Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Mastering Physics - Vectors Inertia Lab
Transféré par
palparasDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Mastering Physics - Vectors Inertia Lab
Transféré par
palparasDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Vectors Tutorial
Work through the tutorial by clicking the image or link below, then answer the questions below. Vectors
Part A
The length of a force vector indicates the ________. ANSWER: magnitude of force direction of force
Correct
The magnitude of the force is the strength of the force.
Part B
Two vectors are shown in the figure. Which of the four vectors also shown best represents the resultant vector?
Hint 1. Parallelogram rule
Use the parallelogram rule to add the two vectors. ANSWER: vector A vector B vector C vector D
Correct
The horizontal component of the resultant vector is equal to the sum of the individual horizontal components of the two vectors, and the vertical component of the resultant vector is equal to the sum of the individual vertical components of the two vectors.
Part C
For which situation is the tension of the ropes higher?
Hint 1. What is supporting the force of gravity?
Only the components of the tension in the vertical direction support against the force of gravity. ANSWER: case B The tension of the ropes in case A is the same as that for case B. case A
Correct
Since the vertical components of the two tension vectors must add up to the persons weight, the tension must be higher when the ropes are more horizontal.
Part D
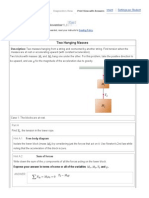
A person is hanging from two ropes, as shown in the figure. Which rope is supplying the higher tension force?
Hint 1. Using the horizontal forces
The net force in the horizontal direction is zero. ANSWER:
The rope to the right has the higher tension. The rope to the left has the higher tension. The tensions of the two ropes are equal to each other.
Correct
The resultant of the two tension forces must point directly upward (to support the force of gravity). Since the left rope is directed more vertically than the right rope, the left rope must have a higher tension such that the horizontal component of the two tensions cancels out.
Video Tutor: Ball Leaves Circular Track
First, launch the video below. You will be asked to use your knowledge of physics to predict the outcome of an experiment. Then, close the video window and answer the questions at right. You can watch the video again at any point.
Part A
Consider the video demonstration that you just watched. Which of the following changes would make it more likely for the ball to hit both the white can and the green can?
Hint 1. How to approach the problem
To answer this question, you first have to decide whether changing the balls mass or its speed can change the path it follows after it leaves the track. Newtons second law says that a net force acting on the ball will change the balls motionthat is, its speed and/or direction. Newtons first law says that, in the absence of a net force, the balls motion wont change. After the ball leaves the track, does a net force act on it? Draw a free-body diagram for the ball if youre not sure. To hit the green can, the ball must continue following a curved path. What would be needed to make that happen? ANSWER:
Use a ball that is heavier than the original ball. Use a ball that is lighter than the original ball, but still heavier than an empty can. Roll the ball slower. Roll the ball faster. None of the above
Correct
By Newtons first law, after it has left the circular track, the ball will travel in a straight line until it is subject to a nonzero net force. Thus, the ball can only hit the white can, because that is the only can in the balls straight-line path.
Video: The Old Tablecloth Trick
Watch the video and then answer the following questions.
Part A
When Dr. Hewitt pulls the tablecloth, what happens to the items on the tablecloth?
Hint 1. Property of objects at rest
What does an object at rest tend to do? ANSWER:
They move horizontally in the same direction as the tablecloth. They move vertically upward. They tend to stay where they were. They move horizontally in the opposite direction from the tablecloth.
Correct
Part B
When Dr. Hewitt pulls the tablecloth, why do the items on the tablecloth do what they do?
Hint 1. A property of all objects
What property of an object at rest tends to make it stay at rest? ANSWER: Inertia makes them stay at rest. Friction with the tablecloth is keeping them there. Friction with the table is keeping them there. They are attached to the tablecloth.
Correct
Part C
You tell your friend about the neat tablecloth trick that Dr. Hewitt demonstrated. Your friend tries to repeat this trick at home and later complains to you that it failed. Which of the following is most likely the reason that it failed?
Hint 1. Watching Dr. Hewitt carefully.
Watch carefully as Dr. Hewitt does the trick. Does he gently pull the tablecloth, or does he jerk it out? ANSWER:
Your friend is too clumsy. Your friend pulled the tablecloth too slowly. The items placed on the tablecloth were too light. Your friend pulled the tablecloth too quickly.
Correct
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Joyful Physics Volume II: Learning by Experiencing - Momentum, Gravitational Force, and Weight WorkbookD'EverandJoyful Physics Volume II: Learning by Experiencing - Momentum, Gravitational Force, and Weight WorkbookPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Physics - Projectile Motion and Orbital Motion LabDocument10 pagesMastering Physics - Projectile Motion and Orbital Motion Labpalparas100% (2)
- Mastering Physics - Rotational Motion LabDocument7 pagesMastering Physics - Rotational Motion LabpalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Physics - Newton's Third Law and Vectors LabDocument9 pagesMastering Physics - Newton's Third Law and Vectors LabpalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Physics - Vectors Inertia Lab PDFDocument7 pagesMastering Physics - Vectors Inertia Lab PDFDavid RăscuţoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Physics - Newton's Second Law LabDocument9 pagesMastering Physics - Newton's Second Law LabpalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering PHDocument12 pagesMastering PHDaniela PresiadoPas encore d'évaluation
- HWDocument22 pagesHWSara LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Physics - Kinematics LabDocument11 pagesMastering Physics - Kinematics Labpalparas100% (2)
- Mastering PhysicsDocument22 pagesMastering Physicsozilla_26_me100% (2)
- Forces I: The Basics: Ms. Mikaela Irene Fudolig Physics 71Document30 pagesForces I: The Basics: Ms. Mikaela Irene Fudolig Physics 71Keith SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Q1 Week 1 Module 1 Law of AccelerationDocument27 pagesQ1 Week 1 Module 1 Law of AccelerationAlfredo Buena Rellora82% (11)
- Science 5 Jan 18 22 - ForcesDocument5 pagesScience 5 Jan 18 22 - Forcespriyamail0525Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 2 SolutionsDocument16 pagesExam 2 SolutionssuccinumPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Forces: Figure 1 Information About A Bag of Potato ChipDocument39 pagesEffects of Forces: Figure 1 Information About A Bag of Potato ChipTimmy SzePas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 ScienceDocument4 pagesGrade 9 ScienceChristian jade QuijanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 8: Quarter 1 - Module 1: of MotionDocument35 pagesScience 8: Quarter 1 - Module 1: of MotionirahmaePas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 1 GDocument25 pagesLec 1 GGaiLe AnnPas encore d'évaluation
- PC1431 Assignment 2 AnswersDocument19 pagesPC1431 Assignment 2 AnswersMikael Lee0% (3)
- I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesI. ObjectivesFrancis Philippe CariñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Newtons Law of MotionDocument49 pagesNewtons Law of MotionKrisha PoloanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 04 HomeworkDocument32 pagesChapter 04 HomeworkFatboy9181% (16)
- Law of AccelerationDocument36 pagesLaw of AccelerationRhyzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics in General Science: Forces and CollisionsDocument25 pagesPhysics in General Science: Forces and CollisionsTriks Cae DewePas encore d'évaluation
- PHYSICS Key Answers - Docx-1Document11 pagesPHYSICS Key Answers - Docx-1labonetelabs21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Q1 Week 2 Module 4 Uniform Circular Motion - 102603Document22 pagesQ1 Week 2 Module 4 Uniform Circular Motion - 102603Chay PalaypayonPas encore d'évaluation
- HWCH 11Document9 pagesHWCH 11Eric BarberPas encore d'évaluation
- Darlene Kharell Cuizon Quarter 1 Module 1 NEWTONS FIRST LAW OF MOTIONDocument8 pagesDarlene Kharell Cuizon Quarter 1 Module 1 NEWTONS FIRST LAW OF MOTIONJhoanna Elaine CuizonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Tasks - Essential Questions Group 3Document12 pagesChapter 4 Tasks - Essential Questions Group 3Sofiah Marshialyn PepitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Contextualized Modules in ScienceDocument37 pagesContextualized Modules in ScienceMarie RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Module1 Week1 Law-of-Motion-1st and 2ndDocument35 pagesModule1 Week1 Law-of-Motion-1st and 2ndErmelyn MaranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotational DynamicsDocument24 pagesRotational DynamicsJenneth Cabinto DalisanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ex2 2005 SolDocument8 pagesEx2 2005 SolbockerknickerPas encore d'évaluation
- Demo - Newtons Laws of MotionDocument29 pagesDemo - Newtons Laws of MotionYomiko Danise P. EloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Interactions Unit 3 Chapter 1 Sample Quiz Key: Use Your Scientists' Consensus Ideas Sheets For AssistanceDocument7 pagesInteractions Unit 3 Chapter 1 Sample Quiz Key: Use Your Scientists' Consensus Ideas Sheets For AssistanceAlfi KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- MasteringPhysics: HomeworkDocument5 pagesMasteringPhysics: HomeworkEric JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Learner Module-130708064905-Php Appilcation01 :)Document350 pagesScience Learner Module-130708064905-Php Appilcation01 :)William Bryle Pertos75% (4)
- General Physics (Answers To The Modules That I Passed Incomplete)Document26 pagesGeneral Physics (Answers To The Modules That I Passed Incomplete)Ennyliejor YusayPas encore d'évaluation
- Full On Physics ReviewDocument16 pagesFull On Physics Reviewapi-3191027930% (1)
- Work Sheet-7 Newtons 3laws Work SheetDocument11 pagesWork Sheet-7 Newtons 3laws Work SheetAndy MontesPas encore d'évaluation
- Inbound 3065761028398401936Document21 pagesInbound 3065761028398401936Eric Alvarado SaludaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Education: Name: Score: Grade: 8Document8 pagesDepartment of Education: Name: Score: Grade: 8Emmanz CaballeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Science G8 Student Book ContentsDocument350 pagesScience G8 Student Book Contentslienuj100% (3)
- Weighted Vest Workouts: Supercharge Your Workout for Weight Loss, Muscle Building, Cardio Endurance and Core StrengthD'EverandWeighted Vest Workouts: Supercharge Your Workout for Weight Loss, Muscle Building, Cardio Endurance and Core StrengthPas encore d'évaluation
- Let's Calculate Work! Physics And The Work Formula : Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksD'EverandLet's Calculate Work! Physics And The Work Formula : Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy, Force, & Motion: Sixth Grade Science ExperimentsD'EverandEnergy, Force, & Motion: Sixth Grade Science ExperimentsÉvaluation : 1 sur 5 étoiles1/5 (1)
- Convict Conditioning 2: Advanced Prison Training Tactics for Muscle Gain, Fat Loss and Bulletproof JointsD'EverandConvict Conditioning 2: Advanced Prison Training Tactics for Muscle Gain, Fat Loss and Bulletproof JointsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (15)
- The Best Shoulder Exercises You've Never Heard Of: Maximize Your Shoulder StrengthD'EverandThe Best Shoulder Exercises You've Never Heard Of: Maximize Your Shoulder StrengthPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics of the Martial Arts: A teachers guide to breaking boards and concrete blocks.D'EverandPhysics of the Martial Arts: A teachers guide to breaking boards and concrete blocks.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Power Punching Secrets: The Ultimate Study in Superior Punching DynamicsD'EverandPower Punching Secrets: The Ultimate Study in Superior Punching DynamicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Physics - Temperature, Heat, and Expansion LabDocument5 pagesMastering Physics - Temperature, Heat, and Expansion Labpalparas0% (2)
- MMDocument14 pagesMMpalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ussd CodesDocument3 pagesUssd CodespalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Physics - Kinematics LabDocument11 pagesMastering Physics - Kinematics Labpalparas100% (2)
- Mastering Physics - Energy LabDocument9 pagesMastering Physics - Energy Labpalparas100% (1)
- Ussd CodesDocument3 pagesUssd CodespalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ipho PDFDocument14 pagesIpho PDFpalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Physics - Refraction and Interference LabDocument6 pagesMastering Physics - Refraction and Interference LabpalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Physics - Change of Phase (Temperature), Sound LabDocument10 pagesMastering Physics - Change of Phase (Temperature), Sound LabpalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Physics - Change of Phase (Temperature), Sound LabDocument10 pagesMastering Physics - Change of Phase (Temperature), Sound LabpalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Physics Impq 09 Behaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument12 pages11 Physics Impq 09 Behaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory of GasesJayashree VeeraraghavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Essential Physics 1Document214 pagesEssential Physics 1Zayd Iskandar Dzolkarnain Al-HadramiPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Physics Impq Ch10 Communication SystemsDocument9 pages12 Physics Impq Ch10 Communication SystemspalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Physics Impq Ch05 Electromagnetic WavesDocument6 pages12 Physics Impq Ch05 Electromagnetic WavespalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- 2Document1 page2palparasPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Physics Impq ch08 Atoms and Nuclei PDFDocument15 pages12 Physics Impq ch08 Atoms and Nuclei PDFSwaroop SurendraPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Harmonic MotionDocument14 pagesSimple Harmonic MotionShubham JainPas encore d'évaluation
- CapacitanceDocument8 pagesCapacitancepalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric CurrentDocument9 pagesElectric CurrentpalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- Solved Examples of SystemDocument15 pagesSolved Examples of SystempalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument7 pagesKinetic Theory of GasespalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- RadioactivityDocument7 pagesRadioactivitypalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- ElasticityDocument7 pagesElasticitypalparasPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 5 - Molecular Orbital RepresentationDocument7 pagesExercise 5 - Molecular Orbital Representationapi-235187189Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Differential CalculusDocument35 pages6 Differential CalculusPankaj SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- S.S.S. SAMITI's S.A.M. D. Higher Secondary School of ScienceDocument5 pagesS.S.S. SAMITI's S.A.M. D. Higher Secondary School of ScienceSUPRIYA BHAGATPas encore d'évaluation
- Composite Materials Assignment 1Document2 pagesComposite Materials Assignment 1Danielle Wagner0% (1)
- Advanced Mathematical Methods For Civil Engineering ApplicationsDocument25 pagesAdvanced Mathematical Methods For Civil Engineering ApplicationsRady PurbakawacaPas encore d'évaluation
- Projectile Motion Online LabDocument5 pagesProjectile Motion Online Labpwbddpq585Pas encore d'évaluation
- MIDAS CivilDocument23 pagesMIDAS CivilSaurabh PednekarPas encore d'évaluation
- CHP 3 Part OneDocument57 pagesCHP 3 Part OneMegha GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ibps Numerical Ability Sample PaperDocument5 pagesIbps Numerical Ability Sample PaperPriyaJindalPas encore d'évaluation
- Python GlossaryDocument9 pagesPython GlossaryNoPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Calculus 1Document12 pagesDifferential Calculus 1Jeffcaster ComelPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Test Hkimo Grade 3 (Vòng Sơ Lo I) : Part I: Logical ThinkingDocument7 pagesSample Test Hkimo Grade 3 (Vòng Sơ Lo I) : Part I: Logical ThinkingThu Thủy NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 11 Computer ProjectDocument51 pagesClass 11 Computer ProjectVignesh ChaturvediPas encore d'évaluation
- Confidence Intervals For Proportions Take Home TestDocument5 pagesConfidence Intervals For Proportions Take Home Test1012219Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sarmento 2020Document13 pagesSarmento 2020Kylian MPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 10 Extended Earthquake Investigation Criteria C and DDocument4 pagesMath 10 Extended Earthquake Investigation Criteria C and DJust a GuyPas encore d'évaluation
- D4304-Syllabus-Neural Networks and Fuzzy SystemsDocument1 pageD4304-Syllabus-Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systemsshankar15050% (1)
- Data Structures Through C 1Document209 pagesData Structures Through C 1Abhay DabhadePas encore d'évaluation
- Jordan Vneumann THMDocument3 pagesJordan Vneumann THMJamilu Adamu MusaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4024 w11 QP 11Document20 pages4024 w11 QP 11Muhammad Azhar HayatPas encore d'évaluation
- 1997 1829 Wake-Body InterferenceDocument10 pages1997 1829 Wake-Body InterferenceMarcos SoarPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantifiers in English Author(s) : Ray S. Jackendoff Source: Foundations of Language, Vol. 4, No. 4 (Nov., 1968), Pp. 422-442 Published By: Springer Stable URL: Accessed: 15-07-2015 09:54 UTCDocument22 pagesQuantifiers in English Author(s) : Ray S. Jackendoff Source: Foundations of Language, Vol. 4, No. 4 (Nov., 1968), Pp. 422-442 Published By: Springer Stable URL: Accessed: 15-07-2015 09:54 UTCAnindita PalPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Questions Subject: Research Methodology Paper Code: BBA 206 Unit IDocument15 pagesMultiple Choice Questions Subject: Research Methodology Paper Code: BBA 206 Unit IVicky KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Silabus Manajemen StrategikDocument11 pagesSilabus Manajemen StrategikKarina AprilliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Harold R. Jacobs - Elementary Algebra-W. H. Freeman (1979)Document904 pagesHarold R. Jacobs - Elementary Algebra-W. H. Freeman (1979)Hinduism Ebooks100% (2)
- Modu 18 - FaepDocument60 pagesModu 18 - FaepHAFIDY RIZKY ILHAMSYAHPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Programming With PL/SQL 2-3: Practice Activities: Recognizing Data TypesDocument3 pagesDatabase Programming With PL/SQL 2-3: Practice Activities: Recognizing Data TypesMUHAMAD MAULANA IKSANPas encore d'évaluation
- Maximum & Minimum Problems LagrangeDocument22 pagesMaximum & Minimum Problems LagrangeCarolina Torres Lozano ΨPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.profit MaximizationDocument14 pages4.profit MaximizationRamyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chow TestDocument2 pagesChow TestWhitney LeungPas encore d'évaluation