Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Nephrotic Syndrome
Transféré par
ReyzzhorCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NCP Nephrotic Syndrome
Transféré par
ReyzzhorDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NURSING CARE PLAN Nephrotic Syndrome
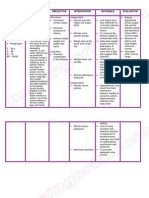
CUES
SUBJECTIVE: Namamaga ang mukha ko (I have facial edema) as verbalized by the patient. OBJECTIVE: Facial puffiness Bipedal edema V ! taken as follo"s# $# %&.' (#)* +# ', B(# '&- *-
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
./cess fluid volume related to compromised regulatory mechanism "ith changes in hydrostatic or oncotic vascular pressure and increased activation of the renninangiotensin0 aldosterone system.
BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE
Nephrotic syndrome is a clinical disorder of unkno"n cause characterized by proteinuria1 hypoalbuminemia1 edema1 and hyperlipidemia. $his conditions result from e/cessive leakage of plasma proteins into the urine because of impairment of the glomerular capillary membrane.
OBJECTIVES
2fter 3 hours of nursing interventions1 the patient "ill display a stable condition1 vital signs "ithin patient4s normal range1 and nearly absence of edema.
INTERVENTION
Independent: 5onitor vital !igns +ecord accurate intake and output of the patient.
RATIONALE
For base line data 2ccurate 8ntake and output is necessary for determining renal function and fluid replacement needs and reducing risk of fluid overload. 5easures the kidney4s ability to concentrate urine. 9aily body "eight is the best monitor of fluid status. 2 "eight gain of more than -.) kg day suggest fluid retention. .dema occurs primarily in dependent tissues of the body. 8t "ill serve as parameter the
EVALUATION
2fter 3 hours of nursing interventions1 the patient "as able to display a stable condition1 vital signs "ithin patient4s normal range1 and nearly absence of edema.
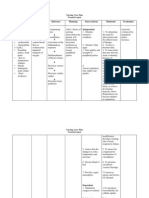
5onitor urine specific gravity. 6eigh daily at same time of the day1 on same scale1 "ith same e7uipment and clothing. 2ssess skin1 face1 dependent areas of edema.
5onitor heart rate and blood pressure.
2ssess level of consciousnes : investigate changes in mentation1 presence of restlessness. Collaborative: 5onitor laboratory and diagnostic studies.
severity of fluid e/cess. $achycardia and hypertension can occur because of failure of the kidneys to e/crete urine. 5ay reflect fluid shifts and electrolyte imbalances.
2dminister diuretics as
(rovide assessment of the progression and management of the dysfunction. $o promote ade7uate urine volume that aids in prevention of further edema.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- NCP For Nephrotic SyndromeDocument2 pagesNCP For Nephrotic SyndromeLee Jenny100% (5)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Nephrotic SyndromeDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Nephrotic Syndromederic80% (45)
- Fluid Volume Deficient Patient with Diabetes MellitusDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Deficient Patient with Diabetes MellitusMarlon AnryPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Glomerulonephritis GCDocument70 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis GCMary Cruz100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan AGNDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan AGNAlexis Coronado50% (2)
- 5 Nursing Diagnosis For GlomerulonephritisDocument2 pages5 Nursing Diagnosis For GlomerulonephritisGeorich Narciso67% (3)
- Acute Glomerulonephritis - AGN - Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis - AGN - Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis80% (10)
- Nursing Care Plan NephritisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Nephritisderic82% (17)
- NCP On Acute GlumrulonephritisDocument11 pagesNCP On Acute GlumrulonephritisJai - Ho89% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM)Document1 pageDiabetes Mellitus (DM)Bheru LalPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP LymphomaDocument3 pagesNCP LymphomaJohn Emmanuel Tatad TudPas encore d'évaluation
- Individual Case Study Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument26 pagesIndividual Case Study Acute GlomerulonephritisBatrisyia HalimsPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Presentation - Nephrotic SyndromeDocument56 pagesCase Study Presentation - Nephrotic SyndromeVivien Marie89% (27)
- Hyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanRenie Serrano100% (1)
- Baby fever nursing careDocument6 pagesBaby fever nursing caregopscharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument42 pagesNephrotic SyndromeSushmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Management - LeukemiaDocument5 pagesNursing Management - LeukemiaReyzzhor80% (5)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPDharline Abbygale Garvida Agullana100% (2)
- Bronchopneumonia Care PlanDocument6 pagesBronchopneumonia Care PlanAbhijit Soundade0% (1)
- Case Study Nephrotic Syndrome Case ReportDocument9 pagesCase Study Nephrotic Syndrome Case ReportAnamika ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- CKD (F&e)Document110 pagesCKD (F&e)Al-nazer Azer Al100% (1)
- Case Study - Acute Glomerulonephritis Sample Case Study Report For PCL Level by Amrit BanstolaDocument15 pagesCase Study - Acute Glomerulonephritis Sample Case Study Report For PCL Level by Amrit BanstolaAmrit Banstola100% (5)
- Improving Neonatal Tissue Perfusion for SepsisDocument2 pagesImproving Neonatal Tissue Perfusion for SepsisNiña Montejo Ealdama100% (1)
- NCP Hydrocephalus With RationaleDocument42 pagesNCP Hydrocephalus With RationaleJulienne Sanchez-Salazar80% (15)
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument17 pagesNephrotic Syndromevishnu0% (1)
- NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitAtheena Diaz50% (4)
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPJet Ray-Ann GaringanPas encore d'évaluation
- Case StudyDocument37 pagesCase StudyAnonymous t78m8ku100% (1)
- NCP For DM1Document2 pagesNCP For DM1Pau Hipol MadriagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study On Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument20 pagesCase Study On Acute GlomerulonephritisJai - Ho87% (15)
- Nephrotic Case Study With AnswersDocument3 pagesNephrotic Case Study With AnswersKBPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation of Nephrotic SyndromeDocument15 pagesPresentation of Nephrotic SyndromeBagas NovandyPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Renal FailureMark Jason Rabadan100% (1)
- HydrocephalusDocument33 pagesHydrocephalusrajan kumar100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Diabetes Mellitusinagasi83% (12)
- Meningocele Case StudyDocument70 pagesMeningocele Case StudyKyssel Seyer100% (2)
- Acute Glomerulonephritis Case StudyDocument12 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis Case StudyPrincess Tindugan100% (1)
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument61 pagesNephrotic SyndromeRanah Julia Garchitorena AyoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Nephrotic SyndromeDocument3 pagesNCP Nephrotic SyndromeThesa Federico100% (1)
- NCP PSHDocument17 pagesNCP PSHMargareth OrtizPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - TBDocument2 pagesNCP - TBPahw BaluisPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP AgnDocument2 pagesNCP Agnj3nann3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan For Patiients With MeningitisDocument35 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patiients With Meningitisixa_morales67% (6)
- NCP DengueDocument3 pagesNCP DengueYeana Alon50% (4)
- Assess and Care for Impaired Oral Mucous MembranesDocument2 pagesAssess and Care for Impaired Oral Mucous MembranesNolan Cabral100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans: Ineffective (Uteroplacental) Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plans: Ineffective (Uteroplacental) Tissue PerfusionVincent Paul SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP For DehydrationDocument1 pageNCP For Dehydrationjxhel63% (8)
- CA - Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDocument13 pagesCA - Amniotic Fluid EmbolismRodelen Maraño100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan for TonsillitisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for TonsillitisEden Cruz50% (6)
- Case Study Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesCase Study Pleural EffusionKhristine Anne FabayPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Deficit - RegorDocument3 pagesKnowledge Deficit - RegorAdrian MallarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Nephrotic SyndromeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Nephrotic SyndromeJhusmin BambicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Glomerulonep Hritis: By: Edelrose D. Lapitan BSN Iii-CDocument29 pagesAcute Glomerulonep Hritis: By: Edelrose D. Lapitan BSN Iii-CEdelrose Lapitan100% (1)
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument24 pagesAcute GlomerulonephritisNipul MondolPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypovolemic ShockDocument36 pagesHypovolemic ShockRia CintyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Glomerulonephritis (GN): Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument6 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis (GN): Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentAnnapoorna SHPas encore d'évaluation
- Genito-Urinary Dysfunctions in Children Commonly Occurring GU DysfunctionsDocument26 pagesGenito-Urinary Dysfunctions in Children Commonly Occurring GU DysfunctionsMaira KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nephrotic Syndrome: by Mr. Sachin Dwivedi M.Sc. (N) Medical Surgical NursingDocument26 pagesNephrotic Syndrome: by Mr. Sachin Dwivedi M.Sc. (N) Medical Surgical NursingAnusikta PandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Medicine Block Seventh Problem: Group 15 Friday, November 3 2017Document94 pagesEmergency Medicine Block Seventh Problem: Group 15 Friday, November 3 2017Stefanie BluePas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Management - LeukemiaDocument5 pagesNursing Management - LeukemiaReyzzhor80% (5)
- Baby FoodDocument3 pagesBaby FoodReyzzhorPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxygen Tanks Incidents and FiresDocument2 pagesOxygen Tanks Incidents and FiresReyzzhorPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformative LearningDocument9 pagesTransformative LearningReyzzhorPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Organizational PatternsDocument6 pagesBasic Organizational PatternsReyzzhorPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 1 and 2 (DOH-CHD Community Reports)Document2 pagesForm 1 and 2 (DOH-CHD Community Reports)ReyzzhorPas encore d'évaluation
- Filipino Preg ProfDocument3 pagesFilipino Preg ProfReyzzhorPas encore d'évaluation
- PBL 2 Session 2 PresentationDocument44 pagesPBL 2 Session 2 PresentationElisaPas encore d'évaluation
- 20.lymphatic DisordersDocument16 pages20.lymphatic DisordersShrestha Anjiv100% (2)
- 2023 MayDocument36 pages2023 MayReshma Shaji PnsPas encore d'évaluation
- Musculoskeletal ExaminationDocument42 pagesMusculoskeletal ExaminationRahulPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument142 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesAndradaLavricPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailurePerry Oliver AlvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPranee diane0% (1)
- 6301d9d841b38 Hesi Fundamentals Practice Test Questions and AnswersDocument27 pages6301d9d841b38 Hesi Fundamentals Practice Test Questions and AnswersCeciliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical Ward ExamDocument8 pagesSurgical Ward ExamJaysellePuguonTabijePas encore d'évaluation
- Weight Gain - Unintentional - MedlinePlus Medical EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesWeight Gain - Unintentional - MedlinePlus Medical EncyclopediaMustafa AlmasoudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Questions on PathologyDocument4 pagesModel Questions on PathologyBhopesh Kadian100% (3)
- EATMS - Discussion On Phlegm Damp WaterDocument4 pagesEATMS - Discussion On Phlegm Damp WaterfernabarbPas encore d'évaluation
- Robeth Jhonson BandageDocument4 pagesRobeth Jhonson BandagegatisetiadiantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bodybuilding Small File SizeDocument32 pagesBodybuilding Small File SizeThế Vỹ100% (4)
- 101 Homeopathic Remedies FormattedDocument36 pages101 Homeopathic Remedies Formattedapi-26938624100% (12)
- Radiologic Pathology Intro 1Document50 pagesRadiologic Pathology Intro 1James MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Discomforts of PregnancyDocument2 pagesCommon Discomforts of PregnancyOfelia SantillanPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Gould's Pathophysiology For The Health Professions 7th Edition VanMeterDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Gould's Pathophysiology For The Health Professions 7th Edition VanMeterYassine HaddadePas encore d'évaluation
- The Child with Proteinuria & Nephrotic SyndromeDocument57 pagesThe Child with Proteinuria & Nephrotic SyndromeRobert FfrenchPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP CP 3 IreneDocument3 pagesNCP CP 3 IreneKenPas encore d'évaluation
- MK Hemodynamics PathologyDocument27 pagesMK Hemodynamics PathologyMoses Jr Kazevu100% (1)
- CASE PRESENTATION NEPHROTIC Syndrome-1Document20 pagesCASE PRESENTATION NEPHROTIC Syndrome-1rohankananiPas encore d'évaluation
- Aim4aiims - In: Pathology Board ExaminationDocument72 pagesAim4aiims - In: Pathology Board ExaminationdorjeesengePas encore d'évaluation
- High-Voltage Pulsed Galvanic Stimulation (HVPGS)Document12 pagesHigh-Voltage Pulsed Galvanic Stimulation (HVPGS)akheel ahammed100% (1)
- Everest/First Ascents: Altitude Danger Begins in PhericheDocument2 pagesEverest/First Ascents: Altitude Danger Begins in PhericheIrigoyen APas encore d'évaluation
- IV Theraphy and Blood TransfusionDocument128 pagesIV Theraphy and Blood TransfusionJoycee BoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Excess Diagnostic TestsDocument5 pagesFluid Excess Diagnostic TestsQueenie Velasquez Reinoso JacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 21 Tissue Integrity: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)Document50 pagesModule 21 Tissue Integrity: Nursing: A Concept-Based Approach To Learning, 2e (Pearson)RNStudent1100% (1)
- 올림포스2 11~15 해석위주 변형문제Document29 pages올림포스2 11~15 해석위주 변형문제chwlove1002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Differences Between Seawater and Freshwater Lung InjuriesDocument1 pageDifferences Between Seawater and Freshwater Lung InjuriesIGD RSMYPas encore d'évaluation