Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Water Chemistry
Transféré par
api-296793567Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Water Chemistry
Transféré par
api-296793567Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
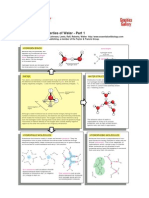
WATER CHEMISTRY
WATER STRUCTURAL MOLECULE
Water consist of 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen atom.
Out of eight electrons, only four are involved in electron pair formation with two
hydoren atoms.
A strong attractive force is exerted by oxygen on the remaining four electrons, making
hydrogen atoms electropositive.
The geometrical shape of water molecule is that of a tetrahedron in which the oxygen
atom is in the center and the two hydrogens occupy two of the corners.
HYDROGEN BOND IN WATER MOLECULE
Water molecules which is the polar molecules, have a weak, partial negative charge at
one region of the molecule (the oxygen atom in water) and a partial positive charge
elsewhere (the hydrogen atoms in water).
Thus when water molecules are close together, their positive and negative regions are
attracted to the oppositely-charged regions of nearby molecules.
The force of attraction, shown here as a dotted line, is called a hydrogen bond. Each
water molecule is hydrogen bonded to four others.
The hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules account for some of the
essential and unique properties of water.
1. The attraction created by hydrogen bonds keeps water liquid over a wider
range of temperature than is found for any other molecule its size.
2. The energy required to break multiple hydrogen bonds causes water to have a
high heat of vaporization; that is, a large amount of energy is needed to
convert liquid water, where the molecules are attracted through their hydrogen
bonds, to water vapour, where they are not.
THERMAL AND SOLVENT PROPERTIES IN WATER.
WATER AS UNIVERSAL SOLVENT
Water forms an excellent solvent system having the capacity to solubilize a large
number of organic and inorganic compounds.
Compounds having OH, NH2, COOH and C=O groups are highly soluble in water
because of their ability to form hydrogen bonds with the oxygen atom.
Water also possesses strong dielectric properties and for this reason it is a good
solvent for salts dissociable into ions.
THERMAL PROPERTIES
Most solids and liquids expand with rising temperature.
Water, the most common and most important liquid on Earth, has a limitation on this
expansion.
Ice water that is at a temperature of 0C or 32F will contract when it is heated.
This contraction continues until after an increase beyond 4C or 39.2F.
Then water that continues to be heated will finally begin to expand like other liquids
until it reaches a gaseous state.
At 4C water has its smallest volume and also its greatest density.
Water that is below 0C has a larger volume and a smaller density.
Therefore the reason why ice floats in your cup of soda is because ice is less dense or
weighs less than water.
This is also the reason why your water pipes may burst in the winter if you are not
careful - the water inside increases in volume and weight as it cools from 4C to 0C.
IONIZATION OF WATER
A unique property of water is its ability to ionize or undergo dissociation.
The hydrogen atom is very light and is held tightly by the oxygen atom.
Because of its mobility and small mass, it has a tendency to dissociate in the manner
of:
H2O H+ + OH-
This is the conventional method to show dissociation of water, but in actual practice
the hydrogen atom of one water molecule after dissociation hops over to the
neighboring water molecule to form a positively charged hydronium (H3O) ions,
leaving behind a negatively charged hydroxyl group (OH-)
H2O OH- + H+
H2O H3O+ (hydronium ion)
OR
H2O + H2O H3O+ + OH-
Electrical conductivity measurements show that one liter of water at 25C contains
1.0X10-7 moles of H3O+ ions and the same amount of OH- ions.
The reason why a hydronium ion is formed is explained by the fact that protons do not
occur as free ions in water, while the hydronium ion has a high electrical mobility.
It is possible to calculate the equilibrium constant of dissociation of water from the
equation :
H2O H+] + [OH-]
Keq = [H+] + [OH-]
[H2O]
When the ions in brackets [ ] represent the concentration in moles per liter.
In pure water the H+ =OH- 1.0X10-7, and the ion product of water, Kw = [H+] [OH-] at
25C is 1.0X10-14
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Lecture 2 - Lifes - Chemical - BasisDocument25 pagesLecture 2 - Lifes - Chemical - BasisPooja ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- StructureandpropertiesofwaterDocument57 pagesStructureandpropertiesofwaterDj Arts Tarpaulin PrintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Tutorial The Chemistry of Water The Polarity of WaterDocument3 pagesChemistry Tutorial The Chemistry of Water The Polarity of WaterAnubha_SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Definition: in The Gaseous PhaseDocument4 pagesWater Definition: in The Gaseous PhaseRica NorcioPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Eportfolio PaperDocument4 pagesChemistry Eportfolio Paperapi-301500945Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1-1 Lecture , additionDocument10 pages1-1 Lecture , additionAnonymous guyPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecules of LifeDocument14 pagesMolecules of LifeVikas Singh PariharPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Water LectureDocument37 pages5 Water Lecturevanessa biliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- AP BIO Campbell Reading Guide Answer KeyDocument3 pagesAP BIO Campbell Reading Guide Answer KeyRocio CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- London Dispersion ForcesDocument4 pagesLondon Dispersion Forceskimdaniel2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 02Document24 pagesLecture 02kblawan03Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrogen BondsDocument2 pagesHydrogen BondsJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Why water has a high specific heat capacity and the importance of its unique propertiesDocument6 pagesWhy water has a high specific heat capacity and the importance of its unique propertiespangaroad200Pas encore d'évaluation
- Zartasha#48Document20 pagesZartasha#48Usman AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Water BME-211 (2120)Document50 pagesWater BME-211 (2120)Jack WengroskyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1c8eaproperties of Water, Acids Bases and BuffersDocument27 pages1c8eaproperties of Water, Acids Bases and BuffersAnita NegiPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 Lesson 2 Water AbstractionDocument3 pagesModule 1 Lesson 2 Water AbstractionMarialPas encore d'évaluation
- Water, Polarity, and Dissolving - Student ReadingDocument8 pagesWater, Polarity, and Dissolving - Student Readingapi-279918311Pas encore d'évaluation
- CHEMICAL PROPER Abe Assignment-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesCHEMICAL PROPER Abe Assignment-WPS OfficeCarpenter BreadPas encore d'évaluation
- Water ChemDocument5 pagesWater ChemJohn harold De GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Chemical Basis of Life ExplainedDocument87 pagesThe Chemical Basis of Life ExplainedTiyasha SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- T02 Quiz AssignmentDocument3 pagesT02 Quiz AssignmentJhon Rey LagosPas encore d'évaluation
- 16 Water ChemistryDocument21 pages16 Water ChemistryMohit KambojPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of Water: Hydrogen Bonds, Liquidity, ReactionsDocument2 pagesProperties of Water: Hydrogen Bonds, Liquidity, ReactionsasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Why Is Water PolarDocument3 pagesWater Why Is Water PolarDaneilla BanksPas encore d'évaluation
- WaterDocument24 pagesWaterAshley M NcubePas encore d'évaluation
- Why oil and water separate into layersDocument2 pagesWhy oil and water separate into layersShahir AshuPas encore d'évaluation
- Water QuestionsDocument3 pagesWater QuestionsLouie BalouiePas encore d'évaluation
- Water's Polarity and Hydrogen Bonding Support LifeDocument17 pagesWater's Polarity and Hydrogen Bonding Support LifeLisandrea BrownPas encore d'évaluation
- ch1 .ST - Medical - WaterDocument55 pagesch1 .ST - Medical - Watersultan khabeebPas encore d'évaluation
- The Structure and Function of WaterDocument23 pagesThe Structure and Function of WaterThomas JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrogen Bonds - WikipediaDocument10 pagesHydrogen Bonds - WikipediaJaira Denisse PedrajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Unit # 1 Module 1 - Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument15 pagesBiology Unit # 1 Module 1 - Cell and Molecular BiologyLton LuisPas encore d'évaluation
- Water: Hydrogen Bonding Gives Water Its Unusual PropertiesDocument7 pagesWater: Hydrogen Bonding Gives Water Its Unusual PropertiesFayez AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrogen: Syllabus: Unitix: Hydrogen 04 PeriodsDocument70 pagesHydrogen: Syllabus: Unitix: Hydrogen 04 Periodsanikesh JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Chemistry BybtyuDocument8 pagesWater Chemistry BybtyutulsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Ice Solid: WaterDocument16 pagesEarth Ice Solid: Waterbrent tobiasPas encore d'évaluation
- C 10ab 2 0 Explain Stemscopedia StudentDocument8 pagesC 10ab 2 0 Explain Stemscopedia Studentapi-2368267470% (1)
- (A) Water and PHDocument53 pages(A) Water and PHSapana SubediPas encore d'évaluation
- Acosta, Niel Task 5Document3 pagesAcosta, Niel Task 5Algrin AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water 1Document9 pagesWater 1Michael NyaongoPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Hydrogen BondingDocument6 pagesWhat Is Hydrogen BondingKate MagpayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Water ChemistryDocument15 pagesChapter 2 Water ChemistryKathy Del CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3.1. Acid-Base ChemistryDocument6 pagesLesson 3.1. Acid-Base ChemistryGemma CabañasPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrogen Bonding: Yoshita - O Level CandidateDocument31 pagesHydrogen Bonding: Yoshita - O Level CandidateYoshitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomolecules and Cells:: Mr. Derrick Banda MSC, BSCDocument42 pagesBiomolecules and Cells:: Mr. Derrick Banda MSC, BSCAmon SangulubePas encore d'évaluation
- Chap04 - Science of Water Sources - Part 1Document68 pagesChap04 - Science of Water Sources - Part 1gua leePas encore d'évaluation
- Water: The Solvent of Life Where There Is Water, There Is LifeDocument18 pagesWater: The Solvent of Life Where There Is Water, There Is LifeIsaiah Fidelis MajiPas encore d'évaluation
- BSC 450 CH 2 NotesDocument15 pagesBSC 450 CH 2 NotesMaddie NPas encore d'évaluation
- AquaScams HomeDocument46 pagesAquaScams HomeavisenicPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd LectureDocument72 pages3rd Lecturebliss polleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Panel 2Document1 pagePanel 2Ram ShewalePas encore d'évaluation
- Water Chemistry PropertiesDocument19 pagesWater Chemistry Propertiesyuvimessi100% (2)
- 1.1 Bio 3Document4 pages1.1 Bio 3aelinsmy93Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 - WaterDocument7 pagesUnit 3 - WaterWinrich Louise M. MontanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Capitulo AguaDocument7 pagesCapitulo AguaJaquelinee Pérez ViverosPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of WaterDocument1 pageProperties of WaterBelinda NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Water's Unique PropertiesDocument82 pagesWater's Unique Propertiessayedrezha1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Water on Earth: Physicochemical and Biological PropertiesD'EverandWater on Earth: Physicochemical and Biological PropertiesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lactic AcidosisDocument19 pagesLactic Acidosisapi-303084660Pas encore d'évaluation
- 20151126161134case Biochem 2015 Answer GuideDocument24 pages20151126161134case Biochem 2015 Answer Guideapi-296793567Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fluoroacetate ToxicDocument11 pagesFluoroacetate ToxicIsmi Nadzatul Elya100% (1)
- Slide 1Document16 pagesSlide 1api-299952878Pas encore d'évaluation
- 20151126161134case Biochem 2015 Answer GuideDocument24 pages20151126161134case Biochem 2015 Answer Guideapi-296793567Pas encore d'évaluation
- CholesterolDocument30 pagesCholesterolIsmi Nadzatul ElyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 20151126161134case Biochem 2015 Answer GuideDocument24 pages20151126161134case Biochem 2015 Answer Guideapi-296793567Pas encore d'évaluation
- Carnitine DeficiencyDocument29 pagesCarnitine Deficiencyapi-303542051Pas encore d'évaluation
- Haze and Cloud SeedingDocument18 pagesHaze and Cloud SeedingSyifa NawwarPas encore d'évaluation
- 20151126161134case Biochem 2015 Answer GuideDocument24 pages20151126161134case Biochem 2015 Answer Guideapi-296793567Pas encore d'évaluation
- Redox ReactionDocument4 pagesRedox Reactionapi-296793567Pas encore d'évaluation
- SAFETY TITLEDocument10 pagesSAFETY TITLEAlejandro VescovoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit IV Coating of Technical Textiles Coating TechniquesDocument55 pagesUnit IV Coating of Technical Textiles Coating TechniquesPandurang PawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Examination of UrineDocument7 pagesPhysical Examination of UrineChie HisuganPas encore d'évaluation
- Dialyzer: by Daniel V Dialysis LecturerDocument52 pagesDialyzer: by Daniel V Dialysis LecturerDani Dany100% (2)
- Heise 1948Document7 pagesHeise 1948George AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anionic Chain PolymerizationDocument32 pagesAnionic Chain PolymerizationBùi Bảo NgânPas encore d'évaluation
- Marea Moarta PsoriazisDocument7 pagesMarea Moarta PsoriazisAndreea FrunuzPas encore d'évaluation
- Utilization of Geopolymer Fly Ash As Concrete BinderDocument50 pagesUtilization of Geopolymer Fly Ash As Concrete BinderRonald PanaliganPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Chemistry 9701/11Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Chemistry 9701/11NjoroPas encore d'évaluation
- ICSE Class 10 CHEMISTRY Previous Year Question Paper 2011Document8 pagesICSE Class 10 CHEMISTRY Previous Year Question Paper 2011Madhu SudanPas encore d'évaluation
- Prep and Properties of Alkane Alkene and AlkyneDocument38 pagesPrep and Properties of Alkane Alkene and AlkyneSEBASTIEN ANDREI BUENAFEPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report 3 EtDocument15 pagesLab Report 3 EtPeach BabyPas encore d'évaluation
- Using Pop-Culture To Engage Students in The ClassroomDocument11 pagesUsing Pop-Culture To Engage Students in The ClassroomJean VasconcelosPas encore d'évaluation
- Table of Fitting Material Chemical Resistance - Tubes InternationalDocument4 pagesTable of Fitting Material Chemical Resistance - Tubes Internationalعبد اللهPas encore d'évaluation
- SD FINE Price List 22-23Document161 pagesSD FINE Price List 22-23bhartipkoliPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Bulletin: New NXT Seat Material For: F20, F90, F91, 20 and 35 Series Ball ValvesDocument3 pagesProduct Bulletin: New NXT Seat Material For: F20, F90, F91, 20 and 35 Series Ball ValvesMohammad FouladiPas encore d'évaluation
- LAS Sci9 q2 Week2 v3Document12 pagesLAS Sci9 q2 Week2 v3Jim TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Lab ActivitiesDocument14 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage Forms Lab ActivitiesSHEENA JOY HABITANPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagarama de Fase de Los CupratosDocument97 pagesDiagarama de Fase de Los CupratosjamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Physics LettersDocument7 pagesChemical Physics LettersJust teñ minutesPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 AutoclaveDocument13 pagesUnit 2 AutoclavehamdanforaeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Tribological Coatings For Heavy-Duty Applications: Case StudiesDocument148 pagesAdvanced Tribological Coatings For Heavy-Duty Applications: Case StudiesAngel LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Waterborne Epoxy Primer Based On SW-111Document8 pagesWaterborne Epoxy Primer Based On SW-111A L.GPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstracts: Journal of Applied ChemistryDocument64 pagesAbstracts: Journal of Applied ChemistryVasant HiremathPas encore d'évaluation
- Offer Letter: Price ListDocument11 pagesOffer Letter: Price ListJose CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- CA Lesson 5 Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument16 pagesCA Lesson 5 Aromatic HydrocarbonsAlbaraaAliPas encore d'évaluation
- 11th - Kalviexress Std-Chemistry (EM) - Public-Exam-Question-Paper-With-Answers-2019Document8 pages11th - Kalviexress Std-Chemistry (EM) - Public-Exam-Question-Paper-With-Answers-2019STIR FLY GAMINGPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Form V Ifunda Home PackageDocument15 pagesChemistry Form V Ifunda Home Packagenassorussi9Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S2238785421003227 MainDocument18 pages1 s2.0 S2238785421003227 MainManikandan ChinnachamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Studies in Building Rehabilitation: J. M. P. Q. Delgado EditorDocument163 pagesCase Studies in Building Rehabilitation: J. M. P. Q. Delgado EditorHanane BenGamraPas encore d'évaluation