Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
7.2.1 Lateral Pressure of Concrete Forms For Wall
Transféré par
Anonymous YgEKXgW0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
40 vues1 pagecoffrage
Titre original
Calcul de Coffrage2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentcoffrage
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
40 vues1 page7.2.1 Lateral Pressure of Concrete Forms For Wall
Transféré par
Anonymous YgEKXgWcoffrage
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
188
7.2.1
Chapter 7
Lateral Pressure of Concrete Forms for Wall
Formwork should be designed to resist the lateral pressure loads
exerted by the newly placed concrete in the forms. If concrete is
placed rapidly in wall or column forms, the pressure can be equivalent to the full liquid head pressure. This requires that rate of placement exceed the initial set time of the concrete mix. Excessive
deep vibration can liquefy the initial set of concrete within the effective coverage of the vibrations. Retarder additives or cool
weather can also delay the initial set and result in higher than anticipated lateral pressure. The formula for wall pressure established
by the American Concrete Institute (ACI-347) considers the mix
temperature and the rate of placement of concrete. The rate of
placement is expressed in terms of feet per hour of concrete rise
in the forms. Table 7.1 shows pressure values for concrete walls
of different temperature and rate of lling.
Table 7.1 Pressure Values for Concrete Walls: Relation among the
Rate of Filling Wall Forms, Maximum Pressure, and Temperature
(ACI)
Maximum concrete pressure, lb/ft2
Rate of
lling
forms, ft/h
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
15
20
Temperature, F
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
375
600
825
1050
1275
1500
1725
1793
1865
1935
2185
2635
330
510
690
870
1050
1230
1410
1466
1522
1578
1858
2138
300
450
600
750
900
1050
1200
1246
1293
1340
1573
1806
279
409
536
664
793
921
1050
1090
1130
1170
1370
1570
262
375
487
600
712
825
933
972
1007
1042
1217
1392
250
350
450
550
650
750
850
877
912
943
1099
1254
240
330
420
510
600
690
780
808
836
864
1004
1144
These values are limited to 2000 lb/ft 2.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Lecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignD'EverandLecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 Waste Water TreatmentDocument5 pages06 Waste Water TreatmentVijith29Pas encore d'évaluation
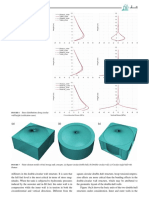
- Importance of Controlling Temperature Rise Due To Heat of Hydration in Massive Concrete Elements - Anura Nanayakkara PDFDocument7 pagesImportance of Controlling Temperature Rise Due To Heat of Hydration in Massive Concrete Elements - Anura Nanayakkara PDFsreesh001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design Considertions For Concrete FormworkDocument10 pagesDesign Considertions For Concrete FormworklahirujayasiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Importance of Controlling Temperature Rise Due To HeatDocument8 pagesImportance of Controlling Temperature Rise Due To Heatroshanfonseka6298Pas encore d'évaluation
- Temperature - 1Document2 pagesTemperature - 1ksshashidharPas encore d'évaluation
- p2 PDFDocument16 pagesp2 PDFtinsaePas encore d'évaluation
- Hurd Revised Formwork FormulasDocument3 pagesHurd Revised Formwork Formulasshaikhaziz84100% (2)
- The Crucial Role Played by The Concrete in The Formwork DesignDocument6 pagesThe Crucial Role Played by The Concrete in The Formwork DesignKennard GeorgiusPas encore d'évaluation
- Hot - Weather Creaton 2Document7 pagesHot - Weather Creaton 2Pankaj PriyadarshiPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Analysis of A Concrete Diaphragm Wall: 10.1 Problem StatementDocument30 pages10 Analysis of A Concrete Diaphragm Wall: 10.1 Problem StatementHumza MubarikPas encore d'évaluation
- Assaad - Kinetics of Formwork Pressure Drop of Self Consolidating Concrete Containing Various Types and Contents of Binder - 2005Document9 pagesAssaad - Kinetics of Formwork Pressure Drop of Self Consolidating Concrete Containing Various Types and Contents of Binder - 2005Ha LämPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Cold Joint On Strength of ConcreteDocument9 pagesEffect of Cold Joint On Strength of ConcreteWladimir Gonzalez VelezPas encore d'évaluation
- Min Temp Mass Concrete Whittier 536Document4 pagesMin Temp Mass Concrete Whittier 536apocalypsevoid83Pas encore d'évaluation
- Buling Thermal Analysis GoodDocument19 pagesBuling Thermal Analysis GoodAhsan SattarPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017 Hot Weather ConcretingDocument6 pages2017 Hot Weather Concretingmohammedelliyas7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cracking Tendency of Bridge Deck Concrete: Benjamin E. Byard, Anton K. Schindler, Robert W. Barnes, and Akash RaoDocument10 pagesCracking Tendency of Bridge Deck Concrete: Benjamin E. Byard, Anton K. Schindler, Robert W. Barnes, and Akash RaoBekele AmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lateral Pressures For Formwork Design: A Review of The Formulas To Determine The Pressure of Fresh ConcreteDocument3 pagesLateral Pressures For Formwork Design: A Review of The Formulas To Determine The Pressure of Fresh ConcretetecanasioPas encore d'évaluation
- Early-Age Compressive Strength Assessment of Oil Well Class G Cement Due To Borehole Pressure and Temperature ChangesDocument10 pagesEarly-Age Compressive Strength Assessment of Oil Well Class G Cement Due To Borehole Pressure and Temperature ChangesrosyffPas encore d'évaluation
- Wet-Mix-or-DryDocument1 pageWet-Mix-or-DryHuaman Chavez Jesus Angel100% (1)
- 1.1 General: Temperature Control in Mass ConcreteDocument13 pages1.1 General: Temperature Control in Mass Concreteಸಿದ್ದು ಎ ವಿ ಹಳ್ಳಿPas encore d'évaluation
- On CracksDocument30 pagesOn CracksSyed Mohd Mehdi75% (8)
- Crack Control in Concrete Masonry WallsDocument4 pagesCrack Control in Concrete Masonry WallsAnonymous Re62LKaACPas encore d'évaluation
- Carson Baker Maturity EssayDocument12 pagesCarson Baker Maturity EssayCarsonBakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Cracking of ConcreteDocument2 pagesThermal Cracking of ConcreteChatchai ManathamsombatPas encore d'évaluation
- Hotcon PDFDocument7 pagesHotcon PDFjack21abPas encore d'évaluation
- Hot Weather ConcretingDocument10 pagesHot Weather ConcretingAgramovic PetarPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Formwork Loads and Pressure CalculationsDocument7 pagesConcrete Formwork Loads and Pressure CalculationsAravindan100% (1)
- Thermal Engineering For The Construction of Large Concrete Arch DamsDocument10 pagesThermal Engineering For The Construction of Large Concrete Arch DamsOscar LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 PBDocument7 pages1 PBSertaç KaramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Expansion Joint - 1Document12 pagesExpansion Joint - 1Danish YaseenPas encore d'évaluation
- DIN Standard On Formwork Pressures UpdatDocument3 pagesDIN Standard On Formwork Pressures UpdatRoberto CecchinatoPas encore d'évaluation
- TEK 10-01A Crack Control in CMU WallsDocument8 pagesTEK 10-01A Crack Control in CMU WallsAdam JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- C2 Curado Del Concreto - PCADocument7 pagesC2 Curado Del Concreto - PCAJancarlo Mendoza MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- Axial Shortening of ColumnsDocument10 pagesAxial Shortening of Columnshaitham aliPas encore d'évaluation
- 16 Effect of Freezethaw Cycling On Fatigue Behaviour in Concrete2019IOP Conference Series Materials Science and EngineeringDocument7 pages16 Effect of Freezethaw Cycling On Fatigue Behaviour in Concrete2019IOP Conference Series Materials Science and EngineeringВладиславPas encore d'évaluation
- Diff Strain Concrete 13 1 FinalDocument8 pagesDiff Strain Concrete 13 1 FinalDoug JenkinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter ThermalCracksinConcreteStructure BasicIssuestobeUnderstoodDocument13 pagesChapter ThermalCracksinConcreteStructure BasicIssuestobeUnderstoodmirvahid HOSSiNiPas encore d'évaluation
- Use of Geotextiles For Reinforcement andDocument21 pagesUse of Geotextiles For Reinforcement andGen Bam Gils™Pas encore d'évaluation
- sms11 5801 PDFDocument7 pagessms11 5801 PDFNalin D. EdiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Crack Control in Concrete Masonry WallsDocument4 pagesCrack Control in Concrete Masonry WallsMohamed Mostafa IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Use of Admixture and Its Effects On Setting TimeDocument3 pagesUse of Admixture and Its Effects On Setting Timegemotorres100% (1)
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument35 pagesChapter 3 PDFrzrzzrzPas encore d'évaluation
- Early Age CrackingDocument4 pagesEarly Age CrackingAngga Fajar SetiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- DIN Standard On Formwork Pressures UpdatDocument3 pagesDIN Standard On Formwork Pressures UpdatTùng HìPas encore d'évaluation
- 20 388 PDFDocument10 pages20 388 PDFvidal3213Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Detailing of Movement JointsDocument28 pagesDesign and Detailing of Movement JointsTanveer AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- E3sconf Form2021 01008Document10 pagesE3sconf Form2021 01008lamvantang_638986441Pas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Concrete Curing (PCA)Document6 pagesRole of Concrete Curing (PCA)Ivan BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Jiang - 21: Et AlDocument4 pagesJiang - 21: Et AlvisvisvisvisPas encore d'évaluation
- 607 003 PDFDocument7 pages607 003 PDFShikhar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Jiangsu University of Science and TechnologyDocument20 pagesJiangsu University of Science and TechnologyMd ShoagPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Formwork Loads and Pressure Calculations PDFDocument8 pagesConcrete Formwork Loads and Pressure Calculations PDFmohamed.s.elsayedPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Ant - Intbarnet Bungey 2004Document18 pages02 Ant - Intbarnet Bungey 2004anzogu128Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete-Block Manufacture - Processes and MachinesD'EverandConcrete-Block Manufacture - Processes and MachinesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignD'EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- 11.4 Formulas For at Plates With Straight Boundaries and Constant ThicknessDocument1 page11.4 Formulas For at Plates With Straight Boundaries and Constant ThicknessAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- BLDocument1 pageBLAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- 11.4 Formulas For at Plates With Straight Boundaries and Constant ThicknessDocument1 page11.4 Formulas For at Plates With Straight Boundaries and Constant ThicknessAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Steel Connection 1Document1 pageSteel Connection 1Anonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Boat L EnergyDocument1 pageBoat L EnergyAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Vessel1Document1 pagePressure Vessel1Anonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Saddle 1Document1 pageSaddle 1Anonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- dofxo G Dvvhpeodjh 3Rxwuh3Rxwuh Sodwlqh G DerxwDocument1 pagedofxo G Dvvhpeodjh 3Rxwuh3Rxwuh Sodwlqh G DerxwAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Tandard: Detail A Detail BDocument1 pageTandard: Detail A Detail BAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Reinforcement Basic Training: Productversion 13.1 May 2008Document1 pageReinforcement Basic Training: Productversion 13.1 May 2008Anonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- © 2008 Tekla Corporation and Its Licensors. All Rights ReservedDocument1 page© 2008 Tekla Corporation and Its Licensors. All Rights ReservedAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Pages de Mechanics of Materials-2Document1 pagePages de Mechanics of Materials-2Anonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- AISC Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesAISC Cheat SheetLaura Sophia Icaza Estrada100% (1)
- Company Document Identification Owner Document Identification Validity Status Revisi On #Sheet of SheetsDocument1 pageCompany Document Identification Owner Document Identification Validity Status Revisi On #Sheet of SheetsAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Schema de Calcul PDFDocument1 pageSchema de Calcul PDFAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Pages de Calcul de Coffrage-4Document1 pagePages de Calcul de Coffrage-4Anonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Pages de Calcul de Coffrage6Document1 pagePages de Calcul de Coffrage6Anonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Pages de Calcul de Coffrage1Document1 pagePages de Calcul de Coffrage1Anonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Pages de Calcul de Coffrage1Document1 pagePages de Calcul de Coffrage1Anonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Pages de Calcul de Coffrage2Document1 pagePages de Calcul de Coffrage2Anonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Assem ExistantDocument1 pageAssem ExistantAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- BoltsDocument2 pagesBoltsAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Annexe 04 Trap DWG Bravo Rev0Document1 pageAnnexe 04 Trap DWG Bravo Rev0Anonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Pages de Mechanics of MaterialsDocument1 pagePages de Mechanics of MaterialsAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Example Ed5Document40 pagesExample Ed5Anonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Example E4dDocument1 pageExample E4dAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Example E.1dDocument1 pageExample E.1dAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation
- Example E.2dDocument1 pageExample E.2dAnonymous YgEKXgWPas encore d'évaluation