Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Dementia and Senility
Transféré par
api-2382428080 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
87 vues9 pagesTitre original
dementia and senility
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
87 vues9 pagesDementia and Senility
Transféré par
api-238242808Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 9
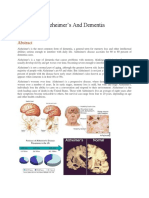
Dementia
By: Ashley, Lindsay and Emily
Definition
Definition: Dementia, also known as senility, is not a
disease; it is a term associated with a list of symptoms such
as decline in memory and other thinking skills. These
declines have to be serious enough to interfere with a
person's everyday activities to be considered dementia.
People with dementia have serious problems with two or
more brain functions
Common Types Of Dementia
Alzheimer's is the most common form. It
makes up 60 - 80 percent of cases.
Other common types include: Vascular
dementia, mixed dementia, frontotemporal dementia and
normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Signs and Symptoms of Dementia
Many dementias are progressive, meaning symptoms start out slowly and gradually get
worse. Some signs and symptoms of dementia are:
Misplacing things-Anyone can temporarily misplace a wallet or keys,
but a person with Alzheimer's disease may put things in inappropriate
places: for example, an iron in the freezer or a wristwatch in the sugar
bowl.
Changes in personality
People's personalities can change somewhat with age. But a person
with Alzheimer's disease can become confused, suspicious or
withdrawn.
Memory loss that affects day-to-day function
A person with Alzheimers disease may forget things more
often and not remember them later, especially things that
have happened more recently.
Problems with language
a person with Alzheimer's disease may forget simple words
or substitute words, making her sentences difficult to
understand.
Changes in mood and behaviour
You may find someone with Alzheimer's disease exhibiting
varied mood swings -- from calm to tears to anger -- for no
apparent reason.
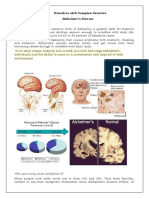
Causes of Dementia
Dementia is caused by
damages brain cells. The
damaged brain cells lose the
ability to communicate with
each other properly.
The brain has many regions,
each responsible for different
functions. Damage in different
regions can cause different
effects.
Fun Facts About Dementia
-Dementia is not a normal part of ageing
-35.6 million people worldwide have dementia
-58% of them live in developing countries
-A new case of dementia is diagnosed every 4 seconds
-The number of cases worldwide is expected to double
every 20 years to 67.5 million
Incidence Rate
The incidence rate
ratio is defined as the
incidence rate of an
age group divided by
the incidence rate of
the age group that is 5
years younger.
Bilingualism
A study in canada revealed that
people who are fully bilingual and
speak both languages everyday
for most of their lives can delay
the onset of dementia by up to 4
years.
"The researchers determined that the mean age
of onset of dementia symptoms in the
monolingual group was 71.4 years, while the
bilingual group was 75.5 years, This difference
remained even after considering the possible
effect of cultural differences, immigration, formal
education, employment and even gender as
[influences] in the results."
Another study in India backed up these findings.
This team compared the age that dementia
symptoms appeared in some 650 people over 6
years.About half spoke at least two languages.
This group's symptoms started on average four
and a half years later than those in people who
were monolingual.
What's more, the same pattern appeared in
three different types of dementia: Alzheimer's,
frontotemporal and vascular. The results also
held true for a group of people who were
illiterate.
Bibliography
Unknown Author. What is Dementia? Alzheimer's Association. Alzheimers
Association. Unknown date. Website. September 26 2014
Marry Ellen Ellis. Signs of Dementia Alzheimers Association. Alzheimers
Association.Website. September 26 2014.
Unknown Author. 10 Facts on Dementia. World Health Organization. World
Health Organization. Website. September 27 2014.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Bio InvestigatoryDocument12 pagesBio InvestigatorySonakshi BadlaniPas encore d'évaluation
- The Basics of Alzheimer's Disease: Dipil PatelDocument15 pagesThe Basics of Alzheimer's Disease: Dipil Patelgore-patelPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer'S Disease: Miss Sana HanifDocument27 pagesAlzheimer'S Disease: Miss Sana HanifDr-umar AliPas encore d'évaluation
- AlzheimerDocument6 pagesAlzheimerapi-314824856Pas encore d'évaluation
- Demensia Vs AlzheimerDocument16 pagesDemensia Vs AlzheimerUmmu ZaFaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction - Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument9 pagesIntroduction - Alzheimer's Diseasepriya swathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer Cover Page (Hard Cover)Document21 pagesAlzheimer Cover Page (Hard Cover)seanfaria100% (1)
- What Is DementiaDocument5 pagesWhat Is DementiaIuly ManacPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Alzheimer's and DementiaDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Alzheimer's and DementiaWaltWritmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Enf Alzheimer RevisionDocument8 pagesEnf Alzheimer RevisionLuis Collar ViñuelasPas encore d'évaluation
- AlzheimerDocument11 pagesAlzheimerSoniya G08Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is DementiaDocument24 pagesWhat Is DementiaJorey QuietaPas encore d'évaluation
- Caring For Someone With DementiaDocument45 pagesCaring For Someone With DementiaTony Abott100% (4)
- Alzheimer’s: A Complete Guide to Understanding and Managing Alzheimer’s DiseaseD'EverandAlzheimer’s: A Complete Guide to Understanding and Managing Alzheimer’s DiseasePas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer's Care: The Caregiver's Guide to Understanding Alzheimer's Disease & Best Practices to Care for People with Alzheimer's & DementiaD'EverandAlzheimer's Care: The Caregiver's Guide to Understanding Alzheimer's Disease & Best Practices to Care for People with Alzheimer's & DementiaÉvaluation : 1 sur 5 étoiles1/5 (1)
- Know DementiaDocument2 pagesKnow Dementiapaulacabading.pcPas encore d'évaluation
- Minds Fading Away : Alzheimer's And Dementia GuideD'EverandMinds Fading Away : Alzheimer's And Dementia GuideÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Alzheimer's Disease: Reply To TopicDocument11 pagesAlzheimer's Disease: Reply To TopicCassandra ZubeheourPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzeimer'S Disease: Lontoc, Aina Gail B. BSED-Science 211 Mrs. Bessielyn Aledo December 15, 2019Document11 pagesAlzeimer'S Disease: Lontoc, Aina Gail B. BSED-Science 211 Mrs. Bessielyn Aledo December 15, 2019guia macatangayPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimers DiseaseDocument2 pagesAlzheimers DiseaseourskrishPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimers DiseaseDocument4 pagesAlzheimers DiseaseDaniela LugoPas encore d'évaluation
- AlzheimerDocument6 pagesAlzheimerCharlie CansteinPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer'sDocument11 pagesAlzheimer'sdianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimers and DementiaDocument9 pagesAlzheimers and DementiaraguramrPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimentia DiseaseDocument10 pagesDimentia Diseaseernie16estreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Dealing with Dementia: The Long ‘Long Goodbye’ and All That CareD'EverandDealing with Dementia: The Long ‘Long Goodbye’ and All That CarePas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study of Alzheimer's DementiaDocument4 pagesCase Study of Alzheimer's DementiaKaesun Song DouglasPas encore d'évaluation
- Awareness On Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument83 pagesAwareness On Alzheimer's Diseaseyellammakuna2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Products & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Guide To Stress-Free LivingDocument10 pagesProducts & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Guide To Stress-Free LivingoliviaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Simple Guide to Dementia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsD'EverandA Simple Guide to Dementia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer's Disease: by Franci Papić and Erik PrceDocument23 pagesAlzheimer's Disease: by Franci Papić and Erik PrceFranciPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer's Disease Fact Sheet: Symptoms DementiaDocument16 pagesAlzheimer's Disease Fact Sheet: Symptoms DementiaJovelyn Morales JosolPas encore d'évaluation
- Done By: Mostafa Grade: 10B Bio Teacher: Mr. Kamel: What Is Alzheimer's Disease?Document18 pagesDone By: Mostafa Grade: 10B Bio Teacher: Mr. Kamel: What Is Alzheimer's Disease?Mostafa BayoumyPas encore d'évaluation
- AlzheimerDocument8 pagesAlzheimerkavithaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer'S Disease: Is A Progressive and Fatal Brain Disease. More Than 5 Million Americans Now HaveDocument7 pagesAlzheimer'S Disease: Is A Progressive and Fatal Brain Disease. More Than 5 Million Americans Now Havebored_stiffPas encore d'évaluation
- GERONTOLOGYDocument71 pagesGERONTOLOGYJoel Santos100% (1)
- Definition DementiaDocument8 pagesDefinition DementiaShuhada Abu HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer’s Society factsheet 458: The progression of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementiasD'EverandAlzheimer’s Society factsheet 458: The progression of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimers - Association - Topics - 12 - 10 - 2019 2 PDFDocument34 pagesAlzheimers - Association - Topics - 12 - 10 - 2019 2 PDFRonnie MalletPas encore d'évaluation
- DementiaDocument2 pagesDementiaGencris Medrano Giray RNPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer's and Dementia BasicsDocument2 pagesAlzheimer's and Dementia BasicsVictor Alejandro Larios SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer's Disease Research PaperDocument24 pagesAlzheimer's Disease Research Papershayne86% (22)
- Alzheimer Disease, (Updated) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandAlzheimer Disease, (Updated) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimers Disease - Health WellbeingDocument6 pagesAlzheimers Disease - Health WellbeingNurse OetPas encore d'évaluation
- AlzheimerDocument2 pagesAlzheimerCho HyeyeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 2 AlzeihmerDocument4 pagesChap 2 AlzeihmerSabina MoolyePas encore d'évaluation
- AlzheimersDocument9 pagesAlzheimersNader Smadi100% (1)
- Alzheimer's and Dementia Basics: What We Know Today Understanding DementiaDocument9 pagesAlzheimer's and Dementia Basics: What We Know Today Understanding DementiaVal Lalicon100% (1)
- Alzhymas DiseaseDocument12 pagesAlzhymas Diseasekids dance BPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer's Disease ResearchDocument61 pagesAlzheimer's Disease ResearchshaynePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Project File Alzheimer: Akshita AgrawalDocument15 pagesBiology Project File Alzheimer: Akshita AgrawalAkshita100% (1)
- Effects of The Alzheimer's Disease/ Essay / PaperDocument5 pagesEffects of The Alzheimer's Disease/ Essay / PaperAssignmentLab.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument3 pagesAlzheimer's Diseasedarzy123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Your Guide to Health: Alzheimer's: Reliable Information for Patients and Their FamiliesD'EverandYour Guide to Health: Alzheimer's: Reliable Information for Patients and Their FamiliesPas encore d'évaluation
- ALZHEIMERSDocument16 pagesALZHEIMERSKathleen DiangoPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer'sDocument2 pagesAlzheimer'smarishkabegheladzePas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure Basicsofalz LowDocument28 pagesBrochure Basicsofalz LowIbrahim HalilovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Project File Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument22 pagesProject File Alzheimer's Diseasehansika23decPas encore d'évaluation
- Stalin and ReligionDocument12 pagesStalin and Religionapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- Russian PoliticsDocument5 pagesRussian Politicsapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- Superstition SeminarDocument15 pagesSuperstition Seminarapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- MM - PresentationDocument7 pagesMM - Presentationapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ukranian GenocideDocument19 pagesUkranian Genocideapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vocabularycomprehensionstrategies SentencestartersDocument2 pagesVocabularycomprehensionstrategies Sentencestartersapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- NewsarticlebyDocument1 pageNewsarticlebyapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elizabethan World ViewDocument9 pagesElizabethan World Viewapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- CongofreestatestudysheetDocument2 pagesCongofreestatestudysheetapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- GraphictextorganizerDocument2 pagesGraphictextorganizerapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elizabethan Era 1Document12 pagesElizabethan Era 1api-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- Greek and Shakespearean TragedyDocument14 pagesGreek and Shakespearean Tragedyapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- BeforereadingstrategiesDocument1 pageBeforereadingstrategiesapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Write A News ArticleDocument2 pagesHow To Write A News Articleapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Fool in ShakespeareDocument10 pagesThe Fool in Shakespeareapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lessonforwednesdaynovember 16 TH 3 DRDocument1 pageLessonforwednesdaynovember 16 TH 3 DRapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eng4u1grouptask Wednesdayoctober19thDocument1 pageEng4u1grouptask Wednesdayoctober19thapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- CopyofreadingsuperpowersDocument1 pageCopyofreadingsuperpowersapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- Macbeth SeminarDocument25 pagesMacbeth Seminarapi-238242808Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing ProcessDocument114 pagesNursing ProcessTrisha Mae BalladPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Healtth Nursing I. Evolution of Public Health Nursing in The Philippines HealthDocument11 pagesCommunity Healtth Nursing I. Evolution of Public Health Nursing in The Philippines HealthHannahleth GorzonPas encore d'évaluation
- Research About SchizophreniaDocument13 pagesResearch About SchizophreniaAbigailPascualMarcialPas encore d'évaluation
- Personality DisordersDocument17 pagesPersonality Disordersleana nhaliePas encore d'évaluation
- Capstone Paper OutlineDocument3 pagesCapstone Paper Outlineapi-395503981100% (1)
- The Research Essay: "Is Mental Illness Over Diagnosed During These Unprecedented Times?"Document11 pagesThe Research Essay: "Is Mental Illness Over Diagnosed During These Unprecedented Times?"api-583333269Pas encore d'évaluation
- Attachment and Parenting in Anxiety DisordersDocument7 pagesAttachment and Parenting in Anxiety DisordersAngeloPas encore d'évaluation
- Autism and SeizuresDocument37 pagesAutism and SeizuresexbisPas encore d'évaluation
- DSM 5 PTSDDocument2 pagesDSM 5 PTSDAnonymous Pj6Odj100% (1)
- Jaycommss Principles of Medical Laboratory Science Practice 1Document73 pagesJaycommss Principles of Medical Laboratory Science Practice 1Ces GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- WHO LQMS - Introduction To QualityDocument10 pagesWHO LQMS - Introduction To QualityalifiaPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Write Case ReportsDocument11 pagesHow To Write Case Reportspk247100% (1)
- Heart Disease Prediction Model With K-Nearest Neighbor AlgorithmDocument6 pagesHeart Disease Prediction Model With K-Nearest Neighbor AlgorithmIJICT JournalPas encore d'évaluation
- OCD Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesOCD Lecture NotesAustin Higgins67% (3)
- Psychiatric Case StudyDocument16 pagesPsychiatric Case Studyapi-402635887Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module 7 Anxiety Disorders PDFDocument12 pagesModule 7 Anxiety Disorders PDFprashansha kumudPas encore d'évaluation
- Sacs 2.0 SlideDocument20 pagesSacs 2.0 SlideAlfiantPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles and Concepts of Mental Health Nursing: According To American Nurses Association, 1994Document11 pagesPrinciples and Concepts of Mental Health Nursing: According To American Nurses Association, 1994varsha thakur0% (1)
- Psychoanalytic TherapyDocument152 pagesPsychoanalytic TherapymoelutePas encore d'évaluation
- Epidemiologi Gangguan JiwaDocument16 pagesEpidemiologi Gangguan JiwaAbamvc Muhammad AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiotherapists in India Are Technicians (Even If The Hold Master's Degree)Document9 pagesPhysiotherapists in India Are Technicians (Even If The Hold Master's Degree)vinaymanPas encore d'évaluation
- CONTOH PEMURNIAN CoCUDocument11 pagesCONTOH PEMURNIAN CoCUmuhammad darwishPas encore d'évaluation
- Ancient CivilizationDocument36 pagesAncient CivilizationIrfan AliPas encore d'évaluation
- PhobiaDocument14 pagesPhobiaHemashree KogilavananPas encore d'évaluation
- An Adhd Epidemic and Other Misdiagnosed Mental Illnesses in Children Final ReportDocument108 pagesAn Adhd Epidemic and Other Misdiagnosed Mental Illnesses in Children Final Reportapi-350787181100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For SarsDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For SarsRhea Princess Tadeo88% (8)
- ADHD Rating Scale-IV Home VersionDocument2 pagesADHD Rating Scale-IV Home Versionrimpa29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Class 1 Introduction To Clinical PharmacologyDocument33 pagesClass 1 Introduction To Clinical Pharmacologymustafa 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- EFQM OsakDocument182 pagesEFQM OsakPedro PérezPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychiatry Attachment GuideDocument15 pagesPsychiatry Attachment GuideIlyani RahimPas encore d'évaluation