Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Solubility Test
Transféré par
أفيق .яIDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Solubility Test
Transféré par
أفيق .яIDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SOLUBILITY TEST ON ASPHALT BITUMEN
PROCEDURE FOR SOLUBILITY TEST ON BITUMEN In the standard test for bitumen content (ASTM D4), a small sample of about 2 g of the asphalt is dissolved in 100 ml of carbon disulfide and the solution is filtered through a filtering mat in a filtering crucible. The material retained on the filter is then dried and weighed, and used to calculate the bitumen content as a percentage of the weight of the original asphalt. Due to the extreme flammability of carbon disulfide, solubility in trichloroethylene, rather than solubility in carbon disulfide, is usually used in asphalt cement specifications. THE STANDARD SOLUBILITY TEST USING TRICHLOROETHYLENE IS DESIGNATED AS ASTM D 2042. The solubility test is used to detect contamination in asphalt cement. Specifications for asphalt cements normally require a minimum solubility in trichloroethylene of 99.0 percent. Unfortunately, trichloroethylene has been identified as a carcinogen and contributing to the depletion of the earths ozone layer. The use of trichloroethylene will most likely be banned in the near future. There is a need to use a less hazardous and non-chlorinated solvent for this purpose. Results of several investigations have indicated that the solvent n-Propyl Bromide appears to be a feasible alternative to trichloroethylene for use in this application.
ASPHALT CONSISTS PRIMARILY OF BITUMENS, WHICH ARE HIGH-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HYDROCARBONS SOLUBLE IN CARBON DISULFIDE. THE BITUMEN CONTENT OF A BITUMINOUS MATERIAL IS MEASURED BY MEANS OF ITS SOLUBILITY IN CARBON DISULFIDE.
FROM LEFT TO RIGHT: KEROSENE,KEROSENE PLUS TAR, KEROSENE PLUSASPHALT CEMENT OR ASPHALT CUTBACK.
BEADS FORMED BY ASPHALT EMULSION INKEROSENE.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- BP s25 Wwta-DataDocument20 pagesBP s25 Wwta-DatajnmanivannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Wet Air Oxidation - A Review of Process Technologies and Reactor Design - S.T. Kolaczkowski - 1999Document18 pagesWet Air Oxidation - A Review of Process Technologies and Reactor Design - S.T. Kolaczkowski - 1999Jose M. Gomez RuedaPas encore d'évaluation
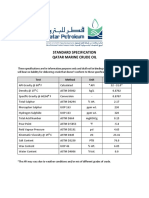
- Qatar Crude Specification (Qatar Marine Crude)Document2 pagesQatar Crude Specification (Qatar Marine Crude)ابوالحروف العربي ابوالحروف0% (1)
- FCC Catalyst EvaluationDocument40 pagesFCC Catalyst EvaluationAnilú BarreraPas encore d'évaluation
- SAES-A-012-Process Design Criteria For Produced Water Treatment and DisposalDocument31 pagesSAES-A-012-Process Design Criteria For Produced Water Treatment and Disposalnadeem shaikh100% (1)
- FCC Facilities KFUPMDocument8 pagesFCC Facilities KFUPMAMAPas encore d'évaluation
- R56 - MSDSDocument9 pagesR56 - MSDSMuhammad100% (1)
- IS3370-2021 UserGuideDocument67 pagesIS3370-2021 UserGuideMuhammad HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Saep 287Document13 pagesSaep 287OMER ELFADILPas encore d'évaluation
- Saes A 102Document21 pagesSaes A 102Ziyad ShaathPas encore d'évaluation
- PDFDocument6 pagesPDFjamy862004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chloride Management in Reformer Product StreamsDocument5 pagesChloride Management in Reformer Product StreamsAmda AmdaPas encore d'évaluation
- HPCL Vizag RefineryDocument26 pagesHPCL Vizag RefinerykshitijPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced FCC Troubleshooting Via Ecat Data InterpretationDocument4 pagesAdvanced FCC Troubleshooting Via Ecat Data Interpretationsaleh4060Pas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of Different Possibilities For Biogas Use by Life Cycle AssessmentDocument12 pagesComparison of Different Possibilities For Biogas Use by Life Cycle AssessmentJay TrambadiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Achieve Success in Gasoline HDTDocument6 pagesAchieve Success in Gasoline HDTmujeeb84Pas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 4 Introduction To Petrochemicals PDFDocument39 pagesTopic 4 Introduction To Petrochemicals PDFCHOON CHEAK YOK100% (1)
- Research Paper On Pour Point DepressantDocument10 pagesResearch Paper On Pour Point DepressantRohit AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Solvent Deasphalting of Saudi Residue To Produce Hard AsphaltDocument7 pagesSolvent Deasphalting of Saudi Residue To Produce Hard AsphaltBahar MeschiPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 Chemical Recycling - Wim Hoenderdaal PDFDocument11 pages14 Chemical Recycling - Wim Hoenderdaal PDF7ferpac7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Generic Design Assessment - Step 4 - Assessment of Westinghouse AP1000 - Civil Engineering and External Hazards PDFDocument244 pagesGeneric Design Assessment - Step 4 - Assessment of Westinghouse AP1000 - Civil Engineering and External Hazards PDFKhan SalimPas encore d'évaluation
- BFD Coal To PropyleneDocument1 pageBFD Coal To PropyleneEmir DjafarPas encore d'évaluation
- Creep CorrosionDocument28 pagesCreep CorrosionMohamad EshraPas encore d'évaluation
- PHR-ICM-DTL-105253 Piping and Instrument Diagrams, Process Flow Diagrams, and Material Flow DiagramsDocument54 pagesPHR-ICM-DTL-105253 Piping and Instrument Diagrams, Process Flow Diagrams, and Material Flow Diagramsmashari budiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment-2 (UCH850 - 101601010) PDFDocument7 pagesAssignment-2 (UCH850 - 101601010) PDFarpit thukralPas encore d'évaluation
- Uop Olex Process For Olefin Recovery: Stephen W. SohnDocument4 pagesUop Olex Process For Olefin Recovery: Stephen W. SohnAshraf SeragPas encore d'évaluation
- BITUMENDocument35 pagesBITUMENIZIMBA0% (1)
- Biogas Scrubber PDFDocument8 pagesBiogas Scrubber PDFjustmaul100% (1)
- Desulfurization v1.2 (Final)Document35 pagesDesulfurization v1.2 (Final)Talha JamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste ReductionDocument108 pagesWaste ReductionJust Semsem100% (1)
- Innovation For Refinery With ModellingDocument5 pagesInnovation For Refinery With ModellingJulio Adolfo López PortocarreroPas encore d'évaluation
- Au5 Online Operating ManualDocument414 pagesAu5 Online Operating ManualkeshavPas encore d'évaluation
- Wet Air Oxidation of Refinery Spent Caustic Sept 2000Document13 pagesWet Air Oxidation of Refinery Spent Caustic Sept 2000DAN IN-MARPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes On Petroleum ProcessingDocument94 pagesNotes On Petroleum ProcessingVânia CunhaPas encore d'évaluation
- FINAL Presentation For ARA ConferenceDocument26 pagesFINAL Presentation For ARA Conferencesaleh4060Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Treating Products and Services PDFDocument16 pagesGas Treating Products and Services PDFProcess EngineerPas encore d'évaluation
- Project PPT 1Document22 pagesProject PPT 1Swarnalatha Katta0% (1)
- Chapter6a Hydrotreating 170106114901 PDFDocument26 pagesChapter6a Hydrotreating 170106114901 PDFMI MPas encore d'évaluation
- Amberjet 4200 DatasheetDocument2 pagesAmberjet 4200 DatasheetXiaLUPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Vapor Pressure of Crude Oil: VPCR (Expansion Method)Document7 pagesDetermination of Vapor Pressure of Crude Oil: VPCR (Expansion Method)Cristhian Emmanuel GarridoPas encore d'évaluation
- Zyme-Flow Decon Technology R6 Promo PDFDocument4 pagesZyme-Flow Decon Technology R6 Promo PDFĐậu BắpPas encore d'évaluation
- Techno Economic Evaluation of Waste Lube Oil Re-Refining in Saudi ArabiaDocument7 pagesTechno Economic Evaluation of Waste Lube Oil Re-Refining in Saudi ArabiaArifPas encore d'évaluation
- BREF RefineríasDocument518 pagesBREF RefineríasJUAN ANTONIO MOLINAPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Catalytic Cracking of Heavy (Residual) Oil Fractions A Review PDFDocument21 pagesFluid Catalytic Cracking of Heavy (Residual) Oil Fractions A Review PDFMmediong UdofiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethylene Tech Sheet 30M092014Hv4 PDFDocument2 pagesEthylene Tech Sheet 30M092014Hv4 PDFsuhas pawarPas encore d'évaluation
- B.E. Semester-I Engineering Chemistry Unit (Fuel: Dr. R. M. KharateDocument68 pagesB.E. Semester-I Engineering Chemistry Unit (Fuel: Dr. R. M. KharateKrushna DeorePas encore d'évaluation
- HSFCCDocument22 pagesHSFCCdonald55555100% (1)
- Butadiene Production ProcessDocument5 pagesButadiene Production ProcessRohit SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Optimization of Crude Oil Distillation Using Different Designs of Pre-Flash Drums PDFDocument7 pagesEnergy Optimization of Crude Oil Distillation Using Different Designs of Pre-Flash Drums PDFGabriela Urdaneta100% (1)
- Feedstock Recycling and Pyrolysis of Waste Plastics - IndexDocument30 pagesFeedstock Recycling and Pyrolysis of Waste Plastics - Indexprem101Pas encore d'évaluation
- BFD Dan PFDDocument37 pagesBFD Dan PFDIlham Kiki ShahilaPas encore d'évaluation
- UOP Mercury Removal For Natural Gas Production BrochureDocument4 pagesUOP Mercury Removal For Natural Gas Production BrochureRoberth Perez VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- SIMULATION AND DESIGN FOR PROCESS TO CONVERT PLASTIC WASTE TO Liquid Fuel Using Aspen Hysys ProgramDocument5 pagesSIMULATION AND DESIGN FOR PROCESS TO CONVERT PLASTIC WASTE TO Liquid Fuel Using Aspen Hysys ProgramhanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Extraction of Aromatics From Naphtha With Ionic LiquidsDocument187 pagesExtraction of Aromatics From Naphtha With Ionic LiquidsATHUL100% (1)
- Oil Demulsifier Selection and Optimization - PetroWikiDocument10 pagesOil Demulsifier Selection and Optimization - PetroWikiahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Improving Fuel Quality by Whole Crude Oil HydrotreatingDocument10 pagesImproving Fuel Quality by Whole Crude Oil HydrotreatingAlexanderPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Process Retrofitting and Revamping: Techniques and ApplicationsD'EverandChemical Process Retrofitting and Revamping: Techniques and ApplicationsGade Pandu RangaiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparation of Catalysts II: Scientific Bases for the Preparation of Heterogeneous CatalystsD'EverandPreparation of Catalysts II: Scientific Bases for the Preparation of Heterogeneous CatalystsPas encore d'évaluation
- UNITEC-Highway Engineering 2 6202 2013 s2Document12 pagesUNITEC-Highway Engineering 2 6202 2013 s2donPas encore d'évaluation
- Plot No - C-98 SEC-NSG FINAL-ModelDocument1 pagePlot No - C-98 SEC-NSG FINAL-ModelSAKET TYAGIPas encore d'évaluation
- 97Document20 pages97Joe TorrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Report (Beam Strengthening)Document4 pagesReport (Beam Strengthening)Ankita Baban GavadePas encore d'évaluation
- Proposed Residential BLDG.: Single Line DiagramDocument1 pageProposed Residential BLDG.: Single Line DiagramTUDELA MUNICIPAL ENGINEERING OFFICEPas encore d'évaluation
- 2090-Series Power and Feedback Cables: Installation InstructionsDocument12 pages2090-Series Power and Feedback Cables: Installation InstructionsMisael PiñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Precast Cement Concrete Block Construction - Seminar Report, PPT, PDF For Civil EngineeringDocument12 pagesPrecast Cement Concrete Block Construction - Seminar Report, PPT, PDF For Civil EngineeringSoc Rua NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Method Statement For Installation of Soil Nails SK Kauluan, Ranau .Document9 pagesMethod Statement For Installation of Soil Nails SK Kauluan, Ranau .Asdia Aseffah FathiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Control and Quality AssuranceDocument37 pagesQuality Control and Quality AssuranceManoj SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- # 18-0031 - Southwest Specialty Contractors Office & Warehouse - Assembly DrgsDocument94 pages# 18-0031 - Southwest Specialty Contractors Office & Warehouse - Assembly Drgsdavid Lang578Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arup NGV Melbourne P. BowtellDocument5 pagesArup NGV Melbourne P. BowtellPaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Kimmco-Isover KBR BrochureDocument8 pagesKimmco-Isover KBR BrochurePhan LongPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabo Repair Manual HWW 4500 - 25 Inox (00972000)Document4 pagesMetabo Repair Manual HWW 4500 - 25 Inox (00972000)Jernej SevšekPas encore d'évaluation
- Facade PortfolioDocument21 pagesFacade PortfolioGAURAV PANDEYPas encore d'évaluation
- BSD - Plate 13-Reflected Ceiling Plan - BSCE 2B - (Silvestre, Michael A.)Document1 pageBSD - Plate 13-Reflected Ceiling Plan - BSCE 2B - (Silvestre, Michael A.)Michael SilvestrePas encore d'évaluation
- Plug Socket Price-List 170121Document3 pagesPlug Socket Price-List 170121tesemaPas encore d'évaluation
- CoP Site Supervision 2009 Table5.4Document3 pagesCoP Site Supervision 2009 Table5.4Lap Chun TUNGPas encore d'évaluation
- Fire Performance Euroclass Equivalence in UKDocument1 pageFire Performance Euroclass Equivalence in UKGrant MastersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Peppa PigDocument4 pagesPeppa PigSidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Shear Retrofitting of RC Beams: February 2017Document9 pagesShear Retrofitting of RC Beams: February 2017kiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Method Statements 06 - Drywall Partition WorksDocument7 pagesMethod Statements 06 - Drywall Partition WorksMathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Establisment Clients (In India & Abroad)Document2 pagesEstablisment Clients (In India & Abroad)AdiCPas encore d'évaluation
- Buy Ryobi Band Saw 250W BS-200 BuildersDocument1 pageBuy Ryobi Band Saw 250W BS-200 BuildersReuben De BruynPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Bridge Design Lecture NotesDocument40 pagesFundamentals of Bridge Design Lecture NotesSami IGPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Assessment For RCC Columns & WallsDocument7 pagesRisk Assessment For RCC Columns & WallsBulent AkPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 9: Earth Pressure TheoryDocument15 pagesUnit 9: Earth Pressure Theoryajai chyPas encore d'évaluation
- 20PE90 PLAN 1-MidasDocument8 pages20PE90 PLAN 1-MidasGrant LawagueyPas encore d'évaluation
- CE8401 Construction Techniques and Practices Notes 3Document115 pagesCE8401 Construction Techniques and Practices Notes 3christi SPas encore d'évaluation
- Faculty of Architecture and Planning, Aktu, Lucknow: 5 MuseumsDocument6 pagesFaculty of Architecture and Planning, Aktu, Lucknow: 5 MuseumsTushar SharmaPas encore d'évaluation