Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 4 Solution (Updated)
Transféré par
Jayden ChanCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Tutorial 4 Solution (Updated)
Transféré par
Jayden ChanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
HES2340 Fluid Mechanics 1
Tutorial 4
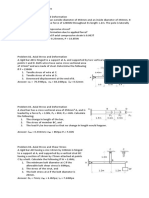
1. In this flow passage the velocity is varying with time. The velocity varies with time at
section A-A as
I = S m s - 2.2S
t
t
0
ms
At time t = 0.50 s, it is known that at section A-A the velocity gradient in the s direction is
+2 m/s per meter. Given that t
0
is 0.5 s and assuming quasi-one-dimensional flow, answer
the following questions for time t = 0.5 s.
a. What is the local acceleration at A-A? |Answcr: o
I
= -4.S ms
2
]
b. What is the convective acceleration at A-A? |Answcr: o
c
= S.S m s
2
]
Problem 1
2. Liquid flows through this two-dimensional slot with a velocity of
I = 2(q
0
b)(tt
0
)
where q
0
and t
0
are reference values. What will be the local acceleration at x = 4B and y =
0 in terms of B, t, t
0
, and q
0
?
|Answcr: o
I
=
4q
0
Bt
0
]
Problem 2
3. The velocity of water flow in the nozzle shown is given by the following expression:
I = 2t (1 - u.Sx I )
2
where V = velocity in meters per second, t = time in seconds, x = distance along the
nozzle, and L = length of nozzle = 1.2 m. When x = 0.5L and t = 3s, what is the local
acceleration along the centerline? What is the convective acceleration? Assume quasi-
one-dimensional flow prevails.
|Answcr: o
I
= S.S6 m s
2
; o
c
= 126.42m s
2
]
Problem 3
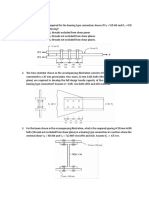
4. If the piston and water ( = 1000 kg/m
3
) are accelerated upward at a rate of 0.4 g, what
will be the pressure at a depth of 0.6 m in the water column?
|Answcr: 824u Po]
Problem 4
po
I
= -
o
ol
(p + yl)
Jp
Jl
+ y = -po
I
Jp
Jl
= -p(g + o
I
)
Jp
Jl
= -(1uuukg m
3
)(9.81 m s
2
+ (u.4 9.81 m s
2
))
= -1S7S4 Pom
Using the pressure gradient obtain, the pressure at a depth of 0.6m is,
P = (1S7S4Po m )(u.6 m)
= 824u Po
Noted that the negative sign for pressure gradient is just to imply the pressure is
decreasing when moving upward along l direction.
5. A liquid with a specific weight of 15,700 N/m
3
is in the conduit. This is a special kind of
liquid that has zero viscosity. The pressures at points A and B are 8.1 kPa and 4.8 kPa,
respectively. Which one (or more) of the following conclusions can one draw with
certainty?
|Answcr: (J)]
(a) The velocity is in the positive l direction.
(b) The velocity is in the negative l direction.
(c) The acceleration is in the positive l direction.
(d) The acceleration is in the negative l direction.
Problem 5
6. If the velocity varies linearly with the distance through this water nozzle, what is the
pressure gradient, dp/dx, halfway through the nozzle? ( = 1000 kg/m
3
).
|Answcr:
op
ox
= -82SkPo m ]
Problem 6
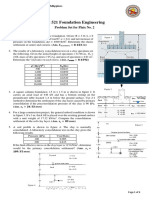
7. Water flows through a vertical contraction (venturi) section. Piezometers are attached to
the upstream pipe and minimum area section as shown. The velocity in the pipe is 3 m/s.
The difference in elevation between the two water levels in the piezometers is 15 cm. The
water temperature is 20C. What is the velocity at the minimum area?
|Answcr: I
2
= S.S m s ]
Problem 7
8. Kerosene at 20
o
C flows through a contraction section as shown. A pressure gage
connected between the upstream pipe and throat section shows a pressure difference of 20
kPa. The gasoline velocity in the throat section is 10 m/s. what is the velocity (m/s) in the
upstream pipe?
|Answcr: I
1
= 7.1Sm s ]
Problem 8
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Extracted Geotechnical Sample ProblemDocument12 pagesExtracted Geotechnical Sample ProblemFrancesca DaisyJanePas encore d'évaluation
- P5 3B Gutierrez JohnPaulDocument5 pagesP5 3B Gutierrez JohnPauljp gutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- CENG 197 Problem Set 2Document5 pagesCENG 197 Problem Set 2edmar limPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Chapter 5Document51 pagesFluid Mechanics Chapter 5Ricky Mak100% (1)
- CE 314 AssignmentDocument6 pagesCE 314 AssignmentMathew YukaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document31 pagesChapter 6Camille LardizabalPas encore d'évaluation
- RCD ShearDocument6 pagesRCD ShearGerald CatiponPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - 1Document3 pagesAssignment - 1chritPas encore d'évaluation
- Vertical forces-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesVertical forces-WPS OfficeJesusa EstradaPas encore d'évaluation
- ColumnasDocument15 pagesColumnasandreinarodPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 Seatwork 4: Calculating Uniform Flow in Various Channel GeometriesDocument11 pagesModule 2 Seatwork 4: Calculating Uniform Flow in Various Channel GeometrieshgfhfghfghgPas encore d'évaluation
- Measure flow using Venturi metersDocument3 pagesMeasure flow using Venturi metersMike Mor'z0% (2)
- Camarines Norte State College: College of Engineering SummDocument3 pagesCamarines Norte State College: College of Engineering SummjefreyPas encore d'évaluation
- RCD Problem SetsDocument4 pagesRCD Problem SetsFlo TVPas encore d'évaluation
- RCD Chapter 3Document58 pagesRCD Chapter 3jereck loquisoPas encore d'évaluation
- Shear ReinforcementDocument7 pagesShear ReinforcementJohn Saniel J. EstacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Strength July2019Document13 pagesStrength July2019Allan Añavisa Ostique Jr.100% (1)
- Hib Bler Arches ExamplesDocument3 pagesHib Bler Arches ExamplesKellesia WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework - Chapter 3Document10 pagesHomework - Chapter 3Poncho NájeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Math word problemsDocument6 pagesMath word problemsjadePas encore d'évaluation
- Review 1Document8 pagesReview 1Lyka Jane Pesigan100% (1)
- GuidelinesDocument15 pagesGuidelinesKenn Fabre0% (1)
- Plate No.1 - Autor JoyDocument6 pagesPlate No.1 - Autor JoyJoy lauriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Masonry Dam Pressure CalculationsDocument3 pagesMasonry Dam Pressure CalculationsJems Mansueto0% (1)
- NCESQ 2018 QuestionsDocument3 pagesNCESQ 2018 QuestionsMelanio VillaverdePas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument19 pagesUntitledRojane FloraPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Quiz Problems To Be MadeDocument16 pagesFinal Quiz Problems To Be MadeRyan ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- PipesDocument4 pagesPipesCamille Joy CucioPas encore d'évaluation
- 980806Solutons Manual (1 2章) 修正搞Document46 pages980806Solutons Manual (1 2章) 修正搞reidPas encore d'évaluation
- 14.3332013AtterbergLimitsData BlankDocument18 pages14.3332013AtterbergLimitsData BlankMewnEProwtPas encore d'évaluation
- ch04 RevDocument39 pagesch04 RevGlenn Midel Delos SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Orifice QuestionsDocument5 pagesOrifice QuestionsCamille Joy Cucio100% (1)
- Registered Civil Engineer Licensure ExamDocument8 pagesRegistered Civil Engineer Licensure ExamMecy Ann RectraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce Board Strength ReviewerDocument1 pageCe Board Strength ReviewerZherrinore RasayPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 6 - TORSION PDFDocument30 pagesLesson 6 - TORSION PDFBaux/比叡0% (1)
- Soil Settlement Activity SolutionsDocument5 pagesSoil Settlement Activity Solutionssenior highPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Sheet 4Document3 pagesActivity Sheet 4Shiebastian ArietaPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil Classification Guide: Geotechnical Engineering FundamentalsDocument57 pagesSoil Classification Guide: Geotechnical Engineering FundamentalsMichaelJamesBanawisPas encore d'évaluation
- PPSDocument94 pagesPPSaamirPas encore d'évaluation
- FDN Eng'g - Plate No. 2Document2 pagesFDN Eng'g - Plate No. 2Jaycee CuarteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce140 PS 3 PDFDocument1 pageCe140 PS 3 PDFAydinAkhtarpour100% (1)
- Class15-Vertical CurveDocument3 pagesClass15-Vertical CurveYihun abraham100% (1)
- Assignment 1Document8 pagesAssignment 1Kenn Fabre100% (2)
- CE5520 PLATE NO. 7 (To Be Submitted On May 20, 2020)Document2 pagesCE5520 PLATE NO. 7 (To Be Submitted On May 20, 2020)Peter Adrian NgoPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimizing flows in a branching pipeline systemDocument13 pagesOptimizing flows in a branching pipeline systemNader Alaa100% (1)
- Chapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersDocument56 pagesChapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersRami DemachkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual 2.3 - LEVEL 0 - Determination of Metacentric HeightDocument6 pagesLab Manual 2.3 - LEVEL 0 - Determination of Metacentric HeightMuhamad IzzanPas encore d'évaluation
- Agacita John PaulDocument10 pagesAgacita John PaulCarlo Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem 7. Structural Design "CE Board Exam Nov. 1992Document1 pageProblem 7. Structural Design "CE Board Exam Nov. 1992AlvinPas encore d'évaluation
- DIMDocument5 pagesDIMCyrus R. FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Example Problems Involving in Situ Stresses Under Hydrostatic ConditionsDocument38 pagesExample Problems Involving in Situ Stresses Under Hydrostatic ConditionsZero AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 2 StructuralDocument20 pagesExam 2 StructuralMs. Engr100% (1)
- Ce 411 MeDocument1 pageCe 411 MeJames Llamera ArgentePas encore d'évaluation
- Components of 2D and 3D ForcesDocument153 pagesComponents of 2D and 3D ForcesblehPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5Document12 pagesLesson 5MIKE ARTHUR DAVID100% (1)
- Chapter 6Document32 pagesChapter 6Merlund Rey ZamoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Properties and HydrostaticsDocument85 pagesFluid Properties and HydrostaticsJemuel FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Archimedes' Pri-Wps OfficeDocument8 pagesArchimedes' Pri-Wps Officeadeifedayo21Pas encore d'évaluation
- FMDocument4 pagesFMvishalPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics - Corrected ExercisesDocument5 pagesFluid Mechanics - Corrected Exercisesug2319311Pas encore d'évaluation
- AME101 LectureNotesDocument142 pagesAME101 LectureNotesShiva Krishna BhagavatulaPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 - Finance and Accounting - Intro PDFDocument12 pages01 - Finance and Accounting - Intro PDFJayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 - Finance and Accounting - Intro PDFDocument12 pages01 - Finance and Accounting - Intro PDFJayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Planning & WBSDocument8 pagesProject Planning & WBSJayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Extra For Chapter 5Document46 pagesExtra For Chapter 5Jayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Robbins Mgmt6 Ch06 BBDocument9 pagesRobbins Mgmt6 Ch06 BBJayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Robbins Mgmt6 Ch07 BBDocument11 pagesRobbins Mgmt6 Ch07 BBJayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Axial LoadDocument17 pagesAxial LoadJayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Robbins Mgmt6 Ch02 BBDocument10 pagesRobbins Mgmt6 Ch02 BBJayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hes2310 Tut1 SolutionsDocument17 pagesHes2310 Tut1 SolutionsJayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematica AssignmentDocument7 pagesMathematica AssignmentJayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- TutorialDocument2 pagesTutorialJayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Amstext 15 PrevDocument130 pagesAmstext 15 PrevJayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- TutorialDocument2 pagesTutorialJayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers For Additional ExercisesDocument4 pagesAnswers For Additional ExercisesJayden ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- HydrostaticsDocument25 pagesHydrostaticsgirish_jagadPas encore d'évaluation
- HydrostaticsDocument25 pagesHydrostaticsgirish_jagadPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth System History 4th Edition Stanley Test BankDocument6 pagesEarth System History 4th Edition Stanley Test BankVernon Hilton100% (31)
- Tank Cleaning Vacuum Residue AsphaltDocument2 pagesTank Cleaning Vacuum Residue AsphaltSushilPas encore d'évaluation
- Suitable dimensions, performance requirements, and processes for optical transmittersDocument1 pageSuitable dimensions, performance requirements, and processes for optical transmittersshruti soniPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Three Amino Acids and Peptides: Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellDocument29 pagesChapter Three Amino Acids and Peptides: Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellSheila GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Structure Calculations For Solids and Molecules: Theory and Computational MethodsDocument387 pagesElectronic Structure Calculations For Solids and Molecules: Theory and Computational MethodsJavier Gómez100% (1)
- RRLDocument1 pageRRLDaniel VasquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbobond 3028 1Document1 pageCarbobond 3028 1Yan TengPas encore d'évaluation
- A176Document2 pagesA176Claudenir AlvesPas encore d'évaluation
- Air PollutionDocument19 pagesAir PollutionMika Hakimie100% (1)
- Copper Filling of Blind Micro Vias and Through Holes Using Reverse Pulse PlatingDocument4 pagesCopper Filling of Blind Micro Vias and Through Holes Using Reverse Pulse PlatingteehowePas encore d'évaluation
- 管径计算表Document11 pages管径计算表Ascend032Pas encore d'évaluation
- Is 8147 PDFDocument170 pagesIs 8147 PDFMangesh GajbhiyePas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogo de PegamentosDocument47 pagesCatalogo de PegamentosJorge Calderon RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Book-1Document216 pagesChem Book-1Ergi HoxhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bm101: Biology For Engineers: Instructor: Yashveer Singh, PHDDocument15 pagesBm101: Biology For Engineers: Instructor: Yashveer Singh, PHDhimanshu singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 3 Biotransformation Reactions - Reduction of Carbonyls With Whole Plant PartsDocument4 pagesExperiment 3 Biotransformation Reactions - Reduction of Carbonyls With Whole Plant PartsTEN CHEANG100% (1)
- Periodic Table Display Poster A4Document1 pagePeriodic Table Display Poster A4Sarah Khan100% (1)
- PNG University of Technology CE322 Hydraulics II Assignment 1Document2 pagesPNG University of Technology CE322 Hydraulics II Assignment 1Nickson KomsPas encore d'évaluation
- CAPE Biology Lab - EnzymesDocument10 pagesCAPE Biology Lab - EnzymesAshleigh SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Structure MCQS: 1 Year N0tes Chemistry NewDocument11 pagesAtomic Structure MCQS: 1 Year N0tes Chemistry NewHaider Jalal100% (8)
- Pamphlet TG-X SeriesDocument2 pagesPamphlet TG-X SeriesrajeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Viscoelastic Creep and Stress-Strain BehaviorDocument11 pagesViscoelastic Creep and Stress-Strain BehaviorHARIMETLYPas encore d'évaluation
- Cleaning AC Coils ArticleDocument5 pagesCleaning AC Coils ArticleTauseefAhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 0.5 UltrafiltrationDocument67 pagesExercise 0.5 UltrafiltrationAntonio MoncayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporation: Heat Transfer Coefficients and Single Effect EvaporatorsDocument26 pagesEvaporation: Heat Transfer Coefficients and Single Effect EvaporatorsIram TahiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science: January 2014Document15 pagesEncyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science: January 2014Khurelbaatar GanboldPas encore d'évaluation
- SOFTENING POINTDocument8 pagesSOFTENING POINTSusi MulyaniPas encore d'évaluation
- XRF BR41146 Arl Optimx WDXRF SpectrometerDocument8 pagesXRF BR41146 Arl Optimx WDXRF SpectrometerGilson JosePas encore d'évaluation
- 4.6.intermolecular ForcesDocument27 pages4.6.intermolecular Forcesspareacc9823Pas encore d'évaluation
- Question Phy 101Document19 pagesQuestion Phy 101Mohammed kashimPas encore d'évaluation