Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Review Sheet For Math Midterm Exam Revised 1
Transféré par
api-294158678Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Review Sheet For Math Midterm Exam Revised 1
Transféré par
api-294158678Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
_____ 1. Which number is divisible by 2 but not by 4?
100, 125, 150, 200
a. 150
b. 200
c. 125
d. 100
_____ 2. Which number is divisible by 3 and by 10?
606, 110, 260, 420
a. 606
b. 110
c. 260
d. 420
_____ 3. Write an algebraic equation for n multiplied by 5.
a. n - 5
b. n + 5
c.
_____ 4. Evaluate the expression by replacing a with 13.
a 10
a. 23
b. 3
n
5
d. 5n
c. 130
d. 2
_____ 5. If n represents any term number, write a relation for the term.
Term Number
Term
7n
1
7
b. 2n + 7
2
14
3
21
c. 2n
4
28
5
35
6
42
d. n+7
_____ 6. Write a relation for the perimeter of the rectangle with length (n + 4) and width n cm.
n+4
a. (4n + 4) cm
b. (2n + 4) cm
c. n(n + 4) cm
d. (4n + 8) cm
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
a.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
_____ 7. The are n players on a sports team. Each player gets 3 pairs of sox and 4 pairs are kept
in reserve. Write a relation for the number of pairs of sox needed.
a. 4n + 3
b. 3n + 4
c. 7n
d. 12n
_____ 8. Use algebra. Write a relation for the Input/Output table.
Input x
Output
1
39
a. x 40
2
38
3
37
b. x + 35
4
36
5
35
c. 40 x
d. 39 x
_____ 9. Write an equation for I subtract 13 from a number. The answer is 24.
n
13
a.
= 24
b. n + 13 = 24
c. n 13 = 24
d. 13 n = 24
_____ 10. Write an equation for the situation.
Patricia has p posters. She sold 7 and has 19 left.
a. p = 19 7
b. p + 7 = 19
c. p 7 = 19
d. p + 19 = 7
_____ 11. Let one white tile represent +1 and one black tile represent -1.
Write the integer modeled by this set of tiles.
a. +6
b. +11
c. +1
d. -1
_____ 12. Let one white tile represent +1 and one black tile represent -1.
What sum is modeled by 17 positive tiles and 19 negative tiles?
a. -1
_____ 13. Add.
(-5) + (+10)
a. -15
b. +2
c. -2
d. +36
b. +15
c. +5
d. -5
_____ 14. David gets on an elevator at the 36th floor. The elevator goes down 26 floors then up
17 floors. At what floor did it finally stop?
a. -7
b. 27
c. 45
d. 79
_____ 15. Copy and complete.
(+9) - = -18
2
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
a. -9
b. -27
c. 9
d. +27
_____ 16. The graph shows the high and low temperatures in a week from Sunday to Saturday.
Hig h and Low T em per atu res
De gre es Cel cius
Days
On which of the following days was the difference between the high and low
temperature the least?
a. Sunday
b. Monday
c. Wednesday
d. Friday
_____ 17. A submarine at sea level dives 7m and then another 4 m.
Write the final depth of the submarine as an integer.
a. +11m
_____ 18. Write
28
36
_____ 19. Subtract.
a. -64.96
_____ 20. Calculate.
a. 17.74
c. -11m
d. -12m
as a decimal. Identify the decimal as terminating or repeating.
a. 0.8; terminating
_____ 21. Add.
b. +12 m
b. 1.8; terminating
7
c. 1. ; repeating
7
d. 0. ; repeating
12.39 7.735
b. 6.496
c. 4.655
d. 20.125
c. 16.34
d. 6.35
10.45 + 6.59 0.7
b. 16.97
0.9 + 0.89 + 0.789
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
a. 0.887
c. 17.69
d. 7.89
b. 14.4
c. 144
d. 1440
_____ 23. Divide.
2.12 0.4
a. 5.3
b. 0.053
c. 0.53
d. 53
_____ 24. Evaluate
17.5 5 x 1.4
a. 10.5
b. 24.5
c. 63
d. 17.5
c. 0.59
d. 59
c. 27%
d. 42%
_____ 22. Multiply.
b. 2.579
2.4 x 60
a. 84
_____ 25. Write 59% as a decimal.
a. 5.9
b. 0.059
12
50
_____ 26. Write
as a percent.
a. 38%
b. 24%
_____ 27. What fraction of the diagram is shaded?
3
////
8
/
a.
////
1
/
8
////
d.
/
_____ 28. What
Write the
2
10
a.
;
c.
4
5
20
b.
1
24
c.
fraction of the diagram is shaded?
fraction as a percent.
6
100
30%
b.
; 6%
; 25%
d.
2
100
; 20%
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
1
12
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
_____ 29. In your last 20 basketball games, you attempted 72 free throws and made 18 of them.
Express your success in making free throws as a percent.
a. 25%
b. 26%
c. 28%
d. 24%
_____ 30. Calculate 50% of 70.
a. 18
b. 35
c. 4
d. 9
_____ 31. Jason wants to buy a bicycle that costs $395.00. His parents ask Jason to raise 40%
of the money. How much does Jason have to raise?
a. $154.00
b. $158.00
c. $118.50
d. $40.00
_____ 32. A circle has a radius of 36.9 cm. What is its diameter?
a. 18.45 cm
b. 12.3 cm
c. 110.7 cm
d. 73.8 cm
_____ 33. Which is not a relationship between the radius r and the diameter d of a circle?
a. d 2 = r
b. d = 2r
c. r + r = d
d. 2d = r
_____ 34. What is the least number in the set?
11 9
1
6 4
6
4,
, ,2
a. 2
1
6
b.
9
4
11
6
c. 4
d.
c. 0.832, 1.054
d. 0.832, 0.943
_____ 35. Find the next two terms in the pattern.
0.277, 0.388, 0.499, 0.61
a. 0.721, 0.943
b. 0.721, 0.832
_____ 36. Determine the cost of 3.54 kg of apples at $1.05/kg.
a. $4.59
b. $3.72
c. $0.46
d. $37.17
_____ 37. A circle has a diameter of 54.2 m. What is the radius?
a. 162.6 m
b. 27.1 m
c. 108.4 m
d. 18.1 m
_____ 38. Four identical circles of the largest possible size are drawn on a square sheet of
paper. The side length of the paper is 6.4 cm. What is the radius of each circle?
a. 1.6 cm
b. 6.4 cm
c. 0.8 cm
d. 3.2 cm
_____ 39. Estimate the circumference of this circle.
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
a. 21 m
b. 42 m
c. 17 m
d. 84 m
c. 30 cm
d. 41 cm
_____ 40. Estimate the circumference of this circle.
a. 81 cm
b. 547 cm
_____ 41. The circumference of a circle is 27 cm.
Calculate the radius. Round your answer to one decimal place.
a. 5.9 cm
b. 4.3 cm
c. 13.5 cm
d. 8.6 cm
_____ 42. Find the diameter of a circle with a circumference of 35.1 cm.
Round your answer to one decimal place.
a. 5.6 cm
b. 11.2 cm
c. 22.3 cm
d. 17.6 cm
_____ 43. Find the area of this parallelogram.
a. 30 m
b. 50 m
c. 25 m
d. 100 m
_____ 44. Find the area of the parallelogram with base 45 cm and height 7.4 cm.
6
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
a. 27.38 cm
b. 333 cm
c. 202.5 cm
d. 52.4 cm
_____ 45. Find the area of this triangle.
a. 80 m
b. 18 m
c. 40 m
d. 160 m
c. P
d. S
_____ 46. Which triangle has an area of 6 square units?
a. Q
b. R
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
_____ 47. Find the area of this circle. Round your answer to two decimal places.
a. 2678.65 m
b. 91.73 m
c. 669.66 m
d. 45.87 m
The circle graph shows how a college student breaks down her study time in a typical week.
_____ 48. What fraction of the time is spent on English and Math?
a. about
1
2
b. about
1
3
c. about
3
4
d. about
2
3
_____ 49. Grade 7 students were surveyed on how many hours per day they spend on various
activities. About how many hours per day are spent on school and homework?
8
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
a. 7 h
b. 10 h
c. 9 h
d. 8 h
_____ 50. Find the central angle of a sector that represents 90% in a circle graph.
Round to the nearest degree if necessary.
a. 342
b. 306
c. 32
d. 324
Short Answer
51.
Divisible by 3
Divisible by 2
Place the numbers in the Venn Diagram.
27, 36, 14, 8, 21, 42, 20, 33
52. Write an algebraic expression for the sentence.
Subtract 14 from a number, then multiply by 3.
53. Evaluate
9
x
6
+ 9 by replacing x with 30.
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
2
54. The pattern is formed using 1 cm tiles.
Term 1
Term 2
Term 3
a) What is the perimeter for each term?
b) Write a relation for the perimeter of the nth term.
55. Write an equation for the sentence.
Nine less than a number is 14.
56. Which equation has the solution x = 12
A: x + 6 + 18
B: 6x = 18
C: 18 + x = 6
10
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
57. Let one white tile represent +1 and one black tile represent -1.
Write the integer modeled by this set of tiles.
58. Let one white tile represent +1 and one black tile represent -1.
Add.
59. Add
(-7) + (-4)
60. Copy and complete.
(-3) +
= (+5)
61. Write the addition equation modeled by the number line.
62. Write the subtraction equation modeled by the number line.
63. Write 0.48 as a fraction in simplest form.
64. Write
11
7
4
as a decimal.
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
5
6
65. Write 1 as a decimal.
66. Use any method. Order the following numbers from least to greatest.
8 5
3 27
3 2 5 10
, ,2 ,
67. Multiply.
3.6 x 4.4
68. Evaluate.
(14.4 2.5) x 4.2 2.16 0.6
69. A strip of cardboard measures 3 cm by 36 cm.
a) What is the diameter of the largest circle you can cut from the strip?
b) How many circles can you cut from the strip?
70. A bicycle wheel has a radius of 36 cm.
How far will the bicycle travel if the wheel makes 400 rotations?
71. Calculate the area of the semicircle. Round your answer to the nearest
square centimeter.
21.2 cm
Problems
72. Write the least 3-digit number that is divisible by 3 and by 4.
73. A number is divisible by 5 and by 6. List at least 5 factors of that number.
74. The diagram consists of a square and a parallelogram. Find the area of the figure.
12
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
75. The outer circle has a diameter of 10 cm. The two smaller circles are identical.
What is the total area of the shaded regions?
Round your answer to two decimal places. Show your work.
13
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
Notes and Study Helps
Some notes and special study helps are given to help with individual questions on the review
sheet. These correspond with the question numbers on the review sheet.
1, 2, 51. Divisibility Rules: A number is said to be divisible by another number if the second number
divides evenly into it and there is no remainder. For example 15 is divisible by 5 because when you
divide 5 into 15 the answer is a whole number (3) and there is no remainder. Divisibility rules are
rules that we can use to quickly check if a number can divide evenly into another number without
having to do the actual division.
The divisibility rules that students should know are as follows:
A whole number is divisible by:
2 if the number is even (ends in 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8).
3 if the sum of the digits is divisible by 3.
4 if the number represented by the last two digits is divisible by 4.
5 if the ones digit is 0 or 5.
6 if the number is divisible by both 2 and 3.
8 if the number represented by the last 3 digits is divisible by 8.
9 if the sum of the digits is divisible by 9
10 if the ones digit is 0.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 6-13 for additional information and practice) Additional help can be
found at the following website.
http://mathforum.org/dr.math/faq/faq.divisibility.html
http://www.vectorkids.com/vkdivisible.htm
http://www.basic-mathematics.com/divisibility-rules-game.html
www.quia.com/rr/124815.html
3, 4, 52, 53, 55, 56. A variable is a letter, such as n, that represents a number that can vary. An
algebraic expression is a mathematical expression containing a variable; for example, 6x 4 is an
algebraic expression.
Some examples of algebraic expressions and their meanings are as follows. In each case, n
represents the number.
Three more than a number: 3 + n or n + 3
Seven times a number: 7n
14
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
Eight less than a number: n 8
n
20
A number divided by 20:
When we replace a variable with a number in an algebraic expression, we evaluate the expression.
That is, we find the value of the expression for a particular value of the variable.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 16-19 for additional information and practice) Additional help can be
found at the following websites.
http://www.mathgoodies.com/lessons/vol7/expressions.html
http://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/substitution.html
http://www.learnalberta.ca/content/mec/html/index.html?launch=true
5, 7. When we compare or relate a variable to an expression that contains the variable, we have a
relation. A relation can be used to describe a pattern and to solve problems. In a growing pattern of
numbers, a relation tells how each term of the pattern relates to the term number, rather than how
each term relates to the term that comes before it.
From a table of values, a relationship can be found. This relationship must be true for all terms in the
table.
Term #
Term
1
7
2
14
3
21
4
28
5
35
6
42
In the above table, if you look at Term 1, you might conclude that Term# + 6 = Term. This works for
Term #1 because 1+6 = 7 but it doesnt work for Term #2 because 2 + 6 does not equal 14, so this is
not the relationship.
You might also conclude that the relationship is Term# x 7 = Term. This works for Term#1, because
1 x 7 = 7. When we check it with the other Term #s we see that it also works. i.e.) 2 x7 = 14, 3 x 7
=21 Therefore we can conclude that we have found the relationship between Term # and Term for
the whole table.
Once we know the relationship for the table, we can use it to find the value for any Term if give the
Term #, without having to calculate all the terms in between. For example, if the above table were
extended the value of the term for Term # 500 would be 500 x 7 = 3500.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 20-24 for additional information and practice)
15
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://www.learnalberta.ca/content/mejhm/index.html?
l=0&ID1=AB.MATH.JR.PATT&ID2=AB.MATH.JR.PATT.PATT&lesson=html/object_interactives/
patterns/explore_it.html
6. Perimeter is the distance around an object. The formula for the perimeter is:
Perimeter = length + width + length + width
or
Perimeter = (2 x length) + (2 x width)
x
x+3
In the rectangle above, Perimeter = x + (x+3) + x + (x+3)
= 4x +6
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 20-24 for additional information and practice)
Additional help can be found at the following websites.
https://ca.ixl.com/math/grade-6/perimeter
http://www.mathplayground.com/geoboard.html
8. When a relation is represented by a table with consecutive Input numbers, a pattern can be
observed in the Output numbers. When a relation is represented as a table of values, we can write the
relation using algebra. Make sure that the relation is true for all pairs of input/output numbers.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 25-28 for additional information and practice)
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://www.mathplayground.com/functionmachine.html
http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/activities/NumberCruncher/
https://ca.ixl.com/math/grade-7/write-a-rule-for-a-function-table
16
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
9, 10. An equation is a mathematical statement that two expressions are equal. An equation must
contain an equal sign. The following are examples of equations:
3n 8 = 55
x + 5 = 10
k + 5 = 2k 7
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 35-37 for additional information and practice)
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://www.math.com/school/subject2/lessons/S2U1L3GL.html
https://ca.ixl.com/math/grade-7/solve-two-step-linear-equations
11, 12, 57. The set of integers is as follows:
I = {, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3, +4 }
The numbers farther to the right are the larger numbers.
Colored tiles can be used to represent integers. A tile representing + 1 and a tile representing -1 form
a zero pair. These tiles combine to model zero.
In the example above each white tile represents + 1 and each black tile represents
-1. Each of the five black tiles can be combined with a white tile to form a zero pair, which equals
zero. When this is done there is still one white tile left over, so the total value of all the tiles
combined is +1.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 52-55 for additional information and practice)
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_162_g_3_t_1.html?
open=instructions&from=category_g_3_t_1.html
13, 14, 58, 59, 60, 61. Colored tiles, as explained above can be used to add integers.
Number lines may also be used. An arrow to the right represents a positive integer. An arrow to the
left represents a negative integer.
The following number line shows the equation (+5) + (-8) = (-3)
17
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
For additional information and practice see the following from Math Makes Sense 7
Adding Integers with Tiles: p.56-59
Adding Integers on a Number Line: p.60-64
Instead of using tiles or a number line, the following rules may be used to add integers:
1. If the signs are the same, add the numbers and keep the same sign.
Examples:
(+3) + (+5) = +8
(-7) + (-5) = -12
2. If the signs of the integers are different, subtract the numbers and take the sign of the
numerically larger number.
Examples:
(-9) + (+4) = -5
(+8) + (-3) = +5
Additional help can be found at the following websites.
http://www.mathwizz.com/integers/index.htm
http://www.mathplayground.com/ASB_OrbitIntegers.html
http://www.mathgoodies.com/games/integer_game/football.html
15. Colored tiles can be used to subtract integers. The concept of zero pairs may be used to subtract
integers.
To add integers, we combine groups of tiles. To subtract integers, we do the reverse, we remove
them from a group. Adding a zero pair to a set of tiles does not change its value. For example, (-3) +
0 = -3. If we do not have enough positive or negative tiles to take away from a group, we can add
zero pairs until we have enough to take away. For example, for the question (+3) (-2), we can do
the following.
We can represent + 3 as follows:
If we want to subtract (-2) from this, we cant because there are no black tiles to take away.
However, if we add two zero pairs to the model it will look different as shown below but the value
will still be the same.
18
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
Now we have two black tiles, representing (-2) to take away. When we do, we are left with 5 white
tiles as shown below, which has a value of (+5).
Therefore (+3) (-2) = (+5).
In addition to using tiles to subtract, we can also use a number line as explained later, or we can use
the following rule to subtract integers:
Instead of subtracting an integer, we can add its opposite.
Example: (-6) (+7) = (-6) + (-7) = (-13)
Example: (-8) (-5) = (-8) + (+5) = (-3)
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 66-70 for additional information and practice)
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://passyworldofmathematics.com/adding-integers-using-zero-pairs/
https://learnzillion.com/lesson_plans/5607-create-zero-pairs-using-integer-chips#fndtn-lesson
16, 17, 61, 62. A number line can be used to subtract an integer. Usually this is done on a horizontal
number line, but it can also be done on a vertical number line as in this question or as can be found
on a thermometer. To subtract a positive integer on a number line, you move to the left. To subtract a
negative integer is the same as adding its opposite, so you move to the right. On a vertical number
line, to subtract a positive integer, you move down. To subtract a negative integer is the same as
adding its opposite, so you move up.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 71-75 for additional information and practice)
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://www.math.com/school/subject1/lessons/S1U1L11GL.html#sm3
18, 64. To convert a fraction to a decimal, you can divide the numerator (top number in the fraction)
by the denominator (bottom number in the fraction). For example, as a decimal is equal to 3 4,
which equals 0.75. Because this has a definite number of decimal places, it is said to be a terminating
decimal. To change 2/3 to a decimal, we calculate 2 3 and get a result of 0.6666666666.When
we do this we can never finish the calculation because some of the digits repeat forever. This is
6
called a repeating decimal and it is written as 0. . Sometimes it is easier to convert a fraction to a
19
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
decimal if you first write it in simplest terms. For example 20/36 can be rewritten as 5/9, which is
easier to divide.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 86-90 for additional information and practice)
Additional help can be found at the following websites.
http://www.mathsisfun.com/converting-fractions-decimals.html
http://www.webmath.com/fract2dec.html
http://math2.org/math/general/arithmetic/fradec.htm
http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/mathgames/fractions/FractionsToDecimals.htm
For certain fractions another method can be used to convert it to a decimal if an equivalent fraction
can be found that has a denominator that is a power of 10 (10, 100, 1000,) See sheet Fractions to
Decimals.
19, 20, 21. When adding decimals, remember to line up the decimal point. Also remember that you
can use the inverse operation (subtraction) to check addition. You can also use estimation to check if
your answer is reasonable.
When subtracting decimals, remember to line up the decimal points. Also remember that you can use
the inverse operation (addition) to check addition. You can also use estimation to check if your
answer is reasonable.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 96- 99 for additional information and practice)
Additional help can be found at the following websites.
http://www.math.com/school/subject1/lessons/S1U1L4GL.html
http://www.math-play.com/soccer-math-adding-decimals-game/adding-decimals-game.html
22, 67. When multiplying decimals the decimals dont have to be lined up. Instead just line up the
numbers and multiply normally. When you have a final answer, you then need to decide where to
place the decimal point. To do this, you add the total number of decimal places in the factors (the
numbers being multiplied). There will be that many decimal places in the answer. For example if you
multiply a number that has one decimal place by a number that has three decimal places, the product
would have a total of four decimal places. Also remember that you can use the inverse operation
(division) to check multiplication. You can also use estimation to check if your answer is reasonable.
(See assignment Canadian Mathematics 7, p. 94 for additional information and practice)
Additional help can be found at the following websites.
20
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
http://www.math-play.com/Decimals-Jeopardy/decimals-jeopardy-game.html
http://www.math-play.com/multiplying-decimals-game.html
23. When dividing decimals, you need to start by making sure the divisor is a whole number. If it
isnt you must multiply both the divisor and the dividend by a power of 10 to make it a whole
number. In the given question, 836.4 3.4, you would begin by multiplying both the dividend and
the divisor by 10 to get a new question, 8364 34. Then you would divide normally. When you
divide, place the decimal in the quotient (the answer) directly above the decimal in the dividend.
If the divisor had two decimal places, you would have to multiply both the divisor and dividend by
100. If it had three decimal places, you would have to multiply by 1000, etc.
Also remember that you can use the inverse operation (multiplication) to check division. You can
also use estimation to check if your answer is reasonable.
(See assignment Canadian Mathematics 7, p. 95 for additional information and practice)
Additional help can be found at the following website.
https://ca.ixl.com/math/grade-7/divide-decimals
24, 68. Order of Operations is the rules that are followed when simplifying or evaluating an
expression. A word that is helpful in remembering the order the steps are to be done in is BEDMAS.
In BEDMAS, each letter stands for an operation:
B: Brackets
E: Exponents
D: Division or M: Multiplication
A: Addition or S: Subtraction
Division and Multiplication are at the same spot in the order so are simply done left to right.
Addition and Subtraction are the same and are simply worked from left to right.
The order of operations for whole numbers can be applied to decimals.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 108-109 for additional information and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following websites.
https://ca.ixl.com/math/grade-5/simplify-expressions-using-order-of-operations-and-parentheses
http://www.math-play.com/Order-of-Operations-Millionaire/division-millionaire.html
21
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
25. Any fraction or decimal can be written as a percent, and vice versa. Percent is another name for
hundredths. To change a percent to a decimal, begin by dropping the % sign and then divide by 100;
(move the decimal point 2 places to the left).
Example #1: Write 82% as a decimal.
Begin by dropping the % sign.
82
Then divide by 100.
82100 = 0.82
Example #2: Write 40% as a decimal.
Begin by dropping the % sign.
40
Then divide by 100.
40 100 = 0.40 or 0.4
(See Math Sheet: Decimals to Percents and Math Makes Sense 7, p.111-113 for additional
information and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following websites.
http://www.mathplayground.com/percent04.html
http://www.math-play.com/Fractions-Decimals-Percents-Jeopardy/fractions-decimals-percentsjeopardy.html
http://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/fraction-matcher/latest/fraction-matcher_en.html
26. Some fractions can easily be converted to percents by first finding equivalent fractions with a
denominator of 100 and then rewriting it as a percent.
Example: Write 15/20 as a percent.
Begin by writing an equivalent fraction for 15/20.
15/20 = 75/100 (Both the numerator and denominator were multiplied by 5)
Then rewrite as a percent.
75/100 = 75%
If the fraction cannot be written as an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 100, then a different
method is used to convert the fraction to a percent. In such cases, you would divide the numerator by
the denominator to get a decimal. Then you would move the decimal two places to the right and add
a % sign.
22
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
Example: Write 3/16 as a percent.
Begin by dividing the numerator (3) by the denominator (16)
3 16 = 0.1875
Then move the decimal point two places to the right and add a % sign.
18.75%
(See Math Sheet: Fractions to Percents and Math Makes Sense 7, p.111-113 for additional
information and practice).
27. To find out what fraction of a diagram is shaded, you would first count the number of shaded
parts. This would be the numerator or top number in your fraction. Then you would count the total
number of parts (shaded + unshaded). This would be your denominator in the fraction. This assumes
that all of the parts are an equal size.
///////////////////////
///////////////////////
///////////////////////
///////////////////////
In the diagram above 4 parts are shaded, so 4 is the numerator. Altogether there are 10 parts, so 10 is
the denominator. The fraction that is shaded then is 4/10. Sometimes fractions can be simplified into
lower terms if there is a number that divides evenly into both the numerator and denominator. In this
case, both 4 and 10 can be divided by 2, to get 2 and 5 respectively. Therefore, this fraction in lowest
terms is 2/5.
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/mathgames/fractions/reduce_fractions_shoot.htm
http://www.math-play.com/simplifying-fractions-game/simplifying-fractions-game.html
28. To find out what fraction of the diagram is shaded, the above method can be used. To extend this
to show the fraction as a percent, the fraction would need to be converted to a percent as explained in
question 26.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.111-113 for additional information and practice).
29. To find your success in making free throws as a percent, you would first need to express it as a
fraction. The numerator would be your successful free throws. The denominator would be your total
attempts. Then the fraction would need to be converted to a percent as explained in question 26.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.111-113 for additional information and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://www.mathgoodies.com/games/conversions/percent_goodies.asp
23
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
30, 31. To find a percent of a number, you can convert the percent to a decimal and then multiply. To
change a percent to a decimal, begin by dropping the % sign and then divide by 100; (move the
decimal point 2 places to the left).
Example: Write 82% as a decimal.
Begin by dropping the % sign.
82
Then divide by 100.
82100 = 0.82
For a question such as this you would do the following:
Calculate 35% of 50.
35% = 0.35
50 x 0.35 = 17.5
(See Math Sheet, Percents to Decimals and Math Makes Sense 7, p.114-116 for additional
information and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://www.mathplayground.com/Decention/Decention.html
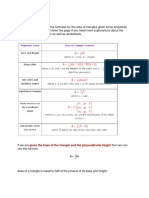
32, 33, 37. Radius is the distance from the center of a circle
to any point on the circle. Diameter is the distance across a
circle, measured through its center. Circumference is the
distance around a circle, also known as the perimeter of a
circle.
The diameter is twice as long as the radius.
d = 2r
The radius is half the length of the diameter.
r = d/2
The circumference is equal to 2 times (pi) times the radius or times the diameter. To calculate
use 3.14 in place of .
C=2r
or
C=d
To calculate the diameter if you are given the radius, multiply the radius by 2.
To calculate the radius if you are given the diameter, divide the diameter by 2.
To calculate the circumference if you are given the radius, multiply the radius by 2 and then
by 3.14.
24
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
To calculate the circumference if you are given the diameter, multiply the diameter by 3.14
To calculate the radius if you are given the circumference, divide the circumference by 2 and
then by 3.14.
To calculate the diameter if you are given the circumference, divide the circumference by
3.14.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.130-137 for additional information and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following website.
https://ca.ixl.com/math/grade-7/circles-calculate-area-circumference-radius-and-diameter
http://www.math4children.com/Grade6/games/other%20games/Calculate%20the%20circumference
%20of%20circles/index.html
34, 66. Before fractions and decimals can be put in order they must first be converted into similar
units. A few methods can be used to put numbers in order.
1
2
1
2
Benchmarks: If a number line is drawn that includes benchmarks such as , 1, 1 , 2 then
the numbers to be compared can be positioned on the number line. Then they can be put in
order by simply reading from the lowest number on the left to the highest number on the
right.
Equivalent Fractions: Before fractions can be compared, they must have the same
denominator. If all of the denominators are the same, then the numerators can be compared.
The fraction with the lowest numerator is the least and the number with the highest
numerator is the greatest.
Decimals: If all of the numbers are converted to decimals, they can then be compared. When
comparing decimals, it is sometimes easier if you add zeroes to the end of each number to
make sure they all have the same number of decimal places.
2
5
Before mixed fractions (such as 3 ) can be compared or converted to equivalent fractions or to
17
5
decimals, they should be written as improper fractions ( ). To convert a mixed fraction to an
improper fraction (where the numerator is larger than the denominator), you must first multiply the
denominator by the whole number part of the mixed fraction. Then add this to the numerator to get a
new sum. Then place this sum as the numerator over the original denominator. In the example above,
17
5
5 x 3=15. Then add the numerator: 15+ 2= 17. Then place this over the original denominator:
25
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
2
5
17
5
Therefore 3 =
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.91-95 for additional information and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://www.mathplayground.com/number_climb.html
35. To complete the missing numbers in sequences, you need to find the pattern of the numbers that
are given and then extend the pattern.
When adding decimals, remember to line up the decimal point. Also remember that you can use the
inverse operation (subtraction) to check addition. You can also use front-end estimation to check if
your answer is reasonable.
When subtracting decimals, remember to line up the decimal points. Also remember that you can use
the inverse operation (addition) to check addition. You can also use front-end estimation to check if
your answer is reasonable. (Front end estimation is simply ignoring the part of the number after the
decimal point and calculating the rest to get an approximate number. This wont give you an exact
answer but it will help you to see if your answer is reasonable and to show you if your decimal point
has been reasonably placed. Example) By using front-end estimation on the question 15.147 +
3.3694, I can simply add 15 + 3 to know that the answer should be somewhere around 18.
Adding and subtracting decimals are extensions of adding and subtracting whole numbers. Therefore
rules such as carrying and borrowing still apply.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.96-99 for additional information and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://www.topmarks.co.uk/Flash.aspx?b=maths/decimals
36. When you multiply decimals, you need to line up the numbers rather than the decimal points.
Ignore the decimal points while calculating, but then insert the decimal into your final answer. To
determine where to insert the decimal point in the final product you must count the total number of
decimal places (places after the decimal point) in the each of the numbers being multiplied. The final
product will have this many decimal places. In the following example, a number with 3 decimal
places is multiplied by a number with 1 decimal place. The final product, then, has 3 + 1 or 4
decimal places.
2.083
x 33.2
69.1556
26
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
Front-end estimation may also be used to help place the decimal point. In the above example, if we
ignore the numbers after the decimal point, we would multiply
2 x 33 = 66. Therefore, our final product should be somewhere around 66. If we had misplaced our
decimal point so our answer read 6.91556 or 691.556 we could quickly tell that our answer wasnt
reasonable.
(See Math Assignment, Canadian Mathematics 7, p. 94 for additional information and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://www.mathplayground.com/howto_multiplydecimals.html
37. See Question 32.
38. For some questions, it is easier to visualize what is being asked for if you draw a diagram. A
diagram for this question may look like the following.
6.4 cm
The distance across both circles would be equal to 2 times the diameter or 4 times the radius.
Therefore the radius of one circle is 6.4 cm 4 or 1.6 cm.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.130-132 for additional information and practice).
39, 40. See question 32.
C=2r
or
C=d
To calculate use 3.14 for .
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.133-137 for additional information and practice).
41. See question 32.
r=C2
To calculate use 3.14 for .
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.133-137 for additional information and practice).
27
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
42. See question 32. d = C
To calculate use 3.14 for .
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.133-137 for additional information and practice).
43, 44. The area of a parallelogram is equal to the area of a rectangle with the same base and height.
To find the area of a parallelogram, multiply its base by its height. The formula for the area of a
parallelogram is A = b x h.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.139-142 for additional information and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://www.mathopolis.com/questions/q.php?
id=9121&site=1&ref=/geometry/parallelogram.html&qs=9121_9122_9123_9124_9125_9126_912
7_9128_9129_9130
45, 46. The area of a triangle is one-half the area of a parallelogram with the same base and height.
(See Math Makes Sense 7,
practice).
p.143-147 for additional information and
Additional help can be found at the following website.
https://www.studyladder.ca/games/activity/area-of-triangles-13135
47. The area of a circle is (or 3.14) multiplied by the square of its radius r;
2
that is A= r .
For this circle the radius is 4.2 m.
2
The area would be 3.14 x 4.2m x 4.2m = 55.3896 m
28
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
To round the area to two decimal places (hundredths), you would need to check what number was in
the next decimal place (thousandths). If it were 0-4 you would simply round off. (Drop everything
after the hundredths place). If it were 5-9 you would round the number in the hundredths place up to
the next number. In the example above, there is a 9 in the thousandths place, so you would round the
digit in the hundredths place up from an 8 to a nine and drop everything after that. The area then
2
would be rounded from 55.3896 m to 55.39 m .
C(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.148-152 for additional information and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following website.
https://campus.mangahigh.com/en-us/px/386/0/0
48. A circle graph is a diagram that uses parts of a circle to display data. In a circle graph, data are
shown as parts of one whole. Each sector of a circle represents a percent of the whole circle. The
whole circle represents 100%. If one sector of the graph was to represent 25% of the data, then it
would be represented by a piece that took up 25% of the total circle.
To estimate how much of a circle graph is represented by different data, you need to estimate how
much of the total circle is represented by that data. If the percents are given in each sector, this can
be used to accurately determine how much data is represented by each sector.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.156-160 for additional information and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://www.mathplayground.com/piechart.html
https://ca.ixl.com/math/grade-8/interpret-circle-graphs
49. To calculate how many stamps Carol has from each country, you need to multiply the percent
given in each sector by the total number of stamps she has. For example, 25% of her stamps are from
Italy so this would be 25% of 500 which equals 125. See question 30 for instructions on finding the
percent of a number). To find how many more stamps she has from one country as compared with
another country you need to find the difference by subtracting.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.156-160 for additional information and practice).
29
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
50. The central angle of a sector on a circle graph is the
angle located at the center of the circle for that sector. In a
complete circle, there are 360. On this circle graph, 25%
of the budget is for rent. Therefore, the sector for rent takes
up 25% of the graph and the central angle for that sector is
25% of 360 or 90.
To calculate the central angle, you must multiply the
percent that represents the data by 360.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.161-164 for additional
information and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://mathcentral.uregina.ca/QQ/database/QQ.09.07/h/libby1.html
51.
1
5
11
13
2
4
8 10
14
16
20
6
12
18
Divisible by 2
3
9
15
17
19
Divisible by 3
A Venn Diagram is used to compare and contrast different items, in this case numbers. In this Venn
Diagram, the circle on the left contains all of the numbers up to 20 that are divisible by 2. The circle
on the left shows all of the numbers that are divisible by 3. The overlapping region shows numbers
that are divisible by both 2 and 3. Those numbers that do not fit into either circle because they are
not divisible by 2 or 3 are placed outside the circles. See question 1 for information about divisibility
rules.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p.8-12 for additional information and practice. Also see question 1).
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://nrich.maths.org/6290
52, 53. See question 3.
54. Since all sides of a square are the same length, the perimeter or distance around the square is
equal to 4 times the length of one side. For additional information on relationships in patterns, see
question 5.
30
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
55, 56. See Question 3.
57. See Question 11.
58-60. See Question 13.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 20-24 for additional information and practice)
61-62. See Question 16.
Additional help can be found at the following website.
Try this game! http://www.funbrain.com/linejump/
63. To change a decimal to a fraction, begin by seeing how many decimal places are in the decimal.
If the decimal has only one decimal place, then write the number as a fraction with a denominator of
10. If there are two decimal places, write the fraction with a denominator of 100.
After you have written the number as a fraction, it can sometimes be simplified by writing an
equivalent fraction in lower terms. To do this simply divide the numerator and denominator by the
same number, a number that divides evenly into both numbers.
Example #1: Write 0.62 as a fraction.
Begin by counting the number of decimal places. There are two decimal places (numbers after the
decimal), which means that the decimal extends to the hundredths place, so the fraction will have a
denominator of 100.
0.62 = 62/100
This can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and denominator by 2.
62/100 = 31/50
Example #2: Write 0.4 as a fraction. 0.4 = 4/10 = 2/5
(See Math sheet Decimals to Fractions and Math Makes Sense 7, p. 86-90 for additional information
and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://www.homeschoolmath.net/worksheets/table-fraction-decimal.php?
op=1&col=2&row=9&morethan1=0&dec=3&easy=50&powten=50&max=100&any=0&minden=
3&maxden=20&exp=8&font=Arial&FontSize=12pt&pad=16&ptitle=&Submit=Submit
64. See Question 18.
65. Before converting a mixed number to a decimal you should first change it to an improper
fraction. See notes for questions 34 & 18.
31
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 86-90 for additional information and practice)
66. See Question 34.
67. See Question 22.
68. See Question 24.
69. To solve this problem, it would be good to draw a diagram to help you visualize the problem.
The diameter would be the same as the width of the cardboard. The number of circles that could be
cut from the strip would the same as the number of times 42 cm could be divided by 3.5 cm.
3.5 cm
42 cm
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 86-90 for additional information and practice)
70. A bicycle wheel is a circle. The circumference of the wheel
the distance around the outside of the circle. The
circumference is the distance the bike would travel in one
rotation of the wheel. See question 32.
C=2r
To calculate the distance the bike would travel you have to
multiply the radius by 2 and then by (3.14) to see how far it
would travel in one rotation of the wheel. Then you would
have to multiply that total by 500 because there were 500
rotations of the wheel.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 133-137 for additional information and practice)
32
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
is
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
71. See question 47 for instructions on calculating the area of a circle. Since a semicircle is simply
half of a complete circle, you would need to divide the area of the circle by 2 to find the area of the
semicircle.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 148-152 for additional information and practice).
Additional help can be found at the following website.
http://mathcentral.uregina.ca/QQ/database/QQ.09.06/melinda1.html
72. Use divisibility rules to list some of the numbers, starting at 100 (the first 3-digit number) that
are divisible by 5. (The number ends in a 5 or 0). Then check which is the first of these numbers that
is also divisible by 9 (The sum of the digits is divisible by 9). For similar questions, use the same
process, though you will have to use different divisibility rules if different numbers are used.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 10-13 for additional information and practice).
73. If a number is divisible by two different numbers, then it must also be divisible by any of the
factors of either of those numbers and by any of the factors of one of those numbers multiplied by
any of the factors of the other number.
The factors of 8 are 1, 2, 4 and 8.
The factors of 9 are 1, 3 and 9.
Therefore, any number that is divisible by both 8 and 9 must also be divisible by 1, 2, 3 and 4 and by
any of the factors of one of the numbers multiplied by any of the factors of the other number: by 6 (2
x 3), by 12 (3 x 4), by 18 (2 x 9), by 24 (3 x 8), by 36 (4 x 9) and by 72 (8x9).
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 12 for additional information).
74. To solve this problem, you should break the question into parts.
Calculate the area of the square first.
A = L x W or 4 x side (since all sides of a square are the same length.)
Then calculate the area of the parallelogram.
A = b x h. (See question 43).
Then add the area of the square and the parallelogram together.
Then subtract the area of the triangle since this part is overlapping and you dont want to
1
2
count it twice. A =
b x h (See question 45).
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 139-147 for additional information and practice).
33
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Review Sheet for Math Midterm Exam
75. To solve this problem, you should break the question into parts.
2
First calculate the area of the large circle. (See question 47) A= r . The diameter of this
circle is given. To find the radius, you need to divide the diameter by 2.
Next find the area of one of the smaller circles. Each circle is half the diameter of the larger
circle and each radius is half the diameter of a smaller circle. Therefore, the radius of each of
2
the smaller circles is the diameter of the larger circle divided by 4. A= r .
To find the total area of both smaller circles, you need to multiply the area of one of the
circles by 2.
Finally, subtract the total area of both smaller circles from the total area of the large circle.
This will leave the total area of the shaded regions.
(See Math Makes Sense 7, p. 148-152 for additional information and practice).
34
The actual test will be very similar to this practice test.
Please see the attached pages for study notes and Internet links to help you do each type of question.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Decimal NumbersDocument20 pagesDecimal Numbersfres7451Pas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet On Word Problems On Linear Equation MATH 7 4TH MIDDocument11 pagesWorksheet On Word Problems On Linear Equation MATH 7 4TH MIDAivy Ylanan100% (1)
- End of Year Test Grade5 PDFDocument14 pagesEnd of Year Test Grade5 PDFwasabi999Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Effective Strategies For Teaching Elementary MathDocument31 pages7 Effective Strategies For Teaching Elementary MathLeorafe C. SosasPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Math # 1Document6 pagesFundamentals of Math # 1Brian CbtngnPas encore d'évaluation
- Mental Math Tricks and Practical Strategies To Make Calculations Faster, Enhance Your Math Skills and Solve Everyday Math... (Thomas Scofield)Document54 pagesMental Math Tricks and Practical Strategies To Make Calculations Faster, Enhance Your Math Skills and Solve Everyday Math... (Thomas Scofield)Rudi Setyawan100% (1)
- End of Year Test Grade4Document17 pagesEnd of Year Test Grade4Mónica Illanes RodríguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Fun Math Warm UpsDocument16 pagesFun Math Warm UpsLorna KennedyPas encore d'évaluation
- Miller IndicesDocument4 pagesMiller IndicesacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Note (G8) : A A A A A' CubedDocument6 pagesMathematics Note (G8) : A A A A A' CubedendalePas encore d'évaluation
- Math 3Document10 pagesMath 3Jessiegwyne Paderanga Lesaca80% (5)
- Packet 2 NotesDocument25 pagesPacket 2 NotesNightwing10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 6 - Units 1-3 Exam /55: Part One - Multiple Choice (20 Questions)Document8 pagesGrade 6 - Units 1-3 Exam /55: Part One - Multiple Choice (20 Questions)api-340282929Pas encore d'évaluation
- End-of-the-Year Test Grade 4Document17 pagesEnd-of-the-Year Test Grade 4Jorge KrjdPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 214 NotesDocument466 pagesMath 214 NotesLuis Javier IxtepanPas encore d'évaluation
- GR 8 MathDocument9 pagesGR 8 MathHirenkumar ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam Review MATH 1201 (Proofs To Know)Document2 pagesFinal Exam Review MATH 1201 (Proofs To Know)Bryan PenfoundPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10Document30 pagesChapter 10api-268597715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Mathematics in PhysicsDocument15 pagesBasic Mathematics in Physicstriyambak100% (1)
- Chapter 5Document46 pagesChapter 5api-268597715Pas encore d'évaluation
- Division of Sarangani Summative Test in Mathematics 6 3 Grading PeriodDocument4 pagesDivision of Sarangani Summative Test in Mathematics 6 3 Grading PeriodmishPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 7 Math Final Review Sheet 2016Document29 pagesGrade 7 Math Final Review Sheet 2016api-294158678100% (1)
- Grade 7 Math Final Review Sheet 2016Document29 pagesGrade 7 Math Final Review Sheet 2016api-294158678100% (1)
- ExamView - Mathematics Grade 7 PRACTICE Final ExamDocument24 pagesExamView - Mathematics Grade 7 PRACTICE Final ExamNel Banas0% (6)
- Commutative, Associative and Distributive Laws: Wow! What A Mouthful of Words! But The Ideas Are SimpleDocument6 pagesCommutative, Associative and Distributive Laws: Wow! What A Mouthful of Words! But The Ideas Are SimpleAnnisa RohmahPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnostic Test Math 6Document4 pagesDiagnostic Test Math 6Neriza JeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Number SenseDocument169 pagesNumber SenseArunkumar MyakalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Arithmetic TipsDocument5 pagesFast Arithmetic TipswhackoPas encore d'évaluation
- 001 - Openfoam SSÇ ÀÚ ÁDocument189 pages001 - Openfoam SSÇ ÀÚ ÁAntonio Martín AlcántaraPas encore d'évaluation
- CET 2018 Simulation Exam 02 Math AnswersDocument7 pagesCET 2018 Simulation Exam 02 Math AnswersJeffrey ClementePas encore d'évaluation
- End of Year Test Grade6Document17 pagesEnd of Year Test Grade6awalalalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch-07 (Permutation and Combinations FINAL 04.01.06)Document26 pagesCh-07 (Permutation and Combinations FINAL 04.01.06)Amit RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- HSC Trigonometric FormulaeDocument1 pageHSC Trigonometric FormulaeAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADER67% (3)
- G10-2NDPART EXAM-FINAL 1st QUARTERDocument3 pagesG10-2NDPART EXAM-FINAL 1st QUARTERMa'am Jayel Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Area of TrianglesDocument7 pagesArea of TrianglesAngelica MontezonPas encore d'évaluation
- A. G. Kurosh - Theory of Groups, Volume Two-Chelsea Pub. Co. (1960) PDFDocument309 pagesA. G. Kurosh - Theory of Groups, Volume Two-Chelsea Pub. Co. (1960) PDFJames100% (2)
- Ela Underground Chapter QuestionsDocument4 pagesEla Underground Chapter Questionsapi-2941586780% (1)
- Math5 Diagnostic TestDocument8 pagesMath5 Diagnostic TestMONICA SANTOSPas encore d'évaluation
- Name of Pupil: - Gr. & SectionDocument3 pagesName of Pupil: - Gr. & SectionNaruffRallibur100% (1)
- THIRD PERIODIC TEST IN MATHEMATICS WITH TosDocument5 pagesTHIRD PERIODIC TEST IN MATHEMATICS WITH Tosaljem tubigon100% (1)
- Third Quarter Test Mathematics 6 SY 2019-2020Document4 pagesThird Quarter Test Mathematics 6 SY 2019-2020Tel Pascua100% (12)
- Radian Measure Arcs Sectors and SegmentsDocument5 pagesRadian Measure Arcs Sectors and SegmentsTitser LaarniPas encore d'évaluation
- Mensuration FormulasDocument6 pagesMensuration FormulasMahaveer SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- LCM and HCFDocument7 pagesLCM and HCFDebasis DuttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric Identities and FormulasDocument6 pagesTrigonometric Identities and FormulasRajesh MauryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFGtech00Pas encore d'évaluation
- Divisibility Math Tricks To Learn The Facts - CompleteDocument1 pageDivisibility Math Tricks To Learn The Facts - CompletePriyank BhargavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratios Choice BoardDocument1 pageRatios Choice BoardKaitlyn AprilPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulas For Prisms and PyramidsDocument2 pagesFormulas For Prisms and PyramidsLady Muffins100% (1)
- Learning Objective: We Will Add and Subtract Positive and Negative IntegersDocument38 pagesLearning Objective: We Will Add and Subtract Positive and Negative IntegersAngeline CuriosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1.3a Segment Addition Postulate Amp Midpoint Theorem CPDocument17 pagesUnit 1.3a Segment Addition Postulate Amp Midpoint Theorem CPgavan_dusbabek4032Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2.6 Using Equations To Solve Word ProblemsDocument4 pages2.6 Using Equations To Solve Word ProblemsSherry WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: - Cubes and Cube Roots: Note SheetDocument4 pagesName: - Cubes and Cube Roots: Note SheetNorhazwaniSelamatPas encore d'évaluation
- GMAT Math Formulas ListDocument3 pagesGMAT Math Formulas ListOlzhas BolatbekulyPas encore d'évaluation
- hw35 Tier1Document3 pageshw35 Tier1api-296347043Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math Mam ZarahDocument8 pagesMath Mam ZarahGarcia KinnPas encore d'évaluation
- Keystone Hs Placement Exam Math Level1Document15 pagesKeystone Hs Placement Exam Math Level1Scott DickersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathlinks9 CH 6 TextbookDocument27 pagesMathlinks9 CH 6 Textbookapi-171445363Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics 6Document5 pagesMathematics 6DitaS IdnayPas encore d'évaluation
- 2011 Sample Final ExamDocument25 pages2011 Sample Final Examapi-114939020Pas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Term Endd 2Document10 pagesMaths Term Endd 2Sumit Shanil SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 Maths ExamDocument8 pagesGrade 9 Maths ExamScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosPas encore d'évaluation
- Long Test Math September 07Document14 pagesLong Test Math September 07Crystel RuizPas encore d'évaluation
- Parallel Exam Module 2Document7 pagesParallel Exam Module 2Math Made Easy With Ma'am APas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd PERIODICAL TESTDocument3 pages3rd PERIODICAL TESTCher An Jie0% (1)
- Refresher Math 1Document4 pagesRefresher Math 1Jocel palganPas encore d'évaluation
- ReviewDocument4 pagesReviewapi-235922849Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2ND Periodical Test in Math 6Document2 pages2ND Periodical Test in Math 6Jonniza AlbitPas encore d'évaluation
- ICGSE Y8 Unit 1 Integers Powers and RootsDocument10 pagesICGSE Y8 Unit 1 Integers Powers and RootsYAP LEE KHIMPas encore d'évaluation
- Gateworkers 1Document1 pageGateworkers 1api-294158678Pas encore d'évaluation
- Timekeepers 1Document1 pageTimekeepers 1api-294158678Pas encore d'évaluation
- Killarney Wawanesa Raiders Roster 2015 1Document1 pageKillarney Wawanesa Raiders Roster 2015 1api-294158678Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 Tourney Draw 1Document2 pages2015 Tourney Draw 1api-294158678Pas encore d'évaluation
- ss3 Review SheetDocument2 pagesss3 Review Sheetapi-294158678Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hockey Tournament Draw 2015Document1 pageHockey Tournament Draw 2015api-294158678Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science 3 NotesDocument4 pagesScience 3 Notesapi-294158678Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ela Midterm Review SheetDocument2 pagesEla Midterm Review Sheetapi-294158678Pas encore d'évaluation
- Timetable Class B Mcauley 2015-2016 WebDocument1 pageTimetable Class B Mcauley 2015-2016 Webapi-294158678Pas encore d'évaluation
- School SuppliesDocument1 pageSchool Suppliesapi-294158678Pas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Algebra For Computational EngineeringDocument21 pagesLinear Algebra For Computational EngineeringCovenant AdeogoPas encore d'évaluation
- Thailand International Mathematical Olympiad Syllabus: Kindergarten GroupDocument5 pagesThailand International Mathematical Olympiad Syllabus: Kindergarten GroupEly SoemarniPas encore d'évaluation
- Errors: Objectives: Errors May Arise From Such Things As Inaccurate Measurements of A PhysicalDocument6 pagesErrors: Objectives: Errors May Arise From Such Things As Inaccurate Measurements of A PhysicalRizky KusumastutiPas encore d'évaluation
- New DashDocument151 pagesNew DashNaveen Garg100% (1)
- Asrat OCP MSC ThesisDocument60 pagesAsrat OCP MSC ThesisasratPas encore d'évaluation
- Liang-Zelich Theorem Proof Simplified Ve PDFDocument7 pagesLiang-Zelich Theorem Proof Simplified Ve PDFRonAlPas encore d'évaluation
- AndiloveyousoDocument15 pagesAndiloveyousoKes DimapilisPas encore d'évaluation
- Cantor SetDocument4 pagesCantor SetNaveen GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Discrete Mathematical Structures Jan 2014Document2 pagesDiscrete Mathematical Structures Jan 2014Prasad C MPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 of 5Document30 pagesLecture 1 of 5awangpaker xxPas encore d'évaluation
- Recurrence Relations: Mathematical Models, Analysis TechniquesDocument38 pagesRecurrence Relations: Mathematical Models, Analysis TechniquesMadeehah AatifPas encore d'évaluation
- Reteach: Solving Inequalities by Adding or SubtractingDocument4 pagesReteach: Solving Inequalities by Adding or SubtractingHala EidPas encore d'évaluation
- Ph304 Problem Set 3 Electrodynamics: Princeton UniversityDocument3 pagesPh304 Problem Set 3 Electrodynamics: Princeton Universitygadas11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nonlinear Representations of The Poincare Group ADocument11 pagesNonlinear Representations of The Poincare Group AwangJPPas encore d'évaluation
- MAT060.Chapter 4 Applications of The Derivatives PDFDocument30 pagesMAT060.Chapter 4 Applications of The Derivatives PDFRuby Alintana PantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Equations Tutorial Sheet 1Document2 pagesDifferential Equations Tutorial Sheet 1AV YogeshPas encore d'évaluation
- MMW Module 1 Nature of MathematicsDocument6 pagesMMW Module 1 Nature of MathematicsJhess GaliciaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Stability Analysis On Models of Cooperative and Competitive SpeciesDocument7 pagesA Stability Analysis On Models of Cooperative and Competitive SpeciesHerald MulanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Introductory Mathematical Analysis For Business Economics and The Life and Social Sciences 14th Edition Paul Test BankDocument44 pagesIntroductory Mathematical Analysis For Business Economics and The Life and Social Sciences 14th Edition Paul Test Bankjesselact0vvk100% (28)
- Hcu Mock 1Document8 pagesHcu Mock 1Kulbir SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Assign. No 1Document7 pagesAssign. No 1getachewbonga09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes On Classical Integrability and On The Algebraic Bethe Ansatz For The XXX Heisenberg Spin ChainDocument36 pagesLecture Notes On Classical Integrability and On The Algebraic Bethe Ansatz For The XXX Heisenberg Spin ChainDieff_Pas encore d'évaluation
- Free Download Engineering Mathematics Ii T Veerarajan Full Chapter PDFDocument51 pagesFree Download Engineering Mathematics Ii T Veerarajan Full Chapter PDFmargaret.martz245100% (23)