Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Acid and Bases
Transféré par
BS0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
59 vues4 pagesAcids and bases (PHARCHEM 1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentAcids and bases (PHARCHEM 1)
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
59 vues4 pagesAcid and Bases
Transféré par
BSAcids and bases (PHARCHEM 1)
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
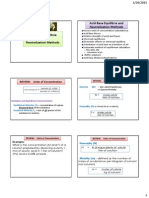
CHAPTER 15
ACIDS AND BASES
Strong acid and base completely ionized
Weak acid and base partially ionized
Law of chemical equilibrium is applicable to
solutions of weak electrolytes.
Ka ionization constant for weak acid
Kb ionization constant for weak base
Ionization constant indicator of the strength
of the acid or base.
What is the pH of a 0.005 M C6H5COOH if Ka =
6.5 x 10-5
To determine the pH, solve first for the H+ ion
concentration.
Solve for the percent ionization? Percent
ionization is the extent by which the acid
ionizes and it is directly proportional to
dilution. This is obtained by divided the H+ by
the original concentration of the acid times
100.
What is the pH of 3.5M NH4OH if Kb = 1.8 x
10-5
1. The Ka for benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5..
Calculate the pH of a 0.10 M benzoic acid
solution.
2. A 0.0560-g quantity of acetic acid is
dissolved in enough water to make 50.0 mL
of solution. Calculate the concentrations of
H+, CH3COO-, and CH3COOH at equilibrium.
(Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5.)
3. The pH of an acid solution is 6.20.
Calculate the Ka for the acid. The initial acid
concentration is 0.010 M.
4. What is the original molarity of a solution
of formic acid (HCOOH) whose pH is 3.26 at
5. Calculate the percent ionization of benzoic
acid having the following concentrations:
(a) 0.20 M, (b) 0.00020 M.
6. Calculate the percent ionization of
hydrofluoric acid at the following
concentrations: (a) 0.60 M, (b) 0.0046 M, (c)
0.00028 M. Comment on the trends. Ka = 7.1
x 10-4
7. A 0.040 M solution of a monoprotic acid is
14 percent ionized. Calculate the ionization
constant of the acid.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisD'EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- The Ka and KB of ItDocument23 pagesThe Ka and KB of ItAditya VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid-Base Equilibria and ApplicationDocument32 pagesAcid-Base Equilibria and Applicationfechem92100% (1)
- Ebbing 17Document26 pagesEbbing 17Neen NaazPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6 Acid-Base Equilibria PDFDocument41 pagesUnit 6 Acid-Base Equilibria PDFNathalie Mae De JesusPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6 Acid-Base Equilibria UST TemplateDocument41 pagesUnit 6 Acid-Base Equilibria UST TemplateCess MontemayorPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 17: Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria: Common-Ion EffectDocument28 pagesChapter 17: Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria: Common-Ion EffectrajPas encore d'évaluation
- Expt 4-Ionic EquilibriaDocument42 pagesExpt 4-Ionic EquilibriatwinkledreampoppiesPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytic ChemistryDocument115 pagesAnalytic ChemistryRalyn BasisPas encore d'évaluation
- Weak Acid Base NotesDocument49 pagesWeak Acid Base NotesJankel L PahuyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid-Base Equilibria in Aqueous SolutionsDocument48 pagesAcid-Base Equilibria in Aqueous SolutionsAdrian ChombaPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 6 - Acids & BasesDocument71 pagesCH 6 - Acids & BasesCharbel RahmePas encore d'évaluation
- 10.b Acid and Base Equilbria Part II-Chemistry Unit IDocument4 pages10.b Acid and Base Equilbria Part II-Chemistry Unit Imcleodtravis14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Isoelectric PointDocument24 pagesIsoelectric PointSangeeta RayPas encore d'évaluation
- Blok 3 - IT 12 - Reaksi Proteolitik & Asam Basa - KSHDocument41 pagesBlok 3 - IT 12 - Reaksi Proteolitik & Asam Basa - KSHSri WahyuniPas encore d'évaluation
- Liat Rumusnya Di Ebook Halaman 677Document2 pagesLiat Rumusnya Di Ebook Halaman 677Julio DavidPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7.5 ChemDocument25 pagesChapter 7.5 ChemElise ChinPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 15 More Equilibrium: Buffers, K, KDocument20 pagesCH 15 More Equilibrium: Buffers, K, KDamris MuhamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Titration: Quantitative Analysis Acid Neutralization ReactionDocument3 pagesTitration: Quantitative Analysis Acid Neutralization Reactionanna reham lucmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid and Salt EquilibriaDocument26 pagesAcid and Salt EquilibriaAnthony AbesadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry of Acids and BasesDocument54 pagesChemistry of Acids and Basesanjankdas50% (2)
- AnachemDocument115 pagesAnachemRochie DiezPas encore d'évaluation
- Buffer SolutionDocument12 pagesBuffer SolutionSonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Buffer SolutionDocument14 pagesBuffer SolutionSony0% (1)
- Acid Base EquilibriumDocument7 pagesAcid Base EquilibriumGervent GaylePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecturer 6Document20 pagesLecturer 6amr.120230006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acid-Base Equilibria and Salt EquilibriaDocument14 pagesAcid-Base Equilibria and Salt EquilibriaRaven LampaPas encore d'évaluation
- VOLUMETRIKDocument38 pagesVOLUMETRIKFans decky metbokiPas encore d'évaluation
- Determine Ka Weak Acid AP Labs 15Document3 pagesDetermine Ka Weak Acid AP Labs 15David AntonitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Acids and BasesDocument81 pagesAcids and BasesThea GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Buffer SolutionDocument15 pagesBuffer SolutionSonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid Base EquilibriaDocument12 pagesAcid Base EquilibriaDoroteo Jose StationPas encore d'évaluation
- BufferDocument25 pagesBuffernaghma KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 18.1 Experiment 4 Ionic EquilibriaDocument21 pagesChem 18.1 Experiment 4 Ionic EquilibriaAbigail Muniz Yambao100% (2)
- 2.acids and Bases Lecture 2Document8 pages2.acids and Bases Lecture 2Protusha RakshitPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 201: Polyprotic Acids and Bases ApplicationsDocument29 pagesChemistry 201: Polyprotic Acids and Bases Applicationspriscila_hdzvPas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument35 pagesIonic EquilibriumYak Raj PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- PH and BufferDocument31 pagesPH and Bufferhelion45Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acid Base Titration - 2015Document40 pagesAcid Base Titration - 2015MaulidinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 3 Presentation Part 2Document22 pagesGroup 3 Presentation Part 2Marianne LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec. 3 Neutralization and PHDocument17 pagesLec. 3 Neutralization and PHrkfw7nq7xrPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract (Lab 2) Ionization ConstantDocument12 pagesAbstract (Lab 2) Ionization Constantmirdza94Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acid Base Equilibrium Worksheet 1Document2 pagesAcid Base Equilibrium Worksheet 1Frank MassiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Weak Acids and Bases Plus Polyprotic AcidsDocument3 pagesWeak Acids and Bases Plus Polyprotic AcidsEvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Edexcel Chemistry A-Level: Topic 12: Acid-Base EquilibriaDocument11 pagesEdexcel Chemistry A-Level: Topic 12: Acid-Base EquilibriaLulwa KhaskiehPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 114A - : Biochemical Structure and FunctionDocument17 pagesChemistry 114A - : Biochemical Structure and FunctionJasminePas encore d'évaluation
- SCH4U0!3!10 - Ka and KB - PostDocument4 pagesSCH4U0!3!10 - Ka and KB - PostArzeen FarzadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Wiki Anal Tit Nonaqueous TitrationDocument5 pagesWiki Anal Tit Nonaqueous TitrationMira JunitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Ion Effect and Buffer SolutionDocument6 pagesCommon Ion Effect and Buffer SolutionNigatu MAmoPas encore d'évaluation
- Buffer Solutions.: Ass. Prof. I. R. BekusDocument27 pagesBuffer Solutions.: Ass. Prof. I. R. BekusNanda ThyarezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Citric AcidDocument1 pageCitric Acidahmad faisal rosidiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Common Ion EffectDocument24 pagesThe Common Ion EffectMothi KarunaPas encore d'évaluation
- 004 2024 Nurullah Aulia Sugiarti Rombel 01 Tugas Ke 01Document85 pages004 2024 Nurullah Aulia Sugiarti Rombel 01 Tugas Ke 01eliPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8.Document21 pagesChapter 8.satheeshpharma6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 142 - N Lab Acid Base Equilibria and Buffer Solutions 2022Document64 pagesChem 142 - N Lab Acid Base Equilibria and Buffer Solutions 2022Jahred CantornaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument46 pagesIonic Equilibriumabhinavsaurabh75% (4)
- AcidDocument14 pagesAcidTochits MatiasPas encore d'évaluation
- ws15 2Document3 pagesws15 2pokeyballPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 15 Worksheet 2 Equilibrium Calculations With Weak Acids and Bases ICE TablesDocument3 pagesChapter 15 Worksheet 2 Equilibrium Calculations With Weak Acids and Bases ICE TablespokeyballPas encore d'évaluation
- Bleh BlehDocument11 pagesBleh BlehAjayi DemiladePas encore d'évaluation
- Catholic Social Teaching2Document16 pagesCatholic Social Teaching2Jaica Mangurali TumulakPas encore d'évaluation
- 13Document3 pages13BSPas encore d'évaluation
- 12Document3 pages12BSPas encore d'évaluation
- 03.historical Development of MicrobiologyDocument27 pages03.historical Development of MicrobiologyBSPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 DDocument2 pagesChapter 5 DAaron ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- LiteratureDocument2 pagesLiteratureBSPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument3 pagesClassification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesJohn Emmanuel SyPas encore d'évaluation
- Title Bathan, G.I., Crisostomo, A.C., Liu, M.I.C., and Santiago, M.RDocument3 pagesTitle Bathan, G.I., Crisostomo, A.C., Liu, M.I.C., and Santiago, M.RBSPas encore d'évaluation
- Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument12 pagesCarboxylic Acid and DerivativesJohn Henrick G. Uy50% (2)
- Classification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument4 pagesClassification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesAJ Pasciolco50% (2)
- Classification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument3 pagesClassification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesJohn Emmanuel SyPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Nelson T. TubonDocument29 pagesDr. Nelson T. TubonBS50% (2)
- Classification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument3 pagesClassification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesJohn Emmanuel SyPas encore d'évaluation
- Arendelle HighDocument399 pagesArendelle HighBS100% (1)
- Pharchem 1 QuestionsDocument1 pagePharchem 1 QuestionsBSPas encore d'évaluation
- OintmentDocument6 pagesOintmentBSPas encore d'évaluation