Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sklerometar Civil Construction
Transféré par
JunctionTDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Sklerometar Civil Construction
Transféré par
JunctionTDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
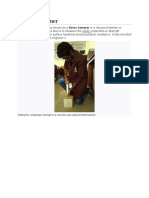
A Schmidt hammer, also known as a Swiss hammer or a rebound hammer, is a device to
measure the elastic properties or strength of concrete or rock, mainly surface hardness and
penetration resistance.
The hammer measures the rebound of a spring-loaded mass impacting against the surface of the
sample. The test hammer will hit the concrete at a defined energy. Its rebound is dependent on
the hardness of the concrete and is measured by the test equipment. By reference to the
conversion chart, the rebound value can be used to determine the compressive strength. When
conducting the test the hammer should be held at right angles to the surface which in turn should
be flat and smooth. The rebound reading will be affected by the orientation of the hammer, when
used in a vertical position (on the underside of a suspended slab for example) gravity will
increase the rebound distance of the mass and vice versa for a test conducted on a floor slab.
The Schmidt hammer is an arbitrary scale ranging from 10 to 100. Schmidt hammers are
available from their original manufacturers in several different energy ranges. These include: (i)
Type L-0.735 Nm impact energy, (ii) Type N-2.207 Nm impact energy; and (iii) Type M-29.43 Nm
impact energy.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Rock Blasting - A Practical Treatise On The Means Employed In Blasting Rocks For Industrial PurposesD'EverandRock Blasting - A Practical Treatise On The Means Employed In Blasting Rocks For Industrial PurposesPas encore d'évaluation
- A Schmidt HammerDocument3 pagesA Schmidt Hammersandy22decedmber100% (1)
- Schmidt Rebound HammerDocument16 pagesSchmidt Rebound HammermorchedtounsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Job7 GeoDocument4 pagesJob7 GeohafizsyedrizwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Origins of The Schmidt Hammer TestDocument1 pageOrigins of The Schmidt Hammer TestAniz DonuTzPas encore d'évaluation
- Schmidt Rebound Hammer TestDocument2 pagesSchmidt Rebound Hammer Testfazil pPas encore d'évaluation
- Rebound HammerDocument6 pagesRebound Hammerahmadfarriz100% (1)
- Rebound Hammer TestDocument8 pagesRebound Hammer TestEvello MercanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sop of Rebound Hammer TestDocument3 pagesSop of Rebound Hammer Testmohd waseemPas encore d'évaluation
- Jumah - NDT - HW1Document11 pagesJumah - NDT - HW1Jumah Musdif TheirPas encore d'évaluation
- Rebound Hammer Test On ConcreteDocument10 pagesRebound Hammer Test On ConcreteSunil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Testing: Non-DestructiveDocument46 pagesConcrete Testing: Non-DestructivekevalPas encore d'évaluation
- Rebound Hammer TestDocument14 pagesRebound Hammer TestChalakAhmed100% (6)
- Rebound Hammer Seminar FinalDocument24 pagesRebound Hammer Seminar FinalsajithPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015.08 POV Gupta SinghDocument10 pages2015.08 POV Gupta SinghNidDouPas encore d'évaluation
- Rebound Hammer TestDocument4 pagesRebound Hammer TestMd Imtiazul AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- NDT by Rebound HammerDocument12 pagesNDT by Rebound HammerPriye RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction Materials and Testing Lab 1Document12 pagesConstruction Materials and Testing Lab 1Doreen Rose B. AVANCEPas encore d'évaluation
- Institute of Civil EngineerinDocument7 pagesInstitute of Civil Engineerinheherson juanPas encore d'évaluation
- Schmidt Hammer: Elastic Concrete RockDocument15 pagesSchmidt Hammer: Elastic Concrete Rockhimanshu tonkPas encore d'évaluation
- Surface Hardness and Related Properties of ConcretDocument8 pagesSurface Hardness and Related Properties of ConcretJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Rebound Hammer PDFDocument6 pagesRebound Hammer PDFAnonymous AJy7S7flB100% (2)
- CPT PDFDocument6 pagesCPT PDFkhemankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Rebound HammerDocument5 pagesRebound HammerSunil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 12Document8 pagesLecture 12Mechanical ZombiePas encore d'évaluation
- LECTURE 1-Rock Mech. PTR 339-2021-2022Document23 pagesLECTURE 1-Rock Mech. PTR 339-2021-2022Marco PlaysPas encore d'évaluation
- ConcreteDocument3 pagesConcretedritz tevesPas encore d'évaluation
- Rebound Hammer (NDT)Document2 pagesRebound Hammer (NDT)rexdindigulPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Pile FoundationDocument77 pagesChapter 6 Pile FoundationZeleke TaimuPas encore d'évaluation
- Schmidt Hammer AbbeyDocument4 pagesSchmidt Hammer AbbeyStephen OgaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Rebound Hammer TestDocument7 pagesRebound Hammer TestP.K.MallickPas encore d'évaluation
- NDT On Concrete: Destructive TestingDocument11 pagesNDT On Concrete: Destructive TestingMITHLESH KUMAR KESHARIPas encore d'évaluation
- Influencie of Shearing Rate On Interfacial Friction Between Sand and SteelDocument16 pagesInfluencie of Shearing Rate On Interfacial Friction Between Sand and SteelMaríaJosé Toledo ArcicPas encore d'évaluation
- S Kahraman 1999Document10 pagesS Kahraman 1999Siva PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Rebound Hammer Test - MOSDocument6 pagesRebound Hammer Test - MOSFaizah Sophi100% (1)
- Concrete Rebound Hammers, Schmidt HammersDocument4 pagesConcrete Rebound Hammers, Schmidt HammersDonny. B TampubolonPas encore d'évaluation
- High Strain Dynamic TestingDocument3 pagesHigh Strain Dynamic TestingWaqas SadiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil On Heel Active Lateral Soil Pressure: Friction Capacity!Document3 pagesSoil On Heel Active Lateral Soil Pressure: Friction Capacity!Rup JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rebound HammerDocument6 pagesRebound HammerDira AzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 5, Deep Foundation Part 1Document61 pagesWeek 5, Deep Foundation Part 1Aw Ting HuiPas encore d'évaluation
- Smidt HammerDocument9 pagesSmidt HammerSANDESHPas encore d'évaluation
- KSNR Amrut ShearDocument12 pagesKSNR Amrut ShearNanjund Rao KsPas encore d'évaluation
- Rebound Hammer Test Procedure For Concrete HardnessDocument4 pagesRebound Hammer Test Procedure For Concrete HardnessSite Engineer.2p2Pas encore d'évaluation
- JME - Volume 5 - Issue 1 - Pages 25-34 PDFDocument10 pagesJME - Volume 5 - Issue 1 - Pages 25-34 PDFAdji SutamaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Schmidt Hammer in Rock Material Characterization: Engineering Geology September 2005Document15 pagesThe Schmidt Hammer in Rock Material Characterization: Engineering Geology September 2005Adriel senciaPas encore d'évaluation
- DrillingDocument4 pagesDrillingHardik KarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Schmidt Hammer, Compressive Strength of Concrete Test Hammer, Concrete Test HammerDocument2 pagesSchmidt Hammer, Compressive Strength of Concrete Test Hammer, Concrete Test HammerRoberto CarlosPas encore d'évaluation
- Wk9 Bearing Capacity From Field TestsDocument35 pagesWk9 Bearing Capacity From Field TestsAli Saeed100% (2)
- A Laboratory Study of Rock Properties Affecting The Penetration Rate of Pneumatic Top Hammer DrillsDocument10 pagesA Laboratory Study of Rock Properties Affecting The Penetration Rate of Pneumatic Top Hammer DrillsFelipe MilhomemPas encore d'évaluation
- PRS ReviewerDocument9 pagesPRS ReviewerRose Diana DecenaPas encore d'évaluation
- For My Students:: Always Treat Your Parents With Utmost Respect and KindnessDocument36 pagesFor My Students:: Always Treat Your Parents With Utmost Respect and KindnessHefon MarketerPas encore d'évaluation
- Module-90A: Design of Rigid PavementsDocument6 pagesModule-90A: Design of Rigid PavementsSaddaqatPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement of in Situ Shear Strength of Rock Mass: Rajbal SinghDocument12 pagesMeasurement of in Situ Shear Strength of Rock Mass: Rajbal SinghManish Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- c1 Mechanical PropertiesDocument46 pagesc1 Mechanical PropertiesHusnal TaufiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Aggregate Impact Value TestDocument10 pagesAggregate Impact Value Testneeraja medapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No. 2 Object-To Determine The Impact Value of Course AggregateDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 2 Object-To Determine The Impact Value of Course AggregateShivang VivekPas encore d'évaluation
- Pme Lab 5Document5 pagesPme Lab 5Shakil Rahman AfidPas encore d'évaluation
- Schmidt HammerDocument8 pagesSchmidt HammerIllud DulliPas encore d'évaluation
- Mahmoud Khlifa Almoghazy Aliraqi 2 Civil Engineering Section 21Document119 pagesMahmoud Khlifa Almoghazy Aliraqi 2 Civil Engineering Section 21Nasir AlsalehPas encore d'évaluation
- Strength Tests On Concrete: (1) Compressive Strength Test (ASTM C 39)Document12 pagesStrength Tests On Concrete: (1) Compressive Strength Test (ASTM C 39)Asghar Hussain ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Glycol Correction FrictionDocument4 pagesGlycol Correction FrictionDave WestbrookPas encore d'évaluation
- AGS CatalogDocument68 pagesAGS CatalogBill100% (1)
- Top of Roof Beam Ceiling Line LineDocument1 pageTop of Roof Beam Ceiling Line Linedominguez margiePas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogxxx CXDocument254 pagesCatalogxxx CXChevronellePas encore d'évaluation
- Seismic Analysis of Multistoreyed RCC Building With Shear WallDocument10 pagesSeismic Analysis of Multistoreyed RCC Building With Shear WallParth SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Epoxy HR: Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesEpoxy HR: Technical Data SheetOrgünOzarPas encore d'évaluation
- DE ZG631 Lecture1 & 2 1578717151764Document26 pagesDE ZG631 Lecture1 & 2 1578717151764Ankith100% (1)
- Resina - TDS - 10200005 - EN - EN-WEICON-F2Document2 pagesResina - TDS - 10200005 - EN - EN-WEICON-F2kakonauta1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Intze Water Tank With Different Frame Staging SystemDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Intze Water Tank With Different Frame Staging SystemThe UnboxaholicPas encore d'évaluation
- BT Innovation Btspannschloss Web enDocument28 pagesBT Innovation Btspannschloss Web enartomiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ventilation Requirements For Indoor Pools: Technical FeatureDocument9 pagesVentilation Requirements For Indoor Pools: Technical FeaturetasabajcPas encore d'évaluation
- To Understand Different Components of VCR System and To Determine Its COPDocument6 pagesTo Understand Different Components of VCR System and To Determine Its COPMohit MinzPas encore d'évaluation
- Especificacion API 5lDocument44 pagesEspecificacion API 5ljpcc1986100% (1)
- Products Range.Document20 pagesProducts Range.sandraatef71Pas encore d'évaluation
- Planejados JoinvileDocument16 pagesPlanejados JoinvileThamires AlvesPas encore d'évaluation
- Arsitektur, Struktur & MEP-1Document128 pagesArsitektur, Struktur & MEP-1JokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Precast Concrete Solutions HumesDocument83 pagesPrecast Concrete Solutions Humespandeshantanu100% (4)
- Lecture 26.20081029.49084b9fe41bc1.76327325.20081029.4908941e13c981.68685807Document9 pagesLecture 26.20081029.49084b9fe41bc1.76327325.20081029.4908941e13c981.68685807Aditya CandratamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fillet WeldsDocument3 pagesFillet WeldsJohn Barroga100% (1)
- L3-Vapor Power SystemsDocument18 pagesL3-Vapor Power SystemsTarun MalviyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 5 Development of Beam Equations: Review Simple Beam Theory Two Methods To Develop Beam EquationsDocument35 pagesChap 5 Development of Beam Equations: Review Simple Beam Theory Two Methods To Develop Beam Equationsparin advaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Photoelasticity ReportDocument11 pagesPhotoelasticity ReportAnis Badshah100% (1)
- SSHL10Document1 pageSSHL10Joel SalvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System III (1.1)Document53 pagesPower System III (1.1)Emmanuel AgyemangPas encore d'évaluation
- Vocational Training ReportDocument56 pagesVocational Training ReportSaksham jainPas encore d'évaluation
- Vernaular Architecture AssamDocument44 pagesVernaular Architecture AssamdidarulPas encore d'évaluation
- CementDocument52 pagesCementSugumar BalasubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Halo Lighting Product Catalog 1974Document68 pagesHalo Lighting Product Catalog 1974Alan Masters100% (1)
- Jowatac 47160 TDSDocument2 pagesJowatac 47160 TDSTruong LeoPas encore d'évaluation
- RSB - 8th FloorDocument1 pageRSB - 8th FloorCyrillePas encore d'évaluation