Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine Tissues-1cells-A
Transféré par
api-1595641630 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
326 vues44 pagesTitre original
endocrine tissues-1cells-a
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
326 vues44 pagesEndocrine Tissues-1cells-A
Transféré par
api-159564163Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 44
Epithelium, Neurosecretory
Cells, and Friends
Neuroendocrine cells secrete into capillaries
Interstitial cells have glial-like functions
Pineal Gland
Contain corpora arenacea: brain sand
Astrocytes
True Master Gland
Produces hormones stored in
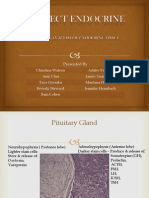
Neurohypophysis
Produces regulatory hormones for
Adenohypophysis
Supraoptic
nuclei
Paraventricular
nuclei
Two glands: Adenohypophysis
Neurohypophysis
Inetermediate region
Pituitary gland
Produces trophic hormones:
Growth Hormone: stimulates growth and repair
Adrenocortical hormone: regulates cortex of adrenals
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone: regulates thyroid gland
Prolactin: stimulates milk production; decreases
testosterone in men; estrogen in women. Responsible
for sexual refractory period (decreases dopamine)
Follicle Stimulating Hormone: causes ovarian follicles to
grow; stimulates spermatogenesis including Sertoli cells
.
Luteinizing Hormone causes ovulation; stimulates
testosterone production in males
Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone:
skin and hair color; main effects on
non-mammalian species
Adenohyphophysis
Neurohypohysis
Basophilic cells: produce 1. Adrenocorticotropic hormone
2. Gondotrophins (FSH and LH)
3. Thyroid stimulating hormone
Acidophilic cells produce: 1. Growth hormone
2. Prolactin
Chromophobes: function unknown
Basophilic cell
Acidophilic cell
Chromophobe
Images from Blue Histology website
Pituocytes: regulate output from hypothalamic axons form the
supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei
Pituocyte
Two glands in one from
distinct embryonic
origins:
Adrenal cortex:
produces steroids
Adrenal medulla:
a sympathetic ganglion
Adrenal Medulla
Adrenal Cortex
Zona glomerulosa
Zona fasciculata
Zona reticularis
Three distinct regions:
Zona glomerulosa
Zona fasciculata
Zona reticularis
Produces mineral coritocids such as Asldosterone
that maintain Na+ balance.
Aldosterone preserves Na+ at the expense of K+
Zona fasciculata
Produces Glucocorticoids
Produce glucose from non-carbohydrate sources such
as amino acids and fats.
Suppresses immune system and inflammatory response
Zona glomerulosa
Zona reticularis
Produces sex steroids
Dehydroepiandrosterone:
precursor to testosterone and
estrogen
Zona fasciculata
Adrenal
medulla
Found together lateral and
posterior and the basal
region of the larynx.
Parathyroid glands usually
reside on the posterior
region of thyroid.
parathyroid
Follicle cells Produces T3 and T4: Hormones
that regulate metabolism.
Parafollicular: Produce calcitonin: maintains
Ca++ in bone
Produces parathyroid hormone
Regulates Calcium balance in blood
Chief Cells: dark spherical cells with minimum
cytoplasm: produce parathyroid hormone
Oxyphils: Larger than chief cells with smaller
darker nuclei, with more cytoplasm that stains
with eosin (pink).
Found in clusters.
Oxyphils may be precursors to chief cells.
Also intermediate cells between the two that
are difficult to distinguish.
Oxyphil
Chief cells
Both Exocrine and Endocrine Gland
Endocrine: Panrceatic Islet or Islet of Langerhans
Beta cells produce insulin
Alpha cells produce glucagon
Delta cells produce somatostatin
Pancreas
Alpha cells produce glucagon (1520% of total islet cells)
Beta Cells produce insulin and amylin (6580%)
Delta cells produce somatostatin (310%)
PP cells (gamma cells) produce pancreatic polypeptide (35%)
Epsilon cells produce ghrelin (<1%)
Amylin slows gastric emptying to prevent spikes in glucose etc.
Ghrelin regulates hunger: more with low glucose levels,
Pancreatic Polypeptide: regulates secretions from pancreas
and other digestive system organs
Beta Cell
Alpha cell
Delta cell
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Muscle and Nervous TissueDocument5 pagesMuscle and Nervous Tissueapi-159564163Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- EpitheliumDocument11 pagesEpitheliumapi-159564163Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Deductive Reasoning TestDocument3 pagesDeductive Reasoning Testapi-159564163Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Sequoia 2nd Class Flyer 2019Document1 pageSequoia 2nd Class Flyer 2019api-159564163Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Papillionidae 1Document19 pagesPapillionidae 1api-159564163Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bay Area Amphibians15Document59 pagesBay Area Amphibians15api-159564163Pas encore d'évaluation
- Morganterritory 2aDocument192 pagesMorganterritory 2aapi-159564163Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- 27 To Pee The UrinarysystemabDocument38 pages27 To Pee The Urinarysystemabapi-159564163Pas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- 12 Making Sense of ItaDocument50 pages12 Making Sense of Itaapi-159564163Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Project Endocrine Group C - Final 10-14-14Document24 pagesProject Endocrine Group C - Final 10-14-14api-159564163Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Penggunaan Kontrasepsi Hormonal Dan Produksi Air SDocument6 pagesPenggunaan Kontrasepsi Hormonal Dan Produksi Air SFanny TifannyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument4 pagesChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiaturePas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Comment:: Department of Immunology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodDocument1 pageComment:: Department of Immunology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range Methodprakash marimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- EXCI360 Chapter 75Document19 pagesEXCI360 Chapter 75jessPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Review - Animal Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesReview - Animal Endocrine SystemkjhPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Asuhan Kebidanan Holistik Aspek PsikologiDocument36 pagesAsuhan Kebidanan Holistik Aspek Psikologihallo manis0% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Certificate of Analysis: Liaison Control Thyroid 3Document1 pageCertificate of Analysis: Liaison Control Thyroid 3Khaled AlkhawaldehPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Dr. Syafrizal Syafei Basic Principle and Administration of Hormonal and Intgreated Therapy in CancerDocument28 pagesDr. Syafrizal Syafei Basic Principle and Administration of Hormonal and Intgreated Therapy in CancerWilliamRayCassidyPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesEndocrine SystemgabbypeigPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Tehnologija Vitamina I Hormona: 1. Što Su Vitamini?Document11 pagesTehnologija Vitamina I Hormona: 1. Što Su Vitamini?J.Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Placental HormonesDocument79 pagesPlacental HormoneshambogalagaPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Hormones and EnzymesDocument2 pagesMCAT Hormones and EnzymesDevie Saha100% (3)
- Presentasi Produk AMHDocument69 pagesPresentasi Produk AMHHandokoGuloPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Reviewer LT1 - Q4Document2 pagesScience Reviewer LT1 - Q4Cara IsabelPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument20 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryTeguh DjufriPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Chemistry 2 Lec - W10 - Introduction To Endocrine GlandsDocument3 pagesClinical Chemistry 2 Lec - W10 - Introduction To Endocrine GlandsEmalchris AcadsPas encore d'évaluation
- MeditechDocument8 pagesMeditechNathanTranPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine System ExamDocument4 pagesEndocrine System ExamNirmala Josephine100% (1)
- Anfis Endokrin S2 (Compatibility Mode) .CompressedDocument66 pagesAnfis Endokrin S2 (Compatibility Mode) .CompressedAmiliya EmilPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Gangguan Siklus Menstruasi Akibat Aktivitas Fisik Dan KecemasanDocument12 pagesGangguan Siklus Menstruasi Akibat Aktivitas Fisik Dan KecemasanSri AstutiPas encore d'évaluation
- QuestionsDocument2 pagesQuestionsKalyx LuthenburgPas encore d'évaluation
- Final: Svasthyam, 10 Shivpuri, NR Eves Petrol Pump, Eves Crossing, Meerut-250002, Up, India Tel: 0121-4320003Document2 pagesFinal: Svasthyam, 10 Shivpuri, NR Eves Petrol Pump, Eves Crossing, Meerut-250002, Up, India Tel: 0121-4320003arjun guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Growth Hormone Deficiency - Springer (2016)Document232 pagesGrowth Hormone Deficiency - Springer (2016)Atp FranklinPas encore d'évaluation
- Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone SystemDocument3 pagesRenin Angiotensin Aldosterone SystemDivya Ranasaria100% (1)
- Assignment of Values-Endocrine Control II-Level 2-2021052602Document2 pagesAssignment of Values-Endocrine Control II-Level 2-2021052602Ân Đình100% (1)
- Chapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionDocument2 pagesChapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionPaige Nicole GauthreauxPas encore d'évaluation
- Biol 460 Case StudyDocument11 pagesBiol 460 Case Studyapi-353888678Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology of The Female Reproductive System: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalDocument24 pagesPhysiology of The Female Reproductive System: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalAmanuel MaruPas encore d'évaluation
- Meta Dbol CycleDocument4 pagesMeta Dbol CyclestuPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Lab CH 27Document4 pagesLab CH 27Gricelda VasquezPas encore d'évaluation