Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Hemodialysis: By: Liana Lee Sención
Transféré par
Kavidu Keshan0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
43 vues14 pageshd
Titre original
Hemodialysis Powerpoint
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documenthd
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
43 vues14 pagesHemodialysis: By: Liana Lee Sención
Transféré par
Kavidu Keshanhd
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 14
Hemodialysis
by: Liana Lee Sencin
What is hemodialysis?
Hemodialysis is a treatment used for
patients to rid blood of metabolic
wastes, urine, harmful toxins and
other extra fluids.
Our Kidneys
Excretory Functions
Maintains plasma osmolarity by
eliminating water
Maintains plasma pH near 7.4 by
eliminating excess hydrogen
Excretes nitrogenous end products of
protein metabolism
Endocrine Functions
Renin- affects sodium, fluid volume, and
blood pressure
Erythropoietin- which regulates red
blood cell productions in bone marrow
Prostaglandin- regulates blood flow in
the kidneys
Chronic Renal Failure
A person with this
disorder will not
benefit from the
normal functions
of kidneys. There
is complete renal
failure.
Diabetes
Hypertension
Glomerolunephritis
Cystic Disorders
Drug toxicity
Damage to supporting
structure of kidneys
Causes:
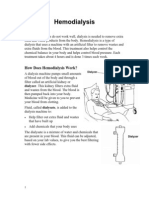
Hemodialysis
Hollow -fiber
Dialyzer
Hollow-fiber Dialyzer
Dialysate inflow tube
Dialysate outflow tube
Blood inflow tube
Blood outflow tube
10,000 hollow fibers
(large surface area)
Process of Dialysis
Blood circulates outside the
body and passed through
the dialyzer
Comes into contact with a
counter flow of dialysate
solution
Toxins are removed from
the blood through diffusion
Excess water is removed
from the blood with a
certain amount of filtration
Process of Dialysis
Blood is injected with
heparin, an anticoagulant.
Blood is then returned
back to the body through
the artery.
Diffusion in Dialysis
Constant movement of dialysate
solution and maintains a high
concentration gradient
Electrolytes are added to dialysate so
that there will be a healthy amount in
blood
Ultrafiltration
Dialysis machine causes hydraulic pressure
There is higher pressure in blood
compartment than in the dialysate
compartment
This forces water and any other molecules
small enough to pass through the
membrane to evacuate the blood.
Works Cited
Sakai, Kiyotaka,2000. Frontiers Medical
Biological Engineering. Dialysis
membranes for blood purification.Vol.
10, No. 2: 117-129.
www.yahoo.com
http://kidney.niddk.nih.gov/kudiseases/p
ubs/hemodialysis/index.htm
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Dialysis: Duaa Farooq Khan 11634 Amina Bashir 11283 Syed Uzair Iftikhar 13608 Qamar Ud Din 13071Document11 pagesDialysis: Duaa Farooq Khan 11634 Amina Bashir 11283 Syed Uzair Iftikhar 13608 Qamar Ud Din 13071Aimal SafdarPas encore d'évaluation
- Dialysis: Notes MS Vol. 2 Krizza Myrrh Gomera Balcita, RNDocument52 pagesDialysis: Notes MS Vol. 2 Krizza Myrrh Gomera Balcita, RNWhimsey CipresPas encore d'évaluation
- Swollen Kidney, (Hydronephrosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandSwollen Kidney, (Hydronephrosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemodialysis 1Document25 pagesHemodialysis 1Jasmine KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 4 Dialysis - Anna Philomena B. FerrerDocument5 pagesActivity 4 Dialysis - Anna Philomena B. FerrerSebs BerebsPas encore d'évaluation
- DialysisDocument14 pagesDialysisAndriKusumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Peritoneal DialysisDocument5 pagesPeritoneal DialysisLisette TupasPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of The Breast: Jonalyn Sotero Esco RN., MANDocument41 pagesAssessment of The Breast: Jonalyn Sotero Esco RN., MANVan MaverickPas encore d'évaluation
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandGastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- HemodialysisDocument14 pagesHemodialysistri utamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemodialysis: NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Injury, Risk For (Loss of Vascular Access) Risk Factors May IncludeDocument10 pagesHemodialysis: NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Injury, Risk For (Loss of Vascular Access) Risk Factors May IncludeChevelle Valenciano-GaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Intradialytic Stretching Exercises On Fatigueand Muscle CrampsDocument6 pagesIntradialytic Stretching Exercises On Fatigueand Muscle CrampsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Replacement TherapyDocument50 pagesRenal Replacement TherapyMalueth Angui100% (1)
- Hemodialysis, Phosphorus and Calcium, Peritoneal DialysisDocument29 pagesHemodialysis, Phosphorus and Calcium, Peritoneal DialysisTrizha MaePas encore d'évaluation
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Peritoneal DialysisDocument23 pagesPeritoneal Dialysismakyofrancis20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Achieve Your Goals. Make A Difference. Join A Community of CaringDocument64 pagesAchieve Your Goals. Make A Difference. Join A Community of CaringvirnzrobzPas encore d'évaluation
- Observation Report - Hemodialysis - Kit P. RoaquinDocument15 pagesObservation Report - Hemodialysis - Kit P. Roaquineljhayar_18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gunshot Wound PeritonitisDocument66 pagesGunshot Wound PeritonitisMia Charisse FigueroaPas encore d'évaluation
- HD TaskDocument3 pagesHD Taskenrique magpilyPas encore d'évaluation
- HemodialysisDocument19 pagesHemodialysisDonita Meña LaroyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dialysis ModuleDocument10 pagesDialysis Moduleapi-370434100Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia IntroductionDocument15 pagesAnemia IntroductionNitesh Kotian100% (1)
- ResearchDocument71 pagesResearchAngeline Lareza-Reyna VillasorPas encore d'évaluation
- CVPDocument13 pagesCVPmeisin kuraesinPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute GlumerulonephritisDocument77 pagesAcute GlumerulonephritisNicolePas encore d'évaluation
- Design Principles:: Hemodialysis MachineDocument30 pagesDesign Principles:: Hemodialysis MachineArio Fitrianto100% (1)
- Post Op Assessment SurgeryDocument20 pagesPost Op Assessment SurgeryAbdullah MatarPas encore d'évaluation
- Transcultural Nursing Nur324Document18 pagesTranscultural Nursing Nur324lidyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of CholeraDocument69 pagesManagement of CholeraNatalia LawrencePas encore d'évaluation
- All About Hemodialysis For English Tatu-FixDocument18 pagesAll About Hemodialysis For English Tatu-FixAgustia Dwi PianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Peritoneal DialysisDocument5 pagesPeritoneal DialysisJulienne Sanchez-SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Liver Cirrhosis: By: Bandna Kumari M.SC (N) 1 YRDocument66 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: By: Bandna Kumari M.SC (N) 1 YRrSPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Replacement TherapyDocument23 pagesRenal Replacement TherapyShelly Dwi SilvitaPas encore d'évaluation
- B.Reprocessing of DialyzerDocument4 pagesB.Reprocessing of DialyzerKyara Mara Gabrielle AnditPas encore d'évaluation
- CNN Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesCNN Practice QuestionsUri Perez MontedeRamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study HemodialysisDocument5 pagesCase Study HemodialysisCharmaine del RosarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Management of Skin and Parasitic DiseasesDocument14 pagesNursing Management of Skin and Parasitic Diseasesyer tagalajPas encore d'évaluation
- The Community Client: Assessment Diagnosis: As andDocument43 pagesThe Community Client: Assessment Diagnosis: As andAbid HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes MellitusDocument10 pagesDiabetes Mellitusjoeln_9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dialysis Basics: DR - Ashutosh Ojha MD, DNB (Gen Med) PDCC-Nephro (Student) GMCH..GuwahatiDocument36 pagesDialysis Basics: DR - Ashutosh Ojha MD, DNB (Gen Med) PDCC-Nephro (Student) GMCH..GuwahatiManish Arya JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- 2011 Revised Dialysis Benefit ScheduleDocument46 pages2011 Revised Dialysis Benefit ScheduleHarby Ongbay AbellanosaPas encore d'évaluation
- How Does Hemodialysis WorkDocument19 pagesHow Does Hemodialysis WorkMaxence KouessiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dialysis - Need and Types in Dialysis - 13131Document23 pagesDialysis - Need and Types in Dialysis - 13131muthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Complications of HemodialysisDocument34 pagesComplications of HemodialysisElza GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Hemodialysis MachineDocument15 pagesHemodialysis MachineLuis Alberto Díaz OlmedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Renal FailureDocument4 pagesAcute Renal FailurePerrilyn PereyPas encore d'évaluation
- Myths of DialysisDocument26 pagesMyths of DialysisSijo Muthukad M100% (1)
- Cushings SyndromeDocument51 pagesCushings SyndromeTina TalmadgePas encore d'évaluation
- Riaz Gul AHN Unit 1Document106 pagesRiaz Gul AHN Unit 1Riaz Gul RindPas encore d'évaluation
- Volume ImpairmentDocument32 pagesVolume ImpairmentAcohCChaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bowel ObstructionDocument6 pagesBowel ObstructionKryza Dale Bunado BaticanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Management Pancreatic CancerDocument2 pagesNursing Management Pancreatic CancerKit NameKo100% (2)
- Renal Replacement Therapy HD, PD, Renal TransplantationDocument65 pagesRenal Replacement Therapy HD, PD, Renal TransplantationparciPas encore d'évaluation
- DialysisDocument34 pagesDialysisAntonio Junior CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines for Measuring Household and Individual Dietary DiversityD'EverandGuidelines for Measuring Household and Individual Dietary DiversityPas encore d'évaluation
- Final ResearchDocument65 pagesFinal ResearchHarbrinder GurmPas encore d'évaluation
- TypesDocument3 pagesTypesProser Faith TabaculdePas encore d'évaluation
- How Does Haemodialysis WorkDocument19 pagesHow Does Haemodialysis Workhello_khay100% (1)
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)D'EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Pas encore d'évaluation
- DialysisDocument20 pagesDialysisShiela Mae Lopez100% (1)
- Fistula First BookletDocument10 pagesFistula First Bookletcharlenetan18100% (2)
- RTD 025 Rev 5092Document2 pagesRTD 025 Rev 5092Kavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Network11 Cannulation ReportDocument3 pagesNetwork11 Cannulation ReportKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Medication and Self-Management in Hemodialysis PatientsDocument14 pagesOral Medication and Self-Management in Hemodialysis PatientsKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Buttonhole Cannulation of AV Fistulas: Vascular Access GuidelineDocument14 pagesButtonhole Cannulation of AV Fistulas: Vascular Access GuidelineKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- FF ChangeDocument3 pagesFF ChangeKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemodialysis Catheter InfectionDocument38 pagesHemodialysis Catheter InfectionKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cannulation TrainingGuideDocument28 pagesCannulation TrainingGuideKavidu Keshan100% (1)
- Appendix H-Care of The Patient With A Hemodialysis CatheterDocument2 pagesAppendix H-Care of The Patient With A Hemodialysis CatheterKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- HemodialysisDocument28 pagesHemodialysischarlenetan18100% (6)
- RTD 025 Rev 5092Document2 pagesRTD 025 Rev 5092Kavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Care of Needling Sites Post Hemodialysis For Fistulas & Grafts (Hemostasis)Document7 pagesCare of Needling Sites Post Hemodialysis For Fistulas & Grafts (Hemostasis)Kavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Your Hemodialysis Options EngDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Your Hemodialysis Options EngKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemodialysis SOMDocument6 pagesHemodialysis SOMKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dialysis Notes 1Document3 pagesDialysis Notes 1Kavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemodialysis ComplicationsDocument10 pagesHemodialysis ComplicationsMuflih NsPas encore d'évaluation
- Cannulation of The AVF Ch3Document53 pagesCannulation of The AVF Ch3maxxine12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cannulation Camp: Basic Needle Cannulation Training For Dialysis StaffDocument7 pagesCannulation Camp: Basic Needle Cannulation Training For Dialysis Staffcharlenetan18100% (3)
- Essentials of Anticoagulation in Hemodialysis: Core CurriculumDocument12 pagesEssentials of Anticoagulation in Hemodialysis: Core CurriculumKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- C Annulation ResourcesDocument1 pageC Annulation ResourcesKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Peritoneal Dialysis: Infections. The Most Common Problem For People Receiving PeritonealDocument6 pagesPeritoneal Dialysis: Infections. The Most Common Problem For People Receiving PeritonealKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- DR ShihDocument3 pagesDR ShihKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Just The Facts: Getting Enough Hemodialysis: What Is Adequate Dialysis?Document2 pagesJust The Facts: Getting Enough Hemodialysis: What Is Adequate Dialysis?Kavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- AL06136 HemodialysisDocument2 pagesAL06136 HemodialysisKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemodialysis For End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) : When Your Kidneys FailDocument5 pagesHemodialysis For End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) : When Your Kidneys FailKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- AL06136 HemodialysisDocument2 pagesAL06136 HemodialysisKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ways Radiation Is Used in Medicine - Cobalt 60 Radiotherapy MachineDocument22 pagesWays Radiation Is Used in Medicine - Cobalt 60 Radiotherapy MachineKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ways Radiation Is Used in Medicine - Cobalt 60 Radiotherapy MachineDocument22 pagesWays Radiation Is Used in Medicine - Cobalt 60 Radiotherapy MachineKavidu KeshanPas encore d'évaluation