Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
MCC Concept Map 9
Transféré par
api-2633570860 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
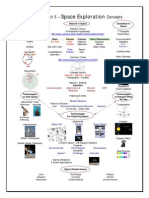
35 vues1 pageSymbol Shapes caution warning danger W.H.I.M.I.S. Hazardous Safety Symbols Chemical Change / Physical Change New Substance Forms Change of State Chemical properties Physical Properties Reaction with acids colour melting point lustre boiling point Reaction with water hardness malleability Ability to burn density ductility Behaviour in air conductivity crystal shape Reaction to heat Formation of Compounds Molecular Compounds Ionic Compounds Glucose Molecular compounds have weak Ionic compounds form when ions
Description originale:
Titre original
mcc concept map 9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentSymbol Shapes caution warning danger W.H.I.M.I.S. Hazardous Safety Symbols Chemical Change / Physical Change New Substance Forms Change of State Chemical properties Physical Properties Reaction with acids colour melting point lustre boiling point Reaction with water hardness malleability Ability to burn density ductility Behaviour in air conductivity crystal shape Reaction to heat Formation of Compounds Molecular Compounds Ionic Compounds Glucose Molecular compounds have weak Ionic compounds form when ions
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
35 vues1 pageMCC Concept Map 9
Transféré par
api-263357086Symbol Shapes caution warning danger W.H.I.M.I.S. Hazardous Safety Symbols Chemical Change / Physical Change New Substance Forms Change of State Chemical properties Physical Properties Reaction with acids colour melting point lustre boiling point Reaction with water hardness malleability Ability to burn density ductility Behaviour in air conductivity crystal shape Reaction to heat Formation of Compounds Molecular Compounds Ionic Compounds Glucose Molecular compounds have weak Ionic compounds form when ions
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
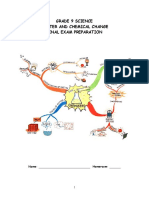
Grade 9 - Unit 2 Matter
and Chemical Change Concepts
Symbol Shapes
caution
warning
danger
W.H.I.M.I.S.
Hazardous
Safety
Symbols
Chemical Change / Physical Change
New Substance Forms
Change of State
Chemical properties
Physical Properties
Reaction with acids
colour
melting point
lustre
boiling point
Reaction with water
hardness
malleability
Ability to burn
density
ductility
Behaviour in air
conductivity
crystal
shape
Reaction to heat
Formation of Compounds
Molecular Compounds
Ionic Compounds
Glucose
Molecular compounds have weak
Ionic compounds form when ions attract
attractions between molecules
Chemical Names
Chemical Formulas
Naming Chemical Compounds (Rules)
Theories of Matter
Stone Age Chemists
Gold/Copper
Iron Age
Alchemy
Robert Boyle
Atomic Models
Antoine Lavoisier
Atomic Theory (John Dalton)
Billiard Ball
JJ Thomson
Raisin Bun
Hantaro Nagaoka
Planetary
Ernest Rutherford
Nucleus
Neils Bohr
Electron Orbit
Modern Chemists
Quantum Model
Chemical Reactions
Lab
Procedures
&
Techniques
(Reactants Products)
Endothermic (takes in energy)
- cold packs
- corrosion
Exothermic (gives off energy)
- fire (combustion)
- cellular respiration
Elements & the Periodic Table
Patterns Dmitri Mendeleev
Symbol Name Atomic Number
Atomic Mass Ionic Charge
Groups Periods
Reaction Rate (Speed)
Factors Affecting Reaction Rate
Catalysts
Concentration
Surface Area
Temperature
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Updated IB MYP GRADE - 9 - CHEMISTRY - TERM 2 - PORTION - 2020-21Document2 pagesUpdated IB MYP GRADE - 9 - CHEMISTRY - TERM 2 - PORTION - 2020-21Krishna Teja67% (3)
- General ChemistryDocument5 pagesGeneral ChemistryJay Mayonte AlmandresPas encore d'évaluation
- Atoms: A. Introduction To Chemistry, Atoms and ElementsDocument21 pagesAtoms: A. Introduction To Chemistry, Atoms and ElementsRazvanPopPas encore d'évaluation
- Trilogy FoundationTopic ListDocument2 pagesTrilogy FoundationTopic ListisheanesuPas encore d'évaluation
- HandoutsDocument36 pagesHandoutsJohn Mark MadrazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Academic English for Materials: Academic EnglishD'EverandAcademic English for Materials: Academic EnglishPas encore d'évaluation
- Yacov Saban The Department of Chemical Engineering Class: English Advance 2, Friday Lecturer: Dr. Noy-Abrahams Guy Summer 2011Document11 pagesYacov Saban The Department of Chemical Engineering Class: English Advance 2, Friday Lecturer: Dr. Noy-Abrahams Guy Summer 2011Kobi Angel SabanPas encore d'évaluation
- Inorganic Chemistry Lecture 1Document46 pagesInorganic Chemistry Lecture 1Nate EducationPas encore d'évaluation
- C7 The Periodic Table: G8 ScienceDocument28 pagesC7 The Periodic Table: G8 ScienceDanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials - Science 15ME32 - Module 1 PDFDocument25 pagesMaterials - Science 15ME32 - Module 1 PDFDevaraj EPas encore d'évaluation
- 12-13chapter 2 Matter and Energy ApesDocument50 pages12-13chapter 2 Matter and Energy ApesFernando MoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Materials ScienceDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Materials Science000001Pas encore d'évaluation
- How Is Mercury Used Today? Chemistry Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Chemistry BooksD'EverandHow Is Mercury Used Today? Chemistry Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Chemistry BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - 1 FinalDocument134 pagesUnit - 1 FinalGLOBAL INFO-TECH KUMBAKONAMPas encore d'évaluation
- Fire Officer ReviewerDocument9 pagesFire Officer ReviewerKobi FækPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Notes-Half YearliesDocument6 pagesChemistry Notes-Half YearliesSharon WuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry: Exam Style QuestionsDocument1 pageChemistry: Exam Style Questionsapi-199070930Pas encore d'évaluation
- MetalDocument5 pagesMetalFritzie Andrea TirolPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry ProjectDocument10 pagesChemistry ProjectShakina FyffePas encore d'évaluation
- Mat SC SolnDocument10 pagesMat SC SolnAlok YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Unit 1 CH 3 Slideshow 09Document26 pages9 Unit 1 CH 3 Slideshow 09api-238589602Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science LT1 IsDocument4 pagesScience LT1 IsManoli MontinolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reactions!: With 25 Science Projects for KidsD'EverandChemical Reactions!: With 25 Science Projects for KidsPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Materials Scholarship: Buy A Course BYJU'S GiveDocument14 pagesStudy Materials Scholarship: Buy A Course BYJU'S GiveGodwin AkpisheyePas encore d'évaluation
- Metal and Non MetalDocument4 pagesMetal and Non MetalphygoPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEMISTRY 16: General Chemistry 1 Course SyllabusDocument5 pagesCHEMISTRY 16: General Chemistry 1 Course Syllabusleksey24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elements and AtomsDocument29 pagesElements and AtomsmalaitamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of Various Groups and Periods of Periodic Table.: Physical ChemistryDocument67 pagesProperties of Various Groups and Periods of Periodic Table.: Physical ChemistryMuhammed Musab100% (1)
- Parent Science Curriculum 7.31.14 PDFDocument31 pagesParent Science Curriculum 7.31.14 PDFJesús Eduardo Carbonó NieblesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Study Notes Grade 10Document10 pagesChemistry Study Notes Grade 10Jynxx1387% (15)
- National Institute of Technology, Durgapur Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering MME 521: Materials ScienceDocument12 pagesNational Institute of Technology, Durgapur Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering MME 521: Materials ScienceAyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument4 pagesChemistry ReviewerCyreel ManaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideD'EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Chemistry Chapter 4 Form 4Document7 pagesChemistry Chapter 4 Form 4IZIKPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM 105 Credit Exam TopicsDocument3 pagesCHEM 105 Credit Exam TopicsNgo Thi ThuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Blocks of MatterDocument20 pagesBuilding Blocks of MatterTi NePas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Chemical Physical: Substances Can Be Identified by Their PropertiesDocument120 pagesNuclear Chemical Physical: Substances Can Be Identified by Their PropertiesRusyidah Mat Zin BoestamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 IbrDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Ibrsusilowati117Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Periodic Table: Discover Incredible Elements that Make Up Everything!D'EverandThe Periodic Table: Discover Incredible Elements that Make Up Everything!Pas encore d'évaluation
- PH211 Physics of MaterialsDocument3 pagesPH211 Physics of MaterialsAbsar BaigPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1-4 Chemistry ChangDocument9 pagesChapter 1-4 Chemistry ChangErwin DoloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistr 1Document31 pagesChemistr 1Deron KofiPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 Science Matter and Chemical Change Final Exam PreparationDocument15 pagesGrade 9 Science Matter and Chemical Change Final Exam PreparationBekki VanderlendePas encore d'évaluation
- Science 9 Chemistry Notes BDocument31 pagesScience 9 Chemistry Notes BJoe HarringtonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Kinematics and Catalysis: Syllabus For Applied Chemistry (Theory) Ist Year B.Tech (Semester I/II)Document2 pagesChemical Kinematics and Catalysis: Syllabus For Applied Chemistry (Theory) Ist Year B.Tech (Semester I/II)KhadhyothPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Kinematics and Catalysis: Syllabus For Applied Chemistry (Theory) Ist Year B.Tech (Semester I/II)Document2 pagesChemical Kinematics and Catalysis: Syllabus For Applied Chemistry (Theory) Ist Year B.Tech (Semester I/II)Sümît DãsPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Kinematics and Catalysis: Syllabus For Applied Chemistry (Theory) Ist Year B.Tech (Semester I/II)Document2 pagesChemical Kinematics and Catalysis: Syllabus For Applied Chemistry (Theory) Ist Year B.Tech (Semester I/II)KhadhyothPas encore d'évaluation
- Matter: Inorganic Chemistry Group 1Document22 pagesMatter: Inorganic Chemistry Group 1Fer-J TagacayPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit A Science NoteDocument89 pagesUnit A Science NoteGurnoor ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Daniel, Reyden R. Abm 11 Sy Reviewer in Physical ScienceDocument23 pagesDaniel, Reyden R. Abm 11 Sy Reviewer in Physical ScienceREYNIEL ANGELIE DANIELPas encore d'évaluation
- Breathing and Gas Exchange PowerpointDocument53 pagesBreathing and Gas Exchange Powerpointapi-263357086100% (1)
- Adaptation and Evolution PowerpointDocument64 pagesAdaptation and Evolution Powerpointapi-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Circulatory SystemDocument67 pagesThe Circulatory Systemapi-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Blood and Immunity PowerpointDocument94 pagesBlood and Immunity Powerpointapi-263357086100% (1)
- Digestive System PowerpointDocument65 pagesDigestive System Powerpointapi-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit D Chapter 1Document41 pagesUnit D Chapter 1api-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit C Chapter 1Document70 pagesUnit C Chapter 1api-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit B Chapter 2Document35 pagesUnit B Chapter 2api-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- MFM Concept Map 8Document1 pageMFM Concept Map 8api-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science 30 Course Outline AliceaDocument3 pagesScience 30 Course Outline Aliceaapi-2633570860% (1)
- Laos Concept Map 8Document1 pageLaos Concept Map 8api-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ept Concept Map 9Document1 pageEpt Concept Map 9api-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fresh and Saltwater Systems: Grade 8 - Unit 5 - ConceptsDocument1 pageFresh and Saltwater Systems: Grade 8 - Unit 5 - Conceptsapi-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ccs Concept Map 8Document1 pageCcs Concept Map 8api-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ms Concept Map 8Document1 pageMs Concept Map 8api-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Se Concept Map 9Document1 pageSe Concept Map 9api-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ec Concept Map 9Document1 pageEc Concept Map 9api-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- BD Concept Map 9Document1 pageBD Concept Map 9api-263357086Pas encore d'évaluation
- Setting and Description in Horror Fiction Extended Short Story WorkshopDocument6 pagesSetting and Description in Horror Fiction Extended Short Story WorkshopMinaEmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Graphs Representing Motion: Distance-Time GraphDocument26 pagesGraphs Representing Motion: Distance-Time GraphRandom GuyPas encore d'évaluation
- CAPE Entrepreneurship Module 1 (2023-2024 Syllabus)Document22 pagesCAPE Entrepreneurship Module 1 (2023-2024 Syllabus)Shimmer100% (1)
- Navigating The Complexities of Modern SocietyDocument2 pagesNavigating The Complexities of Modern SocietytimikoPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction Site & Lifting by CraneDocument68 pagesConstruction Site & Lifting by CraneShammas RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Vertigo TestDocument6 pagesVertigo Testalam saroorPas encore d'évaluation
- Art in Our Life.Document2 pagesArt in Our Life.hhPas encore d'évaluation
- FormulaShell SAE 10W 40 Motor Oil DatasheetDocument3 pagesFormulaShell SAE 10W 40 Motor Oil DatasheetAnonymous YjoCCKPas encore d'évaluation
- Methodology For Bitumen MasticDocument6 pagesMethodology For Bitumen MasticSudip MukhopadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Geotechnical Properties of Soil On Civil Engineering StructuresDocument8 pagesRole of Geotechnical Properties of Soil On Civil Engineering StructuresSaša MarinPas encore d'évaluation
- Engaging Students Via Discussion Boards (DB'S) : Wake Technical Community CollegeDocument31 pagesEngaging Students Via Discussion Boards (DB'S) : Wake Technical Community CollegeAntti SnellmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructions:: Exam Papers Must Not Be Removed From The Exam Room Examiners: R.Russo T.KreouzisDocument9 pagesInstructions:: Exam Papers Must Not Be Removed From The Exam Room Examiners: R.Russo T.KreouziszcaptPas encore d'évaluation
- A Level Physics Units & SymbolDocument3 pagesA Level Physics Units & SymbolXian Cong KoayPas encore d'évaluation
- Malaysia VBI Full ReportDocument116 pagesMalaysia VBI Full ReportHasoPas encore d'évaluation
- MEE20004 Structural Mechanics Outline Sem 2 2023Document11 pagesMEE20004 Structural Mechanics Outline Sem 2 2023MKPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesCirculatory SystemstephaniecrossPas encore d'évaluation
- Local Knowledge, Global GoalsDocument48 pagesLocal Knowledge, Global Goalsecossich123100% (1)
- Activity Sheet 1 Music 1Document2 pagesActivity Sheet 1 Music 1Enah Sazi Ale ArbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Music Laptop Script (WhiteHat JR Customers)Document3 pagesMusic Laptop Script (WhiteHat JR Customers)Yash JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Pavement DesignDocument12 pagesPavement DesignTarun KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Essay For Passage TwoDocument2 pagesPractice Essay For Passage TwoVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- GGCTCDocument7 pagesGGCTCizaizaizaxxx100% (1)
- Executive MBA BrochureDocument36 pagesExecutive MBA BrochureAzad AMİROVPas encore d'évaluation
- ISC Class 12 Maths Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesISC Class 12 Maths Important QuestionsdhinchakclashersPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT-I Impact of Jet On VanesDocument8 pagesUNIT-I Impact of Jet On VanesAjeet Kumar75% (4)
- ANNEX A. Integrated Planning ProcessDocument3 pagesANNEX A. Integrated Planning Processcarlito alvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1Document11 pagesTopic 1Mercy MissionPas encore d'évaluation
- I VR With Speech RecognitionDocument79 pagesI VR With Speech Recognitionshakya ekta mauryaPas encore d'évaluation
- S2 Mathematics Module 1 HandoutDocument32 pagesS2 Mathematics Module 1 HandoutAakanksha KartikPas encore d'évaluation
- Values Development For Citizenship TrainingDocument11 pagesValues Development For Citizenship TrainingAvril SalenPas encore d'évaluation