Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Electron Energies: Instructional Master LSM 12.4-1
Transféré par
i. g.Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Electron Energies: Instructional Master LSM 12.4-1
Transféré par
i. g.Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Instructional Master
LSM 12.4-1
Figure 6
Collected current versus accelerating potential difference
Current Reaching Plate
Electron Energies
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
6.0
7.0
8.0
Accelerating Potential Difference (V)
9.0
10.0
4.0 eV
1.1 eV
0 eV
4.9 eV
electron
4.0 eV
electron
6.0 eV
electron
mercury atom
mercury atom
mercury atom
Figure 7
An incident electron with kinetic
energy less than 4.9 eV bounces off
the mercury atom with no loss of
kinetic energy.
Figure 8
An incident electron with kinetic
energy 4.9 eV collides with the mercury atom and loses all its energy.
Figure 9
The incident electron with kinetic
energy greater than 4.9 eV collides
with the mercury atom, losing
4.9 eV of kinetic energy but
retaining enough energy to be able
to reach the plate.
Energy Above Ground State (eV)
unbound states
10.4 eV
ionization level
8.8 eV
3rd excitation level
6.7 eV
2nd excitation level
4.9 eV
1st excitation level
0 eV
366 Chapter 12 Waves, Photons, and Matter
ground state
Figure 10
Energy-level diagram for mercury.
Although only three excitation levels
are shown, there are many more
above the third level, spaced progressively closer together up to the
ionization level. Beyond the ionization level, electrons are not bound
to the nucleus of an atom.
Copyright 2003 Nelson
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Unit 12345 Learning GoalsDocument2 pagesUnit 12345 Learning Goalsi. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Scattering Of: Particles by Gold FoilDocument1 pageThe Scattering Of: Particles by Gold Foili. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Bubble Chamber Photograph of A K /P Interaction and Schematic From Sample Problem 2, Pages 724-726Document1 pageBubble Chamber Photograph of A K /P Interaction and Schematic From Sample Problem 2, Pages 724-726i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Bubble Chamber Photograph of A K /P Interaction III: Instructional Master LSM 13.6-3Document1 pageBubble Chamber Photograph of A K /P Interaction III: Instructional Master LSM 13.6-3i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Standard Model: A Table of Particles: Instructional Master LSM 13.7-1Document1 pageThe Standard Model: A Table of Particles: Instructional Master LSM 13.7-1i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Blackbody Radiation: Instructional Master LSM 12.1-2Document1 pageBlackbody Radiation: Instructional Master LSM 12.1-2i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Summary of Radiation Decay: Instructional Master LSM 13.1-1Document1 pageSummary of Radiation Decay: Instructional Master LSM 13.1-1i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bubble Chamber Photograph of A K /P Interaction II: Instructional Master LSM 13.6-2Document1 pageBubble Chamber Photograph of A K /P Interaction II: Instructional Master LSM 13.6-2i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Feynman Diagrams of Force Carriers: Instructional Master LSM 13.4-1Document1 pageFeynman Diagrams of Force Carriers: Instructional Master LSM 13.4-1i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Some Subatomic Particles: Instructional Master LSM 13.5-1Document1 pageSome Subatomic Particles: Instructional Master LSM 13.5-1i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Refraction of Waves: Instructional Master LSM 9.1-5Document1 pageRefraction of Waves: Instructional Master LSM 9.1-5i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Partial Reflection-Partial Refraction: Instructional Master LSM 9.4-1Document1 pagePartial Reflection-Partial Refraction: Instructional Master LSM 9.4-1i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Photoelectric Effect: Instructional Master LSM 12.1-3Document1 pageThe Photoelectric Effect: Instructional Master LSM 12.1-3i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Time Dilation: Instructional Master LSM 11.2-1Document1 pageTime Dilation: Instructional Master LSM 11.2-1i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Two-Point Interference Pattern: Instructional Master LSM 9.5-2Document1 pageTwo-Point Interference Pattern: Instructional Master LSM 9.5-2i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Double-Slit Experiment: Instructional Master LSM 9.5-3Document1 pageDouble-Slit Experiment: Instructional Master LSM 9.5-3i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Interference of White, Red, and Blue Light: Instructional Master LSM 9.6-2Document1 pageInterference of White, Red, and Blue Light: Instructional Master LSM 9.6-2i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Frames of Reference (Interferometer Example) : Instructional Master LSM 11.1-2Document1 pageFrames of Reference (Interferometer Example) : Instructional Master LSM 11.1-2i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diffraction of Water Waves: Instructional Master LSM 9.2-2Document1 pageDiffraction of Water Waves: Instructional Master LSM 9.2-2i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Two-Point Interference Pattern: Instructional Master LSM 9.3-3Document1 pageTwo-Point Interference Pattern: Instructional Master LSM 9.3-3i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Learning Tip: in Phase Versus Out of Phase: Instructional Master LSM 9.3-2Document1 pageLearning Tip: in Phase Versus Out of Phase: Instructional Master LSM 9.3-2i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1091)
- Reflection From A Straight Barrier: Instructional Master LSM 9.1-4Document1 pageReflection From A Straight Barrier: Instructional Master LSM 9.1-4i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
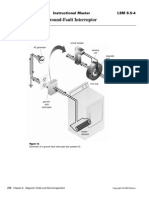
- Ground-Fault Interruptor: Instructional Master LSM 8.5-4Document1 pageGround-Fault Interruptor: Instructional Master LSM 8.5-4i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Reflection: Instructional Master LSM 9.1-2Document1 pageReview of Reflection: Instructional Master LSM 9.1-2i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
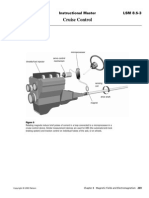
- Cruise Control: Instructional Master LSM 8.5-3Document1 pageCruise Control: Instructional Master LSM 8.5-3i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Guitar Pickup: Instructional Master LSM 8.5-5Document1 pageElectric Guitar Pickup: Instructional Master LSM 8.5-5i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
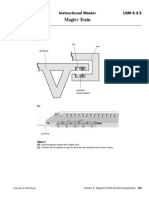
- Maglev Train: Instructional Master LSM 8.3-3Document1 pageMaglev Train: Instructional Master LSM 8.3-3i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Transverse and Longitudinal Waves: Instructional Master LSM 9.1-3Document1 pageReview of Transverse and Longitudinal Waves: Instructional Master LSM 9.1-3i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
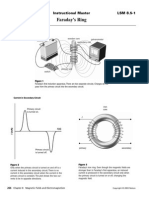
- Faraday's Ring: Instructional Master LSM 8.5-1Document1 pageFaraday's Ring: Instructional Master LSM 8.5-1i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ampère's Law: Instructional Master LSM 8.4-2Document2 pagesAmpère's Law: Instructional Master LSM 8.4-2i. g.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)