Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Rocks and Minerals Website
Transféré par
api-264756260Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Rocks and Minerals Website
Transféré par
api-264756260Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Rocks and Minerals Webquest
Directions: Answer the following questions using the websites provided for each
question (the titles are hotlinks).
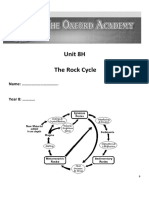
Rock Cycle
1. What are the three main types of rocks? Igneous, metamorphic, and secimentary
2. How does a sedimentary rock turn into a metamorphic rock? Heat and pressure
3. How does an igneous rock turn into a metamorphic rock? Heat and pressure
4. How do metamorphic rocks change into sedimentary rocks? After being weathered into
sediments they are then compacted and cemented into sedimentary rocks
5. How do igneous rocks change into sedimentary rocks? After being weathered into
sediments they are then compacted and cemented into sedimentary rocks
6. What is the beginning of the rock cycle? The end? The rock cycle doesnt really have a
definite starting place because you can start anywhere and go all the way around and the
rock cycle never ends.
View this Rock Cycle animation
7. Quick cooling forms many small what? Crystals
8. When you look at the desert monuments, what eroded away? The sandstone around them
9. The microscopic view of sandstone contains what two components? Sand grains and
cement
10. What two things are needed to turn igneous rock into metamorphic rock? Heat and
Pressure
Rocks
11. List and define the 6 key characteristics that can help you identify rocks within the three
main classes.
a. Crystals- Small, flat surfaces that are shiny or sparkly, like tiny mirrors.
b. Fossils- Imprints of leaves, shells, insects, or other items in the rock
c. Gas Bubbles- "Holes," like Swiss cheese, in the rock
d. Glassy Surface- A shiny and smooth surface, like colored glass.
e. Ribbonlike Layers- Straight or wavy stripes of different colors in the rock.
f. Sand/Pebbles- Individual stones, pebbles, or sand grains visible in the rock.
Rock Identification Key
12. For igneous rock, when magma cools slowly the crystals are large
13. For igneous rock, when magma cools quickly, the crystals are small and somtimes are a
type of black glass you cant see through
14. Of the types of igneous rock formed underground, which one is most familiar? Granite
15. When looking at sedimentary particle size, which material type has the largest particles and
which has the smallest particles? Sand has the largest and clay has the smallest
16. Which metamorphic rock forms under the highest temperature and highest pressure?
Gneiss
Mystery Rocks
17. How much of earths surface is made of sedimentary rock? About 75%
18. Give 4 examples of sediment that might eventually become sedimentary rock. Sand, mud,
pebbles, clay
19. What caused the appearance in the sedimentary rock in picture B? It is sandstone that used
to be a part of a beach during the Triassic period
Mohs Scale
20. What is Mohs Scale used for? To identify the hardness of minerals and their scratch
resistance
21. What mineral is a 10 on Mohs Scale? Diamonds
22. Give an example of a mineral with a hardness of 7 (according to Mohs Scale). Tell me about
that mineral.
23. If a mineral can scratch a penny, what number is it on Mohs Scale? 3.5
Streak
24. Sometimes the color and the streak of a mineral are very different. Which of the
examples shows a difference between color and streak? Specular Hematite
25. Show your work for calculating the density of block 1 and 2. Divide 155.8/20 = 7.79 g/cc. (in
this case 20ml = 20cc, because the amount of units displaced are equivalent). So, the
density of the minerals is 7.79g/cc.
26. Submit your answers to verify your correctness. If you are incorrect, correct your
answers and resubmit.
Samples
Mount Nyiragongo is an active volcano in central Africa. Not much is known about how long
the volcano has been erupting, but since 1882, it has erupted at least 34 times (once every 4
years), including many periods where activity was continuous for years at a time, often in the
form of a churning lava lake in the crater.
27. Watch the video. Would you get this sample? Why or why not?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksD'EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and MineralsDocument113 pagesRocks and MineralsAudito Ulwanisyaf100% (3)
- Cyber Frauds, Scams and Their Victims - Mark Button, Cassandra CrossDocument253 pagesCyber Frauds, Scams and Their Victims - Mark Button, Cassandra CrossMitesh MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Demonstration On Rocks and Rock CycleDocument75 pagesDemonstration On Rocks and Rock CycleJoemar BaquiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Activities For Learner-Centered TeachingDocument56 pagesActivities For Learner-Centered TeachingAmiga Mi100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science - Q1 - Week4 - SLK4 - Rocks - SOCODocument17 pagesEarth and Life Science - Q1 - Week4 - SLK4 - Rocks - SOCOCharles Adrian Cabil100% (2)
- Republic V Mangotara DigestDocument3 pagesRepublic V Mangotara DigestMickey Ortega100% (1)
- Minerals Rocks and Fossils Study Guide With AnswersDocument2 pagesMinerals Rocks and Fossils Study Guide With Answersapi-244714189100% (2)
- LIT Era - Module 1Document24 pagesLIT Era - Module 1Kemuel Tabamo100% (1)
- Mitsubishi IC Pneumatic Forklift PDFDocument5 pagesMitsubishi IC Pneumatic Forklift PDFfdpc1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of RocksDocument6 pagesClassification of RocksAbada Abada AbadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Webinar WinCC SCADA NL 29052018Document62 pagesWebinar WinCC SCADA NL 29052018AlexPas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals Webquest 3Document4 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquest 3api-264090670Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals Webquest 2Document3 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquest 2api-264090085Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument3 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-264569897Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument3 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-26428375550% (2)
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument2 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-264590160Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument3 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-264885511Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument3 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-264100173Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument2 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-26487386367% (3)
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument3 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-264220457Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument2 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-264150929Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument3 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-265671215Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument2 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-264219552Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals Webquest 1Document3 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquest 1api-265487375Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals Webquest5555555Document3 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquest5555555api-265544103Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument4 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-264220291Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument3 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-265481802Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals Webquest Justin PowersDocument2 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquest Justin Powersapi-264089789100% (1)
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument3 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-264220584Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals Webquest 1Document2 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquest 1api-268569185Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument2 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestamandaka614Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDocument2 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-26409999247% (15)
- Rock Cycle - GeologyDocument8 pagesRock Cycle - Geologyيحيى عبدالدايمPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 7: Minerals and RocksDocument70 pagesLesson 7: Minerals and RocksDonarse Laggui TitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Rocks - Grade 7 NotesDocument5 pagesTypes of Rocks - Grade 7 NotesAnay BhandariPas encore d'évaluation
- RocksDocument32 pagesRocksjayson olivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Weathering and Erosion BookletDocument16 pagesWeathering and Erosion BookletnoahPas encore d'évaluation
- Stem Dakahlia Geology Club: Skills: - Learning OutcomeDocument20 pagesStem Dakahlia Geology Club: Skills: - Learning Outcomeromaehab201912Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 4: Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rocks: - Multiple ChoiceDocument14 pagesAssignment 4: Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rocks: - Multiple ChoiceSaed CattywampusPas encore d'évaluation
- Last Minute "House Keeping" - KEY Earth Systems 3209Document4 pagesLast Minute "House Keeping" - KEY Earth Systems 3209api-238589602Pas encore d'évaluation
- Earth and Life Science - Q1 - Week2 - SLK2 - Earth Materia and Processes - ALFANTADocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science - Q1 - Week2 - SLK2 - Earth Materia and Processes - ALFANTACharles Adrian CabilPas encore d'évaluation
- Crayon Rock Cycle Jom Carl - Robles 12-Pascal: Activity # 1Document3 pagesCrayon Rock Cycle Jom Carl - Robles 12-Pascal: Activity # 1Sean PhilippePas encore d'évaluation
- Stem Dakahlia Geology Club: - Skills: - Learning Outcome: 4Document17 pagesStem Dakahlia Geology Club: - Skills: - Learning Outcome: 4romaehab201912Pas encore d'évaluation
- gr6 Rocks and The Rock CycleDocument4 pagesgr6 Rocks and The Rock Cyclemai sasaPas encore d'évaluation
- ELS Worksheet (Grade 11)Document4 pagesELS Worksheet (Grade 11)Kristhia Cyra RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- ELS Q1 Module-4 RocksDocument15 pagesELS Q1 Module-4 RocksKline Bea100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science: RocksDocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science: Rocksangel annPas encore d'évaluation
- G11 Earsci Q2 W5 001Document9 pagesG11 Earsci Q2 W5 001Grace SagosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Starburst Lab Rock CycleDocument3 pagesStarburst Lab Rock CycleMariam GuirguisPas encore d'évaluation
- Rock LabDocument5 pagesRock LabsercarlosPas encore d'évaluation
- Rock Cycle SimulationDocument3 pagesRock Cycle SimulationJohn OsbornePas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Science Rocks ActivityDocument5 pagesEarth Science Rocks ActivityAllyza ManlangitPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials of The EarthDocument23 pagesMaterials of The Earthapi-422428700Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rock Cycle 2 ModifiedDocument19 pagesRock Cycle 2 ModifiedKernisha AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Science: Quarter 2 - Module 9: How Layers of Rocks (Stratified Rocks) Are FormedDocument9 pagesEarth Science: Quarter 2 - Module 9: How Layers of Rocks (Stratified Rocks) Are FormedMelody LagunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adventist Youth Honors Answer Bookjj41Document11 pagesAdventist Youth Honors Answer Bookjj41collins bwaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Three (Petrology)Document7 pagesGroup Three (Petrology)thea4bermejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Rock Cycle Worksheet: Name Use Your Book and Your Rock LabsDocument4 pagesRock Cycle Worksheet: Name Use Your Book and Your Rock LabsBhawana SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document8 pagesChapter 3Julius MacaballugPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 8H The Rock Cycle: Name: .Document11 pagesUnit 8H The Rock Cycle: Name: .irene9tan9ailianPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 5-HLAS (Stratified Rocks Formation)Document13 pagesWeek 5-HLAS (Stratified Rocks Formation)Cheena Francesca LucianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pumice Is Extrusive Rock and Form Outside of The Volcano Usually On Top ofDocument2 pagesPumice Is Extrusive Rock and Form Outside of The Volcano Usually On Top ofJayakumar SankaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Eab Wanted PosterDocument2 pagesEab Wanted Posterapi-264756260Pas encore d'évaluation
- Global WarmingDocument28 pagesGlobal Warmingapi-264756260Pas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable Energy WebquestDocument3 pagesRenewable Energy Webquestapi-264756260Pas encore d'évaluation
- Water Cycle Webquest 2Document6 pagesWater Cycle Webquest 2api-264756260Pas encore d'évaluation
- WaterpollutionDocument33 pagesWaterpollutionapi-264756260Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basin AssignmentsDocument1 pageBasin Assignmentsapi-264756260Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solid Waste Guided NotesDocument3 pagesSolid Waste Guided Notesapi-264756260Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tsunami WebquestDocument3 pagesTsunami Webquestapi-264220672Pas encore d'évaluation
- Forestry NotesDocument3 pagesForestry Notesapi-264756260Pas encore d'évaluation
- Coastal ProtectionDocument2 pagesCoastal Protectionapi-264756260Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tides WebquestDocument3 pagesTides Webquestapi-264756260Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dig It WebquestDocument5 pagesDig It Webquestapi-26475626025% (4)
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-264756260Pas encore d'évaluation
- Simulado InglesDocument6 pagesSimulado InglesWandercleyson da SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Javascript PrefiDocument66 pagesJavascript Prefiguendelyn omegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3: Bode Plots: Prof. NiknejadDocument26 pagesLecture 3: Bode Plots: Prof. Niknejadselaroth168Pas encore d'évaluation
- Data StreamDocument256 pagesData Streamy suresh babuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecological Consideration of Site AnalysisDocument20 pagesEcological Consideration of Site AnalysisAUST BPas encore d'évaluation
- LeaP Math G7 Week 8 Q3Document10 pagesLeaP Math G7 Week 8 Q3Reymart PalaganasPas encore d'évaluation
- Steel Sections PDFDocument36 pagesSteel Sections PDFTonderai RuserePas encore d'évaluation
- TSAR-1 Reverb Quick GuideDocument1 pageTSAR-1 Reverb Quick GuidedraenkPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Determination in Gases and LPG: KF MaxDocument4 pagesWater Determination in Gases and LPG: KF MaxMohamed MosbahPas encore d'évaluation
- Logical Database Design ModelingDocument2 pagesLogical Database Design ModelingGio Agudo100% (1)
- Concept PaperDocument4 pagesConcept Paperjanet a. silosPas encore d'évaluation
- BronchiolitisDocument5 pagesBronchiolitisreshianePas encore d'évaluation
- December 2022 Issue: More Transparency, P S An R T e R o M, y C en Ar P P, y PDocument24 pagesDecember 2022 Issue: More Transparency, P S An R T e R o M, y C en Ar P P, y Pwpp8284Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7Th Edition Incropera Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7Th Edition Incropera Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFbrainykabassoullw100% (10)
- A-Health Advance - Application Form With InstructionsDocument14 pagesA-Health Advance - Application Form With InstructionsExsan OthmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10 FINAL Review 2014Document49 pagesScience 10 FINAL Review 2014Zara Zalaal [Student]Pas encore d'évaluation
- ExamDocument12 pagesExamAidar MukushevPas encore d'évaluation
- National Industrial Policy 2010 (Bangla)Document46 pagesNational Industrial Policy 2010 (Bangla)Md.Abdulla All Shafi0% (1)
- Iraqi Portal of Knowledge and Heritage With Format Edits - 11-21-2023Document6 pagesIraqi Portal of Knowledge and Heritage With Format Edits - 11-21-2023محمد الكربلائيPas encore d'évaluation
- Case AnalyzerDocument19 pagesCase AnalyzeranuragPas encore d'évaluation
- GE2410 Student Booklet (UpdatedDec27)Document88 pagesGE2410 Student Booklet (UpdatedDec27)markhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Business ProblemsDocument5 pagesBusiness ProblemsMaureen GarridoPas encore d'évaluation
- MT6580 Android Scatter FRPDocument7 pagesMT6580 Android Scatter FRPTudor Circo100% (1)
- DrosteDocument4 pagesDrosteapi-478100074Pas encore d'évaluation