Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Animal Bites
Transféré par
Jai - Ho0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
46 vues14 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
46 vues14 pagesAnimal Bites
Transféré par
Jai - HoDroits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 14
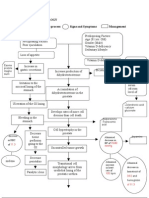
A snakebite is an injury caused by
a bite from a snake, often
resulting in puncture wounds
inflicted by the animal's fangs
and sometimes resulting in
envenomation.
Approximately 1,600 venomous bites from
domestic snakes were reported to the
American Association of Poison Control
Centers in 1998.
•Neuromuscular paralysis
•Excruciating pain
•Purpulish erythema
•Edema
•Dizziness
•Vomiting
•Perspiration
•Weakness
•Hematesis
•Dilated pupils
•Seizures
A loose torniquet applied to
bite delays flow of venom
Suction device such as
Swayer extractor
Dead snake should be
transported for identification
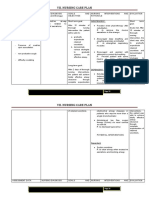
Children often acquire
lacerations from teeth of other
humans in rough play, during
fights, or as victims of child
abuse.
•Discomfort
•Swelling
•Increased Pain
If laceration is less than 0.25
inch long, can be treated at
home with soap and wound
dressing
Ice applicaion
Antibiotic Therapy
Tetanus toxoid
Larger laceration should receive
medical attention
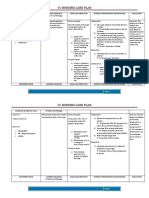
Approximately half of the dog
bites are younger than 5 years of
age: boys are bitten more
frequently than girls.
Pit bulls are the most commonly reported
breeds involved in fatal attacks.
•Redness
•Swelling
•Tenderness
•Purulent
•Serosanguineos drainage
General wound care with
copious amount of saline
Prophylactic antibiotics
Tetanus toxoid
The most important aspect related to
animal bites is prevention
Adequate socialization of puppies and
basic obedience training in dogs
could result in fewer dog bites.
Human Bite
Snake Bite
Cat Bite
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Philippine Constitution: Article VII Section 17, 18, 19Document29 pagesPhilippine Constitution: Article VII Section 17, 18, 19Jai - Ho95% (22)
- CA Emergency: Tumor Lysis SyndromeDocument9 pagesCA Emergency: Tumor Lysis SyndromeJai - HoPas encore d'évaluation
- IVF ProblemsDocument1 pageIVF ProblemsJai - HoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor Lysis SyndromeDocument35 pagesTumor Lysis SyndromeJai - HoPas encore d'évaluation
- CA Emergency: Tumor Lysis SyndromeDocument10 pagesCA Emergency: Tumor Lysis SyndromeJai - HoPas encore d'évaluation
- Color and Art TherapyDocument30 pagesColor and Art TherapyJai - Ho100% (1)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome, STEMI, Anterior Wall, Killips - 1, DM Type II - UncontrolledDocument61 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome, STEMI, Anterior Wall, Killips - 1, DM Type II - UncontrolledJai - Ho100% (5)
- Pa Tho of Prostatic CancerDocument2 pagesPa Tho of Prostatic CancerJai - HoPas encore d'évaluation
- Vii. Nursing Care Plan: Secretions in The AirwaysDocument5 pagesVii. Nursing Care Plan: Secretions in The AirwaysJai - Ho100% (2)
- Case Study Final. Pott's DiseaseDocument50 pagesCase Study Final. Pott's DiseaseJaiRus MagdadaRo100% (3)
- Vi. Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesVi. Nursing Care PlanJai - HoPas encore d'évaluation
- Final - Spinal Stenosis L4, L5 Secondary To Spondylolisthesis L4, L5 Grade II With Hypertrophized Ligament Um and Radiculopathy With Myelopathy Right SidedDocument66 pagesFinal - Spinal Stenosis L4, L5 Secondary To Spondylolisthesis L4, L5 Grade II With Hypertrophized Ligament Um and Radiculopathy With Myelopathy Right SidedJai - Ho100% (1)
- A Case Study On Rectal AdenocarcinomaDocument62 pagesA Case Study On Rectal AdenocarcinomaEyySiEffVee100% (1)
- Lab - Results On Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument16 pagesLab - Results On Acute GlomerulonephritisJai - Ho100% (1)
- Case Study On Prostatic CancerDocument21 pagesCase Study On Prostatic CancerJai - Ho100% (3)
- Acute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAcute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyJai - HoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP On Acute GlumrulonephritisDocument11 pagesNCP On Acute GlumrulonephritisJai - Ho89% (9)
- Case Study On Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument20 pagesCase Study On Acute GlomerulonephritisJai - Ho87% (15)
- Possible Drugs of Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument10 pagesPossible Drugs of Acute GlomerulonephritisJai - HoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP On Diabetes Mellitus Type IIDocument4 pagesNCP On Diabetes Mellitus Type IIJai - Ho78% (9)
- Dynasties and Kingdoms of EgyptDocument5 pagesDynasties and Kingdoms of EgyptJai - HoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study of Patient Having Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument3 pagesDrug Study of Patient Having Electrolyte ImbalanceJai - HoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tabular Sheet of TopicsDocument2 pagesTabular Sheet of TopicsJai - HoPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study (DM)Document28 pagesCase Study (DM)Jai - Ho100% (1)
- Evaluation ToolDocument2 pagesEvaluation ToolJai - HoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)