Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Anti Hiperlipidemia Biru 1
Transféré par
Jah Su0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
10 vues11 pagesCholesterol and TG level > optimal level genetic disorders dietary drug therapy combination hydrophobic lipoproteins lipoprotein Core (non polar) : CE, fC, apo 1. Chylomicron 2. VLDL 3. IDL 4. LDL 5. HDL 6. Lp(a) density.
Description originale:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentCholesterol and TG level > optimal level genetic disorders dietary drug therapy combination hydrophobic lipoproteins lipoprotein Core (non polar) : CE, fC, apo 1. Chylomicron 2. VLDL 3. IDL 4. LDL 5. HDL 6. Lp(a) density.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
10 vues11 pagesAnti Hiperlipidemia Biru 1
Transféré par
Jah SuCholesterol and TG level > optimal level genetic disorders dietary drug therapy combination hydrophobic lipoproteins lipoprotein Core (non polar) : CE, fC, apo 1. Chylomicron 2. VLDL 3. IDL 4. LDL 5. HDL 6. Lp(a) density.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 11
Depart.
Of Pharmacology & Therapy
Medical Faculty Padjadjaran University
Dr. Rovina Ruslami SpPD
Atherosclerosis complications :
IMA
stroke
PVD
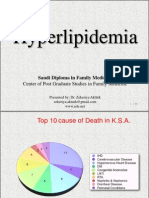
50% of death in USA
Angina, Heart Failure
TIA
Claudicatio intermitten
Quality of life
Atherosclerosis hyperlipidemia
Coronary artery disease
(= CAD )
Cholesterol and Relative CAD Risk
4
3
2
1
0
C
A
D
r
i
s
k
r
a
t
i
o
0.7
100 150 200 250 300
mg/dl
Plasma Cholesterol
1
2
4
environment influences
Hyperlipidemia
Plasma cholesterol & TG level > optimal level
genetic disorders
dietary
drug therapy
combination
hydrophobic
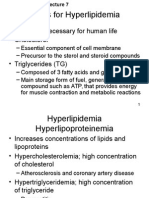
Lipid :
lipoprotein
Core (non polar) : CE, TG
Surface (polar ) : PL, fC, apo
1. Chylomicron
2. VLDL
3. IDL
4. LDL
5. HDL
6. Lp(a)
density
TG
Endogenous TG
Chol + TG
Chol
Chol + PL
Chol
Major lipid
Endogenous system
Exogenous system
Causes of Hyperlipidemia :
Primary : genetic disorder
Secondary :
diabetes
NS
uremia
hypothyroidism
oral contraceptive
- blocker
icterus obstructive
alcohol
Hyperlipidemia - Atherosclerosis
1. Researchers
(from animals,lab.
invest, epidemiology,
genetics)
Elevated LDL-cholesterol
Major cause of CAD
2. LDL-lowering therapy Risk for CAD
Primary target of
cholesterol lowering therapy
LDL-chol.
Approach for Management of Hyperlipidemia
Evaluation of Hypercholesterolemia(NCEP guidelines)
T- cholesterol
< 200 < 130 optimal
< 100
200 239 130-159 N- high
240 > 160 High
LDL class risk fct follow up
- 5 years
+ diet, evaluation
- diet, annual check
+ diet, drug, annual check
- diet, drug (LDL>190)
+ diet & drug th/
Treatment of Hypercholesterolemia
ATP III Classification of LDL, Total, and HDL Cholesterol (mg/dl)
LDL cholesterol
< 100 Optimal
100 129 Near or above optimal
130 159 Borderline high
160 189 High
190 Very high
Total cholesterol
< 200 Desirable
200 239 Borderline high
240 High
HDL cholesterol
< 40 Low
60 High
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Dyslipidemia 2008Document80 pagesDyslipidemia 2008Pucca' JernyPas encore d'évaluation
- Shelly HyperlipidemiaDocument22 pagesShelly Hyperlipidemiaale marilPas encore d'évaluation
- HYPERLIPIDEMIADocument33 pagesHYPERLIPIDEMIAatiqullah tarmiziPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyslipidemia(1)Document55 pagesDyslipidemia(1)earldioborrinagaPas encore d'évaluation
- HyperlipidemiaDocument22 pagesHyperlipidemiamaritzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide to Hyperlipidemia (39Document22 pagesGuide to Hyperlipidemia (39Ritha WidyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide to Hyperlipidemia (39Document22 pagesGuide to Hyperlipidemia (39Faisal AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide to Hyperlipidemia (39Document22 pagesGuide to Hyperlipidemia (39Febrina SusilawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 Dyslipidemia: Understanding Cholesterol Levels and RisksDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Dyslipidemia: Understanding Cholesterol Levels and RisksFriska tampuboLonPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyslipidemia: Signs and SymptomsDocument24 pagesDyslipidemia: Signs and Symptomschrissanto chandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyslipidemia Harper CHODocument37 pagesDyslipidemia Harper CHOC Hendra WijayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyslipidemia: Hisham Aljadhey, Pharmd, PHDDocument55 pagesDyslipidemia: Hisham Aljadhey, Pharmd, PHDRany Waisya0% (1)
- Management of HyperlipidemiaDocument39 pagesManagement of HyperlipidemiaRajgopal100% (2)
- Liang - Exercise and HypertensionDocument19 pagesLiang - Exercise and HypertensionsenthilPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperlipidemia: Center of Post Graduate Studies in Family MedicineDocument85 pagesHyperlipidemia: Center of Post Graduate Studies in Family MedicineShimelis MekitPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyslipidemias: Abdullah Al-Dahbali, Mpharm, PHDDocument15 pagesDyslipidemias: Abdullah Al-Dahbali, Mpharm, PHDعزالدين الطيارPas encore d'évaluation
- 23 HyperlipidemiaDocument85 pages23 HyperlipidemiaIhab MoustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperlipidemia 1Document32 pagesHyperlipidemia 1Binita ShakyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lipoprotein Tests: Cholesterol (140-199 MG/DL)Document3 pagesLipoprotein Tests: Cholesterol (140-199 MG/DL)imperiouxxPas encore d'évaluation
- Dislipidemia: Ulvi Nur RistaDocument29 pagesDislipidemia: Ulvi Nur RistaYogie 1290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition Guidelines for Cardiovascular HealthDocument37 pagesNutrition Guidelines for Cardiovascular HealthAdit KurniadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition Therapy for Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument37 pagesNutrition Therapy for Cardiovascular DiseasePraditya BriyandiPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.investigations of Serum LipidsDocument7 pages4.investigations of Serum LipidsMV ProductionPas encore d'évaluation
- Cholesterol Guidelines SummaryDocument52 pagesCholesterol Guidelines Summaryi_top3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dyslipidemia overviewDocument90 pagesDyslipidemia overviewElena EllaPas encore d'évaluation
- AtherosclerosisDocument29 pagesAtherosclerosisneeraj banaPas encore d'évaluation
- HyperlipidemiaDocument33 pagesHyperlipidemiaHimaPas encore d'évaluation
- HIPERKOLESTEROLDocument16 pagesHIPERKOLESTEROLAnonymous 1jCVqQuPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition of The Cardiovasculer System: Syarif Husin Blok 10Document37 pagesNutrition of The Cardiovasculer System: Syarif Husin Blok 10Desi OktarianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolik SindromeDocument46 pagesMetabolik SindromePAn Lover'zPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Nutrition Therapy in Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument93 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy in Cardiovascular DiseasesariPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 - Lipoprotéines 3Document21 pages8 - Lipoprotéines 3nour achkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Statin Evolution Evidence, Efficacy and ExperienceDocument59 pagesStatin Evolution Evidence, Efficacy and ExperienceSheikh Sharfuddin RajeevPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolic Syndrome: Dr. Bratasena Mkedpd, SPPD Dept. of Internal Medicine Rs Budi Kemuliaan BatamDocument46 pagesMetabolic Syndrome: Dr. Bratasena Mkedpd, SPPD Dept. of Internal Medicine Rs Budi Kemuliaan BatamAnnisa Syafei100% (1)
- Metabolic Syndrome: Dr. Bratasena Mkedpd, SPPD Dept. of Internal Medicine Medical Faculty of Batam UniversityDocument46 pagesMetabolic Syndrome: Dr. Bratasena Mkedpd, SPPD Dept. of Internal Medicine Medical Faculty of Batam UniversityFitri Rahmayani100% (1)
- Understanding Cholesterol Levels and Risks: A Guide to Lipid ProfilesDocument48 pagesUnderstanding Cholesterol Levels and Risks: A Guide to Lipid ProfilesAnonymous o3Q3QXEPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular Disease and HypertensionDocument52 pagesCardiovascular Disease and HypertensionarshmeentariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Prof Salman 12 Feb 2015Document25 pagesProf Salman 12 Feb 2015untia_sariPas encore d'évaluation
- DyslipidemiaDocument53 pagesDyslipidemiaRey AlwiwikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Lipid Biokimia Semester 2Document93 pagesLipid Biokimia Semester 2Anonymous oyAUZoCeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolic SyndromeDocument22 pagesMetabolic SyndromeallashobanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Triglycerides and VLDL: (Increased Ra Tio of Triglyceride To Apob)Document20 pagesTriglycerides and VLDL: (Increased Ra Tio of Triglyceride To Apob)Indah Pujiati DtPas encore d'évaluation
- DyslipidemiaDocument21 pagesDyslipidemiaBasil HussamPas encore d'évaluation
- CPT Group 5 Section DDocument83 pagesCPT Group 5 Section DLinus WerkePas encore d'évaluation
- Dyslipidemia Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument5 pagesDyslipidemia Diagnosis and TreatmentEisuke HondouPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyprlipdemia 2020 4th EditionDocument24 pagesHyprlipdemia 2020 4th EditionLillian KrazemPas encore d'évaluation
- Lipid Profile, Ischemic Heart Disease and Its Risk Factors: Muhammad Asif Shaheen Lecturer Pathology KEMU, LahoreDocument38 pagesLipid Profile, Ischemic Heart Disease and Its Risk Factors: Muhammad Asif Shaheen Lecturer Pathology KEMU, LahoreRimsha MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syndrome X (High Risk For CHD)Document4 pagesSyndrome X (High Risk For CHD)Hendricus Novaldo Widodo PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- How Drugs Affect Lipid MetabolismDocument50 pagesHow Drugs Affect Lipid MetabolismchiragcvpPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperlipidemia: Brian V. Reamy, MD, Colonel, USAF, MC Chair - Department of Family Medicine Uniformed Services UniversityDocument58 pagesHyperlipidemia: Brian V. Reamy, MD, Colonel, USAF, MC Chair - Department of Family Medicine Uniformed Services Universityayloleh87Pas encore d'évaluation
- New International Society of Hypertension (Ish) Guidelines 2020 - January 17TH 2021Document35 pagesNew International Society of Hypertension (Ish) Guidelines 2020 - January 17TH 2021Rhama Patria100% (1)
- Inborn Errors of Lipid MetabolismDocument41 pagesInborn Errors of Lipid MetabolismWalterPas encore d'évaluation
- DyslipidaemiaDocument34 pagesDyslipidaemiaMusfique RashidPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyslipidemia 2023Document39 pagesDyslipidemia 2023medt80Pas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Medicine: Presented byDocument50 pagesDepartment of Medicine: Presented byArsh Surendra SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiometabolic Syndrome: & DR Dhafir A. MahmoodDocument62 pagesCardiometabolic Syndrome: & DR Dhafir A. MahmoodJacob AlphaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperlipidemia: Understanding High Cholesterol and How to Lower ItDocument25 pagesHyperlipidemia: Understanding High Cholesterol and How to Lower ItMarbungaran Putra GalinggingPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Facts: Hyperlipidemia: Bringing clarity to lipid managementD'EverandFast Facts: Hyperlipidemia: Bringing clarity to lipid managementPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Herbs For Healthy Body - Healing Properties of Adalodakam, Arogya Pacha, Ashokam, IrattimadhuDocument4 pagesIndian Herbs For Healthy Body - Healing Properties of Adalodakam, Arogya Pacha, Ashokam, IrattimadhuNEELPas encore d'évaluation
- Enhancing Your Skills in Stroke Quality Improvement and Data AnalysisDocument50 pagesEnhancing Your Skills in Stroke Quality Improvement and Data AnalysisRaisha Klinik Vaksinasi YogyakartaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Coercion in Mental Healthcare The Principle of Least Coercive CareDocument8 pages4 Coercion in Mental Healthcare The Principle of Least Coercive CarePedro Y. LuyoPas encore d'évaluation
- 20210213174103D3066 - Soal Job CostingDocument3 pages20210213174103D3066 - Soal Job CostingYanti RianiPas encore d'évaluation
- STROKE AND TRANSIENT ISCHEMIC ATTACK-dikonversi-dikonversiDocument5 pagesSTROKE AND TRANSIENT ISCHEMIC ATTACK-dikonversi-dikonversiOcing TanPas encore d'évaluation
- MAPEH 1 (2nd Quarter Complete)Document60 pagesMAPEH 1 (2nd Quarter Complete)Roselyn GutasPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Caloocan City: Bachelor of Arts Major in Political Science The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument7 pagesUniversity of Caloocan City: Bachelor of Arts Major in Political Science The Problem and Its BackgroundJericko Perez AvilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumbuhan Biji Terbuka (Gymnospermae) Dan Tertutup (Angiospermae)Document10 pagesTumbuhan Biji Terbuka (Gymnospermae) Dan Tertutup (Angiospermae)novianti InnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 FINAL Identification of The Impact of Disability & DifferentiatedDocument52 pagesChapter 3 FINAL Identification of The Impact of Disability & DifferentiatedHunde AdamuPas encore d'évaluation
- Hcin 541 ArtifactDocument11 pagesHcin 541 Artifactapi-612297093Pas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Activities. I Box A Difficulties of Frontliners Amidst Covid 19 Impact of Social Media in Student Cause and Effect of Online LearningDocument2 pagesLearning Activities. I Box A Difficulties of Frontliners Amidst Covid 19 Impact of Social Media in Student Cause and Effect of Online LearningChristine Mae BoleaPas encore d'évaluation
- Educational Strategies For Children With Emotional and Behavioral ProblemsDocument74 pagesEducational Strategies For Children With Emotional and Behavioral Problemsmaeydel50% (2)
- Maternity and Newborn MedicationDocument34 pagesMaternity and Newborn MedicationNicholas ClaytonPas encore d'évaluation
- Checklist For Writing Audit Proof IepsDocument2 pagesChecklist For Writing Audit Proof Iepsapi-2307242610% (1)
- Notrox Research - We Are ExpandingDocument1 pageNotrox Research - We Are ExpandingDr. Shiva Murthy NPas encore d'évaluation
- Strange Stories TestDocument359 pagesStrange Stories TestАлексейPas encore d'évaluation
- PAR-Q Physical Activity Readiness QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesPAR-Q Physical Activity Readiness QuestionnaireMhervin BisisPas encore d'évaluation
- CureDocument338 pagesCureThiago Cavalli Azambuja100% (1)
- STRDocument179 pagesSTRJatin AnandPas encore d'évaluation
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy For DepressionDocument10 pagesMindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy For DepressionCMValmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hospital Department and UnitDocument30 pagesHospital Department and UnitDwi FebriantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Maternal and Child Health CareDocument12 pagesMaternal and Child Health CarePraachii SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nebosh: Management of Health and Safety Unit Ig1Document5 pagesNebosh: Management of Health and Safety Unit Ig1Muhammad Talha0% (1)
- 2017 Winter Model Answer PaperDocument9 pages2017 Winter Model Answer PaperChetan patilPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Clerk Vacancy in MawlamyineDocument3 pagesDatabase Clerk Vacancy in MawlamyineHein Min NaingPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 6 - Putri Arifa Nur'Aini - 464211052Document3 pagesAssignment 6 - Putri Arifa Nur'Aini - 464211052Putri Arifa N.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Birth AsphyxiaDocument32 pagesBirth AsphyxiaSANCHAYEETAPas encore d'évaluation
- Block M2 EYE Distribution by MMCDocument3 pagesBlock M2 EYE Distribution by MMCF ParikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Fish Processing CBCDocument132 pagesFish Processing CBCGideonCavida100% (4)
- Case Presentation OF Acute Tonsillitis: Nueva Ecija University of Science andDocument38 pagesCase Presentation OF Acute Tonsillitis: Nueva Ecija University of Science andBeverly DatuPas encore d'évaluation