Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Quality Risk Management - Facilities and Equipment
Transféré par
ishtidu34Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Quality Risk Management - Facilities and Equipment
Transféré par
ishtidu34Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 1
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II. 4 Quality risk management as part of
Facilities
&
Equipment
Competent
Authorities
Industry
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 2
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Design of facility / equipment
To determine appropriate
Zones
when designing buildings and facilities, e.g.,
> flow of material and personnel
> minimize contamination
> pest control measures
> prevention of mix-ups
> open versus closed equipment
> clean rooms versus isolator technologies
> dedicated or segregated facilities / equipment
ICH Q9
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 3
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
EXAMPLE
Assessing Facility Needs for the Manufacture of Certain
Medicinal Products Using a Risk Based Approach
Options for facility dedication / segregation
> A physically separate or segregated building
> A separate area which may comprise of one or more rooms
within a multi-purpose facility with its own air-locked
personnel/ material accesses and HVAC systems.
> One or more rooms (Suite) within a multi-purpose facility or
dedicated area that is dedicated to a specific product or
product range, and is identified accordingly
EFPIA. TG dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 4
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
EXAMPLE
Assessing Facility Needs for the Manufacture of Certain
Medicinal Products Using a Risk Based Approach
Options for equipment dedication / segregation
> Equipment that is dedicated to a specific product or product
range, and identified accordingly
> A totally enclosed cabinet (Containment Isolator) that is
specifically designed to contain a specific product or
product range, and is identified accordingly
> An equipment change part (e.g. sieve, filter, etc) that is
dedicated to a specific product or product range, and is
identified accordingly
EFPIA. TG dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 5
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
EXAMPLE
Facility Needs: Risk Assessment of Severity of Harm
EFPIA. TG dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 6
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
EXAMPLE
Facility Needs: Risk Assessment of the process 1/2
EFPIA. TG dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 7
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
EXAMPLE
Facility Needs: Risk Assessment of the process 2/2
EFPIA. TG dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 8
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
EXAMPLE
Facility Needs a Process Risk Control
Consider the need improve the situation by one or more
of the following options:
>Improve the formulation
>Minimise the release of material at source using
the most appropriate equipment and technology.
>Contain any residual material or product by means
of facility, air handling, and other techniques.
>Assure adequate cleaning and/or inactivation.
>Instigate a specific monitoring program
EFPIA. TG dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 9
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
EXAMPLE
Facility Needs: Risk Control
Examples of Process Risk Controls 1/2
EFPIA. TG dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 10
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
EXAMPLE
Facility Needs: Risk Control
Examples of Process Risk Controls 2/2
EFPIA. TG dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 11
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
EXAMPLE
Facility Needs: Risk Control
Examples of Process Risk Controls 1/3
EFPIA. TG dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 12
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
EXAMPLE
Facility Needs: Risk Control
Examples of Process Risk Controls 2/3
EFPIA. TG dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 13
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
EXAMPLE
Facility Needs: Risk Control
Examples of Process Risk Controls 3/3
EFPIA. TG dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 14
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
EXAMPLE
Facility Needs: Risk Control: Operational solutions
A number of different technical solutions are possible:
> Product Campaign in multi-product facility
with campaign/extended cleaning
> Appropriately Dedicated Equipment
> Containment in multi-product area
> Closed Processes
> Dedicated suite (airlock, dedicated HVAC)
> Dedicated area
> Dedicated building
EFPIA. TG dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 15
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
EXAMPLE
Facility Needs: Risk Acceptance profile
EFPIA. TG
dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 16
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Facility Needs: Conclusion
This approach takes into account the risk based criteria:
the potential safety risk to patients from cross contamination,
different scales and/or stages of production
the physical form of the product at each stage of products and
factors which may affect ease of removal or deactivation
the appropriate technical means to minimise and demonstrate
effective ongoing control of the identified objective risk to
patient safety
the controls and supporting evidence necessary to support the
alternative use of facilities and equipment previously used for
materials identified with high potential for adverse medical
effects at low levels
EXAMPLE
EFPIA. TG dedicated facilities, 2006
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 17
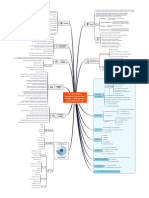
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
Risk Review
R
i s
k
C
o
m
m
u
n
i c
a
t i o
n
Risk Assessment
Risk Evaluation
unacceptable
Risk Control
Risk Analysis
Risk Reduction
Risk Identification
ReviewEvents
Risk Acceptance
Initiate
Quality Risk Management Process
Output / Result of the
Quality Risk Management Process
R
i s
k
M
a
n
a
g
e
m
e
n
t t o
o
l s
QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Risk management of Contamination
and Cross-contamination (zone concept) for API
Initiate the Risk Management Process
> Defining problem or question
- Where will protection be required?
- What kind of protection will be adequate?
> Defining the assessment information
and conclusions
- Managing risk based on a
critical point approach
EXAMPLE
Zone concept for API:
K.-H. Bender, F. Hoffmann-La Roche
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 18
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
Risk Review
R
i s
k
C
o
m
m
u
n
i c
a
t i o
n
Risk Assessment
Risk Evaluation
unacceptable
Risk Control
Risk Analysis
Risk Reduction
Risk Identification
ReviewEvents
Risk Acceptance
Initiate
Quality Risk Management Process
Output / Result of the
Quality Risk Management Process
R
i s
k
M
a
n
a
g
e
m
e
n
t t o
o
l s
Zone concept for API
Risk assessment: Risk identification and analysis
> After the critical point:
Design chemical operations to prevent cross
contamination by/of the API
> Before the critical point:
Protection has to be considered
> Rationale: Ability of a final purification,
filtration and/or crystallisation step
of removing trace levels of
incidental (cross-)contamination
> Notes: Consider industrial hygiene and
safety conditions
EXAMPLE
K.-H. Bender, F. Hoffmann-La Roche
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 19
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
Risk Review
R
i s
k
C
o
m
m
u
n
i c
a
t i o
n
Risk Assessment
Risk Evaluation
unacceptable
Risk Control
Risk Analysis
Risk Reduction
Risk Identification
ReviewEvents
Risk Acceptance
Initiate
Quality Risk Management Process
Output / Result of the
Quality Risk Management Process
R
i s
k
M
a
n
a
g
e
m
e
n
t t o
o
l s
Zone concept for API
Risk assessment: Risk evaluation
> Risk associated with different products
- Contamination by particulate matter
e.g. from equipment, environmental
- Microbiological contamination
e.g. API susceptible to microbiological growth?
- Cross-contamination
e.g. inadequate cleaning and/or material flow,
air-handling, use of closed systems
EXAMPLE
K.-H. Bender, F. Hoffmann-La Roche
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 20
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
Risk Review
R
i s
k
C
o
m
m
u
n
i c
a
t i o
n
Risk Assessment
Risk Evaluation
unacceptable
Risk Control
Risk Analysis
Risk Reduction
Risk Identification
ReviewEvents
Risk Acceptance
Initiate
Quality Risk Management Process
Output / Result of the
Quality Risk Management Process
R
i s
k
M
a
n
a
g
e
m
e
n
t t o
o
l s
Zone concept for API
Risk assessment: Risk evaluation
Risk associated with simultaneous operations
- plant design
(multi-purpose, dedicated, closed systems)
- requirements for special product categories
(e.g. highly toxic)
Risk to product from exposure to work environment
- exposure time, interfaces
(e.g. drums/containers)
EXAMPLE
K.-H. Bender, F. Hoffmann-La Roche
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 21
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
Risk Review
R
i s
k
C
o
m
m
u
n
i c
a
t i o
n
Risk Assessment
Risk Evaluation
unacceptable
Risk Control
Risk Analysis
Risk Reduction
Risk Identification
ReviewEvents
Risk Acceptance
Initiate
Quality Risk Management Process
Output / Result of the
Quality Risk Management Process
R
i s
k
M
a
n
a
g
e
m
e
n
t t o
o
l s
Zone concept for API
Risk control
> A decision-making activity focused on controlling risks
Where will protection be required?
What kind of protection is adequate?
What to do?
- Minimize interfaces
- Segregate production facilities
- Closed systems
- control people and material movement
EXAMPLE
K.-H. Bender, F. Hoffmann-La Roche
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 22
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
Risk Review
R
i s
k
C
o
m
m
u
n
i c
a
t i o
n
Risk Assessment
Risk Evaluation
unacceptable
Risk Control
Risk Analysis
Risk Reduction
Risk Identification
ReviewEvents
Risk Acceptance
Initiate
Quality Risk Management Process
Output / Result of the
Quality Risk Management Process
R
i s
k
M
a
n
a
g
e
m
e
n
t t o
o
l s
Zone concept for API
Risk control: Risk reduction
> Physical and technical solutions
- closed systems
- endless bag system
- closed sampling
> Intermittently closed product handling (hybrid solutions)
- glove boxes
- enclosed room or cabin
> Open product handling
- air flow controlled sampling
EXAMPLE
K.-H. Bender, F. Hoffmann-La Roche
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 23
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
Risk Review
R
i s
k
C
o
m
m
u
n
i c
a
t i o
n
Risk Assessment
Risk Evaluation
unacceptable
Risk Control
Risk Analysis
Risk Reduction
Risk Identification
ReviewEvents
Risk Acceptance
Initiate
Quality Risk Management Process
Output / Result of the
Quality Risk Management Process
R
i s
k
M
a
n
a
g
e
m
e
n
t t o
o
l s
Zone concept for API
Risk control: Risk reduction
> Patient impact
- Occurrence of harm
- Detection of harm
> Procedural/ structural/ logistical solutions
- gowning procedures
- operational monitoring
- optimising material flow
- standardized drums/ containers
-
EXAMPLE
K.-H. Bender, F. Hoffmann-La Roche
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 24
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
Risk Review
R
i s
k
C
o
m
m
u
n
i c
a
t i o
n
Risk Assessment
Risk Evaluation
unacceptable
Risk Control
Risk Analysis
Risk Reduction
Risk Identification
ReviewEvents
Risk Acceptance
Initiate
Quality Risk Management Process
Output / Result of the
Quality Risk Management Process
R
i s
k
M
a
n
a
g
e
m
e
n
t t o
o
l s
Zone concept for API
Risk control: Risk Acceptance
- No additional risk control activities are necessary
- Supported by the decision maker(s).
- Includes acceptance of risks
that have not been identified
> Design appropriate levels of protection
> Accept the critical point of the process
> Appropriate monitoring may be performed
EXAMPLE
K.-H. Bender, F. Hoffmann-La Roche
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 25
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
Risk Review
R
i s
k
C
o
m
m
u
n
i c
a
t i o
n
Risk Assessment
Risk Evaluation
unacceptable
Risk Control
Risk Analysis
Risk Reduction
Risk Identification
ReviewEvents
Risk Acceptance
Initiate
Quality Risk Management Process
Output / Result of the
Quality Risk Management Process
R
i s
k
M
a
n
a
g
e
m
e
n
t t o
o
l s
Zone concept for API
Risk communication
> Internal:
- GMP-Master plan to demonstrate that
the risk management process is used
- Capital investment plan can be supported or even
changed by the quality risk management process
> External:
- e.g. Site Master File
EXAMPLE
K.-H. Bender, F. Hoffmann-La Roche
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 26
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
Risk Review
R
i s
k
C
o
m
m
u
n
i c
a
t i o
n
Risk Assessment
Risk Evaluation
unacceptable
Risk Control
Risk Analysis
Risk Reduction
Risk Identification
ReviewEvents
Risk Acceptance
Initiate
Quality Risk Management Process
Output / Result of the
Quality Risk Management Process
R
i s
k
M
a
n
a
g
e
m
e
n
t t o
o
l s
Zone concept for API
The review phase
> Audits / Inspections
> Regularly assessment of complaints/ deviations
on (cross-) contamination topics
EXAMPLE
K.-H. Bender, F. Hoffmann-La Roche
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 27
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Design of facility / equipment
To determine appropriate
Product contact materials for equipment and containers
> Selection of stainless steel grade, gaskets, lubricants, etc.
Utilities
> steam, gases, power source, compressed air, heating,
ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC), water, etc.
Preventive maintenance for associated equipment
> Inventory of necessary spare parts, etc.
ICH Q9
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 28
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Design of facility / equipment
Risk criteria for Facility qualification (DQ/IQ/OQ/PQ)
> Probability: Equipment has contact with product
full surface (vessel) / partial (gasket) / no contact
> Severity: possible source for contamination
(e.g. Process validation) or cross contamination
(e.g. Cleaning validation)
yes / no
> Severity: Product quality affected? Impact on patient?
yes / no
> Detectability: Knowledge of this attribute may affect the
release decision
EXAMPLE
B. Dreissig, F. Hoffmann-La Roche
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 29
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Design of facility / equipment
Master Qualification Plan of a new facility:
Document reduction initiative
EXAMPLE
B. Dreissig, F. Hoffmann-La Roche
Document consolidation equals risk
reduction via constancy, easy
maintenance/training
reduces non compliance risk to patient
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 30
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Hygiene aspects in facilities
> To protect the product from environmental hazards
including chemical, microbiological, physical hazards
determining appropriate clothing and gowning
hygiene concerns
> To protect the environment from hazards
related to the product being manufactured
personnel, potential for cross-contamination
ICH Q9
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 31
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Calibration/preventive maintenance
> To set appropriate calibration and maintenance schedules
Qualification of facility/equipment/utilities
> To differentiate scope and efforts and decisions
based on the intended use
multi-versus single-purpose
batch versus continuous production
Cleaning of equipment and environmental control
> To determine acceptable (specified)
cleaning validation limits
ICH Q9
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 32
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Potency Scale max. daily dose (severity)
> 10 < 1mg
> 6 1-10mg
> 4 10-100mg
> 2 100mg-1000mg
> 1 >1000mg
Solubility Scale in cleaning medium (probability)
> 5 low solubility
> 4 slightly soluble
> 3 moderately soluble
> 2 soluble
> 1 highly soluble
Interactions Scale (detectability)
> 9 serious - patients life threatened
> 4 moderate patient feels adverse effect
> 1 low none patient does not notice
EXAMPLE
P. Gough, D. Begg Ass.
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 33
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Computer systems and computer controlled equipment
> To select the design of computer
hardware and software
- Modular
- Structured
- Fault tolerance
> To determine the extent of validation
- Identification of critical performance parameters
- Selection of the requirements and design
- Code review
- The extent of testing and test methods
- Reliability of electronic records and signatures
ICH Q9
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 34
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Computer systems and computer controlled equipment
Which risks could be considered?
> Patient risk
> Compliance risk
> Application risk
> Business risk (influenced by other than Q-risks)
> Infrastructure risk
EXAMPLE
W. Schumacher, Roche
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 35
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Risks on Comp. systems & comp. controlled equipment
Patient risk
EXAMPLE
W. Schumacher, Roche
A: Death
B: Serious harm but not death
C: Minor harm
Patient harm
Will the failure of the system
result in
D: No effect on patient health
A: Yes
P
a
t
i
e
n
t
R
i
s
k
Secondary
assurance of safety
Is/are there down stream
processes to the subject system
that could assure safety of the
product.
B: No
Category Questions Choices
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 36
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Risks on Comp. systems & comp. controlled equipment
Compliance risk
EXAMPLE
W. Schumacher, Roche
A: Yes
Business process
regulation
Is the business process subject
to predicate rule requirements?
OR
Is the business process regulated
by an agency?
B: No
A: Yes, submitted
B: Yes, may be inspected
C
o
m
p
l
i
a
n
c
e
R
i
s
k
Degree of Exposure
Are the data or records made
available to regulatory agencies?
C: No
Category Questions Choices
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 37
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Risks on Comp. systems & comp. controlled equipment
Application risk 1/2
EXAMPLE
W. Schumacher, Roche
A: 0
B: 1
How many technology enablers
are interfaced to the system?
C: more than 1
A: firmware
B: standard software packages
C: configurable software
packages
D: configurable software
package with custom
additions
A
p
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
Complexity
What is the technology category
for the system?
E: fully custom software
Category Questions Choices
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 38
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Risks on Comp. systems & comp. controlled equipment
Application risk 2/2
EXAMPLE
W. Schumacher, Roche
Category Questions Choices
A: New technology
B: Mature technology but new to
us
C: Mature technology previously
used by us
Experience
What is our experience with the
technology?
D: Technology approaching
obsolescence
A: Yes
Security
Is the application capable of limiting
access at the individual authorized
user level?
B: No
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 39
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Risks on Comp. systems & comp. controlled equipment
Business risk 1/3
EXAMPLE
W. Schumacher, Roche
Category Questions Choices
A: Discovery Research
B: GLP Research
C: Development GMP
D: Development GCP
E: API Manuf.
F: Form. Manuf. & Pack
G: Marketing / Dem. Manag.
H: Prod. Plann. & Log.
I: Supp. Proc. HR
K: Supp. Proc. Informatics
Position in Value
Chain
Identify where in the value chain the
system is used
L: Supp Proc Finance
A: 1
B: 2 to 20
C: 21 to 100
Number of users
(Usage)
Estimate the number of users of the
system
D: more than 100
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 40
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Risks on Comp. systems & comp. controlled equipment
Business risk 2/3
EXAMPLE
W. Schumacher, Roche
Category Questions Choices
A: < yearly
B: monthly
Frequency of Usage
(Usage)
Estimate how frequently the system
users operate or interface with the
system
C: daily
A: One site
B: Within a region Location of system
(Usage)
Select where the System is
implemented
C: Throughout the global
organization
A: There is no alternative system
or manual procedure
B: YES, with a backup system or
an alternative system
C: YES, with manual processes - a
major resource impact
Criticality of business
system
Can the business continue to operate
if the system fails
D: YES, with manual processes - a
minimum resource impact
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 41
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Risks on Comp. systems & comp. controlled equipment
Business risk 3/3
EXAMPLE
W. Schumacher, Roche
Category Questions Choices
A: Yes Criticality of records
contained in the
system
Is the system the sole source of data
for the business process? B: No
A: Yes
Cross organizational
boundaries
Does this system supply critical data
from this
business process to other business
processes (outside of this one)?
B: No
Annex II: Potential Applications
prepared by some members of the ICH Q9 EWG for example only; not an official policy/guidance July 2006, slide 42
ICH Q9 QUALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
II.4: QRM for facilities, equipment and utilities
Risks on Comp. systems & comp. controlled equipment
Infrastructure risk
EXAMPLE
W. Schumacher, Roche
A: Local - Proprietary
B: Local
C: Regionally
On which geographical
infrastructure the system will
operate?
D: Globally
A: New technology
B: Mature technology but new
to us
C: Mature technology
previously used by us
Complexity
What is our experience with the
infrastructure?
D: Technology approaching
obsolescence
A: Yes
I
n
f
r
a
s
t
r
u
c
t
u
r
e
Security
Does the system rely on the
"public internet" in the operation
of the system?
B: No
Category Questions Choices
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Biocontamination Control for Pharmaceuticals and HealthcareD'EverandBiocontamination Control for Pharmaceuticals and HealthcareÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- 09-Q9 HaccpDocument8 pages09-Q9 HaccpKristof MCPas encore d'évaluation
- 1-4 ChangeControlDocument62 pages1-4 ChangeControlarm_1919Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturing Facilities A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionD'EverandManufacturing Facilities A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbial Risk Assesment in Pharmaceutical CleanroomsDocument9 pagesMicrobial Risk Assesment in Pharmaceutical CleanroomsteaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cross ContaminationDocument47 pagesCross ContaminationAKKAD PHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Good Documentation Practices - IVT - JVTDocument7 pagesGood Documentation Practices - IVT - JVTdcharliesPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of ContaminationControlDocument19 pagesAnatomy of ContaminationControlVinay PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Development of CCSDocument54 pagesDevelopment of CCSDiana Oldani100% (2)
- 2-4 ProcessValidationDocument37 pages2-4 ProcessValidationnikuPas encore d'évaluation
- QRM SOP Issue# 01 ApprovedDocument9 pagesQRM SOP Issue# 01 ApprovedibrahimgomaaPas encore d'évaluation
- EU - Risk AssesmentDocument23 pagesEU - Risk Assesmentapi-3859063Pas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Assessment in PharmaDocument2 pagesRisk Assessment in PharmaPrince MoniPas encore d'évaluation
- EU-GMP.2014 - Annex - 20 (Quality Risk Management)Document25 pagesEU-GMP.2014 - Annex - 20 (Quality Risk Management)bvsc77035Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hazop PharmaDocument7 pagesHazop PharmaismailayarPas encore d'évaluation
- Required GMP Standards and Inspections: Alain KupfermanDocument47 pagesRequired GMP Standards and Inspections: Alain KupfermanGV Narayana ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Validation Cross ContaminationDocument13 pagesValidation Cross ContaminationZolla Verbianti SuwitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cross Contamination Prevention in HVACDocument8 pagesCross Contamination Prevention in HVAChuynhhaichauchauPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Assessment Template 1.2Document5 pagesRisk Assessment Template 1.2Jorge Humberto Herrera100% (1)
- Site Validation Master Plan: Releasing Its Full PotentialDocument32 pagesSite Validation Master Plan: Releasing Its Full PotentialnophadonPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Assessment Template 1.2 PDFDocument5 pagesRisk Assessment Template 1.2 PDFGanesh KashinathPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Quality Risk Management To Pharmaceutical OperationsDocument13 pagesApplication of Quality Risk Management To Pharmaceutical Operationsshah777100% (2)
- GMP Audit Inspections and Audit PreparationsDocument19 pagesGMP Audit Inspections and Audit PreparationsabhijitPas encore d'évaluation
- Good Documentation PracticeDocument3 pagesGood Documentation PracticeVladimir SiraPas encore d'évaluation
- GMP Training SlideshowDocument54 pagesGMP Training SlideshowcavanacngPas encore d'évaluation
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients - Development, Manufacturing, and Regulation, Second Edition (Drugs and The Pharmaceutical Sciences) - 9781439803363 - Medicine & Health Science Books @Document13 pagesActive Pharmaceutical Ingredients - Development, Manufacturing, and Regulation, Second Edition (Drugs and The Pharmaceutical Sciences) - 9781439803363 - Medicine & Health Science Books @Marwa Ahmed100% (1)
- GMP Slide ShareDocument77 pagesGMP Slide SharePenmetsa Satyanarayana RajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental Monitoring and Control A Complete GuideD'EverandEnvironmental Monitoring and Control A Complete GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- ПЕТ Центар- Производство и Контрола На Квалитет- Е. ЈанеевиќDocument30 pagesПЕТ Центар- Производство и Контрола На Квалитет- Е. ЈанеевиќEmilija Janevik100% (1)
- Quality Risk Management PDFDocument9 pagesQuality Risk Management PDFisak23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clean Room Training 2023Document17 pagesClean Room Training 2023LoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Risk ManagementDocument56 pagesQuality Risk ManagementTim Sandle100% (4)
- GUIDE-MQA-013-008 (Guidance Notes of Good Distribution Practices)Document18 pagesGUIDE-MQA-013-008 (Guidance Notes of Good Distribution Practices)William ChandraPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Study in Quality Risk ManagementDocument30 pagesA Case Study in Quality Risk Managementrodcam1Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5 GMP Case Studies Including FDA Analysis PDFDocument10 pages5 GMP Case Studies Including FDA Analysis PDFAbdul KalimPas encore d'évaluation
- FDA - Level 2 Guidance - Records and ReportsDocument9 pagesFDA - Level 2 Guidance - Records and ReportsaabbPas encore d'évaluation
- Cytopro Clinical Study ProtocolDocument19 pagesCytopro Clinical Study ProtocolbeequesadaPas encore d'évaluation
- IQ Compression PDFDocument19 pagesIQ Compression PDFPhani MadhaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Procedure For Recall - AOCDocument6 pagesProcedure For Recall - AOCMohamed EzzatPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 Breakout D-Quality Risk Management-Key MessagesDocument26 pages06 Breakout D-Quality Risk Management-Key Messageshenrykayode4100% (1)
- ECA Deviation Management CAPADocument4 pagesECA Deviation Management CAPATaniparthy Madhusudhana ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- A Cleanroom Contamination Control SystemDocument8 pagesA Cleanroom Contamination Control SystemTorres XiaPas encore d'évaluation
- User Requirements Template RAJADocument25 pagesUser Requirements Template RAJAdrs_mdu480% (1)
- Analytical Method TransferDocument36 pagesAnalytical Method Transferimawan_wast100% (1)
- As Far As Possible - en ISO 14971Document19 pagesAs Far As Possible - en ISO 14971Kanwal Jit Singh100% (1)
- SOP For Power FailureDocument3 pagesSOP For Power FailureRofiqul Ala100% (1)
- Access Control To GMP AreaDocument4 pagesAccess Control To GMP AreaNishit SuvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Metrics Status Report ISPEDocument4 pagesQuality Metrics Status Report ISPEvg_vvgPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit IV - Complaints and DocumentsDocument103 pagesUnit IV - Complaints and DocumentsIndu VattiPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Systems For Pharmacovigilance SME Workshop "Focus On Pharmacovigilance" 19 April 2012, EMA LondonDocument20 pagesQuality Systems For Pharmacovigilance SME Workshop "Focus On Pharmacovigilance" 19 April 2012, EMA LondonHala MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Temp MappingDocument13 pagesTemp MappingJoshua JumaPas encore d'évaluation
- EU GMP Requirements-Quality SystemsDocument70 pagesEU GMP Requirements-Quality Systemsishtidu34100% (1)
- Qualification - Validation CPOB 2018 PDFDocument145 pagesQualification - Validation CPOB 2018 PDFmela milaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Aseptic Processing Case StudyDocument28 pagesAseptic Processing Case Studykavya nainitaPas encore d'évaluation
- SOP of URS 1657011596Document5 pagesSOP of URS 1657011596Huỳnh Ngọc SángPas encore d'évaluation
- Personal Protective Equipment ProceduresDocument7 pagesPersonal Protective Equipment ProceduresIbrahim Azam IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio-Validation of Steam Sterilization - 758572676Document11 pagesBio-Validation of Steam Sterilization - 758572676venkats_001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sop Fumigation Vapour Hydrogen Peroxide-H2o2 VHPDocument6 pagesSop Fumigation Vapour Hydrogen Peroxide-H2o2 VHPMohamed FetouhPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharma Change Control Peither ExecSeriesDocument55 pagesPharma Change Control Peither ExecSeriesLuc12Pas encore d'évaluation
- ICH PPT - QRM For Facilities, Utilities & EquipmentDocument42 pagesICH PPT - QRM For Facilities, Utilities & EquipmentDEVESH SINGHPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Assessment and ManagementDocument52 pagesRisk Assessment and Managementishtidu34100% (1)
- EU GMP Requirements-Quality SystemsDocument70 pagesEU GMP Requirements-Quality Systemsishtidu34100% (1)
- Quality Risk ManagementDocument30 pagesQuality Risk ManagementNenad MihajlovPas encore d'évaluation
- The New Quality Paradigm in Ich q8 q9 q10 q11Document30 pagesThe New Quality Paradigm in Ich q8 q9 q10 q11ishtidu34Pas encore d'évaluation
- Interim Technical Guidance Note On Capping For Landfill SitesDocument8 pagesInterim Technical Guidance Note On Capping For Landfill SitesRonen MarkoPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 04 17 SisemaqDocument175 pages05 04 17 SisemaqOsmar JrPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Policy: Health and Safety Arrangements For The Appointment and Management of Sub-ContractorsDocument8 pagesModel Policy: Health and Safety Arrangements For The Appointment and Management of Sub-ContractorsSophie-Louise Mercedes100% (1)
- ISO 37301 - 2021 Compliance Management SystemsDocument1 pageISO 37301 - 2021 Compliance Management Systemskhalilguesmi50Pas encore d'évaluation
- AIMS Manual - 2021Document82 pagesAIMS Manual - 2021Randyll TarlyPas encore d'évaluation
- 0454 Enterprise Teacher Guide WEBDocument33 pages0454 Enterprise Teacher Guide WEBLissa JacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- HIRA For DPP-2 Project in I BlockDocument20 pagesHIRA For DPP-2 Project in I BlockSiddharth PPas encore d'évaluation
- SVFC BS Accountancy - 5th Set Online Resources SY20-19 1st Semester PDFDocument19 pagesSVFC BS Accountancy - 5th Set Online Resources SY20-19 1st Semester PDFLorraine TomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Capstone 2Document14 pagesCapstone 2Carmela Ayessa PiguerraPas encore d'évaluation
- Auditing TheoryDocument88 pagesAuditing TheoryCristineJoyceMalubayIIPas encore d'évaluation
- David Brewer - IsO - IEC 27001 - 2013 - Mastering Risk Assessment and The Statement of Applicability-David Brewer (2021)Document110 pagesDavid Brewer - IsO - IEC 27001 - 2013 - Mastering Risk Assessment and The Statement of Applicability-David Brewer (2021)Khobar SurveyPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Assess T-27 - HousekeepingDocument1 pageRisk Assess T-27 - HousekeepingMAB AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Hand Arm Vibration PDFDocument19 pagesControl Hand Arm Vibration PDFmalik jahanPas encore d'évaluation
- Asset ManagementDocument31 pagesAsset ManagementRhama Wijaya100% (1)
- Customizing School-Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management CapabilityDocument6 pagesCustomizing School-Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management CapabilityRanel Ranran ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- SAES B 014 Safety Requirements For PlantDocument38 pagesSAES B 014 Safety Requirements For Plantliuyx866Pas encore d'évaluation
- Water Distribution Systems by C. J. ParsloeDocument48 pagesWater Distribution Systems by C. J. Parsloebahiniy286Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fire Hazard Categorization and Risk Assessment ForDocument12 pagesFire Hazard Categorization and Risk Assessment Fornil julfikar0% (1)
- Safety in The Storage and Handling of Steel and Other Metal StockDocument93 pagesSafety in The Storage and Handling of Steel and Other Metal StockvolkanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hazard Risk Assessment Dismantling of Sulphonation - Pas DryingDocument26 pagesHazard Risk Assessment Dismantling of Sulphonation - Pas DryingKhia Aragon PepitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Implementation of Chemical Management System in Apparel IndustryDocument3 pagesImplementation of Chemical Management System in Apparel IndustryVIJAYAKUMAR K APas encore d'évaluation
- Toxicology HandbookDocument542 pagesToxicology HandbookBioMariaMC75% (4)
- BT RA 01 WeldingDocument6 pagesBT RA 01 Weldingnandha gopalPas encore d'évaluation
- The Risk Based AuditDocument6 pagesThe Risk Based AuditHana AlmiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Contoh HIRACDocument6 pagesContoh HIRACPeri YantoPas encore d'évaluation
- BP Road Safety - Contractor Hse Management ProgrammeDocument49 pagesBP Road Safety - Contractor Hse Management ProgrammeKama EfendiyevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module IIIDocument29 pagesModule IIImanoj mlpPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Identification For BusinessDocument11 pagesRisk Identification For Businessravan snghPas encore d'évaluation
- ConstructioRiskAssessment of Riser InstallationDocument13 pagesConstructioRiskAssessment of Riser InstallationMario JacobsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Hazards Analysis Guide A Reference Manual For Analyzing Safety Hazards On Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment PDFDocument46 pagesHazards Analysis Guide A Reference Manual For Analyzing Safety Hazards On Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment PDFdckristantoPas encore d'évaluation