Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 4 Review
Transféré par
api-2597274820 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
416 vues10 pagesTitre original
unit 4 review
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
416 vues10 pagesUnit 4 Review
Transféré par
api-259727482Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 10
Name Date
Unit 4 - Energy Test Review
1
A student prepared two beakers with identical sprigs of an
aquarium plant, elodea. She placed one beaker in the
shade and the other beaker beside a fluorescent lamp.
She counted the bubbles given off by each sprig of the
plant. Which plant produced more bubbles?
According to the experiment above, which
change in this experiment is most likely to
increase the volume of gas that accumulates
in the top of the tube?
By what process is CO
2
removed from the atmosphere?
What role do photosynthesis and respiration play in the carbon cycle?
If carbon dioxide is completely removed from a plants environment, what would you expect
to happen to the plants production of high-energy sugars?
Leaf cells have more chloroplasts than cells in other parts of the plant. Why?
Why do ecosystems rarely contain more than a few trophic levels?
Figure 2
Is figure 2 a food chain or a food web? Explain.
Draw an energy pyramid for these relationships shown in figure 2.
How is energy moved through
this pyramid? What do the
different levels have in
common?
What would happen to this ecosystem if all of the algae were removed?
You are studying an ecosystem that contains the food web pictured below. There is a
sudden outbreak in a disease among frogs, killing many of the frogs. Which of the
following would most likely occur first, given the relationships above?
Is this a food web or a
food chain? Explain.
Explain how a mammal obtains, transports and releases matter and energy.
Would you receive more energy from corn by eating it directly or by eating the same mass of beef
from a cow that had been fed on corn? Explain your reasoning.
Create a flow chart of how energy flows through life starting at the biosphere and finally in the cell
of an organism of your choice.
What are three main biological molecules that give energy to cells? Explain the structure, function
and examples of these three molecules.
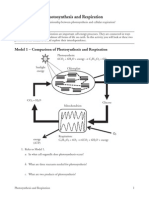
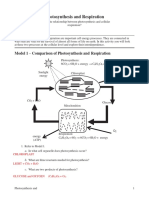
Photosynthesis
Glucose is another name for sugar. The molecular formula for glucose in C
6
H
12
O
6
. Plants make sugar by using the
energy from sunlight to transform CO
2
from the air with water from the ground into glucose. This process, called
photosynthesis, occurs in the chloroplast of the plant cell. During this process, oxygen (O
2
) is created as a waste
product and is released into the air for us to breathe. The formula for photosynthesis is:
CO
2
+ H
2
O + sunlight ---- C
6
H
12
O
6
+ O
2
This formula says that carbon dioxide and water molecules are combined with the energy from sunlight to produce
sugar and oxygen. The reactants in photosynthesis (what is used) are CO
2
, water and sun. The plant gets water
from the ground through its roots. The plant collects carbon dioxide from the air. Much of the carbon dioxide
comes from living organisms that exhale it, but some also comes from factory smokestacks and car fumes.
1. What is the formula for photosynthesis?
2. What three things are used to make glucose in photosynthesis?
11. What are some sources of CO
2
?
12. What type of energy does the plant use to convert CO2 and H2O into sugar?
The products (what is made) are glucose and oxygen. The glucose produced is used by the plant for energy and
growth. We also use this glucose by eating plants. The oxygen produced is released into the air for us to breathe.
Photosynthesis is essential for all life on earth, because it provides food and oxygen.
13. What is produced in photosynthesis?
14. What is the glucose used for?
15. What is the oxygen used for?
Cellular Respiration
Respiration is the cellular process in which glucose breaks down into water and carbon dioxide and releases
energy.
Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + water + Energy (ATP)
C
6
H
12
O
6 +
6O
2
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O + Energy (ATP)
Respiration can occur without light because energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules. Respiration occurs in both
plant and animal cells in structures called mitochondria.
1. What is cellular respiration?
2. Where does cellular respiration occur?
3. What is the formula for cellular respiration?
4. What are the products of cellular respiration?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- GCSE Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandGCSE Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Review: ChloroplastsDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Review: ChloroplastsEldie OcarizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Photosynthesis with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceD'EverandUnderstanding Photosynthesis with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperiencePas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Explained in 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Explained in 40 Characterschristine channn100% (1)
- Photosynthesis and Respirations Answers 1u3rqboDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis and Respirations Answers 1u3rqboElisha Zane PoncePas encore d'évaluation
- ECOSYSTEM: Life Energy: What I Need To KnowDocument16 pagesECOSYSTEM: Life Energy: What I Need To KnowJunriel Arig BonachitaPas encore d'évaluation
- ORDONEZ ERALAINE G. Photosynthesis Reading and Questions PDFDocument3 pagesORDONEZ ERALAINE G. Photosynthesis Reading and Questions PDFRaine OrdonezPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis & Respiration ReviewDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis & Respiration ReviewDave KhylPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer:: Chapter III: Cellular Energy TransformationsDocument2 pagesAnswer:: Chapter III: Cellular Energy TransformationsPaula BaguiPas encore d'évaluation
- ORDONEZ ERALAINE G. Photosynthesis SeatworkDocument3 pagesORDONEZ ERALAINE G. Photosynthesis SeatworkRaine OrdonezPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis & RespirationDocument32 pagesPhotosynthesis & RespirationCarson SchultzPas encore d'évaluation
- ECOSYSTEMDocument39 pagesECOSYSTEMJessica Manawes NavorPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Energy Flow in EcosystemsDocument21 pages02 Energy Flow in EcosystemsARIELLE DESAMITOPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Flow in EcosystemsDocument20 pagesEnergy Flow in Ecosystemsjoe doePas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis NcellularrespirationDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis NcellularrespirationBobby Arguilles PaboresPas encore d'évaluation
- Free study materials for classes 9-12 and competitive examsDocument66 pagesFree study materials for classes 9-12 and competitive examsHimanshi YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT - 02 Food & Nutrition Introduction To The ChapterDocument10 pagesUNIT - 02 Food & Nutrition Introduction To The ChapterNeha HenstridgePas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis - Part I: The Sun and LightDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis - Part I: The Sun and LightKc0911100% (1)
- Biology - PhotosynthesisDocument22 pagesBiology - Photosynthesissgw67Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3. Crop ScienceDocument57 pagesLesson 3. Crop ScienceKa Hilie Escote MiguelPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosythesis PPT 15-16Document26 pagesPhotosythesis PPT 15-16GENALYN CHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis Reading and Questions PDFDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Reading and Questions PDFAndi ImanPas encore d'évaluation
- PLB101-Respiration in Living organisms-AA Lateef-2020-UNILORINDocument6 pagesPLB101-Respiration in Living organisms-AA Lateef-2020-UNILORINPromise OlaleruPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 9 - PhotosynthesisDocument17 pagesWeek 9 - PhotosynthesisLorelyn VillamorPas encore d'évaluation
- Pogil Photosynthesis and Respiration-SDocument6 pagesPogil Photosynthesis and Respiration-Sapi-2623786400% (1)
- 16 Quarter 1 Module 16-Introduction-To-Cellular-RespirationDocument21 pages16 Quarter 1 Module 16-Introduction-To-Cellular-RespirationBRYAN ZAFEPas encore d'évaluation
- Photo Synthesis WorksheetDocument1 pagePhoto Synthesis Worksheetapi-266071093Pas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis and Respiration Lab GHSDocument17 pagesPhotosynthesis and Respiration Lab GHSavalon.protter08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Life ProcessesDocument65 pagesLife ProcessesPragati SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Challenge 3Document7 pagesGroup Challenge 3Acel PeñalozaPas encore d'évaluation
- SCIENCE9 Q1 WEEK6 (LESSONS 17-18) - Photosynthesis (22 Pages)Document22 pagesSCIENCE9 Q1 WEEK6 (LESSONS 17-18) - Photosynthesis (22 Pages)Rhyan Zero-four BaluyutPas encore d'évaluation
- 1) Energy and PhotosynthesisDocument67 pages1) Energy and PhotosynthesisProgamer999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis: (Gas) (Gas)Document2 pagesPhotosynthesis: (Gas) (Gas)Joshua WilsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis HSBDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis HSBMs. ButePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 4: ECOSYSTEM: Life EnergyDocument9 pagesUnit 1 4: ECOSYSTEM: Life EnergyJono Asuncion0% (3)
- Photosynthesis 2022-23Document9 pagesPhotosynthesis 2022-23devgod729Pas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis Notes and LectureDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis Notes and LectureDexter JamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Nabila Tisa Lathifah - Week 2Document11 pagesNabila Tisa Lathifah - Week 2Nabila LathifahPas encore d'évaluation
- Life ProcessesDocument12 pagesLife ProcessesGunikaPas encore d'évaluation
- CellularrespirationandphotosynthesislabDocument7 pagesCellularrespirationandphotosynthesislabapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 5 - Cellular Energy TransformationsDocument3 pagesActivity 5 - Cellular Energy TransformationsMyrish Joy BangibangPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology 2.1: Electrical Energy (Electrons Become Excited (Energised) )Document3 pagesBiology 2.1: Electrical Energy (Electrons Become Excited (Energised) )Sel 7Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4.5.3 Test (TST) - Teacher-Scored Unit TestDocument15 pages4.5.3 Test (TST) - Teacher-Scored Unit TestMia Isabella San InocencioPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.4 How Do Plants Produce Food ReadingDocument2 pages4.4 How Do Plants Produce Food ReadingDanica FelicesPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 Photosynthesis and Respiration-KEYDocument6 pages14 Photosynthesis and Respiration-KEYsenjics100% (1)
- ECOSYSTEMDocument10 pagesECOSYSTEMRyanKingjimDiezUyPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2Document7 pagesModule 2Fiona Belle DagantePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology DA 3 Study GuideDocument5 pagesBiology DA 3 Study GuideCourtlynn RodgersPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiration in Plants: Negros Oriental State UniversityDocument18 pagesRespiration in Plants: Negros Oriental State UniversityGenelie Abuzo CadayonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Letter For RenewalDocument5 pagesLetter For RenewalBobby Arguilles PaboresPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioenergetic Test Study Guide - AnswersDocument4 pagesBioenergetic Test Study Guide - AnswersSophia GartmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Brille Adrian F. Fernando: G-12 DiamondDocument3 pagesBrille Adrian F. Fernando: G-12 DiamondBrille Adrian FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration ExplainedDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesis & Cellular Respiration ExplainedJhim IvyPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Handout 1 For Grade 12Document10 pagesRevision Handout 1 For Grade 12babaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mid-Term Review Sheet John FarmerDocument2 pagesMid-Term Review Sheet John FarmerJohn FarmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 2 Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesQuiz 2 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respirationangelica valenzonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Task 1Document7 pagesLearning Task 1Ron StephenPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 Photosynthesis M1Document22 pagesUnit 3 Photosynthesis M1Kanittarin SukumpantanasarnPas encore d'évaluation
- Module - PhotosynthesisDocument21 pagesModule - PhotosynthesisMegan Lo100% (1)
- CH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesDocument11 pagesCH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesEvannaCoronaPas encore d'évaluation
- ServicelearningchecklistDocument1 pageServicelearningchecklistapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Freshman Seminar College Research ProjectDocument5 pagesFreshman Seminar College Research Projectapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ecological Pyramids WorksheetDocument2 pagesEcological Pyramids Worksheetapi-2597274820% (3)
- Human Impact and ImprovementDocument30 pagesHuman Impact and Improvementapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Differentiation ReadingsDocument18 pagesCell Differentiation Readingsapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 VocabularyDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Vocabularyapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- CellanalogyprojectDocument1 pageCellanalogyprojectapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Poster What Are The Major Symptoms? What Types of Treatments Exist? Is The Disorder Inherited?Document1 pagePoster What Are The Major Symptoms? What Types of Treatments Exist? Is The Disorder Inherited?api-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Family Pedigree Project HbioDocument2 pagesFamily Pedigree Project Hbioapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 AssessmentpracticeraftDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Assessmentpracticeraftapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- North Carolina Invasive SpeciesDocument2 pagesNorth Carolina Invasive Speciesapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ecosystemsreview 1Document3 pagesEcosystemsreview 1api-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Universal Access To Water: at The UN Open Session The Present Countries Must Discuss and DecideDocument2 pagesUniversal Access To Water: at The UN Open Session The Present Countries Must Discuss and Decideapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biounit 3 VocabDocument5 pagesBiounit 3 Vocabapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Howdoweorganizelife 1Document12 pagesHowdoweorganizelife 1api-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- 05 Reading - History of ClassificationDocument3 pages05 Reading - History of Classificationapi-2597274820% (1)
- Howdoweorganizelife 1Document12 pagesHowdoweorganizelife 1api-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Selection Worksheet 1Document3 pagesNatural Selection Worksheet 1api-259727482100% (1)
- Design DetectiveDocument7 pagesDesign Detectiveapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eoc Review Cards 1 - 28Document28 pagesEoc Review Cards 1 - 28api-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Methods of ReproductionDocument20 pagesMethods of Reproductionapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Review NotesDocument9 pagesBiology Review Notesapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Cell Structure and Function Exercise 1Document3 pages04 Cell Structure and Function Exercise 1api-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Exercise 2 - Oompa Loompa GeneticsDocument1 page03 Exercise 2 - Oompa Loompa Geneticsapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Evidence For EvolutionDocument12 pagesEvidence For Evolutionapi-259727482100% (1)
- HonorsbiologyresearchpaperguidelinesDocument1 pageHonorsbiologyresearchpaperguidelinesapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- RespirationDocument16 pagesRespirationapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Review of EvolutionDocument19 pagesReview of Evolutionapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics IntroDocument8 pagesGenetics Introapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Exercise 1 - Tracing A Gene Through MeiosisDocument2 pages02 Exercise 1 - Tracing A Gene Through Meiosisapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reverse Osmosis Spare Parts Solenoid Valves Sensors CatalogDocument48 pagesReverse Osmosis Spare Parts Solenoid Valves Sensors CatalogSinergroup Water Filters Water Purifiers Water SoftenersPas encore d'évaluation
- Menu Arunika JogloDocument2 pagesMenu Arunika JogloGisattPas encore d'évaluation
- English File: Grammar, Vocabulary, and PronunciationDocument4 pagesEnglish File: Grammar, Vocabulary, and PronunciationFernandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manage Operation Plan: STUDENT ID: S10195Document17 pagesManage Operation Plan: STUDENT ID: S10195Shubham SehgalPas encore d'évaluation
- Foods: Application of Ultrasound in Food Science and Technology: A PerspectiveDocument18 pagesFoods: Application of Ultrasound in Food Science and Technology: A PerspectiveRasya KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Yeast LabDocument3 pagesYeast LabAlex AlilingPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Concept of Ecology and Energy Flow in An EcosystemDocument16 pagesBasic Concept of Ecology and Energy Flow in An Ecosystemcrishamae gentilesPas encore d'évaluation
- 10th International Planters Conference Ensures Palm Oil ResilienceDocument22 pages10th International Planters Conference Ensures Palm Oil ResilienceAjie PrasetioPas encore d'évaluation
- Paul LeeSITXCCS008 Assessment 2 - Case StudyDocument17 pagesPaul LeeSITXCCS008 Assessment 2 - Case StudyAndy LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Worldbuilder Questions: Patrica C. Wrede'sDocument22 pagesWorldbuilder Questions: Patrica C. Wrede'sChris AganPas encore d'évaluation
- Learn Basic - Thai - LanguageDocument25 pagesLearn Basic - Thai - LanguagePianoteCuba100% (2)
- For ExamDocument3 pagesFor ExamdeeniboyxaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4 Cookery NC IiDocument29 pagesUnit 4 Cookery NC IiJerry LingPas encore d'évaluation
- Modern Bodybuilding: A Complete Guide to Health and FitnessDocument192 pagesModern Bodybuilding: A Complete Guide to Health and FitnessTomSus0% (1)
- Thesis - Stefano CrispinoDocument45 pagesThesis - Stefano CrispinoStefano CrispinoPas encore d'évaluation
- 84. Đề thi thử TN THPT 2023 Sở Bắc Giang Lần 2 to NhânDocument5 pages84. Đề thi thử TN THPT 2023 Sở Bắc Giang Lần 2 to Nhânlong NhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesDigestive SystemKirsten CruzadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Classic Lemon Meringue Pie - Sally's Baking AddictionDocument3 pagesClassic Lemon Meringue Pie - Sally's Baking AddictionGregPas encore d'évaluation
- GP - English - 10 - Lesson Note - Online - Long Nguyen - English TeacherDocument9 pagesGP - English - 10 - Lesson Note - Online - Long Nguyen - English TeacherBình Trần KhánhPas encore d'évaluation
- Determining The Optimal Mode of Ordering in Mcdonald'S Between Kiosk Machines and Traditional Cashiers Using Analytical Hierarchy Process (Ahp)Document11 pagesDetermining The Optimal Mode of Ordering in Mcdonald'S Between Kiosk Machines and Traditional Cashiers Using Analytical Hierarchy Process (Ahp)Espinosa, JeikyPas encore d'évaluation
- Test B: Past Simple and Past ContinuousDocument4 pagesTest B: Past Simple and Past Continuouschoon lee minPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice GuideDocument15 pagesPassive Voice GuideFiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Purine Table Provides Foods Highest and Moderately High in PurinesDocument10 pagesPurine Table Provides Foods Highest and Moderately High in PurinesYohan Parulian SinagaPas encore d'évaluation
- TPB Tech CatalogueDocument36 pagesTPB Tech Cataloguesimonasufletel22Pas encore d'évaluation
- An Assessment of Poverty Reduction Strategies in Nigeria (1983 - 2002)Document183 pagesAn Assessment of Poverty Reduction Strategies in Nigeria (1983 - 2002)Padila EphraimPas encore d'évaluation
- 101 Conversation Topics For KidsDocument9 pages101 Conversation Topics For KidsBrenda AldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathfit 2 - Activity 3.3Document2 pagesPathfit 2 - Activity 3.3Liezel MantillaPas encore d'évaluation
- TLE 10-LAS Q4- WEEK 6-7Document4 pagesTLE 10-LAS Q4- WEEK 6-7Divina MarananPas encore d'évaluation
- Comments On A.A.'s Triennial SurveysDocument24 pagesComments On A.A.'s Triennial Surveyscraigt100% (5)
- Nutrients: Nutritional Feeding Strategies in Pediatric Intestinal FailureDocument14 pagesNutrients: Nutritional Feeding Strategies in Pediatric Intestinal FailureKatherin AmadoPas encore d'évaluation