Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
FM Telephone Bug Transmitter
Transféré par
Hector QuezadaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
FM Telephone Bug Transmitter
Transféré par
Hector QuezadaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
FM Telephone Transmitter, Bug
FM Telephone Transmitter
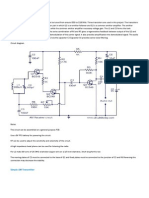
The complete schematic of the telephone bug is shown in Fig.1. This circuit connects in parallel with
the telephone line. Power for the circuit is full wave bridge rectified from the phone line by diodes D1
through D4. When the telephone receiver is on hook the voltage across the lines will be about 48 volts. At
this voltage the Zener diode D5 will be in breakdown and the transistor Q1 will conduct. This makes the
transistor Q2 OFF. When the receiver is off hook, the line voltage drops to about 12 volts. This makes the
transistor Q1 OFF and subsequently the Q2 ON. The Q2 in switched ON condition will provide a DC path
for the transistor Q3 in the FM transmitter section. The transmitter section is actually a small FM
transmitter that can be turned to a vacant spot on your Fm radio. In the FM frequency range, only a small
antenna is needed to radiate a usable signal through out a building. Its range is 50 to 100 feet with a
10cm antenna. The range can be increased by using a longer antenna. Transistor Q3 oscillate at a signal
frequency which is determined by turned circuit L1, C6, VC and the inter electrode capacitance of the
transistor. Capacitor C7 provides the needed positive feed back from the collector to the emitter for the
circuit to oscillate. The audio signals applied to the base of Q3 cause collector current to vary at an audio
rate and modulate the oscillator output. This type of modulation produces both FM and AM, but AM are
rejected by the discriminator and limiters in the FM receiver and cause no problem. The collector current
variations in turn vary the transistors output capacitance. This capacitance is part of the turned circuit and
varies the frequency of the output signal which is coupled to the antenna by C9.
FM Telephone Transmitter Circuit Diagram
FM Telephone Transmitter PCB
FM Telephone Transmitter PCB Component Side
Parts list
Transistor
Q1, Q2
Q3
: BC547
: BF494
Diode
D1D4
D5
: 1N4007
: 18V Zener-diode
Resistors
R1
R2, R6
R3, R8
R4
R5
R7
R9
: 100K
: 22K
: 47K
: 470K
: 33K
: 150K
: 470R
Capacitors
C1, C3
C2, C4
C5
C6
C7, C8
: 1063V, electrolytic
: 100n or 100Kpf, ceramic-disc
: 1n or 1Kpf, ceramic-disc
: 33p, ceramic-disc
: 10p, ceramic-disc
Additional parts
L1- 4Turns, 22SWG Copper wire, 3mm air core
VC- 2-22pf, Trimmer Capacitor
ANT- 10 to 80cm copper wire
common PCB
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- How To Make Cell Phone Signal JammerDocument12 pagesHow To Make Cell Phone Signal JammerMoata Haile50% (2)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsD'EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorD'Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- 3V FM Transmitter CircuitDocument6 pages3V FM Transmitter CircuitMahmood AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple AM Receiver&TransmitterDocument4 pagesSimple AM Receiver&TransmitterGokulk2011100% (2)
- Flue-Cured Tobacco Production GuideDocument96 pagesFlue-Cured Tobacco Production GuideHector Quezada100% (1)
- FM Bugger CircuitDocument44 pagesFM Bugger CircuitBathrinath 00750% (4)
- Cell Phone JammerDocument5 pagesCell Phone Jammerkapildave21100% (1)
- Sclerocarya Birrea Seed LeafletDocument2 pagesSclerocarya Birrea Seed LeafletHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Évaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- 6 Inch Crossette Canister ShellDocument16 pages6 Inch Crossette Canister ShellHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 KM FM TransmitterDocument1 page2 KM FM TransmitterradianfmPas encore d'évaluation
- Native Seeds CatalogDocument52 pagesNative Seeds CatalogHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On FM Transmitter ProjectDocument22 pagesPresentation On FM Transmitter Projectpandey9985% (20)
- Simple FM TransmitterDocument6 pagesSimple FM Transmitterxtra4web100% (1)
- FM TransmitterDocument9 pagesFM TransmitterMuhammad MujtabaPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple FM Radio Jammer Circuit IntroDocument14 pagesSimple FM Radio Jammer Circuit IntroYoussef lamraniPas encore d'évaluation
- Rockets BPDocument33 pagesRockets BPpamos1111100% (3)
- FM TransmitterDocument38 pagesFM TransmitterTushar Goel100% (1)
- How To Make Your Own High Quality Salvia Divinorum ExtractDocument4 pagesHow To Make Your Own High Quality Salvia Divinorum ExtractHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Amateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileD'EverandAmateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- 3V FM TransmitterDocument9 pages3V FM TransmitterHabib RkPas encore d'évaluation
- Film Canister ShellsDocument4 pagesFilm Canister ShellsHector Quezada100% (1)
- Radi0Kit 180 English Ver2.0Document11 pagesRadi0Kit 180 English Ver2.0MR XPas encore d'évaluation
- Shimizu Aerial Shell Ballistic PredictionsDocument12 pagesShimizu Aerial Shell Ballistic PredictionsHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3172V21 - Synthesised WBFM TransmitterDocument6 pages3172V21 - Synthesised WBFM Transmitterjoniez14Pas encore d'évaluation
- AM Transmitter'n'receiver CircuitDocument9 pagesAM Transmitter'n'receiver Circuitkapil singh100% (1)
- Ground Wave Propagation 2. Sky Wave PropagationDocument18 pagesGround Wave Propagation 2. Sky Wave PropagationajiistanPas encore d'évaluation
- FM Transmitter DesignDocument5 pagesFM Transmitter DesignLaty Bayb100% (1)
- 433MHz Transmitter DetailsDocument7 pages433MHz Transmitter DetailskaushikrejaPas encore d'évaluation
- Long Range FM TransmitterDocument12 pagesLong Range FM Transmittertaniafawz100% (2)
- Fig Growing in The SouthDocument28 pagesFig Growing in The SouthHector Quezada100% (1)
- FM Transmitter PDFDocument5 pagesFM Transmitter PDFAndrés HoytePas encore d'évaluation
- Spy Phone Transmitter Circuit DiagramDocument1 pageSpy Phone Transmitter Circuit DiagramALFAKPas encore d'évaluation
- DIY Wireless Audio Video Sender CircuitDocument5 pagesDIY Wireless Audio Video Sender CircuitK Raja SekarPas encore d'évaluation
- 3V FM Transmitter 3V FM Transmitter CircuitDocument4 pages3V FM Transmitter 3V FM Transmitter Circuitpeter.gomes20087216Pas encore d'évaluation
- Phone BroadcasterDocument1 pagePhone BroadcastermishranshulPas encore d'évaluation
- ECD Lab - CEA - Report..Document12 pagesECD Lab - CEA - Report..Muhammad kamran AmjadPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter One: 1.1 OverviewDocument17 pagesChapter One: 1.1 OverviewSamson TimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Wave AM TransmitterDocument1 pageShort Wave AM Transmitter2711323Pas encore d'évaluation
- Telecom Headset Project 1Document1 pageTelecom Headset Project 1jaykrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Wave AM Transmitter, Design of Am Transmitter - Schematic. ComputationsDocument2 pagesShort Wave AM Transmitter, Design of Am Transmitter - Schematic. ComputationsECE_209xxxxPas encore d'évaluation
- FM DemodulatorDocument8 pagesFM DemodulatorYash BudhwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Wave AmDocument1 pageShort Wave AmChirag VadgamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Team Members: Name USN Roll NumberDocument10 pagesTeam Members: Name USN Roll Number01fe20bec113Pas encore d'évaluation
- FM Transmitter With Only One TransistorDocument2 pagesFM Transmitter With Only One Transistorsaul camposPas encore d'évaluation
- FM Radio Jammer: DescriptionDocument4 pagesFM Radio Jammer: DescriptionnickususPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Development of Low-Range Frequency ModuDocument7 pagesDesign and Development of Low-Range Frequency ModuMohamed Amine TahiriPas encore d'évaluation
- FM Phone TransmitterDocument2 pagesFM Phone TransmittertriggereffectPas encore d'évaluation
- FM RADIO TRANSMITTER (Report)Document3 pagesFM RADIO TRANSMITTER (Report)Teja Reddy100% (1)
- Automatic Telephone Answering MachineDocument1 pageAutomatic Telephone Answering MachineSaroj TimsinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple FM Walkie TalkieDocument4 pagesSimple FM Walkie TalkieNeo Mechatron0% (2)
- 6 Frequency Modulation Part2Document29 pages6 Frequency Modulation Part2Ahmad AkramPas encore d'évaluation
- FM 1Document25 pagesFM 1Azhar AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Analog Project ReportDocument3 pagesAnalog Project Reportfahadsaeed93Pas encore d'évaluation
- AM Stereo TunerDocument33 pagesAM Stereo TunerMuhammad DharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Stage FM TransmitterDocument1 page4 Stage FM TransmitterNikhil R. LalwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On Industrial Summer Training (JUNE-JULY 2014)Document33 pagesPresentation On Industrial Summer Training (JUNE-JULY 2014)Utkarsh KathuriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analogue Electronics: 14. Transistor Circuits For The ConstructorDocument27 pagesAnalogue Electronics: 14. Transistor Circuits For The ConstructorNuraddeen MagajiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Reactance ModulatorDocument17 pagesA Reactance ModulatorAldrin Sagum100% (1)
- CK 200Document3 pagesCK 200Shrikanth SundarPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuit DescriptionDocument1 pageCircuit DescriptionzahidkjatoiPas encore d'évaluation
- To Design and Implement An FM Receiver For A Desired Frequency Band 1Document3 pagesTo Design and Implement An FM Receiver For A Desired Frequency Band 1নিঝুমPas encore d'évaluation
- Long Range FM TransmitterDocument2 pagesLong Range FM TransmitterHaspreet SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Sawtooth Wave GeneratorDocument2 pagesSawtooth Wave GeneratorShahid AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 ART Banda de TransmisionDocument3 pages6 ART Banda de TransmisionFELIX PARCA ACEVEDOPas encore d'évaluation
- Angle Modulation Receivers and SystemsDocument4 pagesAngle Modulation Receivers and SystemsRoss EdwardPas encore d'évaluation
- Phytochemical Analyses of Banisteriopsis Caapi and Psychotria ViridisDocument7 pagesPhytochemical Analyses of Banisteriopsis Caapi and Psychotria ViridisHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Viability of Pollen of Two Fruit Crop Cacti of The Genus HylocereusDocument3 pagesViability of Pollen of Two Fruit Crop Cacti of The Genus HylocereusHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Time Fuse & SpolettesDocument7 pagesTime Fuse & SpolettesHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of The LSD FlashbackDocument7 pagesAnalysis of The LSD FlashbackHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- FM Telephone Bug TransmitterDocument2 pagesFM Telephone Bug TransmitterHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Shading Screens For Frost ProtectionDocument14 pagesShading Screens For Frost ProtectionHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- The PyrotechnistsTreasury. KentishDocument293 pagesThe PyrotechnistsTreasury. KentishHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- AmTide Imidacloprid 2F LabelDocument44 pagesAmTide Imidacloprid 2F LabelHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sclerocarya Birrea Seed GerminationDocument1 pageSclerocarya Birrea Seed GerminationHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Decomposition of Urea NitrateDocument21 pagesDecomposition of Urea NitrateHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Use of Colored Shade Netting in HorticultureDocument3 pagesUse of Colored Shade Netting in HorticultureHector Quezada100% (1)
- Environmental Physiology of Cherimoya Under Heat Stress ConditionsDocument108 pagesEnvironmental Physiology of Cherimoya Under Heat Stress ConditionsHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravity-Fed Drip Irrigation Design ProcedureDocument12 pagesGravity-Fed Drip Irrigation Design ProcedureHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- CRFG Growing Rare Fruit From SeedDocument17 pagesCRFG Growing Rare Fruit From SeedHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Commercial Vegetable Disease Control Guide 2012Document86 pagesCommercial Vegetable Disease Control Guide 2012Hector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aluminium AnodizingDocument10 pagesAluminium AnodizingHector QuezadaPas encore d'évaluation