Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
FRUSEMIDE
Transféré par
krishna chandrakani100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
226 vues3 pagesFrusemide is a strong diuretic used to treat edema caused by heart failure, liver or kidney disease, and hypertension. It works by increasing urine output, which reduces blood pressure by lowering fluid volume. Common side effects include dizziness, weakness, and electrolyte imbalances. Special precautions are needed in pregnancy, children, the elderly, and with concurrent use of other drugs due to interaction risks.
Description originale:
FRUSEMIDE
(LASIX)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentFrusemide is a strong diuretic used to treat edema caused by heart failure, liver or kidney disease, and hypertension. It works by increasing urine output, which reduces blood pressure by lowering fluid volume. Common side effects include dizziness, weakness, and electrolyte imbalances. Special precautions are needed in pregnancy, children, the elderly, and with concurrent use of other drugs due to interaction risks.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
226 vues3 pagesFRUSEMIDE
Transféré par
krishna chandrakaniFrusemide is a strong diuretic used to treat edema caused by heart failure, liver or kidney disease, and hypertension. It works by increasing urine output, which reduces blood pressure by lowering fluid volume. Common side effects include dizziness, weakness, and electrolyte imbalances. Special precautions are needed in pregnancy, children, the elderly, and with concurrent use of other drugs due to interaction risks.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
FRUSEMIDE
It is a strong diuretic but lacks specific anti-hypertensive
action. ( has no direct effect on resistance vessels).
Thus anti hypertensive efficacy is directly related to
diuretic potency.
Fall in BP is due only to reduced plasma extracellular fluid
volume.
INDICATIONS :
Oedema in congestive heart failure,
hepatic and renal disease.
Cerebral oedema,
forced diuresis for poisoning,
toxaemia of pregnancy.
Hypertension and hypertensive crisis.
DOSAGE :
ADULT : 20-80 mg as a single dose. if satisfactory
results are not obtained than 20-40 mg after 6 hrs.
INFANT & CHILDREN : 2mg /kg body wt increased
by 1-2 mg/kg 6-8 hrs after the previous dose.
MAX : 40 mg /day.
CONTRA INDICATIONS :
Renal failure with anuria,
potassium deficiency ( i.e. malnutrition, diarrhoea).
Hypersensitivity to frusemide & sulphonamides,
Hypokalaemia
Hyponatraemia
Hepatic coma
Hypovolaemia with/without hypotension.
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS :
Electrolyte imbalance (monitor serum electrolyte)
Paediatrics : can be used safely.
Pregnancy : Contraindicated.
Lactation : Used if clearly indicated.
Elderly : Increased risk of side effects. Dose to be reduced.
SIDE EFFECTS :
Vertigo.
Visual impairment.
Sodium deficiency may cause orthostatic hypotension.
Calf muscle cramps.
Anorexia.
Weakness.
Dizzinesss.
Drowsiness.
Vomiting.
hyperuricaemia reduced glucose tolerance.
Deafness.
DRUG INTERACTIONS :
Aminoglycoside antibiotics may enhance the risk of
deafness, potentiates anti hypertensives, causes litihum
toxicity in those receiving both drugs. With cotrimoxazole
produces thrombocytopenia. NSAIDs diminish the diuretic
effects.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Digoxin Drug CardDocument1 pageDigoxin Drug CardMahsa Ahmadzadeh100% (2)
- Emergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Document13 pagesEmergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Marichu BajadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Digoxin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDigoxin Drug StudyHarline GonzagaPas encore d'évaluation
- AmloDocument1 pageAmloamy navajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Serratiopeptidase Is An Enzyme Having AntiDocument12 pagesSerratiopeptidase Is An Enzyme Having Antidracula386Pas encore d'évaluation
- BrivaracetamDocument110 pagesBrivaracetamBendisDacicaPas encore d'évaluation
- EzetimibeDocument3 pagesEzetimibeapi-3797941Pas encore d'évaluation
- Urokinase Dosage WheelDocument2 pagesUrokinase Dosage WheelNidhiPas encore d'évaluation
- DextroseDocument1 pageDextroseAdrianne BazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Indications Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilityDocument1 pageDrug Indications Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilityJona Phie Domingo MonteroPas encore d'évaluation
- QuinidineDocument5 pagesQuinidineCharleen Joyce Usacdin0% (1)
- Lanoxin (Digoxin)Document3 pagesLanoxin (Digoxin)E100% (5)
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityChelsea WuPas encore d'évaluation
- PrimaquineDocument3 pagesPrimaquineVijayakumar NsPas encore d'évaluation
- Miglitol (Glyset)Document1 pageMiglitol (Glyset)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Er-Drug StudyDocument41 pagesEr-Drug Studyrc_lacampuinganyahooPas encore d'évaluation
- Albendazol PDFDocument8 pagesAlbendazol PDFDANIBATAPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsKatrina PoncePas encore d'évaluation
- ENT Drug StudyDocument3 pagesENT Drug StudyMcmac YangoPas encore d'évaluation
- GravolDocument5 pagesGravoldrugcardrefPas encore d'évaluation
- Generic / Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesGeneric / Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJommel Ryan Corpus LumibaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument7 pagesAntimalarial DrugsHilmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Prazosin Tablet (Prazosin)Document6 pagesPrazosin Tablet (Prazosin)Chenta Bulan MerinduPas encore d'évaluation
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayPas encore d'évaluation
- IsoprenalineDocument2 pagesIsoprenalineImmanuel Victor GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- FlagylDocument3 pagesFlagylAdrianne BazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency ContraceptionDocument7 pagesEmergency Contraceptionyogita_itsme7560Pas encore d'évaluation
- CholestyramineDocument1 pageCholestyramineKatie McPeekPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study On EPINEPHRINEDocument6 pagesDrug Study On EPINEPHRINEshadow gonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- Isoprenaline Infusion 2016Document3 pagesIsoprenaline Infusion 2016Glory Claudia KarundengPas encore d'évaluation
- Antianginal Drugs - Classification and MechanismDocument1 pageAntianginal Drugs - Classification and MechanismAhmed YT100% (1)
- ClindamycinDocument3 pagesClindamycinShaira TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study - CaseDocument9 pagesDrug Study - CaseMay EvelynPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Profile - AmantadinDocument14 pagesDrug Profile - AmantadinAna TanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System (RAAS)Document22 pagesThe Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System (RAAS)Chandra pranataPas encore d'évaluation
- IndomethacinDocument9 pagesIndomethacinQuiKe PvPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Pre Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCase Pre Drug StudyJoule PeirrePas encore d'évaluation
- Carbidopa Levodopa SinemetDocument3 pagesCarbidopa Levodopa SinemetTodd ColePas encore d'évaluation
- Sick Sinus Syndrome 1Document23 pagesSick Sinus Syndrome 1Salman HabeebPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study - CapDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CapABARAJPas encore d'évaluation
- AtroventDocument1 pageAtroventSheri490100% (1)
- Pepcid IV FamotidineDocument2 pagesPepcid IV FamotidineAdrianne BazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study 1Document15 pagesDrug Study 1Czarina Isabela TuazonPas encore d'évaluation
- CiprofloxacinDocument3 pagesCiprofloxacinapi-3797941Pas encore d'évaluation
- (Generic Name) ® Drotaverine 40mgDocument2 pages(Generic Name) ® Drotaverine 40mgSangar Sardar100% (1)
- Drug Card ToradolDocument2 pagesDrug Card ToradolAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Anxiolytic and Hypnotic AgentsDocument50 pagesAnxiolytic and Hypnotic AgentsMoxie Macado100% (1)
- Pharma CardsDocument5 pagesPharma CardsazanchePas encore d'évaluation
- HaemaccelinfDocument9 pagesHaemaccelinfSisca YulistianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study KeterolacDocument2 pagesDrug Study KeterolacKillerBall RegioPas encore d'évaluation
- Metoclopramide (Reglan)Document1 pageMetoclopramide (Reglan)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Phenobarbitone InjectionDocument13 pagesPhenobarbitone InjectionBrian HarrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Furosemide Mims EngDocument17 pagesFurosemide Mims EngNur Ilmi SofiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanPas encore d'évaluation
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudySharwen_R_Rome_5572Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyEzshkha OnguePas encore d'évaluation
- LisinoprilDocument3 pagesLisinoprilLIEZEL GRACE VELAYOPas encore d'évaluation
- Pritor PlusDocument4 pagesPritor Plusianecunar100% (2)
- Dobutamine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageDobutamine Hydrochloridekrishna chandrakaniPas encore d'évaluation
- DopamineDocument2 pagesDopaminekrishna chandrakani100% (1)
- NicorandilDocument2 pagesNicorandilkrishna chandrakani100% (1)
- Mechanical Ventilation For NursingDocument55 pagesMechanical Ventilation For NursingAmira AttyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hiv Infection in PediatricsDocument44 pagesHiv Infection in Pediatricskrishna chandrakaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Orientation Program: On Eye DonationDocument18 pagesOrientation Program: On Eye Donationkrishna chandrakaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Growth & Development Difference & PrinciplesDocument30 pagesGrowth & Development Difference & Principleskrishna chandrakani100% (5)
- Anatomy & Physiology QuestionsDocument10 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Questionskrishna chandrakani100% (2)
- Child Hood Accidents Prevention in ChildrenDocument5 pagesChild Hood Accidents Prevention in Childrenkrishna chandrakaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Weaning Food PPT & Health TalkDocument26 pagesWeaning Food PPT & Health Talkkrishna chandrakani81% (32)
- NTR University BSC Nursing Supplymentary June 2013 ResultsDocument89 pagesNTR University BSC Nursing Supplymentary June 2013 Resultskrishna chandrakani100% (1)
- SchizophreniaDocument36 pagesSchizophreniakrishna chandrakani86% (7)
- Incubator CareDocument4 pagesIncubator CareBasant karn94% (33)
- 1st2nd3rdand4thYrBSc (Nursing) 4YDC (NEWSCHEME) Nov2012Document229 pages1st2nd3rdand4thYrBSc (Nursing) 4YDC (NEWSCHEME) Nov2012krishna chandrakaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Hepatitis BDocument3 pagesHepatitis Bkrishna chandrakani100% (1)
- Eugenio NCP 2Document2 pagesEugenio NCP 2Bethrice MelegritoPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Medical StudentsDocument132 pagesInternational Journal of Medical StudentsDan BoicuPas encore d'évaluation
- Q1. Chronic Disease Prediction Using Administrative Data and Graph Theory, The Case of Type 2 DiabetesDocument12 pagesQ1. Chronic Disease Prediction Using Administrative Data and Graph Theory, The Case of Type 2 DiabetesFahmiPas encore d'évaluation
- West Bengal COVID-19 RestrictionsDocument2 pagesWest Bengal COVID-19 RestrictionsNDTV80% (10)
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) : The Impact and Role Of: Mass Media During The PandemicDocument3 pagesCoronavirus Disease (COVID-19) : The Impact and Role Of: Mass Media During The PandemicShariz DinoyoPas encore d'évaluation
- OET Reading Test 13 Part ADocument6 pagesOET Reading Test 13 Part ATavi Nicolae100% (1)
- A Review On Influence of Ahara Diet On Mental HealDocument4 pagesA Review On Influence of Ahara Diet On Mental HealPablo M. MauroPas encore d'évaluation
- Tropical MCQS: C. Visceral LeishmaniasisDocument29 pagesTropical MCQS: C. Visceral Leishmaniasisساره ابوالقاسمPas encore d'évaluation
- מצגת מערכת עיכולDocument74 pagesמצגת מערכת עיכולnataliya36Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chinese Food Therapy RX For Self HealingDocument117 pagesChinese Food Therapy RX For Self HealingDiego Alejandro Gomez Arandia100% (4)
- This Study Resource Was: AssignmentDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: AssignmentJOEY MEAD ARUGAYPas encore d'évaluation
- AB-M02-CH2.3-LIVER PATH-Focal Abnormalities PDFDocument40 pagesAB-M02-CH2.3-LIVER PATH-Focal Abnormalities PDFThomas AndersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 1 Focus On The Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 1 Focus On The Digestive SystemJane Limsan Paglinawan67% (3)
- Chapter One 1.1 Background of The StudyDocument65 pagesChapter One 1.1 Background of The StudyIgbani VictoryPas encore d'évaluation
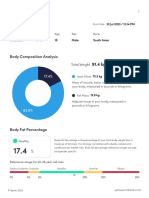
- Bodyfat PercentageDocument4 pagesBodyfat PercentageBadass PolapainPas encore d'évaluation
- Elias, Adikwu, Et Al. 2014Document15 pagesElias, Adikwu, Et Al. 2014priya panalePas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Template - Jurnal SaintekesDocument5 pagesTugas Template - Jurnal Saintekesnoor sidik putraPas encore d'évaluation
- Case StudyDocument6 pagesCase StudyLauren HollidgePas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesAdvanced Pathophysiologyulc33% (3)
- Autoimmune Hemolytic AnemiasDocument13 pagesAutoimmune Hemolytic Anemiasb101103139Pas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Educational Programme On Patients HealtDocument14 pagesImpact of Educational Programme On Patients HealtArpita KulkarniPas encore d'évaluation
- IUGRDocument10 pagesIUGRAiman ArifinPas encore d'évaluation
- Lactobacillus Salivarius NK02 A Potent Probiotic For ClinicalDocument11 pagesLactobacillus Salivarius NK02 A Potent Probiotic For ClinicalHossein ShahbaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Kay Maam NitzDocument19 pagesCase Study Kay Maam NitzJay Villasoto100% (1)
- Death Certificate: Shaheed Monsur Ali Medical College HospitalDocument3 pagesDeath Certificate: Shaheed Monsur Ali Medical College HospitalBokul80% (5)
- Drugs in SportsDocument32 pagesDrugs in SportsBerlin AlonzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Members Habiba Jameel Raffia Tariq Amina Zahoor ZunairaDocument27 pagesGroup Members Habiba Jameel Raffia Tariq Amina Zahoor ZunairaMuiz SaddozaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tribal Health in IndiaDocument14 pagesTribal Health in IndiaGautam G JPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 - Spinal Column and Spinal Cord Injuries TestDocument3 pages7 - Spinal Column and Spinal Cord Injuries Testkamilkasim262Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ryan Retina 6t EdDocument3 568 pagesRyan Retina 6t EdANDREAPas encore d'évaluation