Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Relationships Between Elastic Constants
Transféré par
R@XCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Relationships Between Elastic Constants
Transféré par
R@XDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
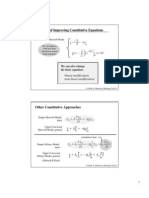
Relationships between elastic constants
Although only 2 independent elastic constants are required to complete the properties of
an isotropic elastic medium, there are many different constants from which to choose. Most
of these constants arise as constants of proportionality between stress and strain for various
loading conditions. For example, the ratio of hydrostatic stress (pressure) to volumetric
strain (dilatation) is
, which is given the name of bulk modulus and the symbol
The elastic constants are:
Lames constant
Shear modulus; sometimes G is used instead of
Poisson's ratio
Young's modulus
Bulk modulus
cL is bulk longitudinal-wave speed
cT is the bulk shear-wave speed
cR is the rayleigh-wave speed
2v
( E 2 )
2
vE
3Kv 3K(3K-E)
(cL2 2cT2 ),
1 2v
3 E
3
(1 v)(1 2v) 1 v
9K E
E
3
1 2v
1 2v
3KE
(K )
3K
cT2 ,
2(1 v) 2
2v
2 2v 9 K E
C11
2
cL
C55
cT
cR
3cL2 4cT2
c 2 2
cL cT
2
T
To these we may add the following combinations that appear frequently:
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Concepts of Fracture MechanicsDocument18 pagesConcepts of Fracture Mechanicsjs kalyana rama100% (1)
- Coupled CFD-DEM Modeling: Formulation, Implementation and Application to Multiphase FlowsD'EverandCoupled CFD-DEM Modeling: Formulation, Implementation and Application to Multiphase FlowsPas encore d'évaluation
- Guia Mastercam v9Document454 pagesGuia Mastercam v9Edson Sawada100% (2)
- Tubular Joint Analysis in Jacket StructureDocument43 pagesTubular Joint Analysis in Jacket StructureDaniel InemughaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-Problems in ElasticityDocument58 pages3-Problems in Elasticityali381100% (1)
- Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)Document17 pagesDynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)nervthcPas encore d'évaluation
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresD'EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Github Markdown CheatsheetDocument2 pagesGithub Markdown CheatsheettechiewickiePas encore d'évaluation
- A Practical Method For Statistical Analysis of Strain-Life Fatigue DataDocument10 pagesA Practical Method For Statistical Analysis of Strain-Life Fatigue DatabloomdidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of ExperimentsDocument31 pagesDesign of ExperimentsTeka KamPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of ExperimentsDocument31 pagesDesign of ExperimentsTeka KamPas encore d'évaluation
- Limit Load SolutionsDocument131 pagesLimit Load SolutionsZaid KamardinPas encore d'évaluation
- Doe HelicopterDocument9 pagesDoe Helicopteriangardiner.iow5796Pas encore d'évaluation
- MSC Adams TutorialDocument78 pagesMSC Adams TutorialcuccuaciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 38Document11 pagesLecture 38Shawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials 15 03481 v2Document15 pagesMaterials 15 03481 v2Ramesh PawarPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fracture MechanicsDocument81 pagesOn Fracture MechanicsDEEPAK100% (1)
- PPT On Fracture MechanicsDocument81 pagesPPT On Fracture Mechanicskamel touilebPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Limit Loads MillerDocument131 pagesReview of Limit Loads Millermarc53042Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fatigue FailureDocument8 pagesFatigue FailureAhmed AymanPas encore d'évaluation
- Truss 3d ExampleDocument16 pagesTruss 3d ExampleangegkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Mechanics (CE-312) : University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument32 pagesStructural Mechanics (CE-312) : University of Engineering and TechnologyHassaan MahmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Mechanics (CE-312) : University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument28 pagesStructural Mechanics (CE-312) : University of Engineering and TechnologyAnwaar SafdarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Maximum Stress Failure Criterion and The Maximum Strain Failure Criterion: Their Unification and RationalizationDocument16 pagesThe Maximum Stress Failure Criterion and The Maximum Strain Failure Criterion: Their Unification and RationalizationBapanapalli jaswanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Aging Model Foral MG SiDocument6 pagesAging Model Foral MG SiashokjkhannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jte20120161 DL.000389308 1Document13 pagesJte20120161 DL.000389308 1Nathalie El BarchePas encore d'évaluation
- MAE 212: Spring 2001 Module III: Material Property Characterization Using Strain Gage InstrumentationDocument7 pagesMAE 212: Spring 2001 Module III: Material Property Characterization Using Strain Gage InstrumentationChulbul PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ajassp 2004 5 11Document7 pagesAjassp 2004 5 11Junk JettisonPas encore d'évaluation
- CH332 L6 MD PDFDocument27 pagesCH332 L6 MD PDFkdsarodePas encore d'évaluation
- FatigueDocument116 pagesFatigueSezgin BayrakPas encore d'évaluation
- Bending and Axial Compression With RestraintsDocument8 pagesBending and Axial Compression With RestraintsszalaijaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lagrangian Slug Ow Modeling and Sensitivity On Hydrodynamic Slug Initiation Methods in A Severe Slugging CaseDocument11 pagesLagrangian Slug Ow Modeling and Sensitivity On Hydrodynamic Slug Initiation Methods in A Severe Slugging CasefanziskusPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 CaravacaDocument9 pages12 CaravacaBerkath Ali KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Yang EncyclopediaofMaterialComposites 2020Document14 pagesYang EncyclopediaofMaterialComposites 2020AnilPas encore d'évaluation
- Elastic Constants Basics (Rock Physics)Document7 pagesElastic Constants Basics (Rock Physics)Hcene HcenPas encore d'évaluation
- Yield Criteria For Anisotropic MetalsDocument23 pagesYield Criteria For Anisotropic Metalswillozzo75Pas encore d'évaluation
- Moritoki - 1996 - Intrinsic Criterion of Plastic InstabilityDocument8 pagesMoritoki - 1996 - Intrinsic Criterion of Plastic InstabilityTakis PlimirasPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 3A Lecture FatigueDocument38 pages2 3A Lecture FatigueEhsanJzrPas encore d'évaluation
- Deterministic Dynamics of Large Solid BodiesDocument99 pagesDeterministic Dynamics of Large Solid Bodiesmohdsolihat1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Materials: Fatigue Life of Aluminum Alloys Based On Shear and Hydrostatic StrainDocument21 pagesMaterials: Fatigue Life of Aluminum Alloys Based On Shear and Hydrostatic StrainvikryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Three-Dimensional CFD Rotordynamic Analysis of Gas Labyrinth SealsDocument7 pagesThree-Dimensional CFD Rotordynamic Analysis of Gas Labyrinth SealsTapanVaishnavPas encore d'évaluation
- Buckling of Thin Metal Shells 73Document1 pageBuckling of Thin Metal Shells 73pawkomPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Fatigue Life Calculation: 6.1Strain-Life Equations With Mean StressDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Fatigue Life Calculation: 6.1Strain-Life Equations With Mean StressAbdelwahabPas encore d'évaluation
- 0142 1123 (92) 90041 A PDFDocument1 page0142 1123 (92) 90041 A PDFSwapnil NarnavarePas encore d'évaluation
- PhononsDocument29 pagesPhononsFikriPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Methods For Life Time Analysis of Creep Loaded Components in Steam Power PlantsDocument11 pagesAdvanced Methods For Life Time Analysis of Creep Loaded Components in Steam Power PlantsvitorPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Mechanics 2012: Determination of Burst Pressure of Thin-Walled Pressure VesselsDocument11 pagesEngineering Mechanics 2012: Determination of Burst Pressure of Thin-Walled Pressure VesselspajadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- w78 2006 tf561Document10 pagesw78 2006 tf561Thomas VanhollePas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement of Creep Crack Growth Times in Metals: Standard Test Method ForDocument25 pagesMeasurement of Creep Crack Growth Times in Metals: Standard Test Method ForCristian DíazPas encore d'évaluation
- The Renormalization Group Yakhot and Smith 1992Document27 pagesThe Renormalization Group Yakhot and Smith 1992ThePriusPas encore d'évaluation
- Derivation of The Adjoint Drift Flux Equations ForDocument21 pagesDerivation of The Adjoint Drift Flux Equations Forbendel_boyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 0142112389904362 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 0142112389904362 Mainzoranperovic3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elastic Buckling Solution Methods For Cold-Formed Steel Elements and MembersDocument18 pagesElastic Buckling Solution Methods For Cold-Formed Steel Elements and Membersnona24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mass Transfer AssignmentDocument4 pagesMass Transfer AssignmentShanmugam GunasekaranPas encore d'évaluation
- What About Polymer Melts?: Green-Tobolsky Temporary Network ModelDocument7 pagesWhat About Polymer Melts?: Green-Tobolsky Temporary Network ModelShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 E Lee 2009Document7 pages5 E Lee 2009tolga memişPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S1877705811002499 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S1877705811002499 MainanuPas encore d'évaluation
- 1974 - Die Swell and Melt Fracture - Effects of Molecular Weight DistributionDocument5 pages1974 - Die Swell and Melt Fracture - Effects of Molecular Weight Distributionmbarete2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Z Angew Math Mech - 2002 - Lee - The Eigenfunctions of The Stokes Operator in Special Domains IIIDocument9 pagesZ Angew Math Mech - 2002 - Lee - The Eigenfunctions of The Stokes Operator in Special Domains IIIDuc DoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fan 2012Document5 pagesFan 2012SwetaSinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem 11Document7 pagesProblem 11FcosmePas encore d'évaluation
- Giesekus ModelDocument18 pagesGiesekus Modelvasopoli1Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of The Dendritic Growth Model DimensionalDocument9 pagesThe Role of The Dendritic Growth Model Dimensionalnazanin timasiPas encore d'évaluation
- InTech-Evaluating The Integrity of Pressure Pipelines by Fracture MechanicsDocument28 pagesInTech-Evaluating The Integrity of Pressure Pipelines by Fracture MechanicsMAT-LIONPas encore d'évaluation
- Bom ManDocument65 pagesBom ManR@XPas encore d'évaluation
- Response: The Text Has Been Revised and A Table (Table 1 in The Revised Manuscript)Document3 pagesResponse: The Text Has Been Revised and A Table (Table 1 in The Revised Manuscript)R@XPas encore d'évaluation
- Monte Carlo MethodDocument16 pagesMonte Carlo MethodHajùrasHajarBenzaroualPas encore d'évaluation
- Monte Carlo MethodDocument16 pagesMonte Carlo MethodHajùrasHajarBenzaroualPas encore d'évaluation
- mATERIAL SC Crystal Directions and PlanesDocument7 pagesmATERIAL SC Crystal Directions and Planessanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- WEN ManualDocument15 pagesWEN ManualR@XPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture6-US. - Ultra Sound WavespdfDocument24 pagesLecture6-US. - Ultra Sound WavespdfSaif ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Ročník 08 - Hardness Tests - Zkoušky Tvrdosti PDocument5 pagesRočník 08 - Hardness Tests - Zkoušky Tvrdosti PEden HazardPas encore d'évaluation
- Defects in CrystalsDocument8 pagesDefects in CrystalsR@XPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture6-US. - Ultra Sound WavespdfDocument24 pagesLecture6-US. - Ultra Sound WavespdfSaif ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Differential Equations For Solid MechanicsDocument2 pages1 Differential Equations For Solid MechanicsR@XPas encore d'évaluation
- Units.: You Have Usually PersonallyDocument4 pagesUnits.: You Have Usually PersonallyR@XPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Differential Equations For Solid MechanicsDocument2 pages1 Differential Equations For Solid MechanicsR@XPas encore d'évaluation
- GearsDocument4 pagesGearsR@XPas encore d'évaluation
- Unlocking The Secrets of SolidworksDocument14 pagesUnlocking The Secrets of SolidworksR@XPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes On Nonlinear Inversion and Tomography - BerrymanDocument173 pagesLecture Notes On Nonlinear Inversion and Tomography - BerrymanR@XPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicios Solidworks PDFDocument50 pagesEjercicios Solidworks PDFRic Frs80% (5)
- Multisim 10 Component Reference GuideDocument450 pagesMultisim 10 Component Reference Guideredoctober24100% (2)
- Flaw Size Evaluation in Immersed Ultrasonic TestingDocument10 pagesFlaw Size Evaluation in Immersed Ultrasonic TestingR@XPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Draw - Drawing and Detailing With Solid WorksDocument52 pagesHow To Draw - Drawing and Detailing With Solid Workspsp71088% (8)
- Multisim 10 Component Reference GuideDocument450 pagesMultisim 10 Component Reference Guideredoctober24100% (2)
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4marifs2002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Standard PC Option/option ASCII Translator PackageDocument0 pageStandard PC Option/option ASCII Translator PackageR@XPas encore d'évaluation