Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Botany Perennial Plant Trunk Woody Lumber Palms Tree Ferns Bananas Bamboo
Transféré par
sarahpierre10Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Botany Perennial Plant Trunk Woody Lumber Palms Tree Ferns Bananas Bamboo
Transféré par
sarahpierre10Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
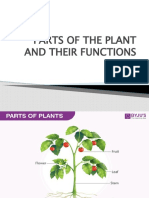
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, supporting branches and
leaves in most species. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including
only woody plants, only plants that are usable as lumber or only plants above a specified height.
At its broadest, trees include the taller palms, the tree ferns, bananas and bamboo.
A tree typically has many secondary branches supported clear of the ground by the trunk. This
trunk typically contains woody tissue for strength, and vascular tissue to carry materials from
one part of the tree to another. For most trees it is surrounded by a layer of bark which serves
as a protective barrier. Below the ground, the roots branch and spread out widely; they serve to
anchor the tree and etract moisture and nutrients from the soil. Above ground, the branches
divide into smaller branches and shoots. The shoots typically bear leaves, which capture light
energy and convert it into sugars by photosynthesis, providing the food for the tree!s growth and
development. Flowers and fruit may also be present, but some trees such as conifers instead
have pollen cones and seed cones, and others such as tree ferns produce sporesinstead.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- TreeDocument1 pageTreemigzpontPas encore d'évaluation
- Botany Perennial Plant Trunk Woody Secondary Growth Lumber Palms Tree Ferns Bananas Bamboos Coast Redwood HyperionDocument1 pageBotany Perennial Plant Trunk Woody Secondary Growth Lumber Palms Tree Ferns Bananas Bamboos Coast Redwood Hyperionaashikapriya3037Pas encore d'évaluation
- Teoria o Analiza AsdaDocument1 pageTeoria o Analiza AsdaCarmenPas encore d'évaluation
- TreesDocument2 pagesTreesTanvi PawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Asdasfasfasfas 213124asdasd 1241241241212412412412 12412124124 Dzsd123123 ZF S Fsadasdsada Asf DasdasdasdxzaxzcazczacaDocument1 pageAsdasfasfasfas 213124asdasd 1241241241212412412412 12412124124 Dzsd123123 ZF S Fsadasdsada Asf DasdasdasdxzaxzcazczacaCarmenPas encore d'évaluation
- Jump To Navigation Jump To Search: For Other Uses, SeeDocument2 pagesJump To Navigation Jump To Search: For Other Uses, Seemansi bavliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Botany Perennial Plant Trunk Woody Lumber Palms Tree Ferns Bananas Bamboo Vascular TissueDocument1 pageBotany Perennial Plant Trunk Woody Lumber Palms Tree Ferns Bananas Bamboo Vascular Tissuescriby765Pas encore d'évaluation
- Asdasfasfasfas 213124asdasd 12412412412sdsa Asdasdasfasfas DZSDZ ZF S Fsadasdsada Asf DasdasdasdxzaxzcazczacaDocument1 pageAsdasfasfasfas 213124asdasd 12412412412sdsa Asdasdasfasfas DZSDZ ZF S Fsadasdsada Asf DasdasdasdxzaxzcazczacaCarmenPas encore d'évaluation
- Asdasfasfasfas 213124asdasd 12412412412sdsa Asdasdasfasfas DZSDZ ZF S Fsadasdsada Asf DasdasdasdxzaxzcazczacaDocument1 pageAsdasfasfasfas 213124asdasd 12412412412sdsa Asdasdasfasfas DZSDZ ZF S Fsadasdsada Asf DasdasdasdxzaxzcazczacaCarmenPas encore d'évaluation
- Asdasfasfasfas 213124asdasd 12412412412sdsa Asdasdasfasfas DZSDZ ZF S Fsadasdsada Asf DasdasdasdxzaxzcazczacaDocument1 pageAsdasfasfasfas 213124asdasd 12412412412sdsa Asdasdasfasfas DZSDZ ZF S Fsadasdsada Asf DasdasdasdxzaxzcazczacaCarmenPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm SolvedDocument8 pagesMidterm SolvedHamna FarooqPas encore d'évaluation
- Asdasfasfasfas 213124asdasd 12412412412sdsa Asdasdasfasfas DZSDZ ZF S Fsadasdsada Asf DasdasdasdxzaxzcazczacaDocument1 pageAsdasfasfasfas 213124asdasd 12412412412sdsa Asdasdasfasfas DZSDZ ZF S Fsadasdsada Asf DasdasdasdxzaxzcazczacaCarmenPas encore d'évaluation
- Treese and Earth PDFDocument29 pagesTreese and Earth PDFDelos NourseiPas encore d'évaluation
- TreeDocument33 pagesTreeToday NewsPas encore d'évaluation
- Upload 4Document24 pagesUpload 4Jurydel RamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jump To Navigationjump To Search: For Other Uses, SeeDocument7 pagesJump To Navigationjump To Search: For Other Uses, SeeBea KaPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF TreeDocument8 pagesPDF TreeChetan RanePas encore d'évaluation
- Wikipedia Page For A Tree.Document25 pagesWikipedia Page For A Tree.CoolioPas encore d'évaluation
- Proper Planting, Growing and Caring of TreesDocument35 pagesProper Planting, Growing and Caring of Treesbeilla swanPas encore d'évaluation
- TreeDocument23 pagesTreegraphicsgriffin100% (1)
- How Does A Tree Grow?: Glossary of Tree TermsDocument3 pagesHow Does A Tree Grow?: Glossary of Tree TermsecarggnizamaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Tree?Document13 pagesWhat Is Tree?Francis Orly LiaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Jump To Navigationjump To Search: For Other Uses, SeeDocument3 pagesJump To Navigationjump To Search: For Other Uses, SeedapaluipaluiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Life of Trees: StructureDocument1 pageThe Life of Trees: StructurePatricia LeahDalyPas encore d'évaluation
- TreesDocument1 pageTreesMidPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Stem - WikipediaDocument29 pagesPlant Stem - WikipediaBashiir NuurPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethiopian Technical University General Wingate Satellite Campus Individual Assignment of Fundamental ForestryDocument14 pagesEthiopian Technical University General Wingate Satellite Campus Individual Assignment of Fundamental ForestryBebi WakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document5 pagesChapter 4Lebanan Aprille MariePas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of A LeafDocument1 pageParts of A LeafMelanio VillaverdePas encore d'évaluation
- Navigation Search: Jump ToDocument3 pagesNavigation Search: Jump ToMari Creon A. BaumgardnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Which Root System Is Best Adapted For Anchorage? Why Do You Say So? (N.D.) - Https://StudyDocument2 pagesWhich Root System Is Best Adapted For Anchorage? Why Do You Say So? (N.D.) - Https://StudyJhey SiPas encore d'évaluation
- Andamun Tle106 ReportDocument34 pagesAndamun Tle106 ReportNaharia RangirisPas encore d'évaluation
- MWN 0 Wu 2 yDocument12 pagesMWN 0 Wu 2 yИван БилецкийPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of The Plant and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesParts of The Plant and Their Functionsmariathea hornilla100% (1)
- Leaf - WikipediaDocument168 pagesLeaf - WikipediaBashiir NuurPas encore d'évaluation
- Specialized StemDocument2 pagesSpecialized StemAldrin Paul TomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Larix Decidua: Coniferous DeciduousDocument24 pagesLarix Decidua: Coniferous DeciduousJay RonssonPas encore d'évaluation
- STEMS PartsDocument3 pagesSTEMS PartsKaren ParkPas encore d'évaluation
- This Article Is About The Part of A PlantDocument51 pagesThis Article Is About The Part of A PlantTess TubieronPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.3 Support in PlantsDocument17 pages2.3 Support in PlantsMichelle ChinPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Botany 2Document92 pagesBasic Botany 2Michael OduorPas encore d'évaluation
- KELOMPOK 6 Offering I: "Plant Organs: Roots, Stems, and Leaves"Document3 pagesKELOMPOK 6 Offering I: "Plant Organs: Roots, Stems, and Leaves"Dewi Sekar MiasihPas encore d'évaluation
- PLANTDocument23 pagesPLANTAngelito HalmainPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 Cycles and Growth How A Forest Works: Tree BiologyDocument8 pagesUnit 3 Cycles and Growth How A Forest Works: Tree Biologyİsviçredeki IşıkPas encore d'évaluation
- Main Function of LeavesDocument3 pagesMain Function of LeavesAndrea AnoverPas encore d'évaluation
- Botany StemDocument36 pagesBotany Stemartadiel28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Growth Eudicot ConiferousDocument2 pagesSecondary Growth Eudicot Coniferousmansi bavliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Commercial Food Crops in The PhilippinesDocument34 pagesTypes of Commercial Food Crops in The Philippinesmarjorie gomezPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 PoaceaeDocument6 pages13 Poaceaeugochuks2014Pas encore d'évaluation
- Botany Handbook For Florida PDFDocument23 pagesBotany Handbook For Florida PDFBá Tùng Phan100% (2)
- Root Modifications Storage RootsDocument17 pagesRoot Modifications Storage Rootsmbg1110100% (1)
- Specialized Roots: Aerating Roots of ADocument2 pagesSpecialized Roots: Aerating Roots of ASelenebluePas encore d'évaluation
- Acs Lab No. 3Document6 pagesAcs Lab No. 3Karyl GregorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Botany 101Document7 pagesBotany 101Gladdin ChloePas encore d'évaluation
- How Plants SurviveDocument16 pagesHow Plants SurviveGilbertPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To CarpentryDocument23 pagesIntroduction To CarpentryClarence JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- PLC 7 and 8Document21 pagesPLC 7 and 8rheyukijPas encore d'évaluation
- Woody Stems and RootsDocument12 pagesWoody Stems and RootsHailey CoutuPas encore d'évaluation
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 4Document18 pagesCSO Olympiad Book For Class 4shinu goyalPas encore d'évaluation