Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
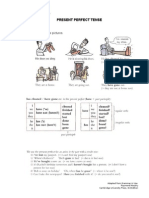
Form of Present Perfect
Transféré par
Yvan Bravo0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
21 vues2 pagesThe present perfect simple tense expresses actions that either began in the past and continue in the present or stopped recently. It emphasizes the result of the action. The document provides the forms of the present perfect tense for positive and negative statements and questions. It also lists irregular verb forms and exceptions for adding "-ed" to regular verbs. Examples are given to illustrate the uses of the present perfect tense to express ongoing actions, recent completed actions, finished actions with present consequences, and actions that occurred once or multiple times before the present. Signal words that can indicate the present perfect tense are also listed.
Description originale:
t
Titre original
Present Perfect
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe present perfect simple tense expresses actions that either began in the past and continue in the present or stopped recently. It emphasizes the result of the action. The document provides the forms of the present perfect tense for positive and negative statements and questions. It also lists irregular verb forms and exceptions for adding "-ed" to regular verbs. Examples are given to illustrate the uses of the present perfect tense to express ongoing actions, recent completed actions, finished actions with present consequences, and actions that occurred once or multiple times before the present. Signal words that can indicate the present perfect tense are also listed.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
21 vues2 pagesForm of Present Perfect
Transféré par
Yvan BravoThe present perfect simple tense expresses actions that either began in the past and continue in the present or stopped recently. It emphasizes the result of the action. The document provides the forms of the present perfect tense for positive and negative statements and questions. It also lists irregular verb forms and exceptions for adding "-ed" to regular verbs. Examples are given to illustrate the uses of the present perfect tense to express ongoing actions, recent completed actions, finished actions with present consequences, and actions that occurred once or multiple times before the present. Signal words that can indicate the present perfect tense are also listed.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
Present perfect
The present perfect simple expresses an action that is still going on or that
stopped recently, but has an influence on the present. It puts emphasis on the
result.
Form of Present Perfect
Positive
Negative
Question
I / you / we / they
I have spoken.
I have not spoken.
Have I spoken?
he / she / it
He has spoken.
He has not spoken.
Has he spoken?
For irregular verbs, use the participle form (see list of irregular verbs, 3rd column).
For regular verbs, just add ed.
Exceptions in Spelling when Adding ed
Exceptions in spelling when adding ed
Example
after a final e only add d
love loved
final consonant after a short, stressed vowel
admit admitted
or l as final consonant after a vowel is doubled
travel travelled
final y after a consonant becomes i
hurry hurried
Adapted from Cambridge
Touchestone TE
Use of Present Perfect
puts emphasis on the result
Example: She has written five letters.
action that is still going on
Example: School has not started yet.
action that stopped recently
Example: She has cooked dinner.
finished action that has an influence on the present
Example: I have lost my key.
action that has taken place once, never or several times before the moment of
speaking
Example: I have never been to Australia.
Signal Words of Present Perfect
already, ever, just, never, not yet, so far, till now, up to now
Adapted from Cambridge
Touchestone TE
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Form of Present Perfect: Positive NegativeDocument2 pagesForm of Present Perfect: Positive NegativeJavier EduardoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Present Perfect Simple Expresses An Action That Is Still Going On or That Stopped RecentlyDocument2 pagesThe Present Perfect Simple Expresses An Action That Is Still Going On or That Stopped RecentlyerickperdomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple PastDocument5 pagesSimple Pastledrac0% (1)
- Name: Paola Ruiz Curse: 4rd Level: HomeworkDocument2 pagesName: Paola Ruiz Curse: 4rd Level: HomeworkPao RuizPas encore d'évaluation
- Form of Present Perfect: Positive NegativeDocument3 pagesForm of Present Perfect: Positive NegativeerickperdomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Perfect SimpleDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect SimpleAndrea Magdolna Moldovan100% (3)
- Present PerfectDocument5 pagesPresent PerfectIlievska CvetankaPas encore d'évaluation
- Present TensesDocument1 pagePresent TensesGabriela GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2. The Simple Present of Verbs Other Than The Verb To BeDocument5 pagesChapter 2. The Simple Present of Verbs Other Than The Verb To Bebáh_leePas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris "Rangkuman Dan Contoh": Disusun Oleh Nama: Candrika Della Vabelia Jurusan: 1 B KeperawatanDocument6 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris "Rangkuman Dan Contoh": Disusun Oleh Nama: Candrika Della Vabelia Jurusan: 1 B KeperawatanJamilah p3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Past Simple and Present Perfect Irregular Verbs ExercisesDocument2 pagesPast Simple and Present Perfect Irregular Verbs ExercisesMarkiyan MyronchukPas encore d'évaluation
- Traditiile Romei AnticeDocument13 pagesTraditiile Romei AnticeAnonymous XsOfDozHauPas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome To Our English Class!: by Ilenia PapilioDocument15 pagesWelcome To Our English Class!: by Ilenia PapilioGiulia TortiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Novel Idea Kamilan TakmilDocument77 pagesA Novel Idea Kamilan TakmilSofia RaheelPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Present: Do You Speak English?Document51 pagesSimple Present: Do You Speak English?Lorela Liliana TudorPas encore d'évaluation
- The Past Continuous Tense Is Most Often Used For Actions Happening at Some Time in The PastDocument4 pagesThe Past Continuous Tense Is Most Often Used For Actions Happening at Some Time in The PastAndreea-Cristina DraganescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Final B.inggrisDocument24 pagesTugas Final B.inggrisLevin LombanPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Perfect Simple LectieDocument3 pagesPresent Perfect Simple LectieCiocan RalucaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A VerbDocument3 pagesWhat Is A VerbAnny TangPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentperfect PrimeroDocument11 pagesPresentperfect PrimeroAnonymous CSudLPP1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ingles Basico 1Document19 pagesIngles Basico 1dulcePas encore d'évaluation
- Present PerfectDocument6 pagesPresent PerfectSagnik RohakPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple PresentDocument2 pagesSimple PresentWardia Ben talebPas encore d'évaluation
- Form of Simple PastDocument2 pagesForm of Simple PastAriadne OrdoñezPas encore d'évaluation
- ACTIVE Pasive VoiceDocument11 pagesACTIVE Pasive VoiceDelta Asesorías AcadémicasPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Perfect Simple Vs Present Perfect ProgressiveDocument3 pagesPresent Perfect Simple Vs Present Perfect ProgressiveAnca MorosanPas encore d'évaluation
- Present ContinuousDocument4 pagesPresent ContinuousHari KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Simple Tense in English - Grammar LessonDocument7 pagesPresent Simple Tense in English - Grammar LessonVerónica PilcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Support Handout For EnglishDocument20 pagesSupport Handout For EnglishLuis Julio Carlos PiresPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Present Tense: English Grammar RulesDocument20 pagesSimple Present Tense: English Grammar RulesVidia darmayanthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Simple TenseDocument18 pagesPresent Simple TenseirmafpdPas encore d'évaluation
- The Simple Present Tense Is UsedDocument8 pagesThe Simple Present Tense Is UsedNOOR AZNIPas encore d'évaluation
- Present SimpleDocument35 pagesPresent SimpleCarlos ImilanPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Present Tense in English GrammarDocument6 pagesSimple Present Tense in English GrammarNhung TâyPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Simple Tense PDFDocument11 pagesPresent Simple Tense PDFCamila Moreno RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Exceptions in Spelling When Adding Ed': Present Perfect SimpleDocument2 pagesExceptions in Spelling When Adding Ed': Present Perfect SimpleGeorkie DimellPas encore d'évaluation
- TKT GlossaryDocument43 pagesTKT GlossaryNurgizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Form of Simple Past: Exceptions in Spelling When Adding Ed'Document1 pageForm of Simple Past: Exceptions in Spelling When Adding Ed'andreiPas encore d'évaluation
- English GrammarDocument4 pagesEnglish GrammarLawrence la AjimPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Perfect TenseDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect TenseFederico Effendy Sañz100% (1)
- ElecDocument15 pagesElecfaith_khp73301Pas encore d'évaluation
- Present SimpleDocument9 pagesPresent SimpleMichell Rezamano RochaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar SummaryDocument4 pagesGrammar SummaryChinhNguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Simple Present Tense in English Is Used To Describe An Action That Is RegularDocument5 pagesThe Simple Present Tense in English Is Used To Describe An Action That Is RegularMarcos Augusto RomanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tiempos InglésDocument43 pagesTiempos InglésFrancisca Ponce HillePas encore d'évaluation
- Master English Tenses: A Short & Comprehensive GuideD'EverandMaster English Tenses: A Short & Comprehensive GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Present Tense: English Grammar RulesDocument6 pagesSimple Present Tense: English Grammar RulesZahrotul JannahPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGLISH PAGE - Present ContinuousDocument5 pagesENGLISH PAGE - Present ContinuousidahashimPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature Shtese Gjuhe AnglezeDocument18 pagesLiterature Shtese Gjuhe AnglezeKastriot HoxhaPas encore d'évaluation
- English Class Ceba 25-03-23Document5 pagesEnglish Class Ceba 25-03-23Alan FarfanPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Perfect and ContinuousDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect and ContinuousledracPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Present Perfect TenseDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Present Perfect TenseGareth JosePas encore d'évaluation
- Silmple Present Tents: Verb Conjugation & SpellingDocument4 pagesSilmple Present Tents: Verb Conjugation & SpellingIta Masyita IskandarPas encore d'évaluation
- Verbs English Language Notes For Bank and Other Competitive Exams Download PDFDocument3 pagesVerbs English Language Notes For Bank and Other Competitive Exams Download PDFShailendra SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- The Verb To DoDocument15 pagesThe Verb To DoSantiago Francisco Zamora100% (1)
- Simple PresentDocument7 pagesSimple PresentJosmary Cuauro QuiñonezPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGLISH PAGE - Future Perfect PDFDocument4 pagesENGLISH PAGE - Future Perfect PDFidahashim100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Test PDFDocument60 pagesMultiple Choice Test PDFInés Amaya Díaz100% (8)
- Analysis of Rake Angle Effect To Stress Distributi PDFDocument13 pagesAnalysis of Rake Angle Effect To Stress Distributi PDFYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- 36 13 Shonin - PronkoDocument8 pages36 13 Shonin - PronkoYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ubc Method MiningDocument5 pagesUbc Method MiningYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Demystifying The Equations of Sedimentary Geology: Instructor's NotesDocument2 pagesDemystifying The Equations of Sedimentary Geology: Instructor's NotesYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Coal Mine Ventilation Systems in The United States of AmericaDocument8 pagesCoal Mine Ventilation Systems in The United States of AmericaYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Other Coal 1Document3 pagesOther Coal 1Yvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Foemula Game StuffDocument1 pageFoemula Game StuffYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- MVLLDocument1 pageMVLLYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Modelling Truck Performance in A Spread SheetDocument9 pagesModelling Truck Performance in A Spread SheetYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Arch IvoDocument1 pageArch IvoYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled 2Document1 pageUntitled 2Yvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Comprehensive Investigation of Loading Variance Influence On Fuel Consumption and Gas Emissions in Mine Haulage OperationDocument22 pagesA Comprehensive Investigation of Loading Variance Influence On Fuel Consumption and Gas Emissions in Mine Haulage OperationYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Perfect ExcercisesDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect ExcercisesYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Size of Living Things: Click Link For An Interactive Animation On Cells AliveDocument30 pagesSize of Living Things: Click Link For An Interactive Animation On Cells AliveYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Manner Adverbs: Quickly Slowly CarefullyDocument1 pageManner Adverbs: Quickly Slowly CarefullyYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformada InversaDocument1 pageTransformada InversaYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Day in The Life of Pedro Suarez Vertiz TerminadoDocument8 pagesA Day in The Life of Pedro Suarez Vertiz TerminadoYvan BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mi Kon AaheDocument62 pagesMi Kon AaheVishal BadavePas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Penggunaan Bahasa Daerah Pada Komunikasi Mahasiswa Di KampusDocument14 pagesJurnal Penggunaan Bahasa Daerah Pada Komunikasi Mahasiswa Di KampusHilman RamayadiPas encore d'évaluation
- REET 2012 Level 2nd Question PaperDocument100 pagesREET 2012 Level 2nd Question Paperashish singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Lord Dattatreya StotramDocument2 pagesLord Dattatreya StotramJagdish PorePas encore d'évaluation
- Prepositions Hebrew PDFDocument2 pagesPrepositions Hebrew PDFBenjamin Gordon100% (1)
- Stifter LeponticDocument15 pagesStifter LeponticBellovesos100% (1)
- Arabic Placement Test Carleton 2010Document8 pagesArabic Placement Test Carleton 2010Khairul ZamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Urdu Phonetic Inventory: Center For Language Engineering (CLE)Document4 pagesUrdu Phonetic Inventory: Center For Language Engineering (CLE)m rauf tabassumPas encore d'évaluation
- Arabic Handwriting Practice - Iqra GamesDocument8 pagesArabic Handwriting Practice - Iqra GameszPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: Visual::Worksheet Number:16: 1 - Find The Odd One OutDocument5 pagesTopic: Visual::Worksheet Number:16: 1 - Find The Odd One OutAnanya BhaduriPas encore d'évaluation
- Bhargava Upapuran - Akhil Bharatiya Sanskrit Parishad LucknowDocument218 pagesBhargava Upapuran - Akhil Bharatiya Sanskrit Parishad LucknowRambhakt Niroj PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Job Sheet 2 Application Letter SalinanDocument3 pagesJob Sheet 2 Application Letter SalinanXIAK101ADE NOVAL ZPas encore d'évaluation
- Dpo TCCLDocument11 pagesDpo TCCLKrish KumaraguruPas encore d'évaluation
- Gayatri Mantra Ki Vilakshan ShaktiDocument33 pagesGayatri Mantra Ki Vilakshan ShaktiSudeep NikamPas encore d'évaluation
- Tsybin Concerto For Oboe Part 1 PDFDocument36 pagesTsybin Concerto For Oboe Part 1 PDFmillneufcentPas encore d'évaluation
- Kartveluri Memkvidreoba I Chantladze, GuledaniDocument4 pagesKartveluri Memkvidreoba I Chantladze, GuledaniKARTVELIAN HERITAGE IPas encore d'évaluation
- Percakapan Bahasa Inggris Perkenalan 2 Orang Di Bebagai TempatDocument4 pagesPercakapan Bahasa Inggris Perkenalan 2 Orang Di Bebagai Tempatandana kanzPas encore d'évaluation
- RPS Bahasa Inggris 1Document4 pagesRPS Bahasa Inggris 1achmad rizkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Typing Guide To The Syriac Phonetic KeyboardDocument12 pagesTyping Guide To The Syriac Phonetic KeyboardGareth HughesPas encore d'évaluation
- Bhagavadgita TipsDocument3 pagesBhagavadgita TipsNaiduPas encore d'évaluation
- Turkic Languages - WikipediaDocument9 pagesTurkic Languages - Wikipediatsvmpm1765Pas encore d'évaluation
- TRDL14 Lonely China Passbook&DictionanyDocument386 pagesTRDL14 Lonely China Passbook&DictionanyUdomsin WutigulpakdeePas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 - Lecture 1 PDFDocument10 pages1.1 - Lecture 1 PDFToshiro NakagauaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tuhfatul-Atfaal Lisan Ul ArabDocument2 pagesTuhfatul-Atfaal Lisan Ul Arabbint_shams50% (2)
- Baybayin Translation Tips: Using Baybayin With Tagalog Using Baybain With EnglishDocument4 pagesBaybayin Translation Tips: Using Baybayin With Tagalog Using Baybain With EnglishMjhay MacaraegPas encore d'évaluation
- A Solemn Music PerusalDocument29 pagesA Solemn Music PerusalLord ZleotsPas encore d'évaluation
- Korean LanguageDocument59 pagesKorean LanguageMohamed Pauzi100% (6)
- PinYin - The Chinese Phonetic AlphabetDocument2 pagesPinYin - The Chinese Phonetic Alphabettiffany hePas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To AtayalDocument62 pagesIntro To AtayalXuan Lajo MartínezPas encore d'évaluation