Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ecologic Model and Pathophy1revised
Transféré par
Shermane Criszen F. Sallan0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
10 vues2 pagesECOLOGIC model of Pneumonia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentECOLOGIC model of Pneumonia
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
10 vues2 pagesEcologic Model and Pathophy1revised
Transféré par
Shermane Criszen F. SallanECOLOGIC model of Pneumonia
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
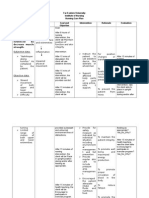
ECOLOGIC MODEL
Interpretation and analysis:
This is useful for examining causes of disease in an individual. It is useful in predicting illness
rather than promoting wellness, although identification of risk factors that result from the interaction of
agent, host environment are helpful in promoting and maintaining health. Because each of the agent-host-
environment factors constantly interacts with others, health is an ever-changing state. The agent, host and
environment interact in ways that create risk factors, and understanding these is important for the
promotion and maintenance of health. An agent is an environmental factor or stressor that must be present
or absent for an illness to occur. A host is a living organism capable of being infected or affected by an
agent. The host reaction is influenced by family history, age, and health habits.
! is a "# year old male who lived in complained of difficulty of breathing last $uly %&, '&().
*atient have productive cough, associated with hoarseness, loss of appetite, weight loss and dysphagia.
The client usually smoked ( box of cigarettesper day and drinks alcohol. Bacteria t that lives in clients
nose, mouth, sinuses, or the surrounding environment entered the lungs and create pneumonia.
+odification of lifestyle including drinking enough amount of water ,at least # glasses- a day,
limiting intake of soft drinks and salty foods, exercising daily and eating a lot of vegetables as well as
fish ,which means decrease consumption of cholesterol laden foods- is highly recommended to alleviate
if not eradicate the condition of the patient. In addition, regular checkups would monitor the patient.s
health condition and would more likely prevent the aggravation of the disease.
/moke
Alcohol
Bacterial
Pneumonia,
Streptococcus
pneumoniae
(pneumococcus)
!, male "# y0o
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:
Predisposing Factor
Age
Sex
Precipitating Factor
Lifestyle
Contributing
Factors
Bacteria
Streptococcus
pneumoniae
Organism enters
the respiratory tract
through
inspiration/aspiratio
n
Alteration in net bacterial lung
resistance caused by either:
ecreased bactericidal
ability of the al!eolar
macrophages
"xtreme !irulence of the
bacteria
#ncreased susceptibility of
host to infection
Acute in$ammation occurs that causes
excess %ater and plasma proteins go to
the dependent areas of the lo%er lobes
&BCs' (brin' and polymorphonuclear
leu)ocytes in(ltrate the al!eoli
Larnyngeal mass t/c Pneumonia
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- NCPPimpaired DocleaderDocument4 pagesNCPPimpaired DocleaderShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Leadership and ManagementTableofcontentsDocument1 pageLeadership and ManagementTableofcontentsShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar - Budget ProposalDocument2 pagesSeminar - Budget ProposalShermane Criszen F. Sallan0% (1)
- Opd Case PresDocument25 pagesOpd Case PresShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tranexamic AcidDocument2 pagesTranexamic AcidShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Feunrmf OpdDocument12 pagesDrugs Feunrmf OpdShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar - Budget ProposalDocument2 pagesSeminar - Budget ProposalShermane Criszen F. Sallan0% (1)
- Sample AttendanceDocument2 pagesSample AttendanceShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Writing ProcessDocument17 pagesThe Writing ProcessShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecologic Model of PneumoniaDocument3 pagesEcologic Model of PneumoniaShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Family Health NursingDocument15 pagesFamily Health NursingShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Body Parts Assessment Technique Interpretation Analysis: Assessment of Head To ToeDocument15 pagesBody Parts Assessment Technique Interpretation Analysis: Assessment of Head To ToeShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaShermane Criszen F. Sallan100% (4)
- Ecologic Model of PneumoniaDocument3 pagesEcologic Model of PneumoniaShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesActivity IntoleranceShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecologic Model of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesEcologic Model of PneumoniaShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecologic Model and Pathophy1Document2 pagesEcologic Model and Pathophy1Shermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- RFBDocument1 pageRFBShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- GoalDocument5 pagesGoalShermane Criszen F. SallanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)