Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Physiology
Transféré par
api-197629670 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
67 vues2 pagesThe cervix dilates during childbirth to allow the baby to pass through and also convulses during orgasm. The fallopian tubes transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus where fertilization usually occurs. The ovaries mature eggs and secrete sex hormones like estrogen and progesterone. The vagina receives the penis during sex and allows for birth and menstrual blood to leave the body. The uterus houses and nourishes the fetus. The endometrium contains glands that secrete fluids, the myometrium contracts to help with birth, and the perimetrium covers the uterus. Estrogen is an important female hormone responsible for secondary sex characteristics and is secreted by the ovaries in response to signals from the hyp
Description originale:
Titre original
8. PHYSIOLOGY
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe cervix dilates during childbirth to allow the baby to pass through and also convulses during orgasm. The fallopian tubes transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus where fertilization usually occurs. The ovaries mature eggs and secrete sex hormones like estrogen and progesterone. The vagina receives the penis during sex and allows for birth and menstrual blood to leave the body. The uterus houses and nourishes the fetus. The endometrium contains glands that secrete fluids, the myometrium contracts to help with birth, and the perimetrium covers the uterus. Estrogen is an important female hormone responsible for secondary sex characteristics and is secreted by the ovaries in response to signals from the hyp
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
67 vues2 pagesPhysiology
Transféré par
api-19762967The cervix dilates during childbirth to allow the baby to pass through and also convulses during orgasm. The fallopian tubes transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus where fertilization usually occurs. The ovaries mature eggs and secrete sex hormones like estrogen and progesterone. The vagina receives the penis during sex and allows for birth and menstrual blood to leave the body. The uterus houses and nourishes the fetus. The endometrium contains glands that secrete fluids, the myometrium contracts to help with birth, and the perimetrium covers the uterus. Estrogen is an important female hormone responsible for secondary sex characteristics and is secreted by the ovaries in response to signals from the hyp
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
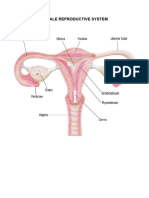
LOCATION &
STRUCTURE FUNCTION
DESCRIPTION
During childbirth, contractions of the uterus
The lower narrower will dilate the cervix up to 10 cm in diameter to
Cervix
portion of the uterus. allow the child to pass through. During orgasm,
the cervix convulses and the external os dilates
Extending upper part of Egg transportation from ovary to uterus
Fallopian tubes
the uterus on either side. (fertilization usually takes place here).
Provides an environment for maturation of
Ovaries (female Pelvic region on either
oocyte. Synthesizes and secretes sex hormones
gonads) side of the uterus.
(estrogen and progesterone).
Receives penis during mating. Pathway
Canal about 8-10 cm through a woman’s body for the baby to take
long going from the
Vagina during childbirth. Provides the route for the
cervix to the outside of menstrual blood (menses) from the uterus, to
the body. leave the body. May hold forms of birth
control, such as an IUD, diaphragm, neva ring,
or female condom
Uterus Located in the center of
the pelvic cavity
House and nourishes the fetus.
The innermost layer of
Endometrium uterine wall.
Contains glands that secrete fluids that bathe
the uterine lining.
Myometrium Smooth muscle in the
uterine wall.
Contract to help expel the baby.
Perimetrium
Outer layer of the uterus
Covers the uterus
ESTROGEN
It is the most important hormone during puberty in female and is
responsible for secondary sexual characteristics (e.g. breast enlargement,
menstruation, pelvic enlargement, long bones). Generally secreted by the
ovary specifically secreted by the Graafian follicle.
Estrogen production
Hypothalamus
↓
GnRH
↓
Anterior Pituitary Gland
↓
FSH
↓
Graafian Follicle
↓
Estrogen
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Female Reproductive System UpdatedDocument84 pagesFemale Reproductive System UpdatedAtie IzzatiPas encore d'évaluation
- KHC 6 Advanced Fingering SessionsDocument20 pagesKHC 6 Advanced Fingering SessionsjustnewaroundPas encore d'évaluation
- m105 Handouts Finals 2015 Family PlanningDocument35 pagesm105 Handouts Finals 2015 Family PlanningBal Ri Mekoleu50% (2)
- Female Reproductive System: Dominguez, Nikka EDocument51 pagesFemale Reproductive System: Dominguez, Nikka EGwyneth100% (1)
- Reproductive SystemDocument39 pagesReproductive SystemCenando Bodanio100% (1)
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesMale Reproductive SystemLatrell GelacioPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive SystemDocument43 pagesReproductive SystemDoc Zay VillafuertePas encore d'évaluation
- Male Reproductive System PDFDocument4 pagesMale Reproductive System PDFPerry SinPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemseongeokPas encore d'évaluation
- Course in The WardDocument2 pagesCourse in The Wardapi-19762967100% (3)
- Ovarian Cyst FinalDocument26 pagesOvarian Cyst FinalReicy Aquino SacularPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemHye JinPas encore d'évaluation
- A Round Ligaments: 1. Which Structure Provides The Major Support To The Uterus and Cervix?Document10 pagesA Round Ligaments: 1. Which Structure Provides The Major Support To The Uterus and Cervix?Nikhil Tyagi100% (1)
- 1.physical AssessmentDocument4 pages1.physical Assessmentapi-19762967100% (2)
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyRuthangela GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemYsthanamhire TolentinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyanglogaliboPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKristine Alejandro100% (1)
- Ana Physio ReprodDocument8 pagesAna Physio ReprodTeodoro Lemuel Ramos Gaela100% (1)
- REPRODUCTIONDocument78 pagesREPRODUCTIONglaizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive System Topic 1 Normal ObDocument68 pagesReproductive System Topic 1 Normal ObNur-Sallah AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Semifinals Notes FinalDocument3 pagesGas Semifinals Notes Finalbevienlynpepito10Pas encore d'évaluation
- OB CA2 ReviewerDocument34 pagesOB CA2 Reviewercresia hidalgoPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 8 Summary (Modifications) - AnasayaDocument15 pagesModule 8 Summary (Modifications) - Anasayafroosedd777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Femalereproductivesystem 120329125448 Phpapp02Document18 pagesFemalereproductivesystem 120329125448 Phpapp02Crapster GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Quarter 1 Unit 2 Day 7 Remediation Female Reporductive System Card SortDocument6 pagesBiology Quarter 1 Unit 2 Day 7 Remediation Female Reporductive System Card SortTeachTappyPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive System - Bio 2 - 12 Stem - l11Document4 pagesReproductive System - Bio 2 - 12 Stem - l11Lyka Lobido CabeltesPas encore d'évaluation
- Maternity and Child Print 1-10Document11 pagesMaternity and Child Print 1-10ZYRHIL ANANOPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomedical PerpectiveDocument22 pagesBiomedical Perpectiveedmaration 2002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiologybadgurl08Pas encore d'évaluation
- MORANDocument3 pagesMORANCubillas P. DerPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Female Sys PresentationDocument4 pagesBio Female Sys PresentationDoc_NeurologistPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 The Reproductive SystemDocument122 pages2 The Reproductive SystemBryan Lloyd Ballestar RayatPas encore d'évaluation
- Archive: Biology of Reproduction of GoatsDocument8 pagesArchive: Biology of Reproduction of GoatshassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Part, Function and Process of Reproduction SystemDocument31 pagesPart, Function and Process of Reproduction SystemSavia NaldiPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive System For ReviewerDocument50 pagesReproductive System For Reviewerzyrle (zayrieeo)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quarter 3 Module 1.3 Reproductive SystemDocument113 pagesQuarter 3 Module 1.3 Reproductive Systemsano.kthPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Cephal-TransDocument7 pagesCase Study Cephal-TransAldjen SetiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Bahan UASDocument4 pagesBahan UASislamiah sybPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument27 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ReproductionÆRO YT CHANNELPas encore d'évaluation
- Female Reproductive Organs, Menstrual Cycles, and FertilizationDocument13 pagesFemale Reproductive Organs, Menstrual Cycles, and FertilizationNurinnisa ShiddiqiyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Gender & Society Lo4Document6 pagesGender & Society Lo4Mark Eugene DeocampoPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesReproductive SystemMiguel Ashi GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation 2Document21 pagesPresentation 2ericasinamagPas encore d'évaluation
- Discussion of The Diseases ProcessDocument4 pagesDiscussion of The Diseases ProcessMica CoveyPas encore d'évaluation
- Sexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)Document40 pagesSexual Reproduction in Human Beings (Part 1)puspita8967628Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemElla PaezPas encore d'évaluation
- NSVDDocument32 pagesNSVDChris Oliver Kevin Ledesma100% (3)
- Pandapatan Paler AnaPhyDocument3 pagesPandapatan Paler AnaPhyShara Lailanie A. AzisPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesDocument13 pages8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesAndre KachigambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdalla MostafaDocument8 pagesAbdalla MostafaDr. Mohammad JamaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Human ReproductionDocument42 pagesHuman ReproductionangelynPas encore d'évaluation
- Aula 1 - Aparelho ReprodutorDocument35 pagesAula 1 - Aparelho ReprodutorLeticia MeirellesPas encore d'évaluation
- Book ReportDocument10 pagesBook ReportSachin NagPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Repro NotesDocument10 pagesHuman Repro NotesElvira Monica SayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gensic Reviewer2 Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument3 pagesGensic Reviewer2 Anatomy and Physiology of Reproductionexplorers.beamaepetracortaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy PhysiologyRouie Björn ABrianPas encore d'évaluation
- Reporductive SystemDocument31 pagesReporductive SystemEmma Joel OtaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Screenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMDocument127 pagesScreenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMqdvvqvxn7gPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproduction AnfismanDocument43 pagesReproduction AnfismanSyahirahPas encore d'évaluation
- Ana ReproDocument4 pagesAna ReproFIONA DANE MAURERAPas encore d'évaluation
- Pointers in Science 5 Long TestDocument2 pagesPointers in Science 5 Long Testshine brightPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Revision NotesDocument8 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 11 Revision NotesShayon BeraPas encore d'évaluation
- MCN LEC (Prelims)Document19 pagesMCN LEC (Prelims)BIANCA ANGELICA GERARDOPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesReproductive SystemkhakimagdalenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Female Voc DiagramDocument3 pagesFemale Voc DiagramAngie Sanchez-GalvezPas encore d'évaluation
- Maternal and ChildDocument20 pagesMaternal and ChildpaderamosPas encore d'évaluation
- This Is It - Myoma Case PresentationDocument93 pagesThis Is It - Myoma Case Presentationapi-1976296791% (11)
- Myoma CaseDocument111 pagesMyoma Caseapi-1976296750% (2)
- PROGNOSISDocument2 pagesPROGNOSISapi-19762967Pas encore d'évaluation
- IV. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument1 pageIV. Anatomy and Physiologyapi-19762967Pas encore d'évaluation
- Myoma CaseDocument111 pagesMyoma Caseapi-1976296750% (2)
- Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plansapi-19762967Pas encore d'évaluation
- Case PresentationDocument50 pagesCase Presentationapi-19762967Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4.discharge PlanninngDocument1 page4.discharge Planninngapi-19762967Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prognosis and EvaluationDocument2 pagesPrognosis and Evaluationapi-19762967Pas encore d'évaluation
- PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiologyapi-19762967100% (1)
- AnatomyDocument1 pageAnatomyapi-19762967Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cervical MucusDocument24 pagesCervical MucusRgn McklPas encore d'évaluation
- Development Reproductive SystemsDocument59 pagesDevelopment Reproductive SystemsAli AbdElnaby SalimPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive SystemDocument35 pagesReproductive SystemNabeel UddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Screenshot 2022-11-30 at 00.28.46Document3 pagesScreenshot 2022-11-30 at 00.28.46prisca wibawaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sperma Bab IvDocument7 pagesSperma Bab IvAmelia nur safitri100% (1)
- Concise Clinical Embryology An Integrated Case Based Approach Mar 18 2021 - 0323696155 - Elsevier 1St Edition Torchia MSC PHD Full ChapterDocument68 pagesConcise Clinical Embryology An Integrated Case Based Approach Mar 18 2021 - 0323696155 - Elsevier 1St Edition Torchia MSC PHD Full Chapterraymond.flores626100% (4)
- Achiever Maza Minor-02 04 June SoDocument6 pagesAchiever Maza Minor-02 04 June SoJeetraj SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam MCQ عين شمس + AnswersDocument118 pagesExam MCQ عين شمس + AnswersIsmail Ahmed0% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJade AltarejosPas encore d'évaluation
- HYPOSPADIUSDocument4 pagesHYPOSPADIUSODONG MARTINPas encore d'évaluation
- TJS Matungao, Bulakan, Bulacan: Name: Grade and Section: I. Matching TypeDocument3 pagesTJS Matungao, Bulakan, Bulacan: Name: Grade and Section: I. Matching Typenina lykka calaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Sonography of The Normal Female Pelvis Disclosures: Rochelle F. Andreotti M.DDocument18 pagesSonography of The Normal Female Pelvis Disclosures: Rochelle F. Andreotti M.DDian Putri NingsihPas encore d'évaluation
- Lifetime Changes in The Vulva and Vagina: ReviewDocument8 pagesLifetime Changes in The Vulva and Vagina: ReviewAblfazl KianiPas encore d'évaluation
- L5 The Menstrual CycleDocument12 pagesL5 The Menstrual CycleKatrina Salas MiclatPas encore d'évaluation
- Personal Project On in Vitro FertilizationDocument41 pagesPersonal Project On in Vitro FertilizationEva Isabelle Suchecki54% (13)
- Lec 10 Medico Legal Aspects of Sex CrimeDocument29 pagesLec 10 Medico Legal Aspects of Sex CrimePaula BalmeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Reproduction Male Reproductive System: (Continued)Document11 pagesHuman Reproduction Male Reproductive System: (Continued)Meeta DeviPas encore d'évaluation
- Cat ReproductionDocument22 pagesCat ReproductionChiela BagnesPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Reproduction: Type A: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesHuman Reproduction: Type A: Multiple Choice Questionsriya sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Document19 pagesThe Reproductive System The Reproductive System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1lourd nabPas encore d'évaluation
- Vulva Vagina (Disambiguation)Document53 pagesVulva Vagina (Disambiguation)ronaldo palpialy1Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH 19Document5 pagesCH 19Ryan Carlo IbayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter:4 Reproductive Health: Assisted Reproductive Technology (Art)Document11 pagesChapter:4 Reproductive Health: Assisted Reproductive Technology (Art)Nikhil BijuPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypospadias and The Embryogenesis of The Penile UrethraDocument6 pagesHypospadias and The Embryogenesis of The Penile UrethraNailahRahmahPas encore d'évaluation