Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Student Feedback VT Corrections
Transféré par
api-3003533320 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
441 vues6 pagesThis document contains an assignment on classical and operant conditioning. It provides 4 examples of classical conditioning, defining the neutral stimulus, unconditioned stimulus, conditioned stimulus, and conditioned response for each. It also contains 5 examples of reinforcement and punishment, requiring the student to identify the type for each (positive/negative reinforcement or positive/negative punishment). The assignment demonstrates an understanding of key concepts in classical and operant conditioning and applies them to examples to test comprehension.
Description originale:
Titre original
student feedback vt corrections
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
ODT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document contains an assignment on classical and operant conditioning. It provides 4 examples of classical conditioning, defining the neutral stimulus, unconditioned stimulus, conditioned stimulus, and conditioned response for each. It also contains 5 examples of reinforcement and punishment, requiring the student to identify the type for each (positive/negative reinforcement or positive/negative punishment). The assignment demonstrates an understanding of key concepts in classical and operant conditioning and applies them to examples to test comprehension.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme ODT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
441 vues6 pagesStudent Feedback VT Corrections
Transféré par
api-300353332This document contains an assignment on classical and operant conditioning. It provides 4 examples of classical conditioning, defining the neutral stimulus, unconditioned stimulus, conditioned stimulus, and conditioned response for each. It also contains 5 examples of reinforcement and punishment, requiring the student to identify the type for each (positive/negative reinforcement or positive/negative punishment). The assignment demonstrates an understanding of key concepts in classical and operant conditioning and applies them to examples to test comprehension.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme ODT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 6
March 1, 2015
[VT]
PSYCHOLOGY 110: Assignment 2
Classical/Operant Conditioning
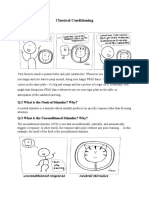
I. CLASSICAL CONDITIONING: Define the NS,
UCS, CS and
CR in the following 2 examples:
1. The nurse says Now this wont hurt a bit just before stabbing you
with a needle. The nurse stabs you with the needle and you cringe in
fear. The next time you hear This wont hurt you cringe in fear.
Neutral Stimulus: _next time you hear this wont hurt,
you cringe in fear because of
the conditioned stimulus
of the needle
NS: This wont hurt.
Unconditioned Stimulus:_the innate tendency to fear
needles
Unconditioned Response: _elicits fear__when you see a
needle and hear Now this wont hurt a bit
X Conditioned Stimulus: _learned stimulus__repeatedly
seeing the the needle
This wont hurt.
(If learning occurs the neutral stimulus becomes the
conditioned stimulus.)
Conditioned Response: elicits fear___presenting the
needle without it even touching you.
March 1, 2015
[VT]
2. People who receive chemotherapy often get sick during or shortly
after the procedure. After several chemotherapy sessions, people
begin feeling sick at the sight of the treatment room.
X Neutral Stimulus: people who receive chemotherapy
NS: Treatment room
(If learning occurs the neutral stimulus becomes the
conditioned stimulus.)
Unconditioned Stimulus: the procedure itself (Yes!)
Unconditioned Response: often getting sick during or
shortly after (Yes!)
Conditioned Stimulus: _the sight of the treatment
room (Yes!)
Conditioned Response: ____feeling sick (Yes!)
3. An individual receives frequent injections of drugs, which are
administered in a small examination room at a clinic. The drug itself
causes increased heart rate, but after several trips to the clinic, simply
being in a small room causes an increased heart rate.
X Neutral Stimulus: individual receives frequent injections of
drugs
NS: small examination room
o
Unconditioned Stimulus : the drug itself increases the heart
rate (Yes!)
X Unconditioned Response _ trips to the clinic
Conditioned Stimulus: simply being_in a small room increases
heart rate (Yes!)
UCS: increased heart rate
March 1, 2015
[VT]
CS: small examination room
Conditioned Response: increased heart rate (Yes!)
In order to be able to punish my Pitt Bull even when I'm not near
enough to reach her, I have paired the sound of a clicker with getting
squirted with water. Now the sound of the clicker causes her to engage in
a startle response.
4.
X Neutral Stimulus: _punishment of the Pitt bull even when I am
not near to reach her
NS: clicker
X Unconditioned Stimulus __the sound of the clicker
UCS: getting squirted with water
X Unconditioned Response _the sound of the clicker and getting
squirted with the
water
UCS: startle response
Conditioned Stimulus using the clicker (Yes!)
Conditioned Response the sound alone of the clicker causes a
startled response
March 1, 2015
[VT]
II. REINFORCEMENT & PUNISHMENT
Identify the type of reinforcement (positive/negative)
or punishment (positive/negative) represented by
each example.
1. X After her 2nd grade teacher yells at her, Lindas
misbehavior in class increases. _positive
punishment
ANSWER: Positive reinforcement.
You must be thinking: What?? But the teacher yelled at her. I
know. I know. But, let's review it. First, Linda's behavior
increased! Ouch. That means it reinforced the behavior. "Yelling"
was not intended to reinforce the behavior, but it did. So, we have
reinforcement.
Now, is it positive reinforcement or negative reinforcement? Well,
if it was positive it means we "added" something. On the other
hand, if it was negative we would have "removed" something. In
this case we "added" yelling. Therefore, the answer is positive
reinforcement!
2. Toms parents took away his car keys because of
his bad grades. _negative punishment (Yes!)
3. Linda receives candy whenever she is quiet in
church. Positive reinforcement_______ (Yes!)
March 1, 2015
[VT]
4. Dan yelled at his young son when he caught him
playing with matches. positive
punishment_________________(Yes!)
5. X After her finger got infected last month, Dawn
quickly took out a splinter today. Positive
reinforcement________________
Answer: Negative Reinforcement
This is often the most difficult behavior to learn for students. The
removal of something unwanted increases the likelihood that an
individual would engage in the same behavior in the future. When
you get into your car, I bet you put on your seatbelt. I dont know
about you, but the sound of that buzzer is pretty annoying. So, I put
on my seatbelt to stop that noise! When I remove something
adverse/unwanted (buzzer noise) from my environment it increases
(reinforces) the likelihood that I will do the same thing again in the
future. I put on my seatbelt, noise stops.
I remove the splinter, infection stops.
Removing something (negative) increases a behavior (reinforcement)
March 1, 2015
[VT]
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Stephen Jones - Secrets of TimeDocument237 pagesStephen Jones - Secrets of TimeKld Brn86% (7)
- Assingment 1 HLTH 2400Document5 pagesAssingment 1 HLTH 2400api-252266570Pas encore d'évaluation
- URGE SURFING-DBT For Sub Use PDFDocument5 pagesURGE SURFING-DBT For Sub Use PDFAmy Powers100% (1)
- The Educated ManDocument6 pagesThe Educated ManSteve B. Salonga80% (5)
- Hernandez v. San Juan-Santos Case DigestDocument2 pagesHernandez v. San Juan-Santos Case DigestReina Fabregas100% (3)
- Right To TravelDocument2 pagesRight To TravelGETTO VOCAB100% (8)
- Learning: Powerpoint® PresentationDocument40 pagesLearning: Powerpoint® PresentationLana AlsalemPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychology 1Document51 pagesPsychology 1Adesh Nidhi TiwaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning: Powerpoint® PresentationDocument67 pagesLearning: Powerpoint® PresentationInas DayeaPas encore d'évaluation
- IES-R Form and ScoringDocument1 pageIES-R Form and ScoringJohn ForresterPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning: & Classical ConditioningDocument24 pagesLearning: & Classical Conditioningronnel palasinPas encore d'évaluation
- LearningDocument49 pagesLearningapi-3828809Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ap Psychology Forest Grove High School Mr. Tusow: Learning: Classical andDocument63 pagesAp Psychology Forest Grove High School Mr. Tusow: Learning: Classical andIsabella T100% (1)
- Behavioral Medicine: Natia Badridze, MDDocument27 pagesBehavioral Medicine: Natia Badridze, MDAbdallah DarwishPas encore d'évaluation
- Posetive and Negative Reinforcment NotesDocument16 pagesPosetive and Negative Reinforcment Notessusu88mumuPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Lab CH 7Document4 pagesLearning Lab CH 7slm.1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Learning: Stimulus: Event That Activates The Behaviour Response: Observable Reaction To A StimuliDocument80 pagesLearning: Stimulus: Event That Activates The Behaviour Response: Observable Reaction To A StimuliclairesanjeevPas encore d'évaluation
- Reinforcement TherapyDocument17 pagesReinforcement TherapyZoya SajidPas encore d'évaluation
- Actvity - Understanding The SelfDocument9 pagesActvity - Understanding The SelfBelle TsukishimaPas encore d'évaluation
- LearningDocument87 pagesLearningDecode MusicPas encore d'évaluation
- The Monster In The Closet: How To Avoid Adult Chronic Illness By Treating Childhood TraumaD'EverandThe Monster In The Closet: How To Avoid Adult Chronic Illness By Treating Childhood TraumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Classical Conditioning Apsi - tc18 PDFDocument38 pagesClassical Conditioning Apsi - tc18 PDFapi-421695293Pas encore d'évaluation
- (English) 6 Daily Habits To Reduce Stress & Anxiety (DownSub - Com)Document4 pages(English) 6 Daily Habits To Reduce Stress & Anxiety (DownSub - Com)Kim HanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Growth Module 3Document16 pagesHuman Growth Module 3Maria Judith Peña JulianesPas encore d'évaluation
- Psyc 4 NotesDocument3 pagesPsyc 4 NotesucsdlliuPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Chapter 6 LearningDocument95 pagesAP Chapter 6 LearningTamene KeneniPas encore d'évaluation
- LearningDocument87 pagesLearningMoazzam AliPas encore d'évaluation
- E141 - How To Handle Your Pandemic Anxiety, With Psychologists Dr. Elena Welsh and Dr. David BurnsDocument14 pagesE141 - How To Handle Your Pandemic Anxiety, With Psychologists Dr. Elena Welsh and Dr. David BurnsGMG EditorialPas encore d'évaluation
- ReinforcementDocument5 pagesReinforcementUsama TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Clearing Limiting BeliefsDocument6 pagesClearing Limiting BeliefsAnonymous Cxi39n100% (5)
- 1-Learningpracticeall KeyDocument13 pages1-Learningpracticeall Keyapi-261267976Pas encore d'évaluation
- Orloff Intuitive HealingDocument21 pagesOrloff Intuitive Healingtansoei100% (6)
- Classical Conditioning: Q:2 What Is The Neutral Stimulus? Why?Document3 pagesClassical Conditioning: Q:2 What Is The Neutral Stimulus? Why?Muhammad MuneebPas encore d'évaluation
- Page 89Document1 pagePage 89Enrique CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Shy - Lecture - LearningDocument12 pagesShy - Lecture - LearningKrisha MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- A I P C ' S F I V e T H e R A P I e S B o o KDocument54 pagesA I P C ' S F I V e T H e R A P I e S B o o Kapi-27357588Pas encore d'évaluation
- Psych and ChemlecDocument6 pagesPsych and ChemlecMish SaidPas encore d'évaluation
- ConditioningDocument64 pagesConditioningRithik ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 3 Cognition Intelligence, Learning and TestingDocument57 pagesTopic 3 Cognition Intelligence, Learning and TestingSarnisha Murugeshwaran (Shazzisha)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Psychology NotesDocument33 pagesPsychology NotesLiesha MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- EFT Basics Handout For Brief PresentationsDocument7 pagesEFT Basics Handout For Brief PresentationsSuzan ThompsonPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.10 Cornelia Kastner - Managing Stress and Burnout After TraumaDocument10 pages1.10 Cornelia Kastner - Managing Stress and Burnout After TraumaMiruna HendrePas encore d'évaluation
- Stress Case StudyDocument3 pagesStress Case Studyapi-631585365Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Vibration of Exceptional Health - Carol LookDocument5 pagesThe Vibration of Exceptional Health - Carol LookMichael CliftonPas encore d'évaluation
- The Wellness Theory: Natural, Effective Ways of Managing Stress and TensionD'EverandThe Wellness Theory: Natural, Effective Ways of Managing Stress and TensionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Concept 6 - Your Defence Mechanism - Astrosutra by Dhruv MehtaDocument6 pagesConcept 6 - Your Defence Mechanism - Astrosutra by Dhruv MehtaAstrosutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Mixed NotesDocument29 pagesMixed Notesjoelmat507Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cognitive Psychology Reviewer PRELIMSDocument35 pagesCognitive Psychology Reviewer PRELIMSOrange Lozada100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Language Teaching: Instructor: Huy PhamDocument31 pagesFundamentals of Language Teaching: Instructor: Huy PhamKiều Dực LinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Positive Reinforcement in Habit FormationDocument3 pagesPositive Reinforcement in Habit FormationMadhumeta RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of PsychologyDocument103 pagesPrinciples of PsychologyYash KalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transference Resistance: A Case Example High Resistant Patient Who Presents With A Transference Resistance in The Forefront by Jon Frederickson, MSWDocument36 pagesTransference Resistance: A Case Example High Resistant Patient Who Presents With A Transference Resistance in The Forefront by Jon Frederickson, MSWanitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Psy Assignment Sem 6Document15 pagesClinical Psy Assignment Sem 6hadiqaasif01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Yuen Method - Stress-Knowing-PainfulDocument4 pagesYuen Method - Stress-Knowing-Painfulsoribo100% (3)
- Fundamentals of Psychology Chapter 4 - Learning and Human NurtureDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Psychology Chapter 4 - Learning and Human NurtureAndrea PietersPas encore d'évaluation
- Learn How You Can Overcome Your Anxiety In Four Simple, Effective And Incredibly Easy StepsD'EverandLearn How You Can Overcome Your Anxiety In Four Simple, Effective And Incredibly Easy StepsPas encore d'évaluation
- Respondent Vs Operant ConditioningDocument6 pagesRespondent Vs Operant ConditioningTamana AzadPas encore d'évaluation
- BehaviorismDocument12 pagesBehaviorismcahazarc98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stress MGT Book - Chapter 1-Whats-Your-Stress-NumberDocument5 pagesStress MGT Book - Chapter 1-Whats-Your-Stress-NumberashayhowardPas encore d'évaluation
- Classical Conditioning Homework AnswersDocument8 pagesClassical Conditioning Homework Answerslrqylwznd100% (1)
- Module 4 - PavlovDocument3 pagesModule 4 - Pavlovapple.chua15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Do You Really Want To Stop The SufferingDocument4 pagesDo You Really Want To Stop The SufferingjosipPas encore d'évaluation
- Self Help CourseDocument64 pagesSelf Help Coursewoahlottainfo2100% (2)
- Lisa Maisano Kennedy Assessment Road MapDocument5 pagesLisa Maisano Kennedy Assessment Road Mapapi-300353332Pas encore d'évaluation
- Slo Template Psych 101 Section Lisa Maisano Kennedy Fall 2013 1 One PracticumDocument1 pageSlo Template Psych 101 Section Lisa Maisano Kennedy Fall 2013 1 One Practicumapi-300353332Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lisa Maisano Kennedy 6 Week Accessibilty Production Plan 1Document12 pagesLisa Maisano Kennedy 6 Week Accessibilty Production Plan 1api-300353332Pas encore d'évaluation
- Accessing The ClassDocument1 pageAccessing The Classapi-300353332Pas encore d'évaluation
- Statement of Acces1Document1 pageStatement of Acces1api-300353332Pas encore d'évaluation
- Psych 101 Welcome Letter Online Certification AccesssibleDocument3 pagesPsych 101 Welcome Letter Online Certification Accesssibleapi-300353332Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lisa Kennedy 1Document1 pageLisa Kennedy 1api-300353332Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lawyers Cooperative Publishing Co. v. TaboraDocument3 pagesLawyers Cooperative Publishing Co. v. TaboraMico Maagma CarpioPas encore d'évaluation
- CodicilDocument2 pagesCodicilJJ Gapol100% (4)
- MedicalVerification PDFDocument3 pagesMedicalVerification PDFOptical RecoveryPas encore d'évaluation
- Lepsl 530 Third Party Doctrine and Csli AnalysisDocument4 pagesLepsl 530 Third Party Doctrine and Csli Analysisapi-462898831Pas encore d'évaluation
- Warriors Dont CryDocument5 pagesWarriors Dont Cryapi-252730671Pas encore d'évaluation
- Modern InventionDocument2 pagesModern InventionLiah CalderonPas encore d'évaluation
- Trial and Error: Failure and Innovation in Criminal Justice ReformDocument5 pagesTrial and Error: Failure and Innovation in Criminal Justice ReformAzim MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyber Bullying ScriptDocument3 pagesCyber Bullying ScriptMonica Eguillion100% (1)
- Araneta Vs GatmaitanDocument1 pageAraneta Vs GatmaitanXyra Krezel GajetePas encore d'évaluation
- SpecPro Rule 77Document13 pagesSpecPro Rule 77angelescrishannePas encore d'évaluation
- Legal Rights and DutiesDocument7 pagesLegal Rights and DutiesHutiya KumPas encore d'évaluation
- Shuffledwords PDFDocument279 pagesShuffledwords PDFHarvey SpectarPas encore d'évaluation
- Brij Pal Vs StateDocument7 pagesBrij Pal Vs StateSatyendra ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Ethics: Felix M. Del Rosario, Cpa, MbaDocument38 pagesBusiness Ethics: Felix M. Del Rosario, Cpa, Mbafelix madayag del rosarioPas encore d'évaluation
- THESIS Significance of The StudyDocument1 pageTHESIS Significance of The Studybillyktoubatts70% (10)
- Mary ToostealDocument4 pagesMary ToostealtesttestPas encore d'évaluation
- Table 1-A: Physical Output MatrixDocument40 pagesTable 1-A: Physical Output MatrixJacquiline TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Agbayani v. PNB, G.R. No. L-23127, April 29, 1971.full TextDocument5 pagesAgbayani v. PNB, G.R. No. L-23127, April 29, 1971.full TextRyuzaki HidekiPas encore d'évaluation
- Admin Case DigestsDocument50 pagesAdmin Case DigestsJennyMariedeLeon100% (1)
- Position PaperDocument9 pagesPosition PaperJamellen De Leon BenguetPas encore d'évaluation
- Bajaj Group4Document4 pagesBajaj Group4cloudyapplePas encore d'évaluation
- BA Third Year Syllabus Com English IIDocument3 pagesBA Third Year Syllabus Com English IIA Samanya KeToPas encore d'évaluation
- The Politics of Transition in Kenya: From KANU To NARC, 2003Document217 pagesThe Politics of Transition in Kenya: From KANU To NARC, 2003jakarta100% (6)
- Yu Tek Vs Gonzales (Final)Document2 pagesYu Tek Vs Gonzales (Final)dollyccruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Ogl 482 Thematic Analysis PresentationDocument34 pagesOgl 482 Thematic Analysis Presentationapi-654870247Pas encore d'évaluation
- Social Studies IiiDocument17 pagesSocial Studies Iiiain_aina9228100% (1)