Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lec 4a
Transféré par
api-245262445Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lec 4a
Transféré par
api-245262445Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
! !
!""#$%&$'"()$*"+$
! !
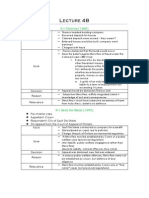
OVERVIEW
Mens Rea + Actus Reus Mens Rea is concerned with consequences of prohibited act (Actus Reus) Ex. Murder as a voluntary act o Prohibited act/Actus Reus = murder o Fault element/Mens Rea = intent to cause death Mens Rea o Focus on subjective capacity of accused ! Could (s)he have foreseen the consequences of the act? ! Did (s)he intend to cause harm? o Why is I didnt mean to not a good defence?
R v Theroux []
Common Law Presumptions Judge made common law When statutes lack clear definitions Upload requirements for Mens Rea o Intentionality, Recklessness, Knowledge, Willful Blindness Criminal offences require Mens Rea in relation to Actus Reus o Unless Parliament indicates otherwise
R v Sault Ste Marie []
Criminalized Fault Fault element in criminal law is different than in civil law o Mens Rea (especially in criminal law) ! Focus on mental state of the accused ! Requires proof of intent or recklessness o Negligence (especially in civil law) ! Less focus on mental state of accused ! Conduct assessed against objective standard reasonable person ! Question of reasonable care, not intent o Why does this distinction matter? Marked Departure o When should the departure from a certain standard of care be criminalized? o If it is not a marked departure, it is a civil case (private law matter) o If it is a marked departure, it is a criminal case (public law) o Risk of over criminalizing
R v Beatty []
SUBJECTIVE MENS REA
Subjective Fault Question of whether accused had guilty knowledge / intent Crown must prove (beyond a reasonable doubt) Question of fact, now law (jury can decide)
! !
!""#$%&$'"()$*"+$
! !
Subjective Mens Rea Intent, purpose, or willfulness Degrees of subjective Mens Rea matter May not have intent, but might have subjective knowledge of consequences Difference between guilty intent and guilty knowledge o Ex. Accused engages in prohibited act, but does so to avoid harm. Driving Robbers to bank, at gunpoint
R v Hibbert []
OBJECTIVE OF MENS REA
Subjective: (s)he knew it was wrong Objective: anybody in that position would have known it was wrong Use objective standard to establish subjective fault o What would a reasonable person have done? Meant to prevent conviction of accused who might lack knowledge and foresight Objective Mens Rea For offences less serious than murder Problem with objective standard: o Who is a reasonable person? o Can it be modified to apply without it becoming a subjective standard? Personal characteristics are not important unless they create an incapacity to appreciate the risk (Roach p. 195) o Ex. Illiteracy leading to mishandling illiterate person in charge of toxic chemicals
Revisit: R v Hibbert & Beatty
RECAP / NEXT CLASS
State v. George Zimmerman Zimmerman accused of 2nd degree murder Prosecution (state) in closing statements o Addressing jury o Arguing that prohibited act arises from ill will (intent) Defence: Zimmerman acted in self defence Outcome: Zimmerman found innocent Recap Courts decide fault Questions of face Consequences of prohibited act Requires proof of intent or recklessness Guilty intent / guilty knowledge Objective Mens Rea and personal characteristics
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Orporate Rime Untouchables: Predatory Lending Fund em Provable Fraud Underwriting Lanny BreuerDocument3 pagesOrporate Rime Untouchables: Predatory Lending Fund em Provable Fraud Underwriting Lanny Breuerapi-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- 12Document3 pages12api-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- 11Document3 pages11api-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- 11Document5 pages11api-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Background: Week 8Document4 pagesBackground: Week 8api-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- ACE Review & Background: Week 9Document3 pagesACE Review & Background: Week 9api-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Week 5Document3 pagesWeek 5api-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- ARX Review & BackgroundDocument3 pagesARX Review & Backgroundapi-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Eminism Review & Background: Week 8Document3 pagesEminism Review & Background: Week 8api-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Week 6Document3 pagesWeek 6api-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Review & Overview: R V Dudley & Stephens (1884)Document3 pagesReview & Overview: R V Dudley & Stephens (1884)api-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- OverviewDocument5 pagesOverviewapi-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- Week 4Document5 pagesWeek 4api-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Lecture 4bDocument3 pagesLecture 4bapi-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Lec 2bDocument3 pagesLec 2bapi-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Week 3Document4 pagesWeek 3api-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Lecture 3bDocument3 pagesLecture 3bapi-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- Week 3Document2 pagesWeek 3api-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- Criminal Law The ConstitutionDocument6 pagesCriminal Law The Constitutionapi-245262445Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scheduled Caste Migrants To Pondicherry Not Eligible For Reservation, Says Madras High CourtDocument41 pagesScheduled Caste Migrants To Pondicherry Not Eligible For Reservation, Says Madras High CourtLive Law100% (1)
- Finals Reviewer CasesDocument48 pagesFinals Reviewer Casesdot_rocksPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Election Offenses:: Preponderance of EvidenceDocument3 pagesElection Offenses:: Preponderance of EvidenceAlexis Elaine BeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation LawDocument24 pagesTransportation Lawjolly faith pariñas100% (1)
- Module 4 STSDocument18 pagesModule 4 STSJohn Michael LaurioPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Impact of Retrospective Application of RERA: 1. MaharashtraDocument3 pagesImpact of Retrospective Application of RERA: 1. MaharashtraDisha LohiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Arnault V Nazareno DigestDocument5 pagesArnault V Nazareno DigestRea RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Agreement of SupportDocument3 pagesAgreement of Supportᜉᜂᜎᜊᜒᜀᜃ ᜎᜓᜌᜓᜎ100% (1)
- G.R. No. L-32860 PDFDocument8 pagesG.R. No. L-32860 PDFrunish venganzaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- Gill V Dhanoa - Response To ClaimDocument3 pagesGill V Dhanoa - Response To ClaimThe Vancouver SunPas encore d'évaluation
- V ISHAKHADocument16 pagesV ISHAKHAnitin0010100% (1)
- Ker v. Lingad 38 SCRA 524Document1 pageKer v. Lingad 38 SCRA 524Kent UgaldePas encore d'évaluation
- 01 PP v. MendozaDocument21 pages01 PP v. MendozaNinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Title G.R. NO.: Contract of Sale v. Contract of SellDocument2 pagesCase Title G.R. NO.: Contract of Sale v. Contract of Sellmark anthony mansuetoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bentir Vs Leanda 330 SCRA 591, GR 128991 (April 12, 2000)Document3 pagesBentir Vs Leanda 330 SCRA 591, GR 128991 (April 12, 2000)Lu CasPas encore d'évaluation
- 30 - G R - No - 208535-DigestDocument2 pages30 - G R - No - 208535-DigestNaomi InotPas encore d'évaluation
- Calalas Vs CADocument2 pagesCalalas Vs CAKenneth Fabia100% (1)
- Darrell Burch v. Apalachee Community Mental Health Services, Inc., 804 F.2d 1549, 11th Cir. (1986)Document12 pagesDarrell Burch v. Apalachee Community Mental Health Services, Inc., 804 F.2d 1549, 11th Cir. (1986)Scribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- Contract ActDocument32 pagesContract ActMonika KauraPas encore d'évaluation
- People V MaquedaDocument3 pagesPeople V MaquedaTiffany AnnPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Analysis of Makhan Singh vs. State of PunjabDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Makhan Singh vs. State of Punjabmeghakain50% (6)
- Adko FormDocument2 pagesAdko FormARTroom2012100% (1)
- Crombonds - OBLICONDocument116 pagesCrombonds - OBLICONAw LapuzPas encore d'évaluation
- Rizal's Saddest ChristmasDocument1 pageRizal's Saddest ChristmasPutee Griño SantiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Supreme Court Rules, 2013Document106 pagesSupreme Court Rules, 2013Latest Laws TeamPas encore d'évaluation
- Rimando v. People, 13 October 2014Document4 pagesRimando v. People, 13 October 2014dondzPas encore d'évaluation
- Marsh V Gaumont MSJ RulingDocument13 pagesMarsh V Gaumont MSJ RulingTHROnlinePas encore d'évaluation
- Fuentes Vs Ca, 253 SCRA 430 (1996)Document6 pagesFuentes Vs Ca, 253 SCRA 430 (1996)Thea Jane MerinPas encore d'évaluation
- 1987 Philippines Constitution: History and Salient Features of The 1987 ConstitiutionDocument9 pages1987 Philippines Constitution: History and Salient Features of The 1987 ConstitiutionQuen RioPas encore d'évaluation
- Leon R. Rouse v. PhilippinesDocument6 pagesLeon R. Rouse v. PhilippinesJessie Josuah Perez HilarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Reasonable Doubts: The O.J. Simpson Case and the Criminal Justice SystemD'EverandReasonable Doubts: The O.J. Simpson Case and the Criminal Justice SystemÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (25)
- Hunting Whitey: The Inside Story of the Capture & Killing of America's Most Wanted Crime BossD'EverandHunting Whitey: The Inside Story of the Capture & Killing of America's Most Wanted Crime BossÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (6)
- For the Thrill of It: Leopold, Loeb, and the Murder That Shocked Jazz Age ChicagoD'EverandFor the Thrill of It: Leopold, Loeb, and the Murder That Shocked Jazz Age ChicagoÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (97)