Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sugar
Transféré par
shujin_sama0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
32 vues2 pagesMalignant primary brain tumours-are most likely to cause problems by spreading into the normal brain tissue which surrounds them. Secondary BRAIN tumors-occur when cancer cells from other parts of the body, such as the lung or breast, spread to the brain. Males have higher overall risk of brain tumors, but women are more prone to meningiomas, the most common brain tumors.
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentMalignant primary brain tumours-are most likely to cause problems by spreading into the normal brain tissue which surrounds them. Secondary BRAIN tumors-occur when cancer cells from other parts of the body, such as the lung or breast, spread to the brain. Males have higher overall risk of brain tumors, but women are more prone to meningiomas, the most common brain tumors.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
32 vues2 pagesSugar
Transféré par
shujin_samaMalignant primary brain tumours-are most likely to cause problems by spreading into the normal brain tissue which surrounds them. Secondary BRAIN tumors-occur when cancer cells from other parts of the body, such as the lung or breast, spread to the brain. Males have higher overall risk of brain tumors, but women are more prone to meningiomas, the most common brain tumors.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
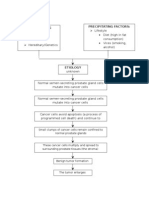
PRIMARY BRAIN TUMOURS - develop from brain cells.
Benign tumours-remain in the part of the brain in
which they started and do not spread into and destroy
other areas of the brain. They do not spread to other
parts of the body.
Malignant primary brain tumours-are most likely to
cause problems by spreading into the normal brain
tissue which surrounds them and causing pressure and
damage to the surrounding areas of the brain. These
tumours rarely spread outside the brain to other parts of
the body.
SECONDARY BRAIN TUMOURS-occur when cancer
cells from other parts of the body, such as the lung or
breast, spread to the brain.
RISK FACTORS
Adults age 40-70 and children age 3-12.
Males have higher overall risk of brain tumors, Side view of the head Parts of the brain
but women are more prone to meningiomas,
the most common brain tumors.
Radiation treatment for leukemia.
Epilepsy
History of cancer of breast or lung.
A parent with cancer of the nervous system,
colon or salivary glands.
Rare inherited disorders such as
neurofibromatos, von hippel-Lindau syndrome
and Turcot’s syndrome.
TYPES OF BRAIN TUMOUR
Acoustic neuroma
Astrocytic tumours
CNS lymphoma
Ependymoma
Haemangioblastoma
Medulloblastoma
Meningioma
Mixed gliomas
Oligodendroglioma
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- New Way To Help Schizophrenia Sufferers' Social SkillsDocument4 pagesNew Way To Help Schizophrenia Sufferers' Social Skillsshujin_samaPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Rights (ROTC)Document6 pagesHuman Rights (ROTC)shujin_samaPas encore d'évaluation
- PSYCHIADocument1 pagePSYCHIAshujin_samaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case StudyDocument41 pagesCase StudychaSeph292784100% (6)
- DPatho ProstateDocument2 pagesDPatho Prostateshujin_sama100% (1)
- AssessmentDocument5 pagesAssessmentshujin_sama100% (2)
- Dpatho CadDocument2 pagesDpatho Cadshujin_samaPas encore d'évaluation
- Generic/ Brand Name Humulin RDocument7 pagesGeneric/ Brand Name Humulin Rshujin_sama100% (2)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)