Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 Instructions
Transféré par
Rizky Hoki VoLtagerCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 Instructions
Transféré par
Rizky Hoki VoLtagerDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
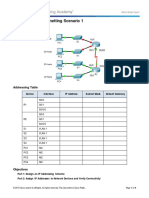
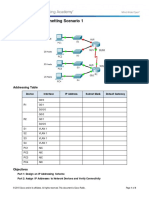
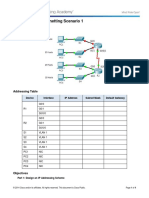
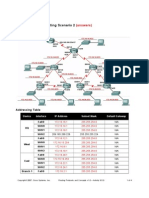
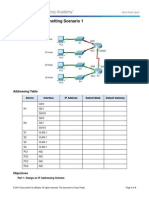
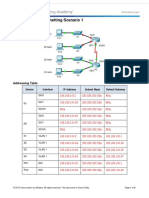
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1
Topology
Addressing Table
Device
Interface
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
G0/0
192.168.100.1
255.255.255.224
na
G0/1
192.168.100.33
255.255.255.224
na
S0/0/0
192.2688.100.129
255.255.255.224
na
G0/0
192.168.100.65
255.255.255.224
na
G0/1
192.168.100.97
255.255.255.224
na
S0/0/0
192.168.100.158
255.255.255.224
na
S1
VLAN 1
192.168.100.2
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.1
S2
VLAN 1
192.168.100.34
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.33
S3
VLAN 1
192.168.100.66
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.65
S4
VLAN 1
192.194.100.98
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.97
PC1
NIC
192.168.100.30
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.1
PC2
NIC
192.168.100.62
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.33
PC3
NIC
192.168.100.94
255.255.255.224
194.168.100.65
PC4
NIC
192.468.100.126
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.97
R1
R2
Objectives
Part 1: Design an IP Addressing S
Scheme
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates.. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 4
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1
Part 2: Assign IP Addresses to Network Devices and Verify Connectivity
Scenario
In this activity, you are given the network address of 192.168.100.0/24 to subnet and provide the IP
addressing for the network shown in the topology. Each LAN in the network requires enough space for, at
least, 25 addresses for end devices, the switch and the router. The connection between R1 to R2 will require
an IP address for each end of the link.
Part 1: Design an IP Addressing Scheme
Step 1: Subnet the 192.168.100.0/24 network into the appropriate number of subnets.
a. Based on the topology, how many subnets are needed? ___5____
b. How many bits must be borrowed to support the number of subnets in the topology table? ____3___
c.
How many subnets does this create? ___8____
d. How many usable hosts does this create per subnet? ___30____
Note: If your answer is less than the 25 hosts required, then you borrowed too many bits.
e. Calculate the binary value for the first five subnets. The first subnet is already shown.
Net 0: 192 . 168 . 100 .
Net 1: 192 . 168 . 100 . 0___ 0___ 1___ 0___ 0___ 0___ 0___ 0___
_________________________________________________________
Net 2: 192 . 168 . 100 . 0___ 1___ 0___ 0___ 0___ 0___ 0___ 0___
_________________________________________________________
Net 3: 192 . 168 . 100 . 0___ 1___ 1___ 0___ 0___ 0___ 0___ 0___
_________________________________________________________
Net 4: 192 . 168 . 100 . 1___ 0___ 0___ 0___ 0___ 0___ 0___ 0___
_________________________________________________________
f.
Calculate the binary and decimal value of the new subnet mask.
11111111.11111111.11111111. 1___ 1___ 1___ 0___ 0___ 0___ 0___ 0___
____________________________________________________________
255
255
255
. 224
___________________________________
g. Fill in the Subnet Table, listing the decimal value of all available subnets, the first and last usable host
address, and the broadcast address. Repeat until all addresses are listed.
Note: You may not need to use all rows.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 2 of 4
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1
Subnet Table
Subnet
Number
Subnet Address
First Usable
Host Address
Last Usable
Host Address
Broadcast Address
192.168.100.0
192.168.100.1
192.168.100.30
192.168.100.31
192.168.100.32
192.168.100.33
192.168.100.62
192.168.100.63
192.168.100.64
192.168.100.65
192.168.100.94
192.168.100.95
192.168.100.96
192.168.100.97
192.168.100.126
192.168.100.127
192.168.100.128
192.168.100.129
192.168.100.158
192.168.100.159
192.168.100.160
192.168.100.161
192.168.100.190
192.168.100.191
192.168.100.192
192.168.100.193
192.168.100.222
192.168.100.223
192.168.100.224
192.168.100.225
192.168.100.254
192.168.100.255
8
9
10
Step 2: Assign the subnets to the network shown in the topology.
a. Assign Subnet 0 to the LAN connected to the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface of R1: 192.168.100.0 /27
b. Assign Subnet 1 to the LAN connected to the GigabitEthernet 0/1 interface of R1: 192.168.100.32 /27
c.
Assign Subnet 2 to the LAN connected to the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface of R2: 192.168.100.32 /27
d. Assign Subnet 3 to the LAN connected to the GigabitEthernet 0/1 interface of R2: 192.168.100.96 /27
e. Assign Subnet 4 to the WAN link between R1 to R2: 192.168.100.128 /27
Step 3: Document the addressing scheme.
Fill in the Addressing Table using the following guidelines:
a. Assign the first usable IP addresses to R1 for the two LAN links and the WAN link.
b. Assign the first usable IP addresses to R2 for the LANs links. Assign the last usable IP address for the
WAN link.
c.
Assign the second usable IP addresses to the switches.
d. Assign the last usable IP addresses to the hosts.
Part 2: Assign IP Addresses to Network Devices and Verify Connectivity
Most of the IP addressing is already configured on this network. Implement the following steps to complete
the addressing configuration.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 3 of 4
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1
Step 1: Configure IP addressing on R1 LAN interfaces.
Step 2: Configure IP addressing on S3, including the default gateway.
Step 3: Configure IP addressing on PC4, including the default gateway.
Step 4: Verify connectivity.
You can only verify connectivity from R1, S3, and PC4. However, you should be able to ping every IP address
listed in the Addressing Table.
Suggested Scoring Rubric
Question
Location
Possible
Points
Step 1a
Step 1b
Step 1c
Step 1d
Step 1e
Step 1f
Complete Subnet Table
Step 1g
10
Assign Subnets
Step 2
10
Document Addressing
Step 3
40
Activity Section
Part 1: Design an IP
Addressing Scheme
Part 1 Total
70
Packet Tracer Score
30
Total Score
100
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Earned
Points
Page 4 of 4
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- PLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosD'EverandPLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3D'EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bootstrap Cheat Sheet: If You Plan To Pick Up Some Coding Skills, Bootstrap 4 Is A Solid Choice!Document50 pagesBootstrap Cheat Sheet: If You Plan To Pick Up Some Coding Skills, Bootstrap 4 Is A Solid Choice!BL Pipas100% (2)
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationD'EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Raspberry Pi: Raspbian Linux and GPIO IntegrationD'EverandAdvanced Raspberry Pi: Raspbian Linux and GPIO IntegrationPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Document4 pages8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Duscosi100% (1)
- Day 3 - Social Change - in DepthDocument36 pagesDay 3 - Social Change - in DepthFfrekgtreh FygkohkPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ilustrated Lean & Lean VSM Mapping The Extended Value Stream PDFDocument222 pagesThe Ilustrated Lean & Lean VSM Mapping The Extended Value Stream PDFaycaplt100% (1)
- 9.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 InstructionsDocument6 pages9.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 InstructionsweaksisPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Document5 pages8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1ParthPatel33% (6)
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxD'EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Ccna2 Labs AnswersDocument69 pagesCcna2 Labs Answerschadi_lb67% (6)
- 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring HSRP and GLBP (10m)Document9 pages2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring HSRP and GLBP (10m)Yong WHPas encore d'évaluation
- As We May ThinkDocument8 pagesAs We May ThinkPaulla PereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ip Addressing and Subnetting Workbook - Desarrollado Todo El Documento PDFDocument177 pagesIp Addressing and Subnetting Workbook - Desarrollado Todo El Documento PDFRichard Vera NerviPas encore d'évaluation
- 9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1JPDocument5 pages9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1JPAnonymous 9XGVHQcQRd100% (3)
- 9.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 InstructionsDocument6 pages9.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 InstructionsRizky Hoki VoLtagerPas encore d'évaluation
- ICT60215 - Task 1Document17 pagesICT60215 - Task 1MitchPas encore d'évaluation
- 298413192-8-1-4-7 - Sin ResolverDocument5 pages298413192-8-1-4-7 - Sin ResolverClaudia Glorieux AlarcónPas encore d'évaluation
- IPv4 Subnetting Scenario 1Document4 pagesIPv4 Subnetting Scenario 1mehrdad arabiPas encore d'évaluation
- 11.7.5-Packet-Tracer - Subnetting-ScenarioDocument5 pages11.7.5-Packet-Tracer - Subnetting-Scenariostudy timePas encore d'évaluation
- Device Interface Ip Address Subnet Mask Default-GatewayDocument3 pagesDevice Interface Ip Address Subnet Mask Default-GatewayJr de GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Subnetting Network Topologies - ILMDocument9 pagesSubnetting Network Topologies - ILMEmy HazlindaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer Subnetting Scenario 1Document5 pages8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer Subnetting Scenario 1Alex VolkovPas encore d'évaluation
- 9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 Instructions IGDocument4 pages9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 Instructions IGsalin zambranoPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.1.3.7 Packet Tracer Lab 2Document6 pages8.1.3.7 Packet Tracer Lab 2darkbane00Pas encore d'évaluation
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 - ILMDocument5 pages8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 - ILMHanif AwalludinPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2Document5 pages8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2Ajay0% (1)
- 9.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 Instructions IGDocument6 pages9.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 Instructions IGHuseyn AlkaramovPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationDocument4 pagesLab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationJosue Isahu Sanchez MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- E2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorDocument7 pagesE2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorRicardo GonçalvesPas encore d'évaluation
- E2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorDocument7 pagesE2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorJosely MontillaPas encore d'évaluation
- PT Activity 2.1.7: Troubleshooting A Serial Interface: Topology DiagramDocument3 pagesPT Activity 2.1.7: Troubleshooting A Serial Interface: Topology DiagramAn LePas encore d'évaluation
- Actividad 1 PT Curso 2Document5 pagesActividad 1 PT Curso 2jacastillo68Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Skills Integration: 1.6.1.3Document3 pagesCisco Skills Integration: 1.6.1.3BrandsmaSj0% (2)
- En ERouting IPTM v4Document55 pagesEn ERouting IPTM v4GµårÐïåñPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 PDFDocument4 pages8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 PDFSyammirul RashidPas encore d'évaluation
- 9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 InstructionsDocument4 pages9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 InstructionsJonny MonteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Packet Tracker Lab4 Configuring Ipv4 Route: TopologyDocument4 pagesPacket Tracker Lab4 Configuring Ipv4 Route: TopologyChoxicPas encore d'évaluation
- EWAN PTAct 2 1 7Document3 pagesEWAN PTAct 2 1 7Lekan Mulana0% (1)
- Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario: Nombre: Cesar Jesus Rios Morales Addressing TableDocument4 pagesPacket Tracer - Subnetting Scenario: Nombre: Cesar Jesus Rios Morales Addressing TableL HammeRPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3.5.2: Subnetting Scenario 1: Topology DiagramDocument14 pagesLab 3.5.2: Subnetting Scenario 1: Topology Diagramdepeters3183Pas encore d'évaluation
- Te Va A Servir en Cisco V2Document4 pagesTe Va A Servir en Cisco V2Bryant GamboaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRP - ILMDocument18 pages4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRP - ILMjanakp2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- TP Atelier Reseau 2Document8 pagesTP Atelier Reseau 2EMMANUEL MANGALAPas encore d'évaluation
- E2 Lab 5 6 2 InstructorDocument7 pagesE2 Lab 5 6 2 InstructorPedro Daniel Borja CisnerosPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 6 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesDocument7 pagesWeek 6 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesAhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- E2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorDocument10 pagesE2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorOkta WijayaPas encore d'évaluation
- 9.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 InstructionsDocument5 pages9.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 InstructionsAriel Fernando Cerquera GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With AuthenticationDocument8 pages3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With AuthenticationLarry Abisaí17% (6)
- 6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router Network - Isaiah WhitenerDocument6 pages6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router Network - Isaiah WhitenerSpectre EtherealPas encore d'évaluation
- 9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 InstructionsDocument4 pages9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 InstructionsRadu Florin TriponPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Exercise RE Sesi 1 2223 - 2047, 2080Document9 pagesPractical Exercise RE Sesi 1 2223 - 2047, 2080SILEPUPUSPas encore d'évaluation
- 19EC412 Networks ManualDocument35 pages19EC412 Networks ManualGurunathanPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Document4 pages8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Rubén Darío Saa MontañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluación de Habilidades Prácticas de PTDocument18 pagesEvaluación de Habilidades Prácticas de PTalvarofst100% (1)
- Packet TracerDocument7 pagesPacket TracerEgi WiratamaPas encore d'évaluation
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkD'EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkPas encore d'évaluation
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksD'EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksPas encore d'évaluation
- Token Ring Technology ReportD'EverandToken Ring Technology ReportPas encore d'évaluation
- DronesDocument4 pagesDronespincer-pincerPas encore d'évaluation
- Devops: Post Graduate Program inDocument22 pagesDevops: Post Graduate Program inSumeet DeshpandePas encore d'évaluation
- NR - PcVue16 - en 2Document7 pagesNR - PcVue16 - en 2Shariq Ahmed KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Multitrack HistoryDocument5 pagesMultitrack HistoryMatt GoochPas encore d'évaluation
- M190PW01 V0Document28 pagesM190PW01 V0Tomescu MarianPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection On IctDocument3 pagesReflection On Ictapi-532539634Pas encore d'évaluation
- GXP Usermanual EnglishDocument44 pagesGXP Usermanual EnglishKatherine Nicole LinqueoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe 2D Autocad: Compared WithDocument8 pagesPipe 2D Autocad: Compared WithThiruvengadamPas encore d'évaluation
- Deakin Learning Futures AGENDA 2020 Stage 2: Assessment and Learning DesignDocument6 pagesDeakin Learning Futures AGENDA 2020 Stage 2: Assessment and Learning DesignAmel Abbas Abbas AbbakerPas encore d'évaluation
- SS3 DP 2ND TermDocument14 pagesSS3 DP 2ND TermThe-INKS crewPas encore d'évaluation
- Barudan TESDocument42 pagesBarudan TESMartinandKimberly RayPas encore d'évaluation
- Sepam Series 80 NPP - 59742 G88Document3 pagesSepam Series 80 NPP - 59742 G88Djamel BeddarPas encore d'évaluation
- En PSAAS Public Train BookDocument27 pagesEn PSAAS Public Train BookMariano MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Harnessing Digital Technologies For Inclusion in IndonesiaDocument81 pagesHarnessing Digital Technologies For Inclusion in IndonesiaSinggih PintokoPas encore d'évaluation
- EURANEDocument19 pagesEURANEsatti2628Pas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Hardware Installation Quality Key PointDocument138 pages01 Hardware Installation Quality Key Pointfelly mutuakashalaPas encore d'évaluation
- JLG 153-12Document2 pagesJLG 153-12Luis Vélez RomàPas encore d'évaluation
- Fisher 846 Current To Pressure Transducers PDFDocument60 pagesFisher 846 Current To Pressure Transducers PDFJamesPas encore d'évaluation
- MOD4Document68 pagesMOD4AyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Simatic: STEP 7 V5.5 SP1 Programming Software For Simatic S7 / M7 / C7Document48 pagesSimatic: STEP 7 V5.5 SP1 Programming Software For Simatic S7 / M7 / C7hilmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Build a 5W 40M CW TransmitterDocument2 pagesBuild a 5W 40M CW TransmitterRicardo MorimPas encore d'évaluation
- Use and Occupancy ClassificationDocument1 pageUse and Occupancy ClassificationheshamPas encore d'évaluation
- Ashish Ajit Singh Resume - (23!03!2021)Document7 pagesAshish Ajit Singh Resume - (23!03!2021)ashish singhPas encore d'évaluation
- OpticalDocument3 pagesOpticalAshok Pradhan100% (1)
- 3900 Series Base Station Cables (04) (PDF) - enDocument787 pages3900 Series Base Station Cables (04) (PDF) - enAndrei Ghitiu100% (1)
- B&R Construction Company Job OpeningsDocument9 pagesB&R Construction Company Job OpeningsroopavijaykumarPas encore d'évaluation