Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Actual Flow To Normal Flow
Transféré par
somucdm6023Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Actual Flow To Normal Flow
Transféré par
somucdm6023Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
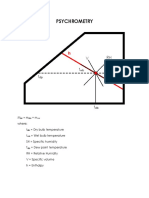
Actual Flow to Normal Flow ,Normal Flow to Actual Flow and Important Useful Calculations
Actual Volume to Normal Volume and Vice Versa
The actual (measured) flow rate is normalized to the flow rate at a certain reference
pressure (P) and temperature (T).
For Metric system, the "normal" condition is
Pref = 1 atm = 1.01325 bar = 101325 Pa
Tref = 0 C = 273.15 k
For Standard (English) system, the "standard" condition is
Pref = 1 atm = 14.6959 psi
Tref = 70 F = 529.67 R
Ideal gas assumes that volume is proportional to temperature and the reciprocal of
pressure. The normalized volume flow rate becomes
Q = QN (Pref / Pa) (T / Tref)
where Pa, the actual pressure, is the sum of surrounding atmospheric pressure and the gage
pressure (Pa = Patm + Pg). The unit of flow temperature T must be either Kelvin (k) or
Rankine degrees (R).
(A) Convert Air Volumetric Flow (@ Std) to Vapor Volumetric Flow (@ Std)Vapor Volumetric Flow @ STD = Air
Volumetric Flow @ STD Vapor Temperature Correction Factor / Vapor Specific Gravity Correction Factor
[Eq.1]
QStd,Vap = QStd,Air [(TStd,Vap+460) (TActual,Vap+460)] / [MWVap / MWAir]
whereQStd,Vap = Vapor Volumetric Flow @ STD (SCFH)
QStd,Air = Air Volumetric Flow @ STD (SCFH)
TStd,Vap = Vapor Temperature @ STD = 60 degFTActual,Vap = Actual Vapor Temperature (degF)MWVap = Vapor Molecular
WeightMW Air = Air Molecular Weight (28.96)
(B) Convert Vapor Volumetric Flow (@ Std) to Vapor Volumetric Flow (@ Actual)
Vapor Volumetric Flow @ PT = Vapor Volumetric Flow @ STD [Actual Temperature / Standard Temperature]
Pressure / Actual Pressure ]
[Std
[Eq.2]
QActual,Vap = QStd,Vap [(TActual,Vap+460) (TStd,Vap+460)] [PStd,Vap/PActual,Vap]
where
QActual,Vap = Actual Vapor Flow (SCF)PStd,Vap = Vapor Pressure @ STD (14.7 psia)PActual,Vap = Actual Vapor Pressure (psia)
Example 1 :
Nitrogen (MW=28) blanketing a tank. The calculated air flow @ std is 50,000 SCFH. The tank is at 1 psig and 68
degF when venting via PVRV occurred. Calculate the equivalent Nitrogen relief load at actual flow condition.
From [Eq.1]
QStd,N2 = QStd,Air [(TStd,N2+460) (TActual,N2+460)] / [MWN2 / MWAir]
QStd,N2 = 50000 [(60+460) (68+460)] / [28 / 28.96]
QStd,N2 = 50463.22 SCFH
From [Eq.2]
QActual,N2 = QStd,N2 [(TActual,N2+460) (TStd,N2+460)] [PStd,N2/PActual,N2]
QActual,N2 = 50463.22 [(68+460) (60+460)] [14.7/(14.7+1)]
QActual,N2 = 47975.91 CFH
Example 2 :
A tank feed from condensate stablizer. In case of gas blowby, flash vapor generated plus displaced vapor (MW = 35)
is 60,000 CFH and tank is at 1.5 psig and 122 degF when venting via PVRV occurred. Calculate the equivalent Air
flow at STD condition.
From [Eq.2]
QAct,Vap = QStd,Vap [(TAct,Vap+460) (TStd,Vap+460)] [PStd,Vap/PAct,Vap]
QStd,Vap = QAct,Vap [(TStd,Vap+460) (TAct,Vap+460)] [PAct,Vap/PStd,Vap]
QStd,Vap = 60000 [(60+460) (122+460)] [(1.5+14.7)/14.7]
QStd,Vap = 59078.48 SCFH
From [Eq.1]
QStd,Vap = QStd,Air [(TStd,Vap+460) (TActual,Vap+460)] / [MWVap / MWAir]
QStd,Air = QStd,Vap [(TActual,Vap+460) (TStd,Vap+460)] / [MWAir/ MWVap]
QStd,Air = 59078.48 [(122+460) (60+460)] / [28.96 / 35]
QStd,Air = 68710.62 SCFH
Concluding Remark
Above equations are pretty useful for conversion of air - vapor and actual-standard condition
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Data Sheet For Spray NozzleDocument3 pagesData Sheet For Spray Nozzlebecpavan100% (1)
- Air Receiver SizingDocument2 pagesAir Receiver Sizingsiby josephPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Eliminator Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesAir Eliminator Datasheet PDFbecpavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pump SelectionDocument2 pagesPump Selectiongroup2sd1314Pas encore d'évaluation
- N2 Regulator and Gauges DatasheetDocument4 pagesN2 Regulator and Gauges DatasheetpavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pump sizing spreadsheet calculates performanceDocument26 pagesPump sizing spreadsheet calculates performancesterling100% (1)
- Erbil Refinery Diesel Filling Pump Data SheetDocument5 pagesErbil Refinery Diesel Filling Pump Data SheetSardar PerdawoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Centrifugal Pumps: Process Calculation / Data SheetDocument3 pagesCentrifugal Pumps: Process Calculation / Data SheetMurali MuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculation Sheet For Pump Hydraulic (Fps Unit)Document1 pageCalculation Sheet For Pump Hydraulic (Fps Unit)chemical todiPas encore d'évaluation
- Suction Heaters and Heating Coils Suction Heaters and Heating CoilsDocument3 pagesSuction Heaters and Heating Coils Suction Heaters and Heating CoilsDaysianne100% (1)
- NPSHa Calculation SpreadsheetDocument3 pagesNPSHa Calculation Spreadsheetprasad durgaPas encore d'évaluation
- Line Sizing GuidelinesDocument2 pagesLine Sizing GuidelinesHarryBouterPas encore d'évaluation
- Scope Matrix PDFDocument5 pagesScope Matrix PDFNathanPas encore d'évaluation
- NSDL Project Technical Data Sheet for 541-Ton Air-Cooled ChillerDocument3 pagesNSDL Project Technical Data Sheet for 541-Ton Air-Cooled ChillerVenu GopalPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipeline Pressurisation & de Pressurisation CalculationDocument4 pagesPipeline Pressurisation & de Pressurisation Calculationhatakerobot50% (2)
- Oil Cooler - Pre Design Data SheetDocument3 pagesOil Cooler - Pre Design Data SheetSakthi VelPas encore d'évaluation
- AutoPIPE QuickStart - Model Modification - WorkbookDocument63 pagesAutoPIPE QuickStart - Model Modification - WorkbookJames100% (1)
- 22-DS-R-001 Rev 1 API 617 GTCPsDocument25 pages22-DS-R-001 Rev 1 API 617 GTCPsChike Nwachukwu100% (1)
- 100-T-1100 Methanol Tank SampleDocument3 pages100-T-1100 Methanol Tank SampleSachinl PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Caltex Indonesia Pump Sizing DocumentDocument5 pagesCaltex Indonesia Pump Sizing DocumentElias EliasPas encore d'évaluation
- Excel SizingDocument10 pagesExcel SizingJolteon JuniorPas encore d'évaluation
- TQ - Air Fin Cooler (CS) - ModificationDocument6 pagesTQ - Air Fin Cooler (CS) - ModificationAvinash ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- CN5191 - L2 - A1-Centrifugal Pump Process Data SheetDocument1 pageCN5191 - L2 - A1-Centrifugal Pump Process Data SheetMochi CumilinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 182268644-CW-Pump-CalculationDocument18 pages182268644-CW-Pump-CalculationPinak ProjectsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe thickness calculations as per ASME B31.3Document1 pagePipe thickness calculations as per ASME B31.3alvinchuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Liquid Overfeed Systems by R. P. ParanjpeyDocument15 pagesLiquid Overfeed Systems by R. P. Paranjpeyurp30234Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tanky 53 KL Rev.1Document187 pagesTanky 53 KL Rev.1Priyo Jati WahyonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Flowrate Calculation For A Draining TankDocument2 pagesFlowrate Calculation For A Draining TankAnonymous bHh1L1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tri P10Document10 pagesTri P10Dvd Davide La CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Blowe DatasheetDocument1 pageAir Blowe DatasheetMoein PPas encore d'évaluation
- Instrument Air Dryer Sizing Calculation FactorsDocument1 pageInstrument Air Dryer Sizing Calculation FactorsAravind Kannan100% (2)
- PVV Cal Sheet LabixDocument45 pagesPVV Cal Sheet LabixPranpath Narupantawart50% (2)
- Design of A Vapor-Liquid SeparatorDocument2 pagesDesign of A Vapor-Liquid SeparatorpowerveePas encore d'évaluation
- Normal Design: Depressurize From Design Pressure To 50% in 15 MinutesDocument2 pagesNormal Design: Depressurize From Design Pressure To 50% in 15 Minutesmatteo2009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design Conditions Datasheet: Unit Tag Qty Model No Net Cooling Capacity (Ton.r) Nominal Voltage Refrigerant TypeDocument2 pagesDesign Conditions Datasheet: Unit Tag Qty Model No Net Cooling Capacity (Ton.r) Nominal Voltage Refrigerant TypeFernando CabreraPas encore d'évaluation
- N2 Purging Demand Calculation Shutdown - Flare SystemDocument54 pagesN2 Purging Demand Calculation Shutdown - Flare SystemMoch FaridPas encore d'évaluation
- Compressor Capacity CalculationDocument4 pagesCompressor Capacity CalculationHoney Tiwari100% (1)
- API 650 Baseplate DesignDocument3 pagesAPI 650 Baseplate DesignmjlazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipeline Pressure Drop Per 100 M - BAK - 14062011Document3 pagesPipeline Pressure Drop Per 100 M - BAK - 14062011Bharat A. KaduPas encore d'évaluation
- Pump Design - 2Document1 pagePump Design - 2kapsarcPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Receiver SizingDocument3 pagesAir Receiver Sizinglutfi awnPas encore d'évaluation
- 18105-Abg-01-Me-das-033 Rev-A Mechanical Data Sheet O2 Stripper Condense...Document5 pages18105-Abg-01-Me-das-033 Rev-A Mechanical Data Sheet O2 Stripper Condense...Avinash ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- LNG Pumps, CMDocument11 pagesLNG Pumps, CMRachitPas encore d'évaluation
- BOQ From (HVAC)Document26 pagesBOQ From (HVAC)Neeta Samir Munj ParkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Table-1 Scope of Work Supply (MR For ACHE)Document6 pagesTable-1 Scope of Work Supply (MR For ACHE)Avinash ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Pressure Reduction StationDocument2 pagesGas Pressure Reduction StationMathias OnosemuodePas encore d'évaluation
- SN74LVC07Document23 pagesSN74LVC07abcdPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Handling Engineers: U S Agency - Taco DivDocument5 pagesFluid Handling Engineers: U S Agency - Taco DivsitehabPas encore d'évaluation
- Data SheetDocument6 pagesData Sheetnalawade_pradeepPas encore d'évaluation
- NPSH Calculations For Reciprocating PumpDocument1 pageNPSH Calculations For Reciprocating PumpMadan YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- P P T T M D: Noise Control of 61-101J & 61-103J Start-Up I Sound PowerDocument7 pagesP P T T M D: Noise Control of 61-101J & 61-103J Start-Up I Sound PowerIrwansyah MuchtarPas encore d'évaluation
- 10P87-D0003-046-R0-WHRU by TEPLDocument23 pages10P87-D0003-046-R0-WHRU by TEPLjigarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nozzle Load - PumpDocument1 pageNozzle Load - Pumpduf fu0% (1)
- Low NPSH & Cases of Vertical Barrel (VS6) Type Pump Selection PDFDocument12 pagesLow NPSH & Cases of Vertical Barrel (VS6) Type Pump Selection PDFMuhammad ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Jsa For Roof Air LiftDocument2 pagesJsa For Roof Air LiftKoshy ThankachenPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Flow Calculations Made Using The V C: Ventilation Test InstrumentsDocument6 pagesHeat Flow Calculations Made Using The V C: Ventilation Test Instrumentsretrospect1000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic conceptDocument59 pagesBasic conceptMinh HoàngPas encore d'évaluation
- Psych RometryDocument6 pagesPsych Rometrypammy313Pas encore d'évaluation
- Heating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning Processes ExplainedDocument25 pagesHeating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning Processes ExplainedAbdalhady JoharjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychrometry: V RH T T SHDocument13 pagesPsychrometry: V RH T T SHKAL ELPas encore d'évaluation
- 42LW5700-TA LG LED TV Start Up Sequence and VoltagesDocument2 pages42LW5700-TA LG LED TV Start Up Sequence and Voltagessomucdm6023100% (1)
- Calibrate Instruments Under 40Document25 pagesCalibrate Instruments Under 40somucdm602350% (2)
- TSUMV59XU Datasheet PDFDocument33 pagesTSUMV59XU Datasheet PDFHamza Abbasi AbbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- PL - MS6M30K.1 Universal LCD LED LCD Panel 120HZ PlateDocument9 pagesPL - MS6M30K.1 Universal LCD LED LCD Panel 120HZ Platesomucdm6023100% (4)
- Key Layout For Game KeyboardDocument1 pageKey Layout For Game Keyboardsomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- Victor Stringing InstructionsDocument5 pagesVictor Stringing Instructionssomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- TSUMV59XU Datasheet PDFDocument33 pagesTSUMV59XU Datasheet PDFHamza Abbasi AbbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- 42LW5700-TA LG LED TV Start Up Sequence and VoltagesDocument2 pages42LW5700-TA LG LED TV Start Up Sequence and Voltagessomucdm6023100% (1)
- 42LW5700-TA LG LED TV Start Up Sequence and VoltagesDocument2 pages42LW5700-TA LG LED TV Start Up Sequence and Voltagessomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- KYC GuidelinesDocument14 pagesKYC GuidelineslovedarylPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 Nissan Service Maintenance Guide PDFDocument61 pages2013 Nissan Service Maintenance Guide PDFk.saravanakumar28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Handy Calibrator ManualDocument126 pagesHandy Calibrator Manualsomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manual MotherboardDocument104 pagesManual Motherboardsomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- LG TV Service ManualDocument115 pagesLG TV Service Manualsomucdm6023100% (1)
- Badminton Design Guide - 2011Document20 pagesBadminton Design Guide - 2011ruk21100% (1)
- 5009TMR OpView Interface ManualDocument52 pages5009TMR OpView Interface Manualsomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pub002 026 00 - 1205Document2 pagesPub002 026 00 - 1205somucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- CONTROL TECHNICIAN TUBING INSTALLATIONDocument19 pagesCONTROL TECHNICIAN TUBING INSTALLATIONsomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- TherMo CoupleDocument10 pagesTherMo Couplesomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pub002 003 00 - 1011Document88 pagesPub002 003 00 - 1011jones0055Pas encore d'évaluation
- STT250 Operator Manual en EN1I-6190Document59 pagesSTT250 Operator Manual en EN1I-6190somucdm6023100% (1)
- Tubes & FittingsDocument29 pagesTubes & Fittingssomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- Handy Calibrator ManualDocument126 pagesHandy Calibrator Manualsomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- Level Transmitter ManualDocument180 pagesLevel Transmitter Manualsomucdm6023100% (2)
- Flow Serve PositionerDocument40 pagesFlow Serve Positionersomucdm6023100% (1)
- Handy Calibrator ManualDocument126 pagesHandy Calibrator Manualsomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- STT250 Operator Manual en EN1I-6190Document59 pagesSTT250 Operator Manual en EN1I-6190somucdm6023100% (1)
- Calculate The Size of Battery Bank & Invertor: Electrical Load DetailsDocument8 pagesCalculate The Size of Battery Bank & Invertor: Electrical Load Detailssomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- Logix 520MD SeriesDocument20 pagesLogix 520MD Seriessomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- Refining Process HBDocument296 pagesRefining Process HBsomucdm6023Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4 SEA 3 Bulk Cargo Operation PDFDocument23 pages4 SEA 3 Bulk Cargo Operation PDFChadAclanParas100% (2)
- AHRI Certifi Ed: Why Certify With AHRI?Document2 pagesAHRI Certifi Ed: Why Certify With AHRI?Benjamin BriceñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Water BalanceDocument2 pagesWater Balancekimran80Pas encore d'évaluation
- Product Data: Features/BenefitsDocument100 pagesProduct Data: Features/BenefitsAustin Dillon50% (2)
- HVAC Fundamentals PDFDocument296 pagesHVAC Fundamentals PDFanthonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller de Humidificacion 2011Document8 pagesTaller de Humidificacion 2011Alejandro Torres CardonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Philisophy: 1. Ahu (Air Handling Unit)Document2 pagesControl Philisophy: 1. Ahu (Air Handling Unit)Anonymous ynJByUsPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 2 - Meteorology PDFDocument23 pagesPart 2 - Meteorology PDFJQPas encore d'évaluation
- 25 90 00 Ahu-Vav-Rev4Document24 pages25 90 00 Ahu-Vav-Rev4PrestoneKPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Transfer Process TUT (After Mid Semester)Document11 pagesHeat Transfer Process TUT (After Mid Semester)vaishnavi singh100% (1)
- GR 11 RELAB - NOTES AND ACTIVITIES - EditedDocument119 pagesGR 11 RELAB - NOTES AND ACTIVITIES - Editedqomoyinhlanhla129100% (2)
- Pipe Friction Loss CalculationDocument5 pagesPipe Friction Loss Calculationapi-26699613100% (6)
- Presentation of Mary School of Clarin, IncDocument5 pagesPresentation of Mary School of Clarin, IncjuicymayPas encore d'évaluation
- Placa ParterdemisolDocument4 pagesPlaca ParterdemisoliuliandurdureanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Sciences. 2nd of ESO: Heat & TemperatureDocument15 pagesNatural Sciences. 2nd of ESO: Heat & TemperatureAlberto DíazPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital ThermometerDocument5 pagesDigital ThermometerAbhijeetPas encore d'évaluation
- Ref MathDocument7 pagesRef MathMd.Tanvir RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cooling Heating CapacityDocument14 pagesCooling Heating CapacityJACK BAKERPas encore d'évaluation
- Tunnel Ventilation of Broiler Houses ExplainedDocument3 pagesTunnel Ventilation of Broiler Houses ExplainedLintangPas encore d'évaluation
- The Layers of Earth's AtmosphereDocument11 pagesThe Layers of Earth's AtmosphereAzrul NizamPas encore d'évaluation
- Everything You Need to Know About Air Pressure and Weather SystemsDocument47 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Air Pressure and Weather Systemsmichaelaapilat026Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project:Lng School at Sur: Chillers MAS Comparision Report ManufactureDocument4 pagesProject:Lng School at Sur: Chillers MAS Comparision Report ManufacturePradeep SukumaranPas encore d'évaluation
- AIR CONDITIONING UNIT REMOTE COOLEDDocument2 pagesAIR CONDITIONING UNIT REMOTE COOLEDAdy PrasetyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On Psychrometry and Air Conditioning UpdatedDocument103 pagesPresentation On Psychrometry and Air Conditioning UpdatedJoshua Phillip Austero FederisPas encore d'évaluation
- Marine MeteorologyDocument49 pagesMarine MeteorologyMahdi Bordbar100% (12)
- Natural Ventilation Study ReportDocument6 pagesNatural Ventilation Study ReportNuratiqah SharifahPas encore d'évaluation
- Ac Midterm Part 1 Key AnswersDocument1 pageAc Midterm Part 1 Key AnswersReden LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT 5 Changes of StateDocument6 pagesUNIT 5 Changes of StatePham Van Tin B1909842Pas encore d'évaluation
- CondenserDocument18 pagesCondenserHusnain AliPas encore d'évaluation
- How air conditioners work in 4 simple stepsDocument2 pagesHow air conditioners work in 4 simple stepsManuel Saez SellerPas encore d'évaluation