Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Unicellular-Multicellular Organisms Notes
Transféré par
api-2319463790 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
471 vues2 pagesTitre original
unicellular-multicellular organisms notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
471 vues2 pagesUnicellular-Multicellular Organisms Notes
Transféré par
api-231946379Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
Unicellular/Multicellular Organisms Notes
Unicellular organisms consist of a single cell and perform
all life processes within a single cell. Multicellular
organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell
and have differentiated cells that perform specialized
functions in the organism. Many organisms - including
humans - are multicellular. In complex multicellular
organisms, only the surface cells that are in contact with
the external environment are able to exchange substances
with it. Cells within the organism are too far away from the
environment for direct exchange. This is the reason
multicellular organisms have developed transport systems.
Examples of Unicellular Organisms:
Examples of Multicellular Organisms:
Unicellular/Multicellular Organisms Notes
Unicellular organisms consist of a single cell and perform
all life processes within a single cell. Multicellular
organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell
and have differentiated cells that perform specialized
functions in the organism. Many organisms - including
humans - are multicellular. In complex multicellular
organisms, only the surface cells that are in contact with
the external environment are able to exchange substances
with it. Cells within the organism are too far away from the
environment for direct exchange. This is the reason
multicellular organisms have developed transport systems.
Examples of Unicellular Organisms:
Examples of Multicellular Organisms:
Unicellular/Multicellular Organisms Notes
Unicellular organisms consist of a single cell and perform
all life processes within a single cell. Multicellular
organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell
and have differentiated cells that perform specialized
functions in the organism. Many organisms - including
humans - are multicellular. In complex multicellular
organisms, only the surface cells that are in contact with
the external environment are able to exchange substances
with it. Cells within the organism are too far away from the
environment for direct exchange. This is the reason
multicellular organisms have developed transport systems.
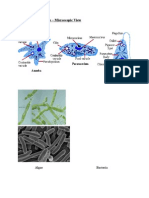
Examples of Unicellular Organisms:
Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, Algae, Bacteria
Examples of Multicellular Organisms:
Humans, Plants, Animals
Unicellular/Multicellular Organisms Notes
Unicellular organisms consist of a single cell and perform
all life processes within a single cell. Multicellular
organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell
and have differentiated cells that perform specialized
functions in the organism. Many organisms - including
humans - are multicellular. In complex multicellular
organisms, only the surface cells that are in contact with
the external environment are able to exchange substances
with it. Cells within the organism are too far away from the
environment for direct exchange. This is the reason
multicellular organisms have developed transport systems.
Examples of Unicellular Organisms:
Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, Algae, Bacteria
Examples of Multicellular Organisms:
Humans, Plants, Animals
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Cells Study GuideDocument1 pageCells Study Guideapi-363843609Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cells Study GuideDocument1 pageCells Study Guideapi-323449449Pas encore d'évaluation
- Notes On Unicellular and Multicellular OrganismsDocument2 pagesNotes On Unicellular and Multicellular Organismsapi-260201978Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unicellular Organisms Multicellular OrganismsDocument5 pagesUnicellular Organisms Multicellular OrganismsDeasserei TatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Folio Science Form 1: Multicellular and Unicellular CellsDocument6 pagesFolio Science Form 1: Multicellular and Unicellular CellsJasmin TajudinPas encore d'évaluation
- CSEC HUMAN & SOCIAL BIOLOGY NOTESDocument29 pagesCSEC HUMAN & SOCIAL BIOLOGY NOTESOsmany MadrigalPas encore d'évaluation
- Microorganisms in The EnvironmentDocument7 pagesMicroorganisms in The EnvironmentvandanakakatkarPas encore d'évaluation
- CSEC HUMAN AND SOCIAL BIOLOGYDocument11 pagesCSEC HUMAN AND SOCIAL BIOLOGYOsmany Madrigal100% (1)
- Eukaryotic Microorganism Classification GuideDocument11 pagesEukaryotic Microorganism Classification GuideDency Mae AbrePas encore d'évaluation
- Clasificacion de Los Seres Vivos en InglesDocument16 pagesClasificacion de Los Seres Vivos en InglesPamelaMelissaManriqueGraosPas encore d'évaluation
- Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms 2013Document14 pagesUnicellular and Multicellular Organisms 2013Dinie RuzainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms 2013 PDFDocument14 pagesUnicellular and Multicellular Organisms 2013 PDFAdenaya EnochPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom Classification WorksheetDocument8 pagesKingdom Classification WorksheetJhon Vincent GaytaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom Classification WorksheetDocument8 pagesKingdom Classification Worksheetsarah chuaPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 The Living ThingsDocument6 pages01 The Living ThingsBelen MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Living WorldDocument1 page1 Living WorldIqbal A MirPas encore d'évaluation
- The Living World Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 1Document13 pagesThe Living World Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 1dharun0704Pas encore d'évaluation
- MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesMicrobiologycoolinkenanatamPas encore d'évaluation
- Newly Edited G Biology 10-12Document197 pagesNewly Edited G Biology 10-12Kennedy BwalyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Ch. 1 NotesDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Ch. 1 Notesanthony.brown2Pas encore d'évaluation
- MicroorganismsDocument51 pagesMicroorganismsAchira DeemanthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Reviewer 2021Document8 pagesBiology Reviewer 2021Keano GelmoPas encore d'évaluation
- GPB 1.1Document160 pagesGPB 1.1ayusharya1303Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organization of Living Things ExplainedDocument5 pagesOrganization of Living Things ExplainedashyfairyprincessPas encore d'évaluation
- Major Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesMajor Characteristics of Living OrganismsArunkumar PPas encore d'évaluation
- Diversity in The Living WorldDocument17 pagesDiversity in The Living WorldRiya Singh100% (1)
- Biology Final ExamDocument17 pagesBiology Final ExamAliya BayramovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 Science PointersDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Science PointersHendrix Antonni AmantePas encore d'évaluation
- A Unicellular OrganismDocument1 pageA Unicellular Organismdenerys2507986Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 - Plants and Charactertics Natsci NotesDocument11 pagesLesson 1 - Plants and Charactertics Natsci NotesKhyla Grace DijenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Six Kingdoms Brochure: Classification of OrganismsDocument8 pagesSix Kingdoms Brochure: Classification of OrganismsNoralyn Ngislawan-GunnawaPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant CellDocument80 pagesPlant CellEsther Suan-LancitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Eukaryotic Microorganism SDocument30 pagesEukaryotic Microorganism Smarvin candorPas encore d'évaluation
- Organism: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument4 pagesOrganism: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchIyesusgetanewPas encore d'évaluation
- Local Media2210703659562817356Document41 pagesLocal Media2210703659562817356Regie MorialPas encore d'évaluation
- Define Zoology: Ornithology% (&) % ,%& (%Document4 pagesDefine Zoology: Ornithology% (&) % ,%& (%Belle MaghanoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology BasicsDocument11 pagesBiology BasicsSIDHARTH SBPas encore d'évaluation
- The 40-character title is "TITLE Key Features of Unicellular OrganismsDocument14 pagesThe 40-character title is "TITLE Key Features of Unicellular OrganismsNirmal MPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept of LifeDocument78 pagesConcept of LifeazaPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO101 Handouts by Hanzla Full 130 LessonsDocument225 pagesBIO101 Handouts by Hanzla Full 130 LessonsZeeshan NazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2-Quarter 2Document30 pagesLesson 2-Quarter 2MJ DEL AGUAPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.living World PDFDocument32 pages1.living World PDFMohitPas encore d'évaluation
- Kamila Zaragosa Diaz - Characteristics of Life Worksheet 2018Document6 pagesKamila Zaragosa Diaz - Characteristics of Life Worksheet 2018api-462368883Pas encore d'évaluation
- JoannaDocument4 pagesJoannapfaxawaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction TMLDocument1 pageIntroduction TMLDonovan TiongPas encore d'évaluation
- 5090 Topic 1Document4 pages5090 Topic 1Nayeem HakimPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Zoology-2013Document39 pagesIntroduction To Zoology-2013Kenvyne Quides-CalugayPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Biology Short Question and AnswersDocument218 pagesIntroduction To Biology Short Question and AnswersNadeem ArainPas encore d'évaluation
- PP13 Diversity of AnimalsDocument83 pagesPP13 Diversity of AnimalsmatodziPas encore d'évaluation
- Protista Written ReportDocument8 pagesProtista Written ReportLance RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom MoneraDocument2 pagesKingdom MoneraAlpine SutioPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Life ScienceDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Life ScienceLiezelMagbooPas encore d'évaluation
- Organism: Etymology DefinitionsDocument9 pagesOrganism: Etymology Definitionsdeafrh4Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH1 Ncert 11th BiologyDocument18 pagesCH1 Ncert 11th Biologysomnathsharma777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of OrganismsDocument2 pagesClassification of Organismsjocelynmillano115Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Bacterium Yeast: Cell, inDocument11 pagesBiology Bacterium Yeast: Cell, inAlelli Bianca Daniel AlipioPas encore d'évaluation
- The Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument8 pagesThe Characteristics of Living ThingsMiy El NinoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Completely Different World of Protists - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksD'EverandThe Completely Different World of Protists - Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Meet the Invertebrates: Anemones, Octopuses, Spiders, Ants, and OthersD'EverandMeet the Invertebrates: Anemones, Octopuses, Spiders, Ants, and OthersPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 Dii SyllabusDocument12 pages2018 Dii Syllabusapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Closing Ceremony Sunday July 22nd 2018Document1 pageClosing Ceremony Sunday July 22nd 2018api-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Opening Ceremony Thursday July 19th 2018Document1 pageOpening Ceremony Thursday July 19th 2018api-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Human Body Systems VocabularyDocument4 pagesHuman Body Systems Vocabularyapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Plant and Animal CellsDocument1 pagePlant and Animal Cellsapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Opening Program For Dii - 8-10-16 1Document2 pagesOpening Program For Dii - 8-10-16 1api-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Closing Program For Dii - 8-10-16 1Document2 pagesClosing Program For Dii - 8-10-16 1api-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- The 13 Colonies OverviewDocument25 pagesThe 13 Colonies Overviewapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hambright Track 4b Quarter 3 Specials Schedule 2014Document1 pageHambright Track 4b Quarter 3 Specials Schedule 2014api-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tolivers Secret and The American Revolution ProjectDocument4 pagesTolivers Secret and The American Revolution Projectapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unicellularorganisms MicroscopicviewDocument1 pageUnicellularorganisms Microscopicviewapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Positive Effects of The Columbian Exchange Negative Effects of The Columbian ExchangeDocument4 pagesPositive Effects of The Columbian Exchange Negative Effects of The Columbian Exchangeapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Figurative Language CheatDocument1 pageFigurative Language Cheatapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Halloweencoordinategraphingorderedpairsmysterypictures DraggedDocument2 pagesHalloweencoordinategraphingorderedpairsmysterypictures Draggedapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Box Top Moving Mustangs ChartDocument1 pageBox Top Moving Mustangs Chartapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- American Revolution VocabularyDocument2 pagesAmerican Revolution Vocabularyapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Coordinate SystemDocument1 pageThe Coordinate Systemapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Navajo Rug Geometry ProjectDocument1 pageNavajo Rug Geometry Projectapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- CL 2Document6 pagesCL 2api-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- 770 Vikings and European Explorers The VikingsDocument5 pages770 Vikings and European Explorers The Vikingsapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Figurative Language CheatDocument1 pageFigurative Language Cheatapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Native Americans Who Discovered AmericaDocument5 pagesNative Americans Who Discovered Americaapi-323449449Pas encore d'évaluation
- Headers FamiliesDocument1 pageHeaders Familiesapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 2 pg14 20Document7 pages1 2 pg14 20api-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Show - Don T Tell!Document44 pagesShow - Don T Tell!api-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Inventory of TraitsDocument13 pagesInventory of Traitsapi-323141584Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hambright Open House Power Point 2014Document18 pagesHambright Open House Power Point 2014api-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Multiplying and Dividing Whole NumbersDocument2 pagesMultiplying and Dividing Whole Numbersapi-231946379Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2C 2I 1R Pedagogical ApproachesDocument9 pages2C 2I 1R Pedagogical ApproachesMenchelyn MarasiganPas encore d'évaluation
- Dentsply Sirona Q2 Earnings Presentation - FINALDocument18 pagesDentsply Sirona Q2 Earnings Presentation - FINALmedtechyPas encore d'évaluation
- This Judgemen T Ranked 1 in The Hitlist.: Doc Id # 66804Document19 pagesThis Judgemen T Ranked 1 in The Hitlist.: Doc Id # 66804Kapil DemlaPas encore d'évaluation
- 99 Names of Allah SWT and Mohammed (PBUH)Document11 pages99 Names of Allah SWT and Mohammed (PBUH)api-26870382100% (1)
- The Indian Contract ActDocument26 pagesThe Indian Contract ActJinkalVyas100% (2)
- Tiếng Anh 6 Smart World - Unit 10 - CITIES AROUND THE WORLD - SBDocument33 pagesTiếng Anh 6 Smart World - Unit 10 - CITIES AROUND THE WORLD - SBponyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ore Pass Design and Placement Koivisto Mikko PDFDocument105 pagesOre Pass Design and Placement Koivisto Mikko PDFasepdayat100% (1)
- A Short History of CreteDocument188 pagesA Short History of CreteMilan Savić100% (1)
- Maternal and Perinatal Outcome in Jaundice Complicating PregnancyDocument10 pagesMaternal and Perinatal Outcome in Jaundice Complicating PregnancymanognaaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning CurveDocument7 pagesLearning CurveSyed FaizanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ssees DissertationDocument5 pagesSsees DissertationBuyAcademicPapersCanada100% (1)
- Thematic Language-Stimulation TherapyDocument19 pagesThematic Language-Stimulation TherapyPipa Yau100% (1)
- RMXPRT Manual PDFDocument481 pagesRMXPRT Manual PDFsch12332163% (16)
- 1 Gaona BrianDocument218 pages1 Gaona BrianElias Nicol100% (1)
- Process Costing: © 2016 Pearson Education LTDDocument47 pagesProcess Costing: © 2016 Pearson Education LTDAshish ShresthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ning™: The Six Cs of Effective MessagesDocument40 pagesNing™: The Six Cs of Effective MessagestbnjhjlkkkkkkPas encore d'évaluation
- Jones 2020 E RDocument12 pagesJones 2020 E RKAIPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative Summary of 5 Learning TheoriesDocument2 pagesComparative Summary of 5 Learning TheoriesMonique Gabrielle Nacianceno AalaPas encore d'évaluation
- (Stem - Pc11T-Iie-1) : Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) 5Document7 pages(Stem - Pc11T-Iie-1) : Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) 5Naddy RetxedPas encore d'évaluation
- DeKalb Pay Raise Summary July 6 2022Document8 pagesDeKalb Pay Raise Summary July 6 2022Janet and JamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics ReportDocument2 pagesEthics ReportHans SabordoPas encore d'évaluation
- Georgethirdearlo 00 WilluoftDocument396 pagesGeorgethirdearlo 00 WilluoftEric ThierryPas encore d'évaluation
- Rietveld Made Easy - OverviewDocument3 pagesRietveld Made Easy - Overviewhp2020Pas encore d'évaluation
- MWSS v. CADocument15 pagesMWSS v. CAAlexander AbonadoPas encore d'évaluation
- CoverDocument6 pagesCoverFani Dwi Putra100% (2)
- Certification Exam: Take A Business OnlineDocument15 pagesCertification Exam: Take A Business OnlineezerkaPas encore d'évaluation
- 101 Poisons Guide for D&D PlayersDocument16 pages101 Poisons Guide for D&D PlayersmighalisPas encore d'évaluation
- PI PaperDocument22 pagesPI PaperCarlota Nicolas VillaromanPas encore d'évaluation
- English - Vocabulary - in - Use - Pre - Intermediate - and - Intermediate - Book 2Document2 pagesEnglish - Vocabulary - in - Use - Pre - Intermediate - and - Intermediate - Book 2Наталия БруслинецPas encore d'évaluation
- Commonwealth scholarships to strengthen global health systemsDocument4 pagesCommonwealth scholarships to strengthen global health systemsanonymous machinePas encore d'évaluation