctionsKella OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Body Tissues: Connective Tissue Ephithelial TissueDocument1 pageBody Tissues: Connective Tissue Ephithelial Tissuemaxine janorasPas encore d'évaluation
- Learn Cell Junction Structures & FunctionsDocument27 pagesLearn Cell Junction Structures & FunctionshusshamPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz #1 Questions A&P 1Document14 pagesQuiz #1 Questions A&P 1trick49Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Exercise No. 2Document4 pagesLab Exercise No. 2JOHN ISAAC BENITEZPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Article: Amnion and Chorion Membranes: Potential Stem Cell Reservoir With Wide Applications in PeriodonticsDocument10 pagesReview Article: Amnion and Chorion Membranes: Potential Stem Cell Reservoir With Wide Applications in PeriodonticsElissa IsdasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Biology and Histology Quiz 6Document27 pagesCell Biology and Histology Quiz 6Umar AwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5Document50 pagesChapter 5kebPas encore d'évaluation
- Typhoid Fever Case StudyDocument18 pagesTyphoid Fever Case Studyiurae50% (2)
- Group 2 Student Examines 4 Basic Body TissuesDocument6 pagesGroup 2 Student Examines 4 Basic Body TissuesAJ EguiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum/Statutes & Regulations 5 Years Degree Programme DermatologyDocument54 pagesCurriculum/Statutes & Regulations 5 Years Degree Programme DermatologyMuhammad Irfan BalochPas encore d'évaluation
- Annsurg00602 0014Document7 pagesAnnsurg00602 0014MogiMediawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Reviewer PrelimsDocument10 pagesBiology Reviewer PrelimsShaira CogollodoPas encore d'évaluation